Abstract
Bacterial endotoxin (LPS)-mediated sepsis involves severe, dysregulated inflammation that injures the lungs and other organs, often fatally. Vascular endothelial cells are both key mediators and targets of LPS-induced inflammatory responses. The nuclear hormone receptor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) exerts anti-inflammatory actions in various cells, but it is unknown whether it modulates inflammation through actions within endothelial cells. To determine whether PPARγ acts within endothelial cells to diminish endotoxemic lung inflammation and injury, we measured inflammatory responses and mediators in mice with endothelial-targeted deletion of PPARγ. Endothelial cell PPARγ (ePPARγ) knockout exacerbated LPS-induced pulmonary inflammation and injury as shown by several measures, including infiltration of inflammatory cells, edema, and production of reactive oxygen species and pro-inflammatory cytokines, along with upregulation of the LPS receptor TLR4 in lung tissue and increased activation of its downstream signaling pathways. In isolated LPS-stimulated endothelial cells in vitro, absence of PPARγ enhanced the production of numerous inflammatory markers. We hypothesized that the observed in vivo activity of the ligand-activated ePPARγ may arise in part from nitrated fatty acids (NFAs), a novel class of endogenous PPARγ ligands. Supporting this idea, we found that treating isolated endothelial cells with physiologically relevant concentrations of the endogenous NFA 10-nitro-oleate reduced LPS-induced expression of a wide range of inflammatory markers in the presence of PPARγ, but not in its absence, and also inhibited neutrophil mobility in a PPARγ–dependent manner. Our results demonstrate a key protective role of ePPARγ against endotoxemic injury, and a potential ePPARγ–mediated anti-inflammatory role for NFAs.
Keywords: LPS, Nrf2, PPAR, ALI, nitrated fatty acid
1INTRODUCTION
Sepsis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality, frequently involving acute lung injury, in hospitalized patients (1, 2). It is often caused by endotoxins, the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) cell wall components of Gram-negative bacteria. LPS acts via Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) (3) to trigger an innate immune response that is usually protective, but that during endotoxemia can become hyperactivated and dysregulated, thus causing excessive inflammation and widespread organ injury. TLR4 stimulation is a multistep process, activating a cascade of downstream pathways that, via the transcription factors NF-κB and AP-1, upregulate expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules. Endogenous anti-inflammatory signaling pathways serve to protect the host by restraining such inflammatory responses. Sepsis represents a failure of these counter-regulatory mechanisms, which normally keep inflammation in check and allow it to perform its protective functions without excessive tissue injury. Understanding these endogenous anti-inflammatory mechanisms is key to developing new tools to control pathogenic inflammation and sepsis.
Cells of the vascular endothelium are among the first to encounter circulating bacteria and their products including LPS, and they play key roles as both initiators and targets of the innate immune response. Activation of TLR4 in endothelial cells promotes increased production of neutrophil-attracting chemokines, along with integrins and adhesion molecules that promote neutrophil adhesion to the endothelium and migration into surrounding tissue, where they promote further inflammation. These actions contribute to the clinical features of severe endotoxemic sepsis, including increased vascular permeability that causes tissue edema, thereby restricting pulmonary gas exchange, and hypotensive shock (4).
The present study seeks to determine whether the ligand-activated nuclear hormone receptor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ), which has anti-inflammatory activity (5), acts within pulmonary vascular endothelial cells to protect against endotoxemic lung damage. PPARγ promotes transcription of genes for anti-inflammatory factors, apparently including the antioxidant nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) (6), and also inhibits activity of NF-κB, AP-1, and other pro-inflammatory transcription factors, in part by competing for essential coactivators (7). PPARγ is expressed in endothelial cells (8), and PPARγ agonists exert beneficial effects in animal models of inflammatory diseases (9–14) and sepsis (15), but it is unknown whether PPARγ acts within endothelial cells to protect against endotoxemia and sepsis. Also, the identities of physiologically relevant endogenous PPARγ ligands are unresolved. Here we used a transgenic mouse model of targeted endothelial cell PPARγ deficiency (16) to test the idea that endothelial PPARγ protects against endotoxemic pulmonary inflammation and lung damage. We also discovered that the nitrated fatty acid (NFA) 10-nitro-oleic acid (OA-NO2), a candidate physiological PPARγ agonist, exerts a broad range of anti-inflammatory actions within pulmonary endothelial cells that are mediated via PPARγ.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals
Wild-type (ePPARγ+/+) and isogenic homozygous endothelial cell PPARγ knockout (ePPARγ−/−) mice on a C57BL/6 genetic background were expanded from breeding pairs. Mice were housed in microisolator cages under specific pathogen-free conditions and fed autoclaved food. Male mice aged 6–8 weeks (20–25 g) were used. All studies were performed according to protocols reviewed and approved by the Atlanta Veterans Affairs Medical Center Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Cells
Mouse lung endothelial cells (MLEC) were isolated as described previously (17). Endothelial identity was confirmed by cobblestone morphology, immunofluorescence staining, and positive Western blotting for PECAM-1, eNOS, vascular endothelial cadherin (BD Pharmingen, San Diego, CA) and negative blots for α-smooth muscle actin (BD Pharmingen). Cells were cultured and grown to confluent monolayers in VascuLife Basal Medium (Lifeline Cell Technology, Frederick, MD) supplemented with 2% FBS, 10 mM L-glutamine, 0.2% EnGS, 5 ng/mL rhEGF, 1 µg/mL hydrocortisone hemisuccinate, 0.75 units/mL heparin sulfate (Lifeline Cell Technology), 10,000 units/mL penicillin, and 10,000 µg/mL streptomycin (HyClone, Logan, UT), at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 – 95% air in tissue culture flasks, plates, or dishes coated with 2% gelatin. All cells were used at passages 3–5.
LPS Administration
Mice were injected i.p. with 10 mg/kg of LPS prepared from Escherichia coli O111:B6 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO). After a further 12 h the mice were euthanized, blood was obtained by cardiac puncture and plasma prepared, and lung and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid samples were collected.
Lung Wet:Dry Weight Ratio
As an index of lung edema, the proportion of extravascular lung water was calculated. The lower lobe of the right lung was ligated, excised and the wet weight was recorded. The lung was then placed in an incubator at 60°C for 24 h, the dry weight recorded, and the wet:dry ratio calculated.
BAL Fluid Collection and Cell Count
Following removal of the lower right lung lobe, BAL fluid was collected by flushing 3 × 1 ml of PBS containing 0.1 mM EDTA into the lung via a tracheal cannula. The pooled BAL fluid was centrifuged at 500 × g at 4°C for 5 min. Pelleted cells were then resuspended in 1 ml of PBS. Total cell number was counted by hemocytometer and a differential cell count was performed by cytospin staining with Diff-Quik stain (Siemens, Newark, DE).
BAL Fluid Protein
Increase in BAL fluid protein concentration was taken as a measure of increased permeability of alveolar-capillary barriers. Total protein concentration in the supernatant following BAL fluid centrifugation was determined using the BCA Protein Assay kit (Pierce, Rockford, IL).
Assessment of Capillary Leakage
To assess lung capillary permeability, Evans Blue dye (EBD; 50 mg/kg; Sigma-Aldrich) dissolved in 200 µl PBS was injected into the tail veins of mice following LPS injection. After 30 min, the animals were euthanized and the lungs perfused with 5 ml of PBS, and the lungs then excised en bloc and snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen. The frozen lungs were then homogenized in 2 ml PBS and the homogenates diluted with 2 vol of formamide, then incubated at 60°C for 18 h followed by centrifugation at 5,000 × g for 30 min. Supernatants were collected and absorbance measured at 620 and 740 nm. The EBD concentration was determined from standard absorbance curves evaluated in parallel. Correction for contaminating heme pigments was calculated by the formula E620 (EBD) = E620 − (1.426 × E740 + 0.030). The EBD concentration was expressed as µg/g lung tissue.
Measurement of Myeloperoxidase Activity
Myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity was determined in BAL fluid and tissue as indices of neutrophil infiltration. Frozen lungs were thawed, weighed, homogenized, and sonicated on ice in radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer. After centrifugation at 10,000 × g at 4°C for 20 min, supernatants were collected. MPO activity in supernatants of tissue and BAL fluid were measured by a fluorometric assay (700160; Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor, MI) and expressed as nmol/min-ml.
Measurement of Oxidant Stress
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) production in lung tissue was determined using the Amplex Red Hydrogen Peroxide Assay kit (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR) according to the manufacturer’s directions. The concentrations of nitrate and malondialdehyde (MDA) in lung homogenates were measured using colorimetric assay kits (Cayman Chemical).
Measurement of Lung and BAL Fluid Cytokine Levels
Lung and BAL fluid levels of TNF-α, IL-6, KC, and MIP-2 were measured using ELISA kits (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Transcription Factor DNA-binding Activity Assay
Nuclear proteins were extracted using a nuclear extraction kit (Active Motif, Carlsbad, CA) and their concentration was determined using the BCA Protein Assay kit (Pierce). Nuclear extracts were used to quantify DNA-binding activity of PPARγ, Nrf2, and the p65 subunit of NF-κB using ELISA-based TransAM kits (40096, 40696, and 50296; Active Motif) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Western Blotting
Total protein extracts were prepared by lysing cells and homogenizing lung tissue in 500 µl of ice-cold radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer supplemented with Halt protease inhibitor cocktail (Pierce). Extracts were incubated for 20 min at 4°C followed by centrifugation at 14,000 × g, for 15 min. The supernatants were collected and stored at −80°C. Samples were mixed with sample buffer, separated on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel and electroblotted onto a polyvinyldifluoride membrane (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA). The membrane was blocked with blocking solution (3% BSA in TBST) for 1 h at room temperature. Blots were then incubated overnight at 4°C with primary antibody against the target protein (1:1000). Antibodies against NFκB-p65, PPARγ, Nrf2, lamin B1, IRAK-4, TRAF6, and β-actin were from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA). Antibodies against TLR4, MyD88, p-ERK, p-Akt, p-IKKα/β, p-JNK and p-p38 MAPK were from Cell Signaling Technology (Beverly, MA). The membrane was then washed in TBST and incubated with secondary antibodies consisting of donkey anti-mouse IR 680 (red; LI-COR, Lincoln, NE) and goat anti-rabbit IR 780 (green; LI-COR), diluted 1:5000, for 1 h at room temperature. The infrared signal was detected using an Odyssey Infrared Imager (LI-COR).
Lung Histopathology
The lungs were inflated and fixed with 10% neutral formalin overnight at room temperature. Lung tissue was dehydrated with increasing ethanol concentrations and then embedded in paraffin. Five-micrometer-thick paraffin sections were stained with H&E.
Immunofluorescence Staining and Confocal Imaging
MLEC were cultured on 2% gelatin-coated glass-bottom dishes (MatTek, Ashland, MA) in VascuLife Basal Medium (Lifeline Cell Technology) without growth factors and treated with 100 ng/ml LPS for 6 h. Cells were then washed twice with PBS and subsequently fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin for 15 min at 37°C. Following fixation, cells were permeabilized with Target Retrieval Solution (Dako, Carpinteria, CA) for 10 min at 95°C, allowed to cool to room temperature, and blocked at 37°C for 1 h with 1% BSA in PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20 (PBST). After being washed, cells were incubated at 37°C for 1 h with primary antibodies to ICAM-1 or PECAM-1 (BD Pharmingen), diluted 1:50 in PBST-1% BSA. After washing with PBST, cells were incubated at 37°C for 1 h with FITC-conjugated goat anti-rat secondary antibody (Jackson ImmunoResearch, West Grove, PA) diluted 1:50 in PBST-1% BSA and then washed three times with PBST. Cover slips were retrieved and mounted on glass slides with Vectashield mounting medium with DAPI (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA). The slides were viewed by an Olympus Fluoview FV1000 confocal microscope (Olympus, Center Valley, PA) using a 60 × fluorescence lens along with Fluoview confocal software (FV10-ASW v1.7, Olympus).
Determination of Cellular ROS
MLEC were cultured and treated with LPS as described under Immunofluorescence Staining. Production of intracellular ROS in live cells was determined using the Amplite Intracellular Fluorimetric Hydrogen Peroxide Assay kit (AAT Bioquest, Sunnyvale, CA). Cover slips were retrieved and mounted on glass slides with Vectashield mounting medium (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA). The slides were viewed by an Olympus Fluoview FV1000 confocal microscope (Olympus) using a 60 × fluorescence lens along with Fluoview confocal software (FV10-ASW v1.7, Olympus).
In vitro Neutrophil Transmigration Assay
MLEC were seeded at a density of 5 × 105 cells in the upper chamber of each Transwell (6.5 mm diameter, 3 µm pore size; Costar, Corning, NY) and the cells were grown to form a confluent monolayer. In some experiments cells were treated with 100 nM OA-NO2 or DMSO along with 100 ng/ml LPS or with PBS and incubated for 6 h. Neutrophils isolated from BAL fluid of LPS-stimulated ePPARγ+/+ mice were added to the top chamber at 4 × 105cells/well and, where indicated, chemoattractant was added to the lower chamber. The neutrophils were incubated at 37°C for 1.5 h, after which neutrophils that had transmigrated into the lower chamber were collected, counted, and transmigration expressed as % of neutrophils added.
RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR
MLEC were cultured and treated with LPS as described under Immunofluorescence Staining, but were pre-treated with 100 nM OA-NO2 or DMSO for 1 h prior to LPS exposure. After 6 h, cells were lysed and RNA was isolated using RNeasy Mini kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA), and cDNA generated from 100 ng of total RNA using MultiScribe reverse transcriptase (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) employing random and oligo-dT primers. Real-time quantitative PCR was performed using 100 ng cDNA with 2X SYBR Green Master mix (Applied Biosystems) and specific primers for the genes of interest (Supplemental Table 1). These experiments were performed on an AB 7500 fast thermal cycler using a three-step protocol employing the melting curve method. The average of each gene cycle threshold (Ct) was determined for each experiment. Relative cDNA levels (2−ΔΔCt) for the genes of interest were determined by using the comparative Ct method, which generates the ΔΔCt as the difference between the gene of interest and the housekeeping genes GAPDH and 9s rRNA for each sample. Each averaged experimental gene expression sample was compared to the averaged control sample, which was set to 1.
Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as mean ± SD. Differences between groups were analyzed using ANOVA, followed by a Bonferroni multiple comparison test using GraphPad Prism 5.03 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA). P < 0.05 was considered significant.
RESULTS
Endotoxemia-induced Capillary Permeability Increases and Lung Injury Is More Severe in Endothelial PPARγ KO Mice
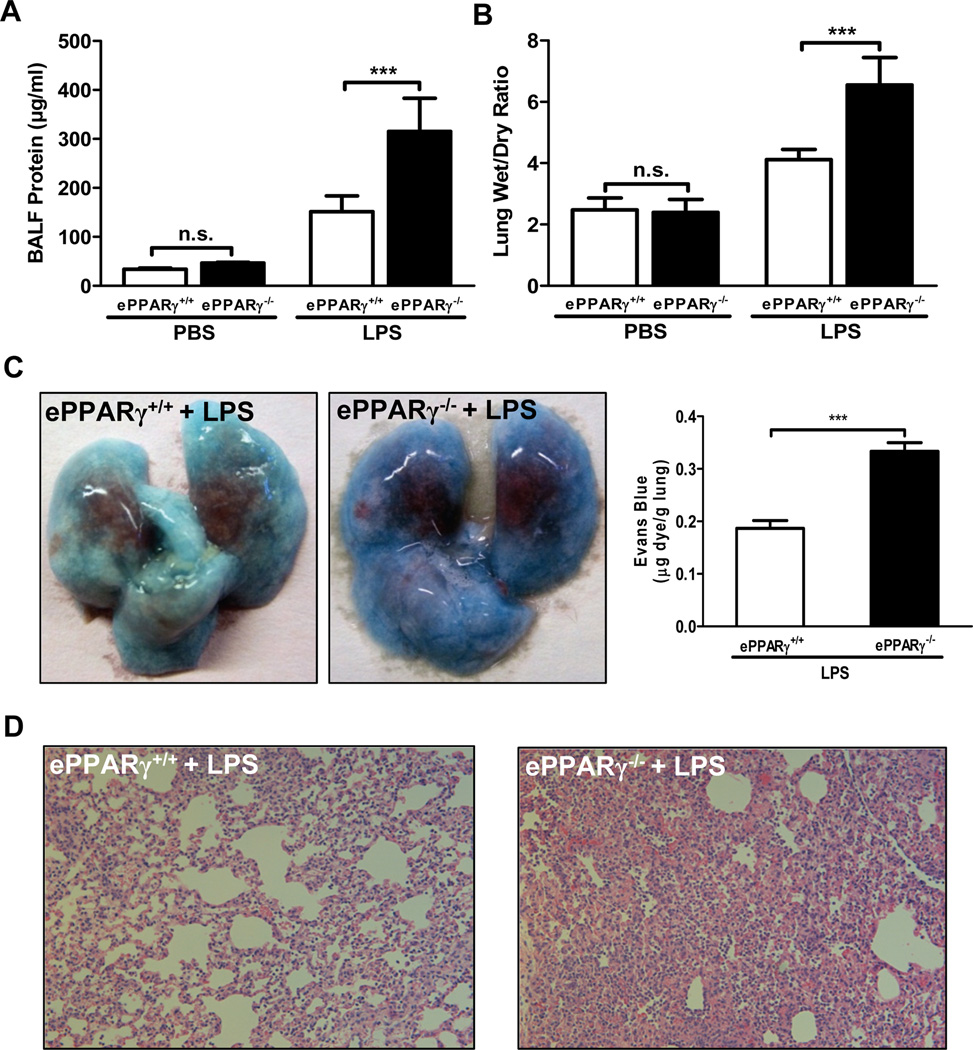
To test our hypothesis that endothelial cell PPARγ modulates endotoxemia-induced lung injury, we compared lung edema and inflammation in endothelial PPARγ knockout (ePPARγ−/−) and wild-type (ePPARγ+/+) control mice 12 h after treatment with LPS (10 mg/kg, i.p.). ePPARγ deficiency markedly increased all measures of lung injury-associated pulmonary edema and capillary leakage. LPS-induced increases in protein content of BAL fluid (Fig. 1A), an indicator of elevated capillary permeability, and lung wet:dry tissue weight ratio (Fig. 1B) were nearly doubled in ePPARγ−/− vs. ePPARγ+/+ mice, as was extravasation of Evans Blue dye 30 min after i.v. injection (Fig. 1C). Both wild-type (Fig. 1D, left) and ePPARγ KO mice (Fig. 1D, right) treated with LPS exhibited leukocyte infiltration, alveolar distortion and edema on histological examination, but these were more severe in ePPARγ KO animals.
Figure 1. ePPARγ Deficiency Exacerbates LPS-induced Lung Injury.
All measures of LPS (10 mg/kg, i.p.)-induced (A, C) capillary leakage, (B) edema, and (D) inflammation were markedly elevated in ePPARγ−/− mice vs. ePPARγ+/+ controls. Mice were euthanized, BAL fluid collected, and lungs excised 12 h after injection. (A) Protein concentration in BAL fluid. (B) Ratio of lung tissue wet:dry weight. (C) Extravasation of Evans Blue dye into the lung after i.v. injection, photographed (left panel; note lighter color) and quantitated by spectrophotometry (right panel). (D) Histological appearance with H&E staining, showing intensified infiltration by inflammatory cells in ePPARγ−/− mice (right panel). Each data set is representative of 2–3 independent experiments with n = 6–8 mice per group; ***P < 0.001.
ePPARγ Deletion Elevates Production of ROS and Pro-inflammatory Cytokines
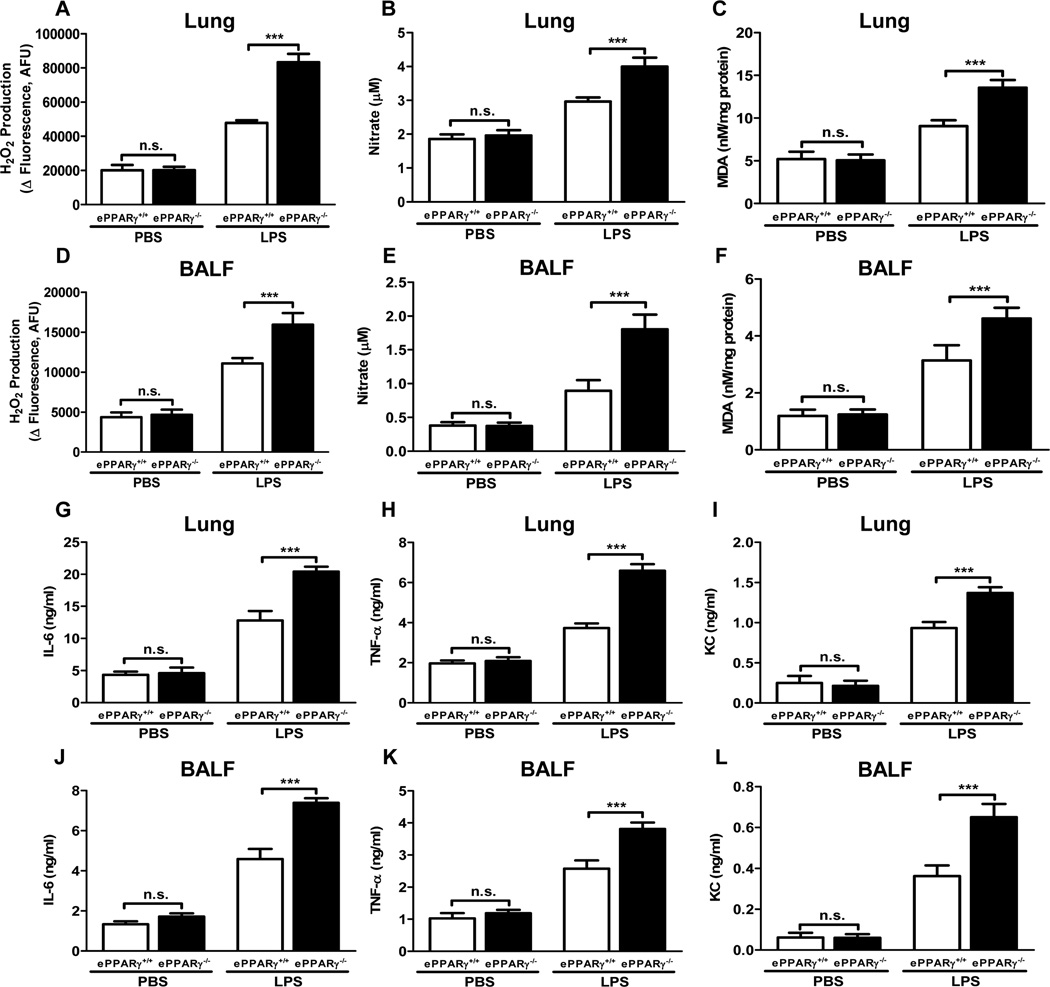
To assess the influence of ePPARγ on endotoxemia-associated mediators of pulmonary inflammation in vivo, we compared pulmonary LPS-induced elevations of relevant ROS and pro-inflammatory cytokines in ePPARγ−/− and ePPARγ+/+ mice. ROS production was assessed in lung tissue and BAL fluid by measuring 3 different indices: H2O2 production (Fig. 2A, D); concentrations of nitrate, which is an end product of the key vasodilator NO generated by a different pathway than H2O2 (Fig. 2B, E); and MDA, a lipid oxidation product that provides an index of overall oxidant stress (MDA:protein ratio; Fig. 2C, F). LPS treatment elevated the levels of all these markers in both mouse strains, but the LPS-induced increases seen were significantly greater in ePPARγ KO mice for all ROS-related analytes tested. We also measured LPS-induced elevations in expression within lung tissue and BAL fluid of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 (Fig. 2G, J) and TNF-α (Fig. 2H, K), for which endothelial cells are important sources, as well as the chemokine KC (Fig. 2I, L). Again, LPS treatment elicited increased cytokine/chemokine levels in both mouse strains, but the increases seen in all markers were significantly greater in ePPARγ KO than in wild-type mice. These results indicate that the greater severity of inflammation seen in ePPARγ KO mice is associated with elevations in a range of ROS and key inflammatory cytokines.
Figure 2. Production of ROS and Pro-inflammatory Cytokines Is Elevated Following ePPARγ Deletion.
ePPARγ+/+ and ePPARγ−/− mice were treated with LPS (10 mg/kg, i.p.), and after 12 h ROS and cytokine levels were measured in BAL fluid and lung tissue extracts. LPS-induced elevations in ROS and cytokine levels were increased by ePPARγ KO in lung and BAL fluid (BALF) for all analytes: (A, D) H2O2; (B, E) total nitrate concentration; (C, F) malonaldehyde (MDA)/protein ratio; (G, J) IL-6, (H, K) TNF-α; and (I, L) KC. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments with n = 6–8 mice per group; ***P < 0.001.
Endotoxemia-induced Neutrophil Infiltration into Alveolar Space Is Increased in ePPARγ KO Mice
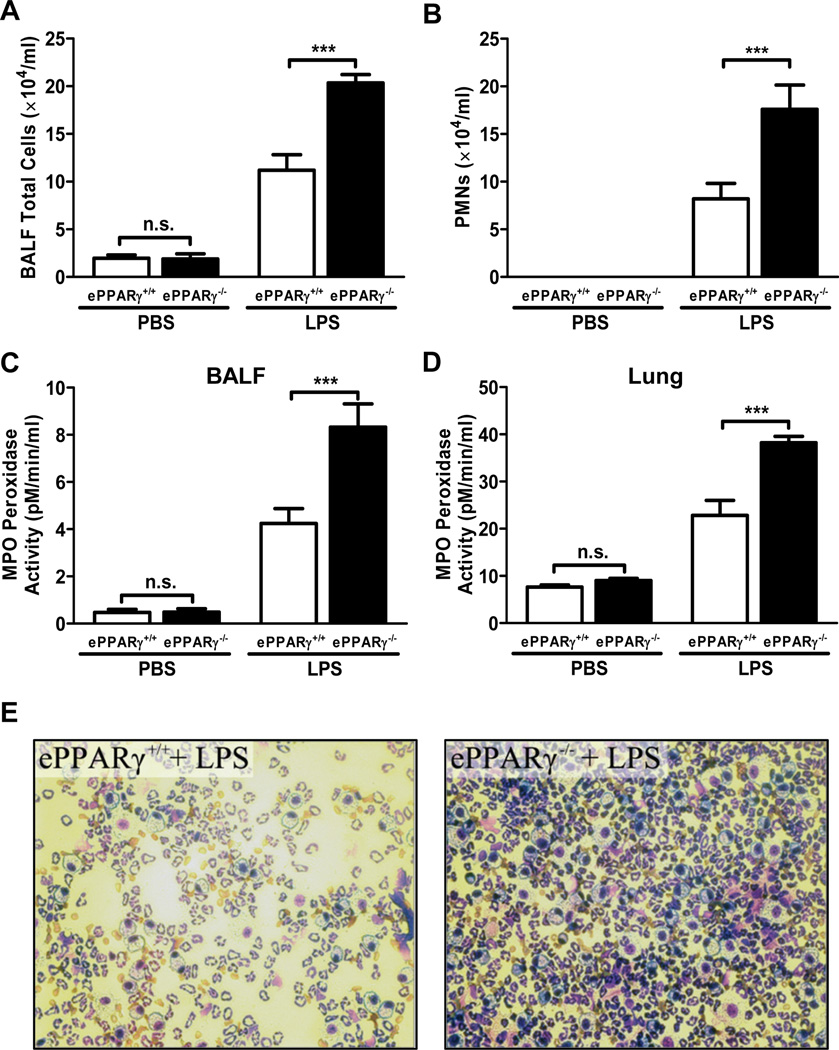
Endotoxemia-induced inflammation is associated with infiltration of neutrophils into target tissues including the lung. We found that multiple measures of LPS-induced neutrophil infiltration were markedly increased in ePPARγ KO vs. in wild-type mice, including: total numbers of cells in alveolar space, assessed by measuring those recovered in BAL fluid (Fig. 3A); numbers of neutrophils identified by differential staining (Fig. 3B); and MPO levels in BAL fluid (Fig. 3C) and whole lung tissue (Fig. 3D). Microscopic examination of BAL fluid with differential staining similarly showed that ePPARγ deficiency led to greater LPS-induced increases in both total cell numbers and proportion of neutrophils (Fig. 3E).
Figure 3. Migration of Neutrophils into the Lung Is Increased in ePPARγ KO Mice.
ePPARγ−/− mice exhibited greater elevations of total numbers of (A) cells, (B) neutrophils (PMNs), and (C) myeloperoxidase activity (MPO) in BAL fluid (BALF), as well as (D) MPO activity in lung tissue 12 h after injection of LPS (10 mg/kg, i.p.). (E) Differential staining of cells in BAL fluid revealed increased numbers of PMNs in ePPARγ−/− (right panel) vs. that seen in ePPARγ+/+ mice (left panel). Data are representative of 2 independent experiments with n = 6–8 mice per group; ***P < 0.001.
Genetic Deletion of ePPARγ Upregulates LPS Signaling
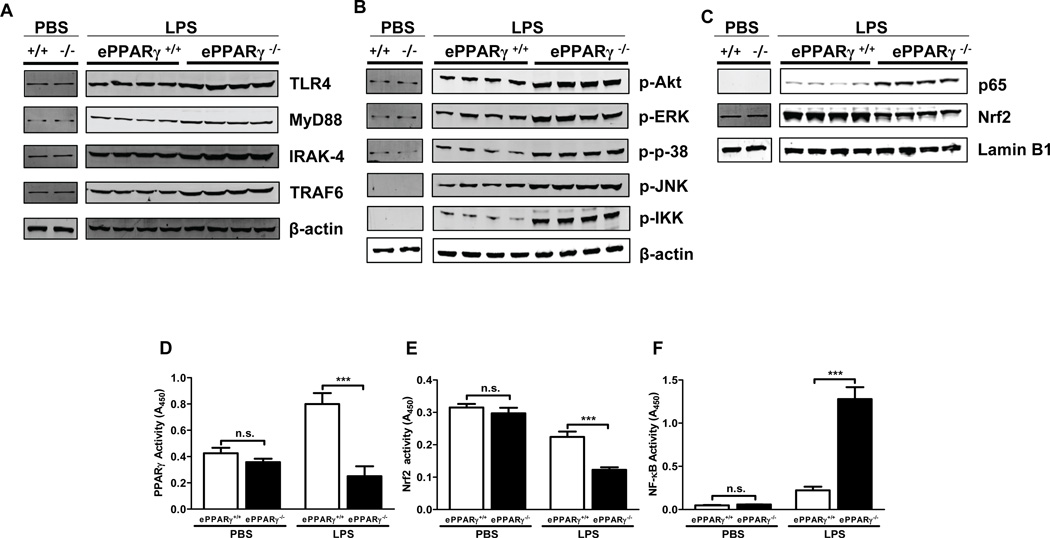
To determine the mechanisms underlying the exaggerated inflammatory responses seen in ePPARγ KO mice, we measured the levels of LPS-associated intermediate signaling proteins following induction of endotoxemia, using Western blots of lung tissue extracts. After LPS treatment, ePPARγ−/− mice exhibited greater expression of TLR4 and the TLR signaling proteins MyD88, IRAK-4, and TRAF6 than did ePPARγ+/+ mice (Fig. 4A). ePPARγ KO mice similarly exhibited greater levels of the phosphorylated (activated) forms of downstream signaling mediators which serve to activate the transcription factors AP-1 and NF-κB, than did ePPARγ+/+ mice.
Figure 4. Genetic Deletion of ePPARγ Upregulates in vivo LPS Signaling.
ePPARγ+/+ and ePPARγ−/− mice were treated with LPS (10 mg/kg, i.p.). Twelve h later lung tissue protein extracts were prepared and the levels of LPS signaling proteins analyzed. Lungs of ePPARγ−/− mice exhibited higher levels of (A) the LPS receptor TLR4 and its downstream signaling molecules MyD88, IRAK-4, and TRAF6; B) the phosphorylated (activated) forms of intermediate signaling molecules further downstream (Akt, ERK, p38, JNK, IKKα/β); and (C) the transcription factors NF-κB (p65) and Nrf2. Blots were simultaneously incubated with lamin B1 or β-actin antibody where indicated. Smaller blot represents PBS treated ePPARγ+/+ mice (left), ePPARγ−/− mice (right). In larger blot left four lanes represent LPS treated ePPARγ+/+ mice, right four lanes represent LPS treated ePPARγ−/− mice. In separate experiments we also determined DNA-binding activities of transcription factors in lung extracts. ePPARγ KO abolished the LPS-induced component of (D) PPARγ activity, while (E) enhancing the LPS-induced decrease in Nrf2 activity and (F) markedly elevating LPS-induced NF-κB activity. Blots are representative of 3 independent experiments with each lane representing a single mouse lung, and activity data of 2 independent experiments (n = 6–8 mice per group). *** P < 0.001.
Absence of ePPARγ Exaggerates LPS-induced Changes in Activity of NF-κB and Nrf2
Endotoxemia-induced inflammation involves upregulation of pro-inflammatory transcription factors including NF-κB, which is transrepressed by PPARγ, as well as downregulation of the antioxidant transcription factor Nrf2, which evidence suggests is upregulated by PPARγ (6). To test the influence of PPARγ on LPS-stimulated expression and activity of these signaling proteins in vivo, we compared their levels in ePPARγ KO and wild-type control mice. Following LPS treatment, ePPARγ KO mice exhibited elevated nuclear p65 and decreased nuclear Nrf2 protein levels vs. those in wild-type controls (Fig. 4C), paralleled by an LPS-induced upregulation of NF-kB activity (Fig. 4F) and a decrease in Nrf2 activity (Fig. 4E). Knockout of PPARγ specifically in endothelial cells did not significantly decrease baseline whole-lung PPARγ activity (Fig. 4D), but it abolished the LPS-induced increase.
PPARγ Deletion Exaggerates Inflammatory Responses of Endothelial Cells in Vitro
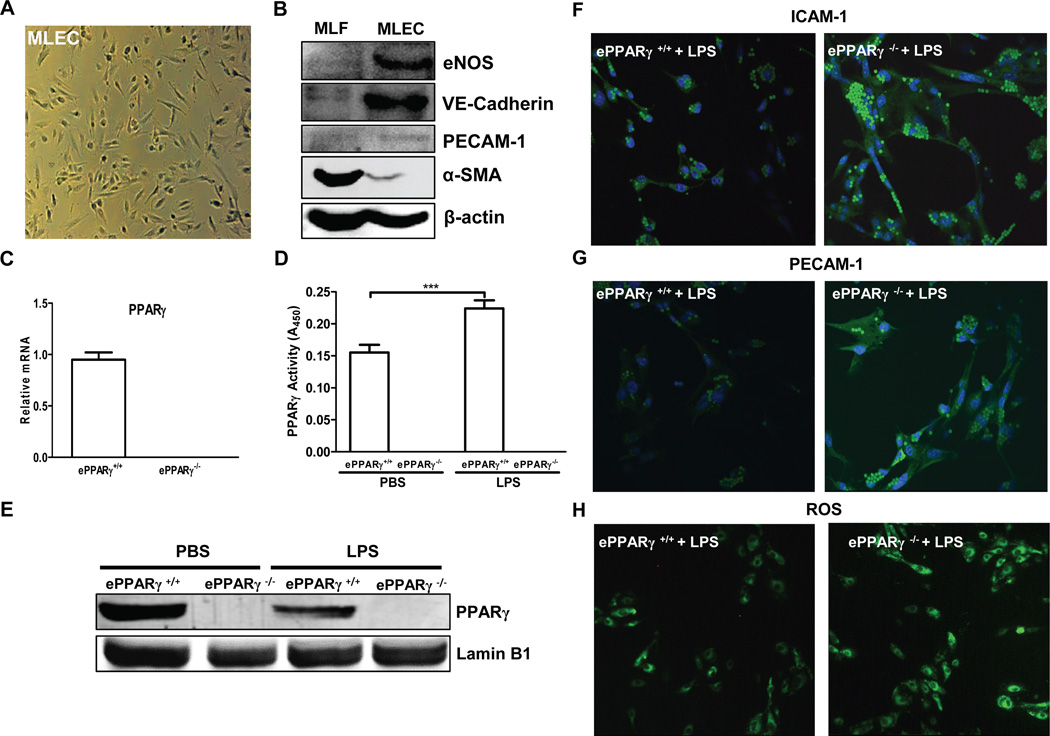
To ascertain whether ePPARγ acts within lung endothelial cells to modulate inflammatory responses, we compared expression of inflammatory markers induced by LPS in vitro, in MLEC isolated from ePPARγ−/− and ePPARγ+/+ mice. Endothelial identity of the isolated cells was confirmed microscopically (Fig. 5A) and by Western blotting (Fig. 5B). Endothelial cells exhibited the expected abundant expression of the endothelial isoform of nitric oxide synthase and the adhesion molecules vascular endothelial cadherin, the related PECAM-1, and near-absence of α-smooth muscle actin, while isolated fibroblasts exhibited an opposite expression profile. We confirmed the absence of PPARγ mRNA and of PPARγ protein in endothelial cells from ePPARγ KO mice by real-time RT-PCR and Western blotting respectively (Fig. 5C, E). After stimulation of MLEC from wild-type and ePPARγ KO mice in vitro with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 6 h, PPARγ-deficient MLEC exhibited increased expression of the inflammation-associated adhesion molecules ICAM-1 (Fig. 5F) and PECAM-1 (Fig. 5G), together with increased ROS production (Fig. 5H) vs. wild type MLEC. These results indicate that PPARγ acts within MLEC to reduce LPS-induced inflammatory markers.
Figure 5. Absence of ePPARγ Exaggerates Inflammatory Responses of MLEC in Vitro.
MLEC were isolated from ePPARγ+/+ and ePPARγ−/− mice (n = 7–8 mice per group) and plated onto 2% gelatin-coated dishes. (A) MLEC exhibit expected endothelial cell morphology. (B) Western blotting showed the expected expression profiles in MLEC and similarly isolated fibroblasts (MLF), respectively, of the endothelium-specific proteins eNOS, vascular endothelial (VE) cadherin, and PECAM-1 and the fibroblast-specific protein α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA). (C) Relative PPARγ mRNA levels were determined by real-time RT-PCR. In some experiments MLEC were isolated from ePPARγ+/+ and ePPARγ−/− mice 12 h after treatment with LPS (10 mg/kg, i.p.), and nuclear protein extracts prepared. (D) PPARγ DNA-binding activity and (E) protein expression by Western blotting were determined. In other experiments after 2 h serum deprivation, monolayer cultures were treated with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 6 h. Following LPS treatment, immunofluorescence microscopy revealed increased ICAM-1 and PECAM-1 in MLEC isolated from (F,G; right panels) ePPARγ−/− vs. those from (F,G; left panels) ePPARγ+/+ mice, and also elevated (H; right panel vs. left panel) intracellular ROS levels. Blots and images are representative of 3 independent experiments.
To determine the effects of endotoxemia on PPARγ, endothelial cells were isolated from ePPARγ+/+ and ePPARγ−/− mice 12 h after stimulation in vivo with PBS or LPS. While there was a significant reduction in PPARγ protein expression (Fig. 5E), a significant increase in PPARγ activity (Fig. 5E) was seen in endothelial cells from LPS-stimulated ePPARγ+/+ mice compared to PBS-stimulated ePPARγ+/+ mice. These data support the concept that LPS induces a PPARγ response via increased production of activating endogenous ligands.
ePPARγ Deletion Abolishes Anti-inflammatory Effect of a Nitrated Fatty Acid
PPARγ is ligand-activated, but it is unknown which of several classes of candidate endogenous ligands may be physiologically relevant. Nitrated fatty acids, including NO-derived positional isomers of nitro-oleic acid and nitrolinoleic acid, comprise one such group of candidate ligands (18, 19). Their concentrations in plasma are similar to their potencies as PPARγ activators, suggesting a physiological role as PPARγ agonists (18). As agonists of the anti-inflammatory PPARγ, NFAs would be expected to exert anti-inflammatory effects, but some findings suggest that the anti-inflammatory effects of NFAs may not be mediated exclusively by PPARγ activation. We tested these ideas by assessing the effects of OA-NO2 on LPS-induced inflammatory responses within MLEC in vitro and the extent of these effects’ dependence on PPARγ.
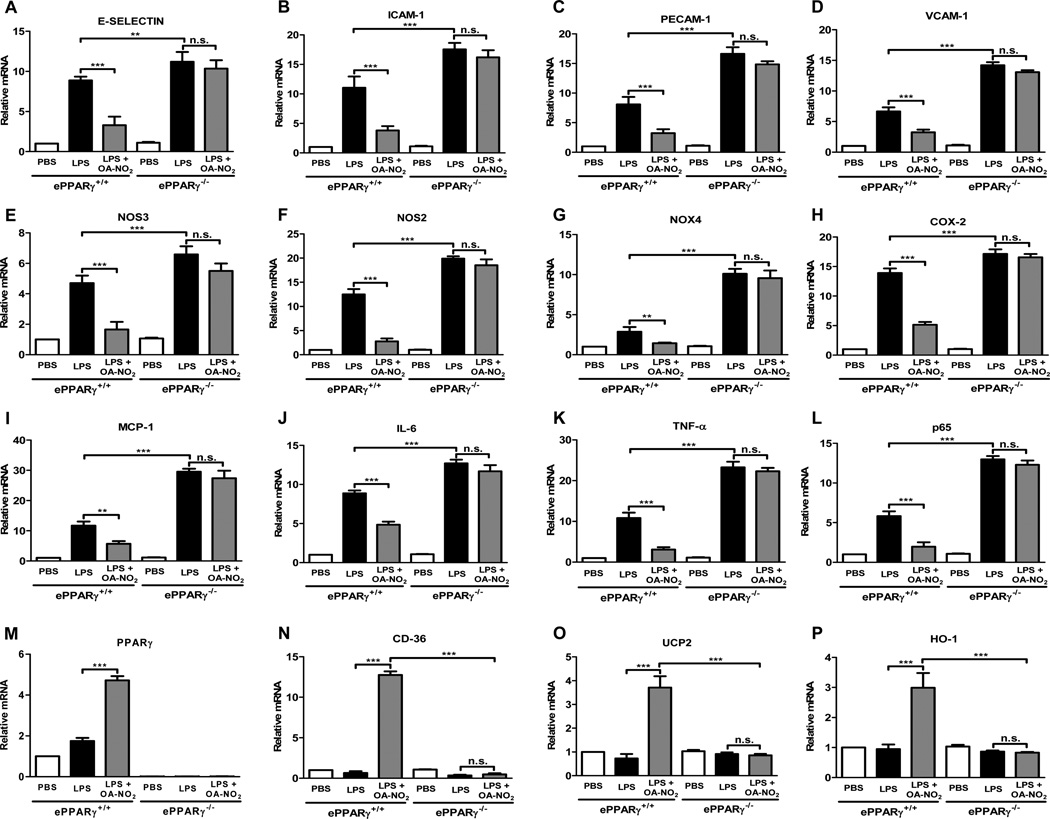
We first tested the ability of OA-NO2 to inhibit LPS-induced cytokine production and expression of pro-inflammatory mediators and adhesion molecules in MLEC. MLEC cultured on 2% gelatin-coated culture dishes without growth factors were pre-treated with OA-NO2 at a concentration similar to that found normally in blood (100 nM) or with DMSO vehicle for 1 h, then treated with 100 ng/ml LPS and incubated for another 6 h. OA-NO2 markedly inhibited the robust LPS-induced transcription of all the following inflammation-associated genes in cells from wild-type mice (Fig. 6A–L): the adhesion-related molecules E-selectin, ICAM-1, PECAM-1, and VCAM-1; the enzymes NOS3, NOS2, NADPH oxidase 4, and cyclooxygenase-2; the chemokine MCP-1; the cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α; and the p65 subunit of NF-κB. The ability of OA-NO2 to reduce LPS-induced expression of each of these genes was completely abolished in MLEC from PPARγ KO mice, indicating strong dependence on the presence of ePPARγ. This was likewise true for expression of the adhesion molecule VE-cadherin (Supplemental Fig. 1A) and the two isoforms of IL-12 (Supplemental Fig. 1B, C). We also found that in wild-type cells OA-NO2 upregulated expression of PPARγ, of the scavenger receptor CD36, which is involved in resolution of inflammation, of mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2, and of the antioxidant enzyme heme oxygenase-1 (Fig. 6M–P). These upregulating actions of OA-NO2 were likewise abolished by PPARγ KO. These findings indicate that OA-NO2 at a physiologically relevant concentration exerts a range of anti-inflammatory effects directly on endothelial cells via a PPARγ–dependent mechanism.
Figure 6. PPARγ Deletion Eliminates OA-NO2-Mediated Suppression of LPS-induced Expression of Inflammatory Markers in MLEC in Vitro.
MLEC were isolated from ePPARγ+/+ and ePPARγ−/− mice (n = 7–8 mice per group) and plated onto 2% gelatin-coated dishes. Monolayer cultures were deprived of serum for 2 h, pre-treated with 100 nM OA-NO2 or DMSO for 1 h, then exposed to 100 ng/ml LPS for 6 h. Cells were then harvested, RNA isolated, and expression of the indicated genes was determined using real-time PCR. Results are normalized to values for the housekeeping genes GAPDH and 9s rRNA. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
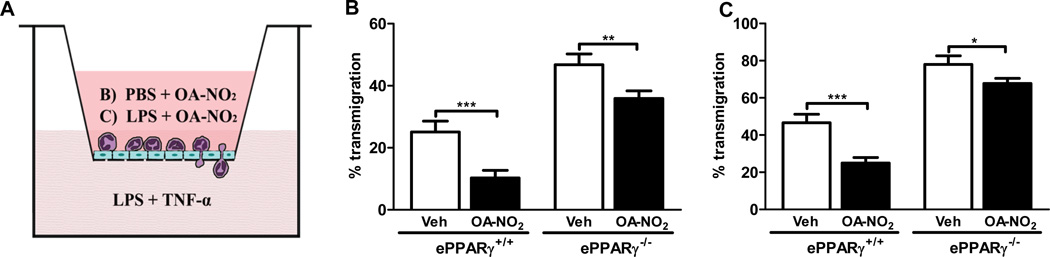
To assess the influence of NFAs on a major cellular route of lung inflammation, we also tested the ability of OA-NO2 to inhibit neutrophil transmigration across MLEC monolayers in vitro. Endothelial cells were isolated from wild-type and PPARγ KO mice and cultured in monolayers in the upper chambers of transwells. Transmigration was assessed after pretreating the MLEC monolayers with LPS along with OA-NO2 or vehicle (Fig. 7A). Wild-type neutrophils were then placed in the upper chamber, the chemoattractant stimulus (LPS + TNF-α) added to the lower chamber, and the number of neutrophils entering each lower chamber in 1.5 h were determined. In wild-type cells, OA-NO2 significantly inhibited neutrophil transmigration (by 45–65%), irrespective of whether LPS was present in the upper chamber (Fig. 7B, C). The extent of OA-NO2– induced inhibition of neutrophil transmigration was substantially reduced (to 9–13%) in ePPARγ−/− MLEC, although it did remain statistically significant. The results suggest that the anti-inflammatory effects of OA-NO2 include inhibition of neutrophil transmigration across the endothelium, and are predominantly PPARγ-dependent.
Figure 7. OA-NO2 Inhibits LPS-induced Neutrophil Transmigration in Vitro via an ePPARγ–dependent Mechanism.
MLEC were isolated from ePPARγ+/+ and ePPARγ−/− mice (n = 7–8 mice per group) and then grown to confluent monolayers in Transwell chambers. As shown schematically in (A), monolayers were treated with 100 nM OA-NO2 or DMSO (Veh) along with (B) PBS or (C) LPS (100 ng/ml) and incubated for 6 h. After 6 h neutrophils (4×105) were added to each upper chamber, and a chemoattractant mixture of LPS (100 ng/ml) plus TNF-α (25 ng/ml) in RPMI 1640 was added to each lower chamber. The chambers were incubated at 37°C for 1.5 h, and neutrophils that had transmigrated into the lower chambers were collected and counted. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
DISCUSSION
Our findings indicate that ePPARγ plays an important protective role in pulmonary endothelial cells during endotoxemia, substantially mitigating lung injury and inflammation. Deficiency of ePPARγ exacerbated LPS-induced pulmonary damage (edema, capillary leakage) and inflammation in vivo, and intensified the activation by LPS of numerous pro-inflammatory genes, signaling proteins, cytokines and other mediators both in vivo and in vitro. In isolated MLEC, robust LPS-induced increases seen in adhesion proteins and pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines and ROS-generating enzymes were similarly enhanced by ePPARγ deficiency. This indicates that ePPARγ modulates LPS responses by acting within endothelial cells in a manner that is not dependent on participation of other cell types. We found that ePPARγ suppressed LPS-induced expression of endothelial pro-inflammatory mediators, including cytokines and adhesion molecules that facilitate migration of neutrophils into alveolar spaces, as well as LPS-induced pathophysiological deficits in endothelial cell function that lead to increased capillary permeability and lung edema. Together, these results clearly underscore the roles of endothelial cells as robust mediators and pathogenic targets of LPS during endotoxemia, and point to ePPARγ acting within endothelial cells as a strong suppressor of endothelial LPS-induced cellular responses.
The exaggerated LPS effects we saw in ePPARγ-deficient mice encompassed upregulated expression of LPS receptors along with increased activation of their downstream LPS signaling pathways. The first step in LPS activation of TLR4 is formation of a ternary complex with LPS binding protein and CD14, which then interacts with TLR4 and the adaptor protein MD2, leading to activation of MyD88, which activates IRAK-4 and TRAF6 (20). We found that ePPARγ deficiency increased the robust LPS-induced upregulation of all these proteins in lungs of mice and that increased expression of additional signaling intermediates with ePPARγ deficiency was associated with increased activation of NF-κB. The enhanced activity of the latter pro-inflammatory transcription factors seen in ePPARγ-deficient mice probably accounts for the enhanced expression we saw in a variety of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules. In addition to these observed effects on TLR signaling pathways and intermediates, PPARγ also inhibits activity of NF-κB, AP-1, and similar pro-inflammatory transcription factors directly, by competing for essential coactivators (7) and by other mechanisms. Although not measured directly in our present study, these known actions likely also contributed to the anti-inflammatory effects we observed.
We found that ePPARγ represents a highly specific, LPS-inducible compartment of total PPARγ activity in lungs, because ePPARγ knockout had no effect on total baseline tissue PPARγ activity levels in lung but abolished the LPS-induced increase in whole-lung PPARγ activity seen in wild-type mice. This implies ePPARγ activity is highly recruited in endothelial cells during sepsis and probably accounts for the entire LPS-induced elevation of whole-lung PPARγ activity. Alternatively, it is conceivable that LPS-activated ePPARγ somehow recruits expression of PPARγ in other cell types, contributing part of the total response seen in PPARγ activity. Considering the broad range and strength of the downregulating actions of ePPARγ upon LPS responses that we observed, our results support the idea that LPS-induced upregulation of ePPARγ activity constitutes an important endogenous pathway for adaptive restraint of inflammatory responses, particularly under the relatively severe conditions (LPS dose) tested here.
ROS contribute both to the adaptive (antibacterial) and maladaptive (tissue-damaging) effects of inflammation. The transcription factor Nrf2 acts to reduce ROS-induced tissue damage by promoting expression of proteins that have antioxidant effects. Additionally, Nrf2 activates the PPARγ transcriptional promoter when transfected into airway epithelial cells, while global deficiency of Nrf2 blocked the ability of PPARγ ligands to suppress hyperoxia-induced lung inflammation and injury (6). Presently, we found that LPS reduced Nrf2 activity, and that ePPARγ deficiency exaggerated the LPS-induced fall in Nrf2 levels, which would thus tend to reduce endogenous protection against deleterious effects of the high ROS levels occurring during sepsis. These findings indicate that the promotion of Nrf2 expression by PPARγ is not limited to hyperoxia but also occurs in the high-ROS context of inflammation and sepsis. Also, these effects of PPARγ are seen specifically in endothelial cells. Thus, the more pronounced LPS-induced decline in lung tissue Nrf2 levels caused by ePPARγ–deficiency probably contributed to the elevated LPS-induced ROS production seen in isolated PPARγ–deficient MLEC.
We found that ePPARγ deficiency in endothelial cells increased their LPS-induced expression of adhesion proteins including ICAM-1, VCAM-1 and E-selectin, indicating that ePPARγ suppresses induction of adhesion proteins. This action may profoundly influence pulmonary inflammation, because production of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 is required for transmigration of neutrophils into the lungs as well as into other organs. Similarly, Wang and colleagues found that constitutively active PPARγ suppressed TNF-α– and PMA-induced VCAM-1, ICAM-1 and E-selectin expression and neutrophil adhesion to HUVECs (21). Also, PPARγ agonists (22–25) and compounds that upregulate PPARγ expression (26, 27) have generally been found to inhibit neutrophil adhesion and VCAM-1 expression elicited by pro-inflammatory stimuli. Not all studies have concurred about whether ICAM-1 is downregulated by PPARγ agonists, and the reported effects of individual agonists on adhesion protein expression have been variable (23, 24, 26). The reasons for such apparent discrepancies among reported actions of PPARγ agonists are unknown, but are not thought to be attributable to differences in cell origin or in pro-inflammatory stimulus, although they may reflect differential dosage effects. In any case, the observed results of altered PPARγ expression have been highly consistent, supporting the idea that PPARγ activation serves to inhibit expression of inflammation-promoting adhesion proteins.
Our findings also point to a role of NFAs as potential endogenous agonists that might contribute to the observed actions of the agonist-driven transcriptional activator PPARγ. A variety of endogenous compounds can bind to and activate PPARγ and have thus been proposed as endogenous agonists, but the physiological relevance of most such agents is doubtful due to insufficient potencies in relation to in vivo concentration ranges. The most plausible identified candidates to date are NFAs, especially positional isomers of nitro-oleic and nitrolinoleic acids (18, 19), which are produced by nonenzymatic reactions of NO and its inorganic reaction products with endogenous unsaturated fatty acids (28). A role of endogenous NFAs as anti-inflammatory mediators has been thought plausible because they are present in body fluids (29), are active at physiological concentrations, and the production of NFA-generating NO is increased during inflammation. We found that exposing MLEC to the NFA OA-NO2 partially or completely blocked LPS-induced expression of adhesion molecules, cytokines, chemokines, and inflammation-associated enzymes in MLEC, in a manner that was completely dependent upon ePPARγ expression. All these wide-ranging anti-inflammatory effects were elicited by a concentration of NFA OA-NO2 that is well within its endogenous concentration range (30). Also, OA-NO2 upregulated the expression by MLEC of several anti-inflammatory molecules, including PPARγ, indicating that the observed inhibitory effects on the expression of pro-inflammatory LPS-induced proteins and mediators are not attributable to any nonspecific toxicity. In addition, we discovered that OA-NO2 inhibited the transmigration of neutrophils across endothelial cell monolayers. Neutrophil transmigration is a function that is fundamental to inflammation, and we have previously found that it is inhibited by PPARγ activation (31). We now show that NFA-mediated inhibition of neutrophil transmigration occurred under both baseline and LPS-stimulated conditions, and is partially dependent on expression of PPARγ by the MLEC. These findings are consistent with, but qualitatively expand, the reported anti-inflammatory actions of NFAs, including inhibition of TNF-α-induced macrophage VCAM-1 and monocyte rolling and adhesion (30); inhibition of superoxide generation, calcium influx, elastase release, and CD11b expression by human neutrophils (32); and upregulation of the anti-inflammatory enzyme heme oxygenase-1 in human aortic endothelial cells (33). Our observations thus support a role for NFAs as physiologically relevant endogenous PPARγ agonists. Further research is required to confirm this possibility in vivo.
Inflammatory responses to pathogens can be destructive and often lethal to the host if unchecked. Endogenous systems operating at many levels have evolved to restrain such damage, while permitting effective antimicrobial defense. Our findings indicate that PPARγ acts within pulmonary endothelial cells during endotoxemia to exert such a key mitigating effect, inhibiting the many pro-inflammatory responses elicited by LPS in endothelial cells, thereby restraining inflammation and reducing pulmonary injury. We also addressed the unresolved question of which candidate molecule(s) serve as endogenous PPARγ agonists by finding unequivocal and novel evidence that the endogenous NFA OA-NO2 completely blocks a wide range of LPS-induced pro-inflammatory responses in MLEC by via a mechanism specifically dependent on PPARγ. As our studies were confined to pulmonary endothelial cells and lung tissue, further research will be needed to determine whether they are also broadly applicable to inflammatory pathogenesis involving endothelial cell populations in other organs. These results may help point the way to new pharmacological interventions for sepsis and lung injury.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by NIH Grant HL093196 (R.C.R.).
Footnotes
Abbreviations used in this paper: BAL, bronchoalveolar lavage; EBD, Evans Blue Dye; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; IRAK-4, interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4; MDA, malonyldialdehyde; MLEC, mouse lung endothelial cells; NFA, nitrated fatty acid; Nrf2, nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2; PBST, PBS + Tween-20; OA-NO2, 10-nitro-oleic acid; PPAR-γ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
REFERENCES
- 1.Hotchkiss RS, Karl IE. The pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. New England Journal of Medicine. 2003;348:138–150. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra021333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Vincent JL. Acute kidney injury, acute lung injury and septic shock: how does mortality compare? Contributions to Nephrology. 2011;174:71–77. doi: 10.1159/000329238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lu YC, Yeh WC, Ohashi PS. LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine. 2008;42:145–151. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2008.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Peters K, Unger RE, Brunner J, Kirkpatrick CJ. Molecular basis of endothelial dysfunction in sepsis. Cardiovascular Research. 2003;60:49–57. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(03)00397-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nencioni A, Wesselborg S, Brossart P. Role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ and its ligands in the control of immune responses. Critical reviews in immunology. 2003;23:1–13. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v23.i12.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cho HY, Gladwell W, Wang X, Chorley B, Bell D, Reddy SP, Kleeberger SR. Nrf2-regulated PPAR{gamma} expression is critical to protection against acute lung injury in mice. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2010;182:170–182. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200907-1047OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kostadinova R, Wahli W, Michalik L. PPARs in diseases: control mechanisms of inflammation. Current medicinal chemistry. 2005;12:2995–3009. doi: 10.2174/092986705774462905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Marx N, Bourcier T, Sukhova GK, Libby P, Plutzky J. PPARgamma activation in human endothelial cells increases plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 expression: PPARgamma as a potential mediator in vascular disease. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 1999;19:546–551. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.19.3.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Belvisi MG, Hele DJ, Birrell MA. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists as therapy for chronic airway inflammation. European journal of pharmacology. 2006;533:101–109. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.12.048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ito K, Shimada J, Kato D, Toda S, Takagi T, Naito Y, Yoshikawa T, Kitamura N. Protective effects of preischemic treatment with pioglitazone, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma ligand, on lung ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery. 2004;25:530–536. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2003.12.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Milam JE, Keshamouni VG, Phan SH, Hu B, Gangireddy SR, Hogaboam CM, Standiford TJ, Thannickal VJ, Reddy RC. PPARg agonists inhibit profibrotic phenotypes in human lung fibroblasts and bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008;294:L891–L901. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00333.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sundararajan S, Jiang Q, Heneka M, Landreth G. PPARgamma as a therapeutic target in central nervous system diseases. Neurochemistry international. 2006;49:136–144. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2006.03.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.van Westerloo DJ, Florquin S, de Boer AM, Daalhuisen J, de Vos AF, Bruno MJ, van der Poll T. Therapeutic effects of troglitazone in experimental chronic pancreatitis in mice. American Journal of Pathology. 2005;166:721–728. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62293-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhao W, Thacker SG, Hodgin JB, Zhang H, Wang JH, Park JL, Randolph A, Somers EC, Pennathur S, Kretzler M, Brosius FC, 3rd, Kaplan MJ. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonist pioglitazone improves cardiometabolic risk and renal inflammation in murine lupus. Journal of Immunology. 2009;183:2729–2740. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0804341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Haraguchi G, Kosuge H, Maejima Y, Suzuki J, Imai T, Yoshida M, Isobe M. Pioglitazone reduces systematic inflammation and improves mortality in apolipoprotein E knockout mice with sepsis. Intensive Care Medicine. 2008;34:1304–1312. doi: 10.1007/s00134-008-1024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nicol CJ, Adachi M, Akiyama TE, Gonzalez FJ. PPARgamma in endothelial cells influences high fat diet-induced hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension. 2005;18:549–556. doi: 10.1016/j.amjhyper.2004.10.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Fehrenbach ML, Cao G, Williams JT, Finklestein JM, Delisser HM. Isolation of murine lung endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009;296:L1096–L1103. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.90613.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Baker PRS, Lin Y, Schopfer FJ, Woodcock SR, Groeger AL, Batthyany C, Sweeney S, Long MH, Iles KE, Baker LMS, Branchaud BP, Chen YE, Freeman BA. Fatty acid transduction of nitric oxide signaling: multiple nitrated unsaturated fatty acid derivatives exist in human blood and urine and serve as endogenous peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor ligands. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2005;280:42464–42475. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M504212200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Schopfer FJ, Lin Y, Baker PRS, Cui T, Garcia-Barrio M, Zhang J, Chen K, Chen YE, Freeman BA. Nitrolinoleic acid: an endogenous peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ ligand. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2005;102:2340–2345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408384102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kawai T, Akira S. TLR signaling. Seminars in Immunology. 2007;19:24–32. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2006.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wang N, Verna L, Chen NG, Chen J, Li H, Forman BM, Stemerman MB. Constitutive activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma suppresses pro-inflammatory adhesion molecules in human vascular endothelial cells. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2002;277:34176–34181. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M203436200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Imamoto E, Yoshida N, Uchiyama K, Kuroda M, Kokura S, Ichikawa H, Naito Y, Tanigawa T, Yoshikawa T. Inhibitory effect of pioglitazone on expression of adhesion molecules on neutrophils and endothelial cells. BioFactors (Oxford, England) 2004;20:37–47. doi: 10.1002/biof.5520200104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jackson SM, Parhami F, Xi XP, Berliner JA, Hsueh WA, Law RE, Demer LL. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor activators target human endothelial cells to inhibit leukocyte-endothelial cell interaction. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 1999;19:2094–2104. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.19.9.2094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jung Y, Song S, Choi C. Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma agonists suppress TNFalpha-induced ICAM-1 expression by endothelial cells in a manner potentially dependent on inhibition of reactive oxygen species. Immunology Letters. 2008;117:63–69. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2007.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tikellis C, Jandeleit-Dahm KA, Sheehy K, Murphy A, Chin-Dusting J, Kling D, Sebokova E, Cooper ME, Mizrahi J, Woollard KJ. Reduced plaque formation induced by rosiglitazone in an STZ-diabetes mouse model of atherosclerosis is associated with downregulation of adhesion molecules. Atherosclerosis. 2008;199:55–64. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2007.10.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hwa JS, Mun L, Kim HJ, Seo HG, Lee JH, Kwak JH, Lee DU, Chang KC. Genipin Selectively Inhibits TNF-alpha-activated VCAM-1 But Not ICAM-1 Expression by Upregulation of PPARgamma in Human Endothelial Cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011;15:157–162. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2011.15.3.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Moon L, Ha YM, Jang HJ, Kim HS, Jun MS, Kim YM, Lee YS, Lee DH, Son KH, Kim HJ, Seo HG, Lee JH, Kim YS, Chang KC. Isoimperatorin, cimiside E and 23-O-acetylshengmanol-3-xyloside from Cimicifugae rhizome inhibit TNF-alpha-induced VCAM-1 expression in human endothelial cells: involvement of PPARgamma upregulation and PI3K, ERK1/2, and PKC signal pathways. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2011;133:336–344. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.O'Donnell VB, Eiserich JP, Bloodsworth A, Chumley PH, Kirk M, Barnes S, Darley-Usmar VM, Freeman BA. Nitration of unsaturated fatty acids by nitric oxide-derived reactive species. Methods in enzymology. 1999;301:454–470. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(99)01109-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Baker PRS, Schopfer FJ, Sweeney S, Freeman BA. Red cell membrane and plasma linoleic acid nitration products: synthesis, clinical identification, and quantitation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2004;101:11577–11582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0402587101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cui T, Schopfer FJ, Zhang J, Chen K, Ichikawa T, Baker PRS, Batthyany C, Chacko BK, Feng X, Patel RP, Agarwal A, Freeman BA, Chen YE. Nitrated fatty acids: Endogenous anti-inflammatory signaling mediators. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2006;281:35686–35698. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M603357200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Reddy RC, Narala VR, Keshamouni VG, Milam JE, Newstead MW, Standiford TJ. Sepsis-induced inhibition of neutrophil chemotaxis is mediated by activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-{gamma} Blood. 2008;112:4250–4258. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-12-128967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Coles B, Bloodsworth A, Clark SR, Lewis MJ, Cross AR, Freeman BA, O'Donnell VB. Nitrolinoleate inhibits superoxide generation, degranulation, and integrin expression by human neutrophils: novel antiinflammatory properties of nitric oxide-derived reactive species in vascular cells. Circulation research. 2002;91:375–381. doi: 10.1161/01.res.0000032114.68919.ef. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wright MM, Schopfer FJ, Baker PRS, Vidyasagar V, Powell P, Chumley P, Iles KE, Freeman BA, Agarwal A. Fatty acid transduction of nitric oxide signaling: nitrolinoleic acid potently activates endothelial heme oxygenase 1 expression. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2006;103:4299–4304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506541103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.