Abstract
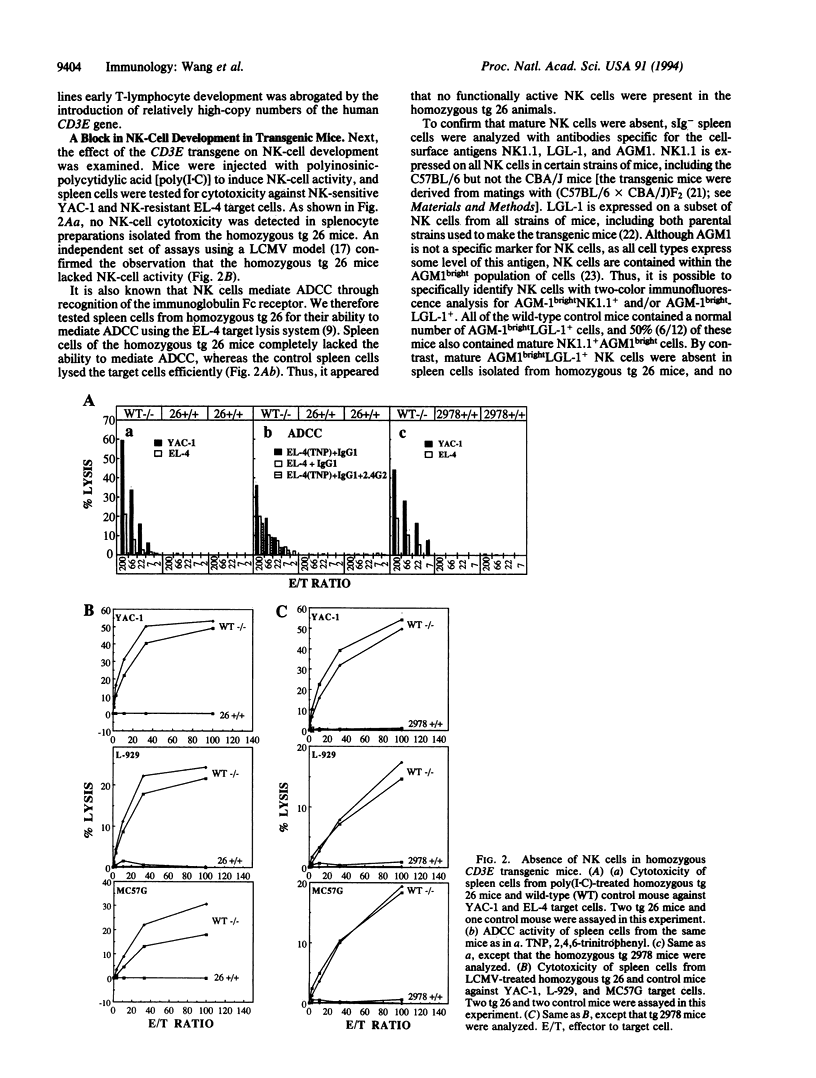
A severe immunodeficiency involving a complete loss of T lymphocytes and natural killer cells was observed in independent lines of transgenic mice containing > 30 copies of the human CD3E gene (pL12). T-cell- natural killer (NK)- mice could also be generated by using a gene fragment pL12 delta 1 (without exons 4A and 5) coding for the CD3-epsilon transmembrane region and its 55-amino acid nonenzymatic cytoplasmic tail. The abnormally small thymus gland in the homozygous transgenic animals, which was approximately 1% the size of a wild-type thymus, contained only a few (2-4%) prethymocytes with a Thy-1+Pgp-1+IL-2R alpha- CD3-4-8- phenotype. In mice with lower copy numbers of the transgene thymocyte development was blocked at the Thy-1+Pgp-1-IL-2R alpha+CD3-4-8- stage, and normal NK activity was detected. Mice generated with high-copy numbers of a transgene pL12 delta 2 (pL12 delta 1 minus exons 6), coding for a truncated protein from which the CD3-epsilon extracellular domain, its transmembrane region, and most of its cytoplasmic region were absent, contained normal numbers of T lymphocytes and NK cells. These transgene effects suggested that recruitment of signal-transduction molecules by the cytoplasmic tail of this protein played an important role in the abrogation of both lineages. Taken together these observations support the notion that T lymphocytes and NK cells stemmed from a common precursor.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashwell J. D., Klusner R. D. Genetic and mutational analysis of the T-cell antigen receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:139–167. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biassoni R., Ferrini S., Prigione I., Moretta A., Long E. O. CD3-negative lymphokine-activated cytotoxic cells express the CD3 epsilon gene. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1685–1689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biron C. A., van den Elsen P., Tutt M. M., Medveczky P., Kumar V., Terhorst C. Murine natural killer cells stimulated in vivo do not express the T cell receptor alpha, beta, gamma, T3 delta, or T3 epsilon genes. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1704–1710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceredig R., Lowenthal J. W., Nabholz M., MacDonald H. R. Expression of interleukin-2 receptors as a differentiation marker on intrathymic stem cells. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):98–100. doi: 10.1038/314098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevers H. C., Dunlap S., Wileman T. E., Terhorst C. Human CD3-epsilon gene contains three miniexons and is transcribed from a non-TATA promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8156–8160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevers H., Lonberg N., Dunlap S., Lacy E., Terhorst C. An enhancer located in a CpG-island 3' to the TCR/CD3-epsilon gene confers T lymphocyte-specificity to its promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2527–2535. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos K., Galson D., Terhorst C. Tissue-specific nuclear factors mediate expression of the CD3 delta gene during T cell development. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):109–115. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08086.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold D. P., Puck J. M., Pettey C. L., Cho M., Coligan J., Woody J. N., Terhorst C. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding the 20K non-glycosylated polypeptide chain of the human T-cell receptor/T3 complex. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):431–434. doi: 10.1038/321431a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunji Y., Vujanovic N. L., Hiserodt J. C., Herberman R. B., Gorelik E. Generation and characterization of purified adherent lymphokine-activated killer cells in mice. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 1;142(5):1748–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habu S., Fukui H., Shimamura K., Kasai M., Nagai Y., Okumura K., Tamaoki N. In vivo effects of anti-asialo GM1. I. Reduction of NK activity and enhancement of transplanted tumor growth in nude mice. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):34–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussey R. E., Clayton L. K., Diener A., McConkey D. J., Howard F. D., Rodewald H. R., D'Adamio L., Dallenbach F., Stein H., Schmidt E. V. Overexpression of CD3 eta during thymic development does not alter the negative selection process. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 15;150(4):1183–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Chang C., Spits H., Phillips J. H. Expression of cytoplasmic CD3 epsilon proteins in activated human adult natural killer (NK) cells and CD3 gamma, delta, epsilon complexes in fetal NK cells. Implications for the relationship of NK and T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 15;149(6):1876–1880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Spits H., Phillips J. H. The developmental relationship between NK cells and T cells. Immunol Today. 1992 Oct;13(10):392–395. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90087-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneur F., Klausner R. D. Activation of T cells by a tyrosine kinase activation domain in the cytoplasmic tail of CD3 epsilon. Science. 1992 Jan 3;255(5040):79–82. doi: 10.1126/science.1532456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levelt C. N., Mombaerts P., Iglesias A., Tonegawa S., Eichmann K. Restoration of early thymocyte differentiation in T-cell receptor beta-chain-deficient mutant mice by transmembrane signaling through CD3 epsilon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11401–11405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason L., Giardina S. L., Hecht T., Ortaldo J., Mathieson B. J. LGL-1: a non-polymorphic antigen expressed on a major population of mouse natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4403–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. B. Myoblast diversity in skeletal myogenesis: how much and to what end? Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90111-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H., Hori T., Nagler A., Bhat N., Spits H., Lanier L. L. Ontogeny of human natural killer (NK) cells: fetal NK cells mediate cytolytic function and express cytoplasmic CD3 epsilon,delta proteins. J Exp Med. 1992 Apr 1;175(4):1055–1066. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.4.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raulet D. H. Expression and function of interleukin-2 receptors on immature thymocytes. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):101–103. doi: 10.1038/314101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancho J., Franco R., Chatila T., Hall C., Terhorst C. The T cell receptor associated CD3-epsilon protein is phosphorylated upon T cell activation in the two tyrosine residues of a conserved signal transduction motif. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jul;23(7):1636–1642. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancho J., Silverman L. B., Castigli E., Ahern D., Laudano A. P., Terhorst C., Geha R. S., Chatila T. A. Developmental regulation of transmembrane signaling via the T cell antigen receptor/CD3 complex in human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 1;148(5):1315–1321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinkai Y., Rathbun G., Lam K. P., Oltz E. M., Stewart V., Mendelsohn M., Charron J., Datta M., Young F., Stall A. M. RAG-2-deficient mice lack mature lymphocytes owing to inability to initiate V(D)J rearrangement. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):855–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90029-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiberghien P., Longo D. L., Wine J. W., Alvord W. G., Reynolds C. W. Anti-asialo GM1 antiserum treatment of lethally irradiated recipients before bone marrow transplantation: evidence that recipient natural killer depletion enhances survival, engraftment, and hematopoietic recovery. Blood. 1990 Oct 1;76(7):1419–1430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tutt M. M., Schuler W., Kuziel W. A., Tucker P. W., Bennett M., Bosma M. J., Kumar V. T cell receptor genes do not rearrange or express functional transcripts in natural killer cells of scid mice. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2338–2344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wileman T., Carson G. R., Concino M., Ahmed A., Terhorst C. The gamma and epsilon subunits of the CD3 complex inhibit pre-Golgi degradation of newly synthesized T cell antigen receptors. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):973–986. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama W. M., Ryan J. C., Hunter J. J., Smith H. R., Stark M., Seaman W. E. cDNA cloning of mouse NKR-P1 and genetic linkage with LY-49. Identification of a natural killer cell gene complex on mouse chromosome 6. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 1;147(9):3229–3236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




