Abstract
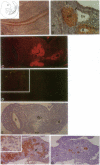
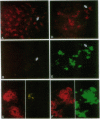
We observe Glut2 protein in day 11 (E11) rat embryos in an endodermal domain containing the pancreatic primordium. Glut2 expression continues as the endodermal epithelium evaginates into the surrounding mesenchyme to form the pancreatic buds. Cells of the dorsal and ventral pancreatic buds maintain Glut2 expression as the epithelium grows and branches to form ducts. As acini form at the ends of the ducts, acinar cells cease Glut2 expression. Insulin protein is first detected in small clusters at the interface between pancreatic epithelium and mesenchyme. These clusters disperse into the interstitial tissue between E13 and E17. At E17 a distinct, larger population of insulin-expressing cells arises in the Glut2-expressing ductal network. Insulin- and Glut2-coexpressing cells then appear to segregate into large aggregates to form the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans. These observations support the hypothesis that two biologically distinct populations of insulin-expressing cells arise during pancreas formation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpert S., Hanahan D., Teitelman G. Hybrid insulin genes reveal a developmental lineage for pancreatic endocrine cells and imply a relationship with neurons. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew A. An experimental investigation into the possible neural crest origin of pancreatic APUD (islet) cells. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1976 Jun;35(3):577–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Krijger R. R., Aanstoot H. J., Kranenburg G., Reinhard M., Visser W. J., Bruining G. J. The midgestational human fetal pancreas contains cells coexpressing islet hormones. Dev Biol. 1992 Oct;153(2):368–375. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90121-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deltour L., Leduque P., Blume N., Madsen O., Dubois P., Jami J., Bucchini D. Differential expression of the two nonallelic proinsulin genes in the developing mouse embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):527–531. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine-Pérus J., Le Lièvre C., Dubois M. P. Do neural crest cells in the pancreas differentiate into somatostatin-containing cells? Cell Tissue Res. 1980;213(2):293–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00234788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine J., Le Douarin N. M. Analysis of endoderm formation in the avian blastoderm by the use of quail-chick chimaeras. The problem of the neurectodermal origin of the cells of the APUD series. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1977 Oct;41:209–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLOSOW N., GROBSTEIN C. Epitheliomesenchymal interaction in pancreatic morphogenesis. Dev Biol. 1962 Apr;4:242–255. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(62)90042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gittes G. K., Rutter W. J. Onset of cell-specific gene expression in the developing mouse pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1128–1132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera P. L., Huarte J., Sanvito F., Meda P., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. Embryogenesis of the murine endocrine pancreas; early expression of pancreatic polypeptide gene. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1257–1265. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Douarin N. M. On the origin of pancreatic endocrine cells. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):169–171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90375-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. C., Li S., Drolet D. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Pituitary ontogeny of the Snell dwarf mouse reveals Pit-1-independent and Pit-1-dependent origins of the thyrotrope. Development. 1994 Mar;120(3):515–522. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.3.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. P., McGehee R. E., Jr, Habener J. F. IDX-1: a new homeodomain transcription factor expressed in rat pancreatic islets and duodenum that transactivates the somatostatin gene. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 1;13(5):1145–1156. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Karlsson K., Edlund T. IPF1, a homeodomain-containing transactivator of the insulin gene. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4251–4259. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06109.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver G., Sosa-Pineda B., Geisendorf S., Spana E. P., Doe C. Q., Gruss P. Prox 1, a prospero-related homeobox gene expressed during mouse development. Mech Dev. 1993 Nov;44(1):3–16. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90012-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pictet R. L., Clark W. R., Williams R. H., Rutter W. J. An ultrastructural analysis of the developing embryonic pancreas. Dev Biol. 1972 Dec;29(4):436–467. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall L. B., Pictet R. L., Rutter W. J. Synthesis and accumulation of proinsulin and insulin during development of the embryonic rat pancreas. Endocrinology. 1979 Sep;105(3):835–841. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-3-835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter W. J. The development of the endocrine and exocrine pancreas. Monogr Pathol. 1980;21:30–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelman G., Alpert S., Polak J. M., Martinez A., Hanahan D. Precursor cells of mouse endocrine pancreas coexpress insulin, glucagon and the neuronal proteins tyrosine hydroxylase and neuropeptide Y, but not pancreatic polypeptide. Development. 1993 Aug;118(4):1031–1039. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.4.1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelman G. Cellular and molecular analysis of pancreatic islet cell lineage and differentiation. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1991;47:259–297. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571147-0.50012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelman G., Lee J. K., Alpert S. Expression of cell type-specific markers during pancreatic development in the mouse: implications for pancreatic cell lineages. Cell Tissue Res. 1987 Nov;250(2):435–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00219089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelman G., Lee J. K. Cell lineage analysis of pancreatic islet development: glucagon and insulin cells arise from catecholaminergic precursors present in the pancreatic duct. Dev Biol. 1987 Jun;121(2):454–466. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90182-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Sarkar H. K., Kaback H. R., Lodish H. F. Cloning and functional expression in bacteria of a novel glucose transporter present in liver, intestine, kidney, and beta-pancreatic islet cells. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Weir G. C., Leahy J. L., Lodish H. F., Bonner-Weir S. Reduced expression of the liver/beta-cell glucose transporter isoform in glucose-insensitive pancreatic beta cells of diabetic rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6492–6496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upchurch B. H., Aponte G. W., Leiter A. B. Expression of peptide YY in all four islet cell types in the developing mouse pancreas suggests a common peptide YY-producing progenitor. Development. 1994 Feb;120(2):245–252. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessells N. K., Evans J. Ultrastructural studies of early morphogenesis and cytodifferentiation in the embryonic mammalian pancreas. Dev Biol. 1968 Apr;17(4):413–446. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(68)90073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]