Abstract
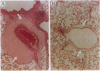
Immunotoxins are hybrid molecules composed of a cell-surface binding domain and a protein toxin moiety that together target specific cell populations for elimination. These agents represent a promising approach for the treatment of many human diseases, most notably cancer. However, it has recently become clear that many immunotoxins when used in human clinical trials induce vascular leak syndrome (VLS), restricting the administration of doses necessary to achieve good therapeutic responses. The lack of an appropriate animal model has hindered efforts to understand and prevent immunotoxin-induced VLS. We have found that in rats, intravenous administration of the single-chain immunotoxin BR96 sFv-PE40 results in symptoms that closely resemble VLS seen in human immunotoxin trials. A large fluid accumulation in the thoracic cavity was observed, along with an increase in hematocrit and body weight and a decrease in serum albumin. The VLS was apparent within 24 hr after administration of immunotoxin and was seen in both immunocompetent and athymic rats. Similar symptoms were not found in mice even at lethal doses. Prophylactic administration of the corticosteroid dexamethasone resulted in prevention of VLS and survival of rats injected with what would otherwise be lethal doses of BR96 sFv-PE40. Prophylactic treatment with dexamethasone in rats xenografted with human tumors either did not inhibit or minimally inhibited the antitumor activity of BR96 sFv-PE40. The use of prophylactic corticosteroids should be considered for immunotoxin clinical trials, since it may improve therapeutic efficacy by decreasing the dose-limiting toxicity of VLS.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amlot P. L., Stone M. J., Cunningham D., Fay J., Newman J., Collins R., May R., McCarthy M., Richardson J., Ghetie V. A phase I study of an anti-CD22-deglycosylated ricin A chain immunotoxin in the treatment of B-cell lymphomas resistant to conventional therapy. Blood. 1993 Nov 1;82(9):2624–2633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajorin D. F., Chapman P. B., Wong G. Y., Cody B. V., Cordon-Cardo C., Dantes L., Templeton M. A., Scheinberg D., Oettgen H. F., Houghton A. N. Treatment with high dose mouse monoclonal (anti-GD3) antibody R24 in patients with metastatic melanoma. Melanoma Res. 1992 Dec;2(5-6):355–362. doi: 10.1097/00008390-199212000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boumpas D. T., Paliogianni F., Anastassiou E. D., Balow J. E. Glucocorticosteroid action on the immune system: molecular and cellular aspects. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1991 Jul-Aug;9(4):413–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers V. S., Henslee P. J., Kernan N. A., Blazar B. R., Gingrich R., Phillips G. L., LeMaistre C. F., Gilliland G., Antin J. H., Martin P. Use of an anti-pan T-lymphocyte ricin a chain immunotoxin in steroid-resistant acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 1990 Apr 1;75(7):1426–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers V. S., Rodvien R., Grant K., Durrant L. G., Hudson K. H., Baldwin R. W., Scannon P. J. Phase I study of monoclonal antibody-ricin A chain immunotoxin XomaZyme-791 in patients with metastatic colon cancer. Cancer Res. 1989 Nov 1;49(21):6153–6160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emminger W., Emminger-Schmidmeier W., Peters C., Susani M., Hawliczek R., Höcker P., Gadner H. Capillary leak syndrome during low dose granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (rh GM-CSF) treatment of a patient in a continuous febrile state. Blut. 1990 Oct;61(4):219–221. doi: 10.1007/BF01744134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falini B., Bolognesi A., Flenghi L., Tazzari P. L., Broe M. K., Stein H., Dürkop H., Aversa F., Corneli P., Pizzolo G. Response of refractory Hodgkin's disease to monoclonal anti-CD30 immunotoxin. Lancet. 1992 May 16;339(8803):1195–1196. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91135-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. N., Chace D. F., Trail P. A., Siegall C. B. Antitumor activity of the single-chain immunotoxin BR96 sFv-PE40 against established breast and lung tumor xenografts. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 1;150(7):3054–3061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossbard M. L., Freedman A. S., Ritz J., Coral F., Goldmacher V. S., Eliseo L., Spector N., Dear K., Lambert J. M., Blättler W. A. Serotherapy of B-cell neoplasms with anti-B4-blocked ricin: a phase I trial of daily bolus infusion. Blood. 1992 Feb 1;79(3):576–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossbard M. L., Lambert J. M., Goldmacher V. S., Spector N. L., Kinsella J., Eliseo L., Coral F., Taylor J. A., Blättler W. A., Epstein C. L. Anti-B4-blocked ricin: a phase I trial of 7-day continuous infusion in patients with B-cell neoplasms. J Clin Oncol. 1993 Apr;11(4):726–737. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1993.11.4.726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMaistre C. F., Rosen S., Frankel A., Kornfeld S., Saria E., Meneghetti C., Drajesk J., Fishwild D., Scannon P., Byers V. Phase I trial of H65-RTA immunoconjugate in patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Blood. 1991 Sep 1;78(5):1173–1182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mier J. W., Vachino G., Klempner M. S., Aronson F. R., Noring R., Smith S., Brandon E. P., Laird W., Atkins M. B. Inhibition of interleukin-2-induced tumor necrosis factor release by dexamethasone: prevention of an acquired neutrophil chemotaxis defect and differential suppression of interleukin-2-associated side effects. Blood. 1990 Nov 15;76(10):1933–1940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemoto K., Sugawara Y., Ogino M., Mae T., Abe F., Takeuchi T. Myeloprotective activity of deoxyspergualin: influence on splenic colony-forming cell injury and antitumor activity of mitomycin C in mice. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1992 Jul;83(7):789–793. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1992.tb01981.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuwelt E. A., Barnett P. A., Ramsey F. L., Hellström I., Hellström K. E., McCormick C. I. Dexamethasone decreases the delivery of tumor-specific monoclonal antibody to both intracerebral and subcutaneous tumor xenografts. Neurosurgery. 1993 Sep;33(3):478–484. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199309000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai L. H., Batra J. K., FitzGerald D. J., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Antitumor effects of B3-PE and B3-LysPE40 in a nude mouse model of human breast cancer and the evaluation of B3-PE toxicity in monkeys. Cancer Res. 1992 Jun 1;52(11):3189–3193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papa M. Z., Vetto J. T., Ettinghausen S. E., Mulé J. J., Rosenberg S. A. Effect of corticosteroid on the antitumor activity of lymphokine-activated killer cells and interleukin 2 in mice. Cancer Res. 1986 Nov;46(11):5618–5623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Chaudhary V., FitzGerald D. J. Recombinant toxins as novel therapeutic agents. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:331–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T., Muul L. M., Chang A. E., Avis F. P., Leitman S., Linehan W. M., Robertson C. N., Lee R. E., Rubin J. T. A progress report on the treatment of 157 patients with advanced cancer using lymphokine-activated killer cells and interleukin-2 or high-dose interleukin-2 alone. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 9;316(15):889–897. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704093161501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstein M., Ettinghausen S. E., Rosenberg S. A. Extravasation of intravascular fluid mediated by the systemic administration of recombinant interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1735–1742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegall C. B., Chace D., Mixan B., Garrigues U., Wan H., Paul L., Wolff E., Hellström I., Hellström K. E. In vitro and in vivo characterization of BR96 sFv-PE40. A single-chain immunotoxin fusion protein that cures human breast carcinoma xenografts in athymic mice and rats. J Immunol. 1994 Mar 1;152(5):2377–2384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick A. A. First immunotoxin therapy for many common solid tumors enters phase I clinical trial. JAMA. 1993 Nov 17;270(19):2280–2280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soler-Rodríguez A. M., Ghetie M. A., Oppenheimer-Marks N., Uhr J. W., Vitetta E. S. Ricin A-chain and ricin A-chain immunotoxins rapidly damage human endothelial cells: implications for vascular leak syndrome. Exp Cell Res. 1993 Jun;206(2):227–234. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitler L. E., del Rio M., Khentigan A., Wedel N. I., Brophy N. A., Miller L. L., Harkonen W. S., Rosendorf L. L., Lee H. M., Mischak R. P. Therapy of patients with malignant melanoma using a monoclonal antimelanoma antibody-ricin A chain immunotoxin. Cancer Res. 1987 Mar 15;47(6):1717–1723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallera D. A., Carroll S. F., Snover D. C., Carlson G. J., Blazar B. R. Toxicity and efficacy of anti-T-cell ricin toxin A chain immunotoxins in a murine model of established graft-versus-host disease induced across the major histocompatibility barrier. Blood. 1991 Jan 1;77(1):182–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetto J. T., Papa M. Z., Lotze M. T., Chang A. E., Rosenberg S. A. Reduction of toxicity of interleukin-2 and lymphokine-activated killer cells in humans by the administration of corticosteroids. J Clin Oncol. 1987 Mar;5(3):496–503. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1987.5.3.496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Stone M., Amlot P., Fay J., May R., Till M., Newman J., Clark P., Collins R., Cunningham D. Phase I immunotoxin trial in patients with B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 1;51(15):4052–4058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Thorpe P. E., Uhr J. W. Immunotoxins: magic bullets or misguided missiles? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 May;14(5):148–154. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90199-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner L. M., O'Dwyer J., Kitson J., Comis R. L., Frankel A. E., Bauer R. J., Konrad M. S., Groves E. S. Phase I evaluation of an anti-breast carcinoma monoclonal antibody 260F9-recombinant ricin A chain immunoconjugate. Cancer Res. 1989 Jul 15;49(14):4062–4067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]