Abstract
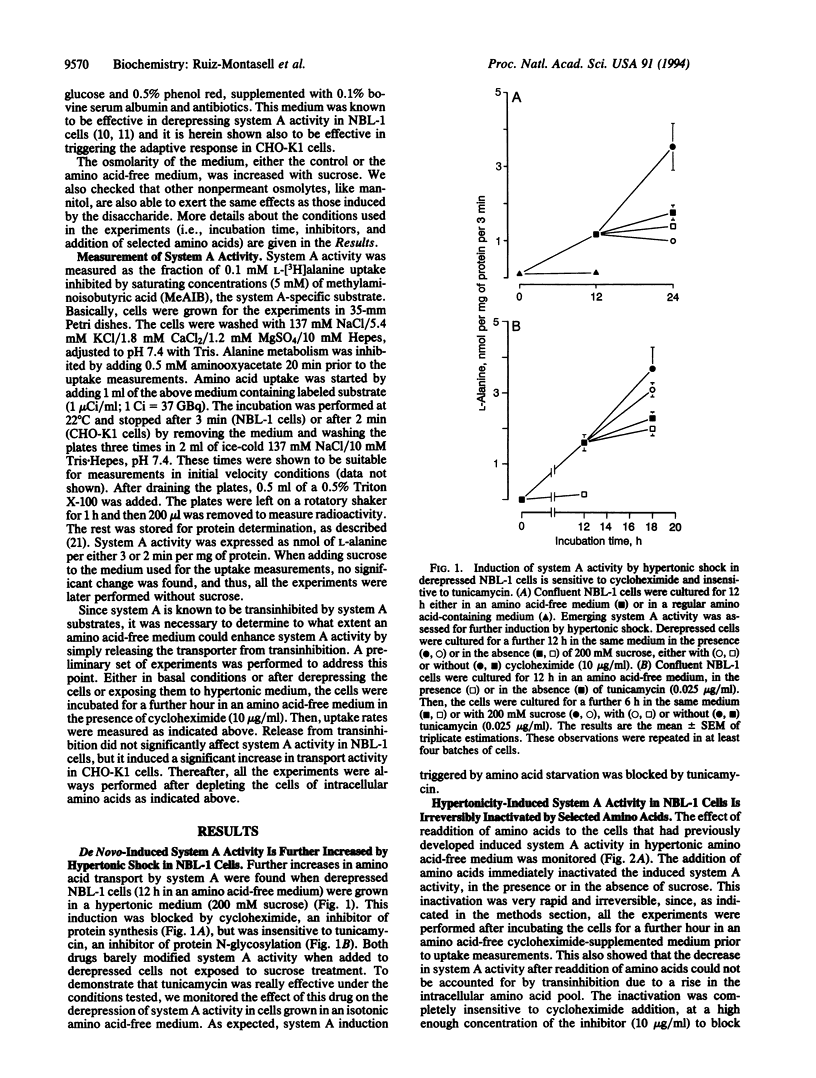
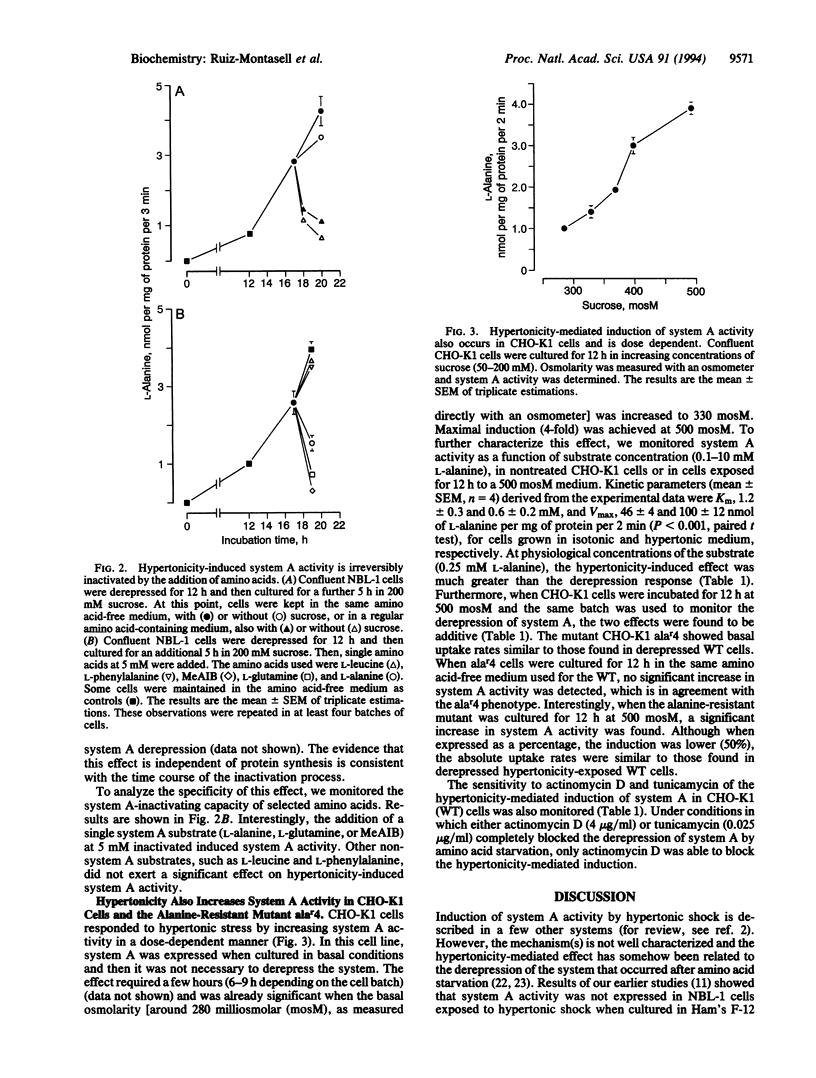
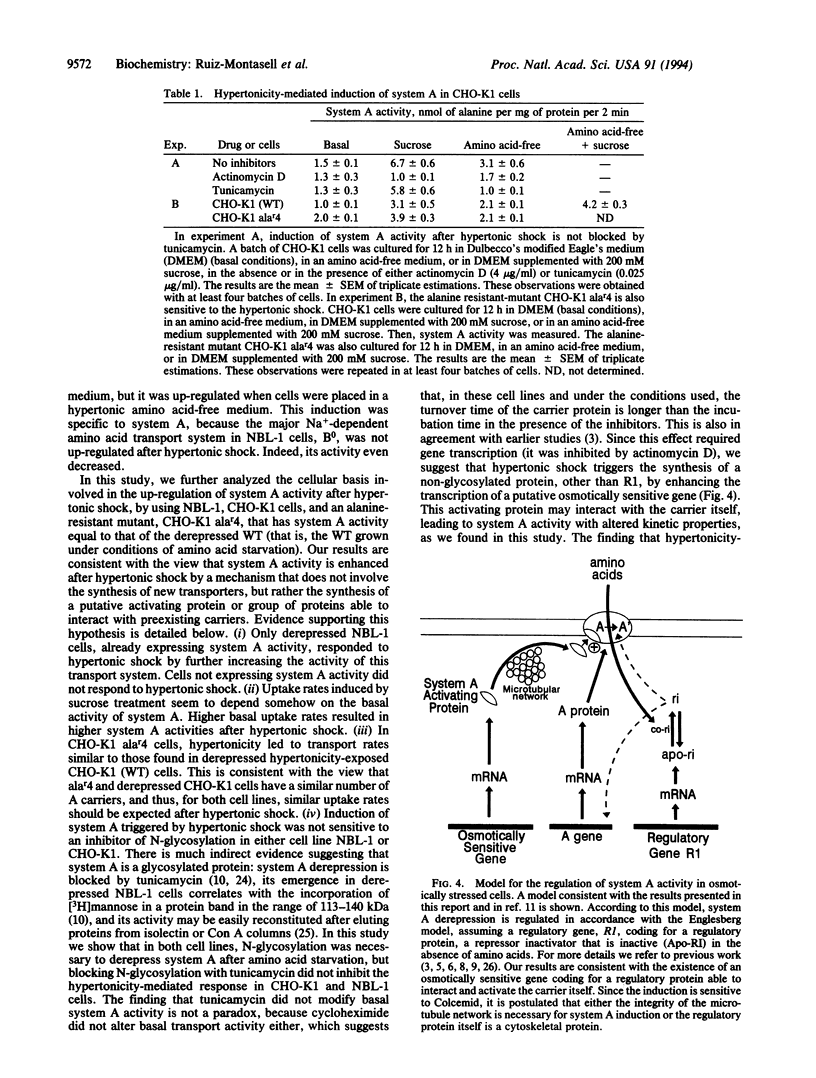
System A for neutral amino acid transport is increased by hypertonic shock in NBL-1 cells previously induced to express system A activity by amino acid starvation. The hypertonicity-mediated effect can be blocked by cycloheximide but is insensitive to tunicamycin. The activity induced may be inactivated irreversibly by the addition of system A substrates, by a rapid mechanism insensitive to cycloheximide. In CHO-K1 cells, hypertonicity increases system A activity, as has been shown in NBL-1 cells. This effect is additive to the activity produced by derepression of system A by amino acid starvation and is insensitive to tunicamycin. Furthermore, the alanine-resistant mutant CHO-K1 alar4, which bears a mutation affecting the regulatory gene R1, involved in the derepression of system A activity after amino acid starvation, is still able to respond to the hypertonic shock by increasing system A activity to a level similar to that described in hypertonicity-induced derepressed CHO-K1 (wild type) cells. These results suggest (i) that the hypertonicity-mediated increase of system A activity occurs through a mechanism other than that involved in system A derepression and (ii) that a regulatory protein coded by an osmotically sensitive gene is responsible for further activation of preexisting A carriers.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barber E. F., Handlogten M. E., Kilberg M. S. Induction of amino acid transport system A in rat hepatocytes is blocked by tunicamycin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11851–11855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantiello H. F., Stow J. L., Prat A. G., Ausiello D. A. Actin filaments regulate epithelial Na+ channel activity. Am J Physiol. 1991 Nov;261(5 Pt 1):C882–C888. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.5.C882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornet M., Ubl J., Kolb H. A. Cytoskeleton and ion movements during volume regulation in cultured PC12 cells. J Membr Biol. 1993 Apr;133(2):161–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00233796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englesberg E., Moffett J. A genetic approach to the study of neutral amino acid transport in mammalian cells in culture. J Membr Biol. 1986;91(3):199–212. doi: 10.1007/BF01868814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felipe A., Soler C., McGivan J. D. Amino acid deprivation leads to the emergence of System A activity and the synthesis of a specific membrane glycoprotein in the bovine renal epithelial cell line NBL-1. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 1;284(Pt 2):577–582. doi: 10.1042/bj2840577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häussinger D., Lang F. Cell volume in the regulation of hepatic function: a mechanism for metabolic control. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 12;1071(4):331–350. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90001-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M., Gupta R. S., Englesberg E. Enhancement in amount of P1 (hsp60) in mutants of Chinese hamster ovary (CHO-K1) cells exhibiting increases in the A system of amino acid transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):858–862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilberg M. S., Stevens B. R., Novak D. A. Recent advances in mammalian amino acid transport. Annu Rev Nutr. 1993;13:137–165. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.13.070193.001033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong C. T., Yet S. F., Lever J. E. Cloning and expression of a mammalian Na+/amino acid cotransporter with sequence similarity to Na+/glucose cotransporters. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1509–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapivinsky G. B., Ackerman M. J., Gordon E. A., Krapivinsky L. D., Clapham D. E. Molecular characterization of a swelling-induced chloride conductance regulatory protein, pICln. Cell. 1994 Feb 11;76(3):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90109-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon H. M., Yamauchi A., Uchida S., Preston A. S., Garcia-Perez A., Burg M. B., Handler J. S. Cloning of the cDNa for a Na+/myo-inositol cotransporter, a hypertonicity stress protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6297–6301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGivan J. D., Pastor-Anglada M. Regulatory and molecular aspects of mammalian amino acid transport. Biochem J. 1994 Apr 15;299(Pt 2):321–334. doi: 10.1042/bj2990321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffett J., Englesberg E. Recessive constitutive mutant Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO-K1) with an altered A system for amino acid transport and the mechanism of gene regulation of the A system. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):799–808. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffett J., Englesberg E. Regulation of the A system of amino acid transport in Chinese hamster ovary cells, CHO-K1: the difference in specificity between the apo-repressor inactivator (apo-ri) and the transporter and the characterization of the proposed apo-ri. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Mar;126(3):421–429. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041260313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffett J., Périer F., Jones M., Englesberg E. Control of A-system amino acid transport by a second regulatory gene R2 in Chinese hamster ovary cells CHO-K1 and the possible connection of this gene with insulin activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8040–8043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitoris B. A., Nelson W. J. Alterations in the establishment and maintenance of epithelial cell polarity as a basis for disease processes. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):3–9. doi: 10.1172/JCI114427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi T., Turner R. J., Burg M. B. Osmoregulatory changes in myo-inositol transport by renal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):6002–6006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.6002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Hammerton R. W. A membrane-cytoskeletal complex containing Na+,K+-ATPase, ankyrin, and fodrin in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells: implications for the biogenesis of epithelial cell polarity. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):893–902. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petronini P. G., De Angelis E. M., Borghetti A. F., Wheeler K. P. Effect of betaine on HSP70 expression and cell survival during adaptation to osmotic stress. Biochem J. 1993 Jul 15;293(Pt 2):553–558. doi: 10.1042/bj2930553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petronini P. G., Tramacere M., Wheeler K. P., Borghetti A. F. Induction of amino acid transport activity in chick embryo fibroblasts by replacement of extracellular sodium chloride with disaccharide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jul 12;1053(2-3):144–150. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90006-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian N. X., Jones M., McDonough A., Englesberg E. alar4, a constitutive mutant of the A system for amino acid transport, has increased abundance of the Na+,K+-ATPase and mRNA for alpha 1 subunit of this enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7984–7988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian N. X., Pastor-Anglada M., Englesberg E. Evidence for coordinate regulation of the A system for amino acid transport and the mRNA for the alpha 1 subunit of the Na+,K(+)-ATPase gene in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3416–3420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quesada A. R., McGivan J. D. A rapid method for the functional reconstitution of amino acid transport systems from rat liver plasma membranes. Partial purification of System A. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 1;255(3):963–969. doi: 10.1042/bj2550963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy G., Malo C. Activation of amino acid diffusion by a volume increase in cultured kidney (MDCK) cells. J Membr Biol. 1992 Oct;130(1):83–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00233740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Daniels G. A., Boerner P., Lin J. Neutral amino acid transport systems in animal cells: potential targets of oncogene action and regulators of cellular growth. J Membr Biol. 1988 Aug;104(1):1–20. doi: 10.1007/BF01871898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soler C., Felipe A., Casado F. J., McGivan J. D., Pastor-Anglada M. Hyperosmolarity leads to an increase in derepressed system A activity in the renal epithelial cell line NBL-1. Biochem J. 1993 Feb 1;289(Pt 3):653–658. doi: 10.1042/bj2890653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strange K., Morrison R., Heilig C. W., DiPietro S., Gullans S. R. Upregulation of inositol transport mediates inositol accumulation in hyperosmolar brain cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Apr;260(4 Pt 1):C784–C790. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.4.C784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veis J. H., Molitoris B. A., Teitelbaum I., Mansour J. A., Berl T. Myo-inositol uptake by rat cultured inner medullary collecting tubule cells: effect of osmolality. Am J Physiol. 1991 May;260(5 Pt 2):F619–F625. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.5.F619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veyhl M., Spangenberg J., Püschel B., Poppe R., Dekel C., Fritzsch G., Haase W., Koepsell H. Cloning of a membrane-associated protein which modifies activity and properties of the Na(+)-D-glucose cotransporter. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):25041–25053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi A., Kwon H. M., Uchida S., Preston A. S., Handler J. S. Myo-inositol and betaine transporters regulated by tonicity are basolateral in MDCK cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jul;261(1 Pt 2):F197–F202. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.1.F197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi A., Uchida S., Kwon H. M., Preston A. S., Robey R. B., Garcia-Perez A., Burg M. B., Handler J. S. Cloning of a Na(+)- and Cl(-)-dependent betaine transporter that is regulated by hypertonicity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):649–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



