Abstract
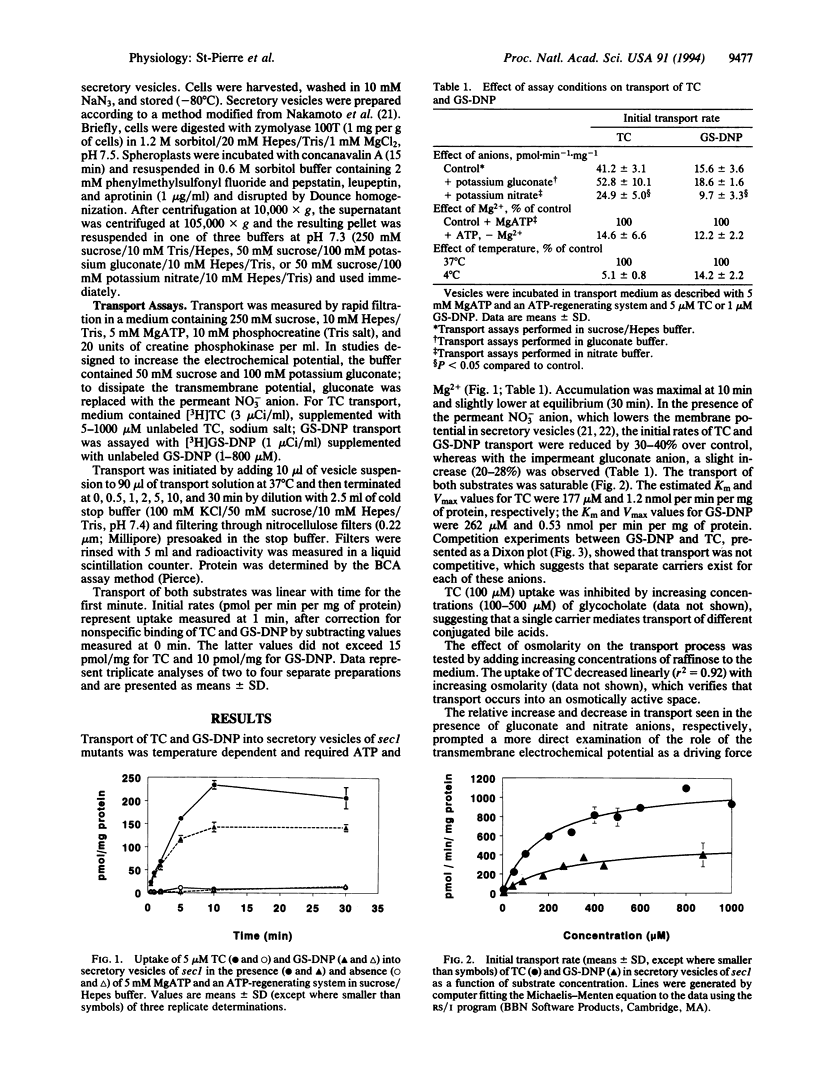
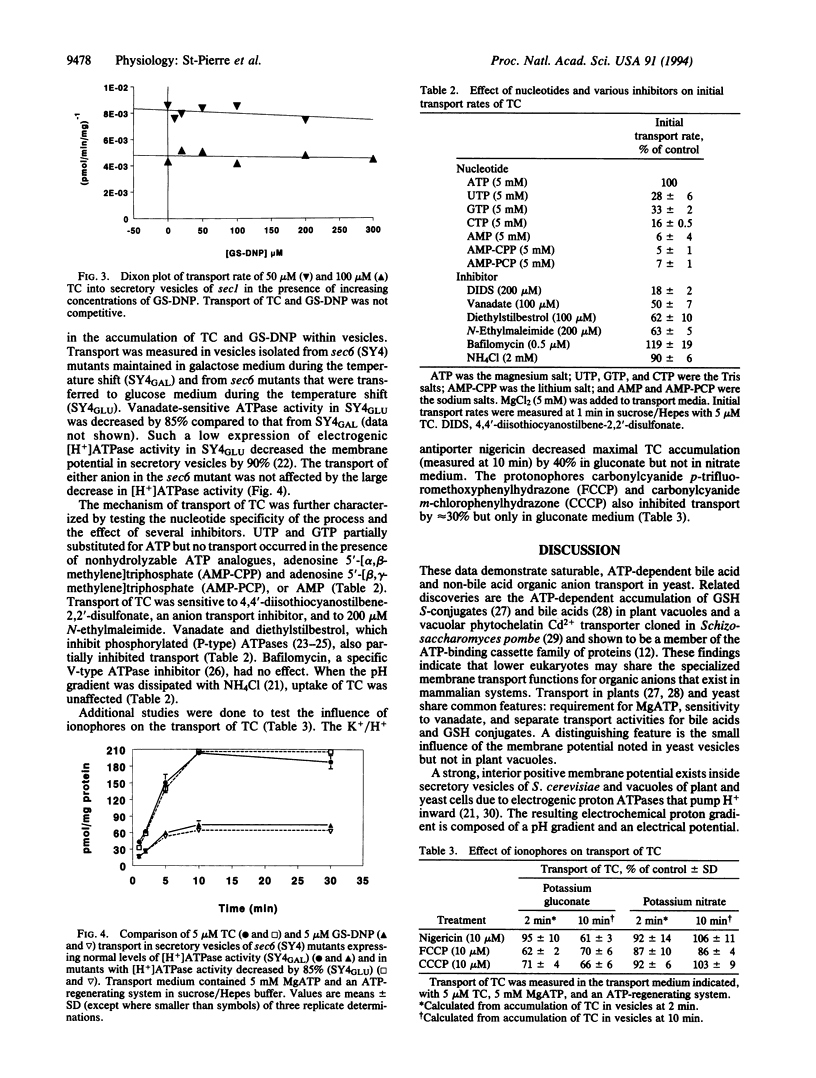
Secretory mutants (sec1, sec6) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae accumulate large pools of secretory vesicles at the restrictive temperature (37 degrees C) because of a block in the delivery of vesicles to the cell surface. We report that secretory vesicles isolated from sec mutants exhibit ATP-dependent uptake of two classes of organic anions that are substrates for the canalicular carriers of mammalian liver. Transport of the bile acid taurocholate (TC) and the glutathione conjugate of 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (GS-DNP) into vesicles was temperature dependent and saturable and required ATP and Mg2+. Estimates of Km and Vmax were 177 microM and 1.2 nmol.min-1.mg-1 and 262 microM and 0.53 nmol.min-1.mg-1 for TC and GS-DNP, respectively. TC and GS-DNP did not complete for transport. TC transport was sensitive to vanadate and 4,4'-diisothiocyanostilbene-2,2'-disulfonate, inhibited by glycocholate, and retained partial activity when UTP and GTP, but not nonhydrolyzable ATP analogues, replaced ATP. Dissipation of the electrochemical potential with a nitrate buffer and ionophores partially decreased (30-40%) the transport of both anions. Direct testing of the influence of membrane potential was performed in sec6-4 mutants, in which the expression of electrogenic [H+]ATPase activity is reduced by > 85% in glucose-containing medium. Vesicles from sec6-4 retained full activity for ATP-dependent TC and GS-DNP transport. These results indicate that the transporters operate independently of the membrane potential and that ATP is required. These findings reveal that yeast possess separate ATP-dependent transport mechanisms for elimination of bile acids and glutathione conjugates. The mechanisms are functionally similar to those present in mammalian systems.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arias I. M., Che M., Gatmaitan Z., Leveille C., Nishida T., St Pierre M. The biology of the bile canaliculus, 1993. Hepatology. 1993 Feb;17(2):318–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balzi E., Wang M., Leterme S., Van Dyck L., Goffeau A. PDR5, a novel yeast multidrug resistance conferring transporter controlled by the transcription regulator PDR1. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):2206–2214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman B. J., Blasco F., Slayman C. W. Purification and characterization of the plasma membrane ATPase of Neurospora crassa. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12343–12349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman B. J., Bowman E. J. H+-ATPases from mitochondria, plasma membranes, and vacuoles of fungal cells. J Membr Biol. 1986;94(2):83–97. doi: 10.1007/BF01871190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman E. J., Siebers A., Altendorf K. Bafilomycins: a class of inhibitors of membrane ATPases from microorganisms, animal cells, and plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7972–7976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calahorra M., Ramírez J., Clemente S. M., Peña A. Electrochemical potential and ion transport in vesicles of yeast plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 May 29;899(2):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90404-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., Allikmets R., Gerrard B., Stewart C., Kistler A., Shafer B., Michaelis S., Strathern J. Mapping and sequencing of two yeast genes belonging to the ATP-binding cassette superfamily. Yeast. 1994 Mar;10(3):377–383. doi: 10.1002/yea.320100310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink R. P., Ottenhoff R., Liefting W., de Haan J., Jansen P. L. Hepatobiliary transport of glutathione and glutathione conjugate in rats with hereditary hyperbilirubinemia. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):476–483. doi: 10.1172/JCI114189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F. ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:67–113. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörtensteiner S., Vogt E., Hagenbuch B., Meier P. J., Amrhein N., Martinoia E. Direct energization of bile acid transport into plant vacuoles. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18446–18449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Akerboom T. P., Sies H., Kinne R., Thao T., Arias I. M. Biliary transport of glutathione S-conjugate by rat liver canalicular membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):4998–5002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Kinne R., Tran T., Arias I. M. Taurocholate transport by rat liver canalicular membrane vesicles. Evidence for the presence of an Na+-independent transport system. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):659–663. doi: 10.1172/JCI111257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa T., Müller M., Klünemann C., Schaub T., Keppler D. ATP-dependent primary active transport of cysteinyl leukotrienes across liver canalicular membrane. Role of the ATP-dependent transport system for glutathione S-conjugates. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):19279–19286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura T., Jansen P., Hardenbrook C., Kamimoto Y., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M. Defective ATP-dependent bile canalicular transport of organic anions in mutant (TR-) rats with conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3557–3561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Sogame Y., Hara H., Hayashi K. Mechanism of glutathione S-conjugate transport in canalicular and basolateral rat liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):7737–7741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malpartida F., Serrano R. Reconstitution of the proton-translocating adenosine triphosphatase of yeast plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4175–4177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Varshavsky A. The yeast STE6 gene encodes a homologue of the mammalian multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):400–404. doi: 10.1038/340400a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier P. J., St Meier-Abt A., Barrett C., Boyer J. L. Mechanisms of taurocholate transport in canalicular and basolateral rat liver plasma membrane vesicles. Evidence for an electrogenic canalicular organic anion carrier. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10614–10622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamoto R. K., Rao R., Slayman C. W. Expression of the yeast plasma membrane [H+]ATPase in secretory vesicles. A new strategy for directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7940–7949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida T., Gatmaitan Z., Che M., Arias I. M. Rat liver canalicular membrane vesicles contain an ATP-dependent bile acid transport system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6590–6594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida T., Gatmaitan Z., Roy-Chowdhry J., Arias I. M. Two distinct mechanisms for bilirubin glucuronide transport by rat bile canalicular membrane vesicles. Demonstration of defective ATP-dependent transport in rats (TR-) with inherited conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):2130–2135. doi: 10.1172/JCI116098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida T., Hardenbrook C., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M. ATP-dependent organic anion transport system in normal and TR- rat liver canalicular membranes. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):G629–G635. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.4.G629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Ferro S., Schekman R. Order of events in the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Field C., Schekman R. Identification of 23 complementation groups required for post-translational events in the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Schekman R. Secretion and cell-surface growth are blocked in a temperature-sensitive mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz D. F., Kreppel L., Speiser D. M., Scheel G., McDonald G., Ow D. W. Heavy metal tolerance in the fission yeast requires an ATP-binding cassette-type vacuolar membrane transporter. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3491–3499. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05431.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond M., Gros P., Whiteway M., Thomas D. Y. Functional complementation of yeast ste6 by a mammalian multidrug resistance mdr gene. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):232–234. doi: 10.1126/science.1348873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruetz S., Gros P. Functional expression of P-glycoproteins in secretory vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 22;269(16):12277–12284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieger B., O'Neill B., Meier P. J. ATP-dependent bile-salt transport in canalicular rat liver plasma-membrane vesicles. Biochem J. 1992 May 15;284(Pt 1):67–74. doi: 10.1042/bj2840067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walworth N. C., Novick P. J. Purification and characterization of constitutive secretory vesicles from yeast. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):163–174. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



