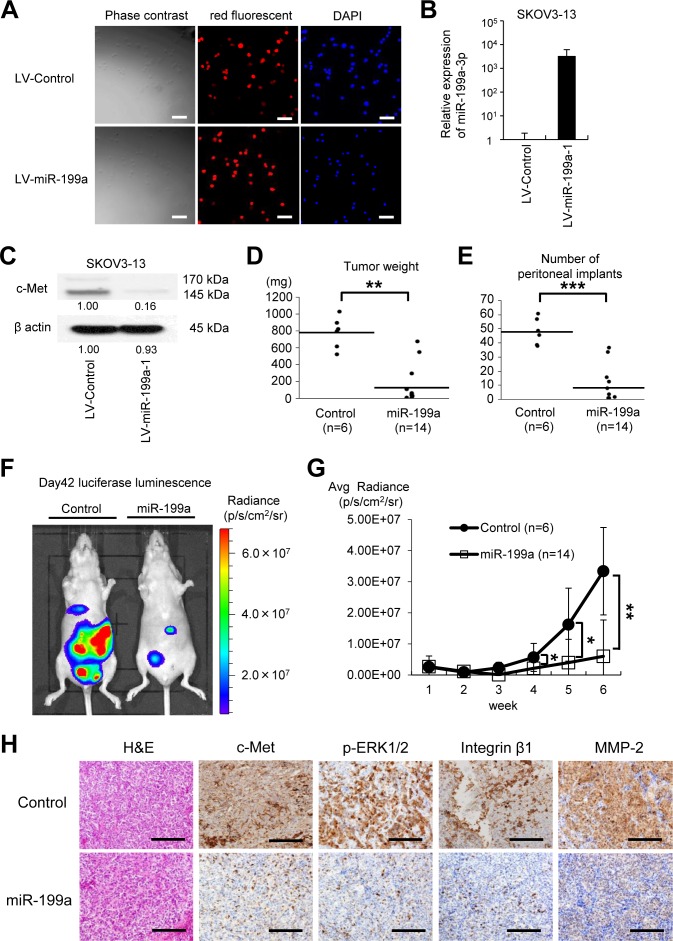
Figure 5. The microRNA miR-199a inhibits peritoneal metastasis in an ovarian cancer xenograft model.
(A) SKOV-3-13 cells, which stably express the firefly luciferase gene, were transduced with a miR-199a-1 lentivirus or a control microRNA (miRNA) lentivirus and then selected by continuous exposure to 10 μg/mL puromycin. High and stable lentiviral transduction efficiency (more than 90%) was confirmed by the red fluorescent puromycin-N-acetyl-transferase from the Lenti-miRNA-vector (BioSettia); cells are counterstained with DAPI (blue). Bar represents 100 μm. (B) miRNA RT-qPCR. RNA was collected from the lentivirus-transduced SKOV3-13 cells. (C) Western blotting. Overexpression of miR-199a-1 decreases c-Met protein expression. Densitometry ratios in each western blotting are shown below each blot. (D) and (E) Xenograft model. The cells (1 × 106 cells) were injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) into female BALB/c nu/nu mice. Six weeks after the inoculation, mice were sacrificed. Overexpression of miR-199a significantly suppressed tumor growth (D) and the number of peritoneal implants (E). Results are expressed as mean ± SEM; control, n = 6; miR-199a-3p, n = 14. (F) Representative pictures of animals (left, control miRNA; right, miR-199a-1) at 6 weeks after inoculation with SKOV3-13 cells. Pictures were taken using an IVIS imaging system with i.p. administration of 150 mg/kg of D-luciferin potassium. (G) Luciferase activities of peritoneal tumors were measured weekly. Mice that were injected with SKOV3-13 cells overexpressing miR-199a-1 expressed significantly lower luciferase luminescence activities. (H) Immunohistochemical analysis of the peritoneal implants. Representative tumor areas were stained with H&E, antibodies against c-Met, phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (p-ERK), integrin β1, and matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2). Bar represents 200 μm; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.