Abstract
Background
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is not a single uniform disease. It consists of several subgroups with different cytogenetic and molecular genetic aberrations, clinical presentations and outcomes. Banding cytogenetics plays a pivotal role in the detection of recurrent chromosomal rearrangements and is the starting point of genetic analysis in ALL, still. Nowadays, molecular (cyto)genetic tools provide substantially to identify previously non-detectable, so-called cryptic chromosomal aberrations in ALL. However, ALL according to banding cytogenetics with normal karyotype - in short cytogenetically normal ALL (CN-ALL) - represent up to ~50 % of all new diagnosed ALL cases. The overall goal of this study was to identify and characterize the rate of cryptic alterations in CN-ALL and to rule out if one single routine approach may be sufficient to detect most of the cryptic alterations present.
Results
Sixty-one ALL patients with CN-ALL were introduced in this study. All of them underwent high resolution fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis. Also DNA could be extracted from 34 ALL samples. These DNA-samples were studied using a commercially available MLPA (multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification) probe set directed against 37 loci in hematological malignancies and/or array-comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH). Chromosomal aberrations were detected in 21 of 61 samples (~34 %) applying FISH approaches: structural abnormalities were present in 15 cases and even numerical ones were identified in 6 cases. Applying molecular approaches copy number alterations (CNAs) were detected in 27/34 samples. Overall, 126 CNAs were identified and only 34 of them were detectable by MLPA (~27 %). Loss of CNs was identified in ~80 % while gain of CNs was present in ~20 % of the 126 CNAs. A maximum of 13 aberrations was detected per case; however, only one aberration per case was found in 8 of all in detail studied 34 cases. Of special interest among the detected CNAs are the following new findings: del(15)(q26.1q26.1) including CHD2 gene was found in 20 % of the studied ALL cases, dup(18)(q21.2q21.2) with the DCC gene was present in 9 % of the cases, and the CDK6 gene in 7q21.2 was deleted in 12 % of the here in detail studied ALL cases.
Conclusions
In conclusion, high resolution molecular cytogenetic tools and molecular approaches like MLPA and aCGH need to be combined in a cost-efficient way, to identify disease and progression causing alterations in ALL, as majority of them are cryptic in banding cytogenetic analyses.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s13039-015-0153-4) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Multitude multicolor banding (mMCB), Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), Cryptic rearrangements, Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA), Array-comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH)
Background
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a malignant disease of the hematological system with clonal proliferation of lymphoid progenitor cells. It arises from genetic alterations that block precursor B and T cell differentiation and predominantly affects children [1]. B-ALL constitutes 80-85 % of ALL cases and T-ALL the remainder ones. B-ALL patients have a favorable prognosis with an overall complete remission rate of 95 % for pediatric (children and adolescent between 1–15 years) but of only 60 % for adults. Adverse prognosis in T-ALL was correlated with presence of hyperleukocytosis, enhanced mediastinal mass, central neural system involvement, male gender and advanced age [1–5]. Cytogenetically detectable structural or numerical chromosomal abnormalities are detected in ~50 % of ALL cases. Such aberrations have prognostic significance [1, 6]. High hyperdiploidy (51–65 chromosomes) has been connected with good survival and excellent outcome in B-ALL, while hypodiploidy (<44 chromosomes) has an adverse prognosis [7–9]. Recurrent structural chromosomal abnormalities found in ALL can also be reciprocal translocations. ALLs with a translocation t(12;21)(p13;q22) leading to the ETV6/RUNX1 gene-fusion are more likely to be cured, than those with a translocation t(9;22) or t(4;11), which tend to have unfavorable outcomes. Complex karyotypes, including three to five or more chromosomal abnormalities, are typically found in ~5 % of ALL cases and are also associated with an adverse outcome [10]. Finally, ALL cases with according to banding cytogenetics normal karyotype - in short cytogenetically normal ALL (CN-ALL) - are classified into intermediate risk group [6, 11, 12]. Malignant bone marrow of T-ALL patients shows a normal karyotype more frequently than those of B-ALL patients. Accordingly in those cases cytogenetic markers cannot be determined and therapeutic decisions may be hampered.
Based on the knowledge that chromosomes in ALL show a low banding resolution and that a good part of ALL cases present with a normal karyotype, it is not far to seek, that small aberration can easily be missed when analyzing ALL derived chromosomes by banding cytogenetics alone [6, 13]. Copy number alterations (CNAs) at the microscopic or submicroscopic level, i.e. focal deletions, but also duplications or sequence/point mutations in genes that primarily serve as transcriptional regulators of the lymphoid developmental pathway can nowadays be detected by approaches like multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) or array-comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH) [12, 14, 15].
The present study includes 61 CN-ALL cases, which were retrospectively studied for the rate of cryptic (sub)chromosomal changes to rule out if one single molecular (cyto)genetic routine approach may be sufficient to detect most if not all of the cryptic alterations present.
Results
Standard cytogenetic analysis by G-banding revealed normal karyotypes in 61 ALL cases included in this study (Additional file 1: Table S1). In a first step all 61 cases were studied by the whole genome oriented fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)-banding based probe set multitude multicolor banding (mMCB) [16]. For further delineation of mMCB results appropriate FISH-probes and probe sets were applied (Additional file 1: Table S1). Based on these results 21/61 (34 %) cases were not cytogenetically normal but had gross acquired chromosomal aberrations: structural abnormalities were found in 15/61 cases (24 %) and even numerical ones were observed in 6/61 cases (10 %) (Table 1). Overall, in GTG-banding cryptic balanced and unbalanced translocations, derivative chromosomes, isochromosomes, interstitial deletions, inverted duplications and/or numerical aberrations were identified in 34 % of the studied CN-ALL cases by means of molecular cytogenetics. In Fig. 1 case P66 is exemplified with a three-way translocation between chromosomes #10, #11 and #14, inversion of second chromosome # 14 and insertion (11;10). The breakpoints of this P66 case were characterized as 10p12.3, 10q11.23, 11p15.3, 11q23.3, 14q11, 14q24.2, and 14q32.3.
Table 1.
Summary of aberrations detected by metaphase directed FISH, interphase FISH to determine the percentage of specific aberrations, and aCGH in 34 ALL patients
| Case number | Age [y] | Metaphase directed FISH | MLPA | LSPs for genes | aCGH – affected cytobands | Localization acc. to GRCH37/hg19 | Size of imbalance [bp] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-ALLs | |||||||
| P1 | 1 | 46,XX | normal | normal | dup(11)(p15.5p15.4) | chr11:1,960,555-3,626,932 | 1,666,377 |
| P8 | 30 | 47,XY,+21[5]/46,XY[2] | dup of 21q22.12 | RUNX1: dup (72 %) | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| P13 | 34 | 46,XY[8] | del of 10q23.3 | del(10)(q23.2q23.31) | chr10:88,906,902-91,189,599 | 2,282,697 | |
| del of 17p13.1 | TP53: del (9 %) | del(17)(p13.1p13.1) | chr17:7,579,695-8,281,928 | 702,233 | |||
| P17 | 27 | 46,XX[7] | n.d. | normal | normal | n.d. | n.d. |
| P23 | 59 | del(3)(p25.3p25.3) | chr3:10,179,706-10,385,195 | 205,489 | |||
| del of 7p12.2 | del(7)(p12.2p12.2) | chr7:50,337,405-50,482,274 | 144,869 | ||||
| del(10)(q23.3q23.3) | chr10:89,570,600-89,676,741 | 106,141 | |||||
| del(11)(q14.2q14.2) | chr11:85,683,188-85,944,362 | 261,174 | |||||
| 47,XX,+14[2]/ | IGH: dup (58 %) | +14 | +14 | 107,349,540 | |||
| 46,XX[3] | del(15)(q26.1q26.1) | chr15:93,390,484-93,463,312 | 72,828 | ||||
| del(17)(p13.1p13.1) | chr17:7,581,198-7,922,308 | 341,110 | |||||
| del(17)(q11.2q11.2) | chr17:30,259,053-30,271,653 | 12,600 | |||||
| del(18)(q21.32q21.32) | chr18:57,517,756-57,718,190 | 200,434 | |||||
| del(21)(q22.3q22.3) | chr21:45,527,941-45,565,198 | 37,257 | |||||
| P28 | 84 | 46,XY, | del of 7p12.2 | del(7)(p12.2p12.2) | chr7:50,353,062-50,444,269 | 91,207 | |
| t(9;22)(q34;q11), | del of 9p21.3 | CDKN2A/B: del (75 %) | del(9)(pterp11.2) | chr9:0–47,212,321 | 47,212,321 | ||
| del(11)(q13q25)[7] | del of 9p13.2 | del(9)(q34.2qter) | chr9:136,917,580-141,213,431 | 4,295,851 | |||
| del(10)(q23.3q23.3) | chr10:89,619,806-89,731,258 | 111,452 | |||||
| del of 11q22.3 | BIRC3: del (75 %) | del(11)(q13.2qter) | chr11:67,773,863-135,006,516 | 67,232,653 | |||
| ATM: del (77 %) | del(15)(q26.1q26.1) | chr15:93,412,860-93,450,773 | 37,913 | ||||
| MLL: del (80 %) | dup(20)(q11.23q12) | chr20:37,305,876-39,130,131 | 1,824,255 | ||||
| del(20)(q12q13.12) | chr20:39,245,111-45,524,952 | 6,279,841 | |||||
| dup(20)(q13.12q13.12) | chr20:45,524,953-45,780,811 | 255,858 | |||||
| del(20)(q13.12q13.32) | chr20: 45,780,812-58,067,678 | 12,286,866 | |||||
| del(21)(q22.2q22.2) | chr21:39,764,621-39,807,169 | 42,548 | |||||
| BCR: del (94 %) | del(22)(q11.23q11.23) | chr22:23,584,037-23,592,537 | 8500 | ||||
| P43 | 69 | 46,XX, | normal | TFG: dup (15 %) | dup(3)(q12.2q12.2) | chr3:100,360,682-100,444,109 | 83,427 |
| der(4)(4pter- > 4q21.3::11q23.3- | del(7)(q21.2q21.2) | chr7:92,252,341-92,475,197 | 222,856 | ||||
| >11q23.3::4q21.3- > 4qter), | MLL: ins (75 %) | ||||||
| der(11)(11pter- > 11q23.3::11q23.3- > 11q24.2::11p15.4- > 11pter), | |||||||
| der(11)(11qter- > 11q24.2::11p15.4- > 11qter)[5] | |||||||
| P48 | 39 | 46,XY, | n.d. | del(6)(q13q14.2) | chr6:73,331,571-84,140,938 | 10,809,367 | |
| t(6;11)(q15;p12), | del(6)(q16.2q21) | chr6:99,282,580-109,703,762 | 10,421,182 | ||||
| ins(6;11)(q22.1;q13q14), | del(6)(q22.31q22.33) | chr6:124,125,069-128,841,870 | 4,716,801 | ||||
| inv(6)(q15q25.3), | ESR1: del (89 %) | del(6)(q25.1q25.3) | chr6:151,725,897-157,531,913 | 5,806,016 | |||
| del(11)(q21q23.2)[8] | del(7)(p12.2p12.2) | chr7:49,991,954-51,207,236 | 1,215,282 | ||||
| dup(11)(p15.5p15.4) | chr11:1,925,114-3,143,116 | 1,218,002 | |||||
| WT1: del (91 %) | del(11)(p15.1p12) | chr11:20,546,133-37,403,781 | 16,857,648 | ||||
| BIRC3: del (90 %) | del(11)(q14.1q14.3) | chr11:85,157,088-88,557,421 | 3,400,333 | ||||
| ATM: del (77 %) | del(11)(q22.1q22.3) | chr11:100,992,179-114,667,959 | 13,675,780 | ||||
| del(13)(q14.2q14.2) | chr13:48,980,623-49,148,073 | 167,450 | |||||
| P49 | 39 | 46,XX[10] | n.d. | normal | dup(11)(p15.5p15.4) | chr11:2,016,406-3,430,378 | 3,430,378 |
| P51 | 59 | 46,XX[6] | normal | normal | del(10)(p12.1p12.1) | chr10:28,057,099-28,220,314 | 163,215 |
| del(15)(q26.1q26.1) | chr15:93,412,860-93,450,773 | 37,913 | |||||
| del(X)(q21.1q21.1) | chrX:76,875,639-77,157,819 | 282,180 | |||||
| P52 | 21 | 46,XY[4] | normal | del(6)(p21.1p21.1) | chr6:45,395,872-45,409,919 | 14,047 | |
| del(7)(q21.2q21.2) | chr7:92,149,393-92,495,958 | 346,565 | |||||
| del of 10q23.3 | del(10)(q23.3q23.3) | chr10:89,610,886-89,722,948 | 112,062 | ||||
| del(11)(q14.2q14.2) | chr11:85,683,188-85,944,362 | 261,174 | |||||
| del(15)(q26.1q26.1)) | chr15:93,433,130-93,450,773 | 17,643 | |||||
| del(17)(q23.1q23.1) | chr17:57,698,768-57,913,528 | 214,760 | |||||
| del(20)(q13.2q13.2) | chr20:52,151,411-52,629,609 | 478,198 | |||||
| del(X)(p22.33p22.33) | chrX:1,327,561-1,684,270 | 1,684,270 | |||||
| P53 | 34 | 46,XY[5] | normal | normal | dup(22)(q11.21q11.21) | chr22:18,706,001-21,561,514 | 2,855,514 |
| P55 | 19 | 46,XY[6] | del of 17p13.1 | TP53: del (100 %) | del(17)(pterp11.2) | chr17:0–20,219,464 | 20,219,464 |
| −20 | −20 | 63,025,520 | |||||
| P56 | 47 | 45,XY,-21[2]/ | normal | normal | del(12)(pterp11.21) | chr12:0–31,260,891 | 31,260,891 |
| 46,XY[4] | |||||||
| P57 | 56 | 46,XY[3] | normal | normal | normal | n.d. | n.d. |
| P58 | 20 | 46,XX, | TBL1XR1: del (68 %) | del(3)(q26.32q26.32) | chr3:176,825,586-177,697,157 | 871,571 | |
| der(14)(pter- > q32::q32- > q13::q32- > qter)[10] | del of 9p21.3 | CDKN2A/B: del (74 %) | del(9)(p21.3p21.3) | chr9:21,252,517-24,289,720 | 3,037,203 | ||
| del(10)(p15.3p15.3) | chr10:1,491,986-1,582,072 | 90,086 | |||||
| IGH: split (78 %) | dup(14)(q13q32.33) | chr14:35,918,265-106,513,022 | 70,594,757 | ||||
| del(16)(q13q13) | chr16:57,275,940-57,331,138 | 55,198 | |||||
| del(21)(q22.2q22.2) | chr21:39,764,621-39,895,171 | 130,550 | |||||
| P64 | 5 | 46,XX, | n.d. | del(5)(q31.3q32) | chr5:142,096,863-145,891,069 | 3,794,206 | |
| t(16;19)(p11.2;q13.3), | |||||||
| der(5)t(5;9)(q31;p13.2), | CDKN2A/B: del (86 %) | del(9)(p21.3p21.3) | chr9:21,218,548-23,002,377 | 1,783,829 | |||
| der(9)t(5;9)(q31;p13.2), | |||||||
| der(9)t(9;9)(q34;p13.2)[10] | FUS: split (75 %) | ||||||
| P66 | 0.5 | 46,XX, | n.d. | MLL: split (70 %) | dup(11)(p15.5p15.4) | chr11:1,008,688-3,669,161 | 3,669,161 |
| der(10)(10pter- > 10p12.31::11q23.3- > 11q23.3::10p12.31- > 10q11.23::14q24.2- > 14qter), | IGH: inv (100 %) | ||||||
| der(11)(10qter- > 10q11.23::11p15.3- > 11q23.3::10p12.31- > 10p12.31::11q23.3- > 11qter), | |||||||
| der(14)t(11;14)(q15.3;q24.2), inv(14)(q11q23)[8] | |||||||
| T-ALLs | |||||||
| P5 | 22 | 46,XX[12] | normal | normal | normal | n.d. | n.d. |
| P6 | 16 | 47,XY, | normal | normal | |||
| +4, | +4 | +4 | 191,154,276 | ||||
| der(3)t(3;5)(p23;q31.1), | |||||||
| der(5)t(3;5)(p23;q35.3), | |||||||
| der(5)t(5;10)(q31.1;p12.3), | |||||||
| der(10)t(5;10)(q35.3;p12.3)[8]/ | |||||||
| 46,XY[13] | |||||||
| P7 | 26 | 46,XY, | del of 9p21.3 | CDKN2A/B: del (64 %) | del(9)(p21.3p21.3) | chr9:21,817,082-23,515,821 | 1,698,739 |
| t(2;9;18)(p23.2;p21.3;q21.33), | del of 13q14.2 | RB1: del (25 %) | del(13)(q14.2q14.2) | chr13:48,982,463-49,062,316 | 79,853 | ||
| t(10;14)(q24;q11)[10] | del(16)(p13.3p13.3) | chr16:3,154,954-4,568,792 | 1,413,838 | ||||
| P18 | 36 | 46,XY[5] | dup of 18q21.2 | DCC: dup (13 %) | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| P32 | 27 | 47,XX, | del of 6q21 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | |
| +21, | del of 6q27 | ||||||
| t(10;14)(q24;q11), | del of 9p21.3 | CDKN2A/B: del (89 %) | |||||
| del(6)(q15q27)[6] | del of 12p13.2 | ETV6: del (78 %) | |||||
| del of 13q14.3 | DLEU1: del (15 %) | ||||||
| dup of 21q22.1 | RUNX1: dup (78 %) | ||||||
| P35 | 40 | 46,XY,i(9)(q21.11)[2] | del(2)(q34q34) | chr2:213,811,279-214,150,984 | 339,705 | ||
| dup(7)(pterp14.1) | chr7:0–38,218,586 | 38,218,586 | |||||
| del(7)(q21.2q21.2) | chr7:92,252,341-92,460,773 | 208,432 | |||||
| del(7)(q36.3qter) | chr7:156,881,580-159,138,663 | 2,257,083 | |||||
| del of 9p21.3 | CDKN2A/B: del (92 %) | del(9)(pterp11.2) | chr9:0–47,212,321 | 47,212,321 | |||
| del of 9p13.2 | dup(9)(q21.11qter) | chr9:71,035,265-141,213,431 | 70,178,166 | ||||
| del(10)(q23.2q23.31) | chr10:89,570,600-89,728,844 | 158,244 | |||||
| del(11)(q22.2q22.2) | chr11:102,106,046-102,529,831 | 423,785 | |||||
| del(13)(q14.2q14.2) | chr13:49,004,123-49,122,923 | 118,800 | |||||
| del(15)(q26.1q26.1) | chr15:93,390,484-93,466,292 | 75,808 | |||||
| del(16)(p13.3p13.3) | chr16:3,808,951-3,839,782 | 30,831 | |||||
| del(18)(q21.32q21.32) | chr18:57,517,756-57,617,796 | 100,040 | |||||
| del(20)(q13.2q13.2) | chr20:52,151,411-52,574,928 | 423,517 | |||||
| P38 | 22 | 46,XY[3] | normal | normal | normal | n.d. | n.d. |
| P61 | 18 | 46,XX,der(2)t(2;7)(q37.3;q34), t(7;10)(q34;q24.1 ~ 25.1) [4]/ | del(1)(p36.31p36.23) | chr1:5,958,728-7,238,618 | 1,279,890 | ||
| del(4)(p16.3p14) | chr4:3,072,509-38,882,925 | 35,810,416 | |||||
| 46,XX[3] | dup of 6q23.3 | MYB: amp (90 %) | dup(6)(q23.3q23.3) | chr6:134,245,761-136,118,354 | 1,872,593 | ||
| del of 9p21.3 | CDKN2A/B: del (88 %) | del(9)(p21.3p21.3) | chr9:21,252,517-23,002,377 | 1,749,860 | |||
| ABL1: amp (95 %) | dup(9)(q34.1q34.1) | chr9:133,658,293-134,092,544 | 434,251 | ||||
| FGFR2: del (57 %) | del(10)(q25.1q26.3) | chr10:112,392,101-135,534,737 | 23,124,636 | ||||
| B- or T ALLs (not clinically well defined) | |||||||
| P11 | 26 | 46,XY[8] | n.d. | normal | normal | n.d. | n.d. |
| P16 | 17 | 46,XX[7] | del(1)(q25.3q31.1) | chr1:184,771,633-185,825,795 | 1,054,162 | ||
| del(4)(p15.33p15.31) | chr4:12,322,760-18,779,457 | 6,456,697 | |||||
| del(4)(q21.22q24) | chr4:82,992,997-106,476,929 | 23,483,932 | |||||
| del(7)(pterp14.2) | chr7:0–36,320,986 | 36,320,986 | |||||
| dup of 7q22.1 | RELN: dup (61 %) | dup(7)(q21.3q22.3) | chr7:96,048,870-106,348,693 | 10,299,823 | |||
| del(9)(p23p22.2) | chr9:12,656,733-17,466,907 | 4,810,174 | |||||
| del of 9p21.3 | CDKN2A/B: del (81 %) | del(9)(p21.3p21.3) | chr9:20,279,653-22,555,566 | 2,275,913 | |||
| del(10)(p14p13) | chr10:6,889,266-12,484,159 | 5,594,893 | |||||
| del of 12p13.2 | ETV6: del (91 %) | del(12)(p13.2p13.1) | chr12:11,761,018-12,934,870 | 1,173,852 | |||
| del(18)(p11.32p11.31) | chr18:2,741,687-3,231,531 | 489,844 | |||||
| P21 | 62 | 46,XY[11] | n.d. | normal | normal | normal | normal |
| P24 | 23 | 46,XY[12] | dup of 18q21.2 | DCC: dup (18 %) | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| P30 | 46 | 46,XY[6] | normal | normal | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| P33 | 76 | 45,X,-X[8] | del(4)(q24q24) | chr4:106,036,993-106,601,946 | 564,953 | ||
| del(7)(q21.2q21.2) | chr7:92,080,855-92,475,197 | 394,342 | |||||
| dup(7)(q36.2q36.2) | chr7:153,039,830-154,467,634 | 1,427,804 | |||||
| del of 10q23.3 | del(10)(q23.3q23.3) | chr10:89,610,886-89,698,312 | 87,426 | ||||
| del(15)(q21.2q21.2) | chr15:51,826,924-51,919,665 | 92,741 | |||||
| del(15)(q26.1q26.1) | chr15:93,433,130-93,450,773 | 17,643 | |||||
| del of 17p13.1 | TP53: del (10 %) | del(17)(p13.1p13.1) | chr17:7,583,457-8,156,734 | 573,277 | |||
| del(17)(q11.2q11.2) | chr17:30,259,193-30,267,204 | 8011 | |||||
| dup of 18q21.2 | DCC: dup (10 %) | dup(18)(q21.2q21.2) | chr18:49,105,579-51,431,815 | 2,326,236 | |||
| del(20)(q13.2q13.2) | chr20:52,151,411-52,554,455 | 403,044 | |||||
| del(21)(q22.12q22.12) | chr21:36,253,465-36,426,708 | 173,243 | |||||
| -X | -X | 155,270,560 | |||||
| P46 | 63 | 46,XY[8] | normal | dup(6)(q25.3q25.3) | chr6:157,944,961-158,033,908 | 88,947 | |
| del of 7p12.2 | del(7)(p12.2p12.2) | chr7:50,452,798-50,492,798 | 40,000 | ||||
| dup(17)(q12q12) | chr17:36,046,040-36,095,204 | 49,164 | |||||
| P47 | 59 | 46,XX[6] | normal | dup(1)(p13.3p13.3) | chr1:107,921,895-107,970,781 | 48,886 | |
| del of 7p12.2 | del(7)(p12.2p12.2) | chr7:50,356,873-50,465,376 | 408,503 | ||||
| del of 9p13.2 | del(9)(p13.2p13.2) | chr9:37,006,073-37,320,759 | 314,686 | ||||
| dup(9)(q31.1q31.1) | chr9:104,126,808-104,167,077 | 40,269 | |||||
| del(15)(q26.1q26.1) | chr15:93,390,484-93,450,773 | 60,289 | |||||
| del(18)(q21.32q21.32) | chr18:57,517,756-57,718,190 | 200,434 | |||||
| del(19)(p13.3p13.3) | chr19:0–2,787,457 | 2,787,457 | |||||
bp basepairs, LSP locus-specific probes as specified in Additional file 2: Table S2, y year
Figure 1.
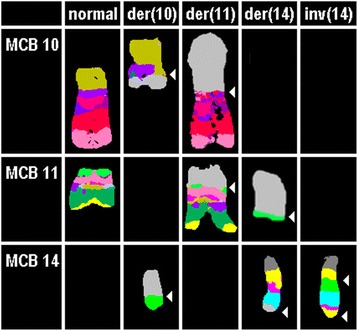
Result of aMCB probesets for chromosomes 10, 11, and 14 are shown, which characterized the breakpoints seen in case P66 as 10q11.23, 11p15.3, 14q11, 14q24.2, and 14q32.3. The final karyotype after application of all approaches as summarized in Additional file 1: Table S1 was 46,XX,der(10)(10pter- > 10p12.31::11q23.3- > 11q23.3::10p12.31- > 10q11.23::14q24.2- > 14qter),der(11)(10qter- > 10q11.23::11p15.3- > 11q23.3::10p12.31- > 10p12.31::11q23.3- > 11qter),der(14)t(11;14)(q15.3;q24.2),inv(14)(q11q23)
34/61 studied CN-ALL cases (18 B-ALL, 8 T-ALL and 8 with undefined ALL) were studied further using MLPA and aCGH. Overall, 126 CNAs were detected by MLPA and aCGH in those cases. CNAs were identified in 27/34 (80 %) of the studied cases. 1 to 13 CNAs per case were detected (Table 1). The distribution of CNAs per chromosome and frequencies of gains and losses are summarized in Fig. 2; i.e. all chromosomes apart from 8 and Y were involved in CNAs in this study.
Figure 2.

Distribution of CNAs as detected by aCGH in 27/34 studied cases. On X-axis the chromosome number is shown, while on Y-axis the total number of CNAs for each chromosome is depicted (scale 2).
Deletions and duplications could be grouped according to their sizes as follows:
focal CNAs (e.g. deletion of CHD2 gene in 7 cases or duplication of DCC gene in 3 cases – Table 1);
CNAs involving variable numbers of genes (e.g. deletion on 9p21.3 in 8 cases or amplification of 9q34.12q34.13 in one case – Table 1);
CNAs involving large parts of whole chromosomal p and/or q arms (e.g. deletion on 4p16.3p14 in one case or duplication of 7p22.3p14.1 in one case – Table 1)
CNAs of whole chromosomes (e.g. monosomy X in one case or trisomy #14 in one case – Table 1).
Most frequently observed deletion was 9p21.3 in 8/34 ALL cases (3x in B-ALL, 4x in T-ALL and 1x in undefined ALL); the CDKN2A/B genes were affected in all these eight cases. Furthermore, PTEN in 10q23.31 (6/34) and IKZF1 in 7p12.2 (5/34) were the hit by deletions regularly. Besides, deletion in 15q26.1 (CHD2 gene) was detected in 7/34 cases and duplication in 18q21.2 (DCC gene) in 3/34 cases.
Conclusions
Cytogenetic analysis has been and still is the standard method for detection of diagnostically relevant recurrent chromosomal aberrations in ALL. It is well known that when using banding karyotyping cryptic chromosomal aberrations may be missed due to several reasons: (i) sensitivity of chromosomal banding techniques is limited, even in case of good chromosomal morphology, to aberrations being at least 10 Mb in size, (ii) aberrations may be cryptic or masked, i.e. they are not resolvable due to a similar or identical GTG-banding pattern and/or poor chromosome morphology, and (iii) metaphases may be difficult to obtain and to evaluated as chromosomes may not be well-spread, clumsy or appearing as fuzzy with indistinct margins; thus even numerical aberrations may be missed [6, 13, 17].
In the past molecular cytogenetic approaches have shown to be efficient to detect in banding cytogenetics cryptic chromosomal aberrations [6, 13, 17]. Besides in metaphase also interphase nuclei can be studied in case of low mitotic (non-dividing) cells and also alterations being at low mosaic level can be easily detected by that approach [12, 14, 18]. In this study, we detected previously cryptic aberrations in 21/61 (34 %) cases with ALL using metaphase directed FISH studies; even complex aberrations were identified in some of these cases (Table 1 and Additional file 1: Table S1).
For 34/61 cases DNA could be extracted from the cytogenetically worked up cell suspension. Thus, in those cases besides FISH also MLPA and aCGH could be applied additionally, i.e. approaches which have much higher resolution than FISH, but can only detect unbalanced aberrations and no low level mosaics. Using these approaches cryptic CNAs were detected in ~80 % of those ALL cases. All 126 CNAs detected by MLPA and aCGH have been checked by UCSC genome browser to exclude benign copy number variations (CNVs) (http://genome-euro.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgGateway?redirect=auto&source=genome.ucsc.edu). Thus, all of them most likely are leukemia-related genetic changes, which were recognized in 27/34 ALL cases.
Of special interest may be a novel recurrent submicroscopic CNA expressed as loss of 15q26.1: focal deletion of CHD2 gene located there was found in 7 of the 34 (20 %) studied ALL cases in this study. The CHD2 gene is a member of the chromodomain helicase DNA-binding (CHD) protein family, which are all characterized by a chromatin-remodeling domain (the chromodomain) and an SNF2-related helicase/ATPase domain [19]. Thus, in future it may be of interest to study CHD2 gene deletions also for presence of mutations in this gene and also to screen ALL patients in general for CHD2 gene mutations.
Besides, duplication of DCC gene in 18q21.2 was present in 3 of the 34 (9 %) studied cases. DCC is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of cell adhesion molecules and acts as a transmembrane dependence receptor for netrins, key factors in the regulation of axon guidance during development of the central nerve system. Amplification of DCC gene was previously reported in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) [20, 21], however, this is the first report for DCC gene amplification in ALL. To evaluate the role of the DCC gene and to elaborate its potential as a molecular marker in ALL still needs more studies.
In general, submicroscopic CNAs were identified most frequently in chromosomes #7 and #9. CNAs in #7 involved deletion of IKZF1 at 7p12.2 that encodes IKAROS protein and is required for the development of all lymphoid lineages in 5 of 34 (14 %) studied CN-ALL cases. According to the literature deletions and/or sequence mutations of IKZF1 are present in 15 % of pediatric B-ALL, including ~70 % of BCR-ABL–positive ALL and with high-risk of relapse ~30 % of BCR-ABL–negative B-ALL [22]. However, deletions of IKZF1 are predominantly monoallelic and involve the N-terminal zinc-finger domain of IKAROS protein and result in expression of dominant-negative isoforms with cytoplasmic localization and oncogenic activity as well as an association with very poor outcome [23, 24]. Thus, IKZF1 has newly been considered as a prognostic marker for B-ALL and might be useful for risk stratification [24, 25].
Cyclin dependent kinase 6 (CDK6) at 7q21.2, is the catalytic subunit of a protein kinase complex that regulates cell cycle G1 phase progression and G1/S transition. Deletion of CDK6 was identified in this study in 4 of 34 (12 %) of ALL cases. It has been shown recently that inhibition of CDK6 may lead to overcome the differentiation block seen in acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) with MLL translocations [26]. Further studied for this gene may also be recommended for better understanding of ALL biology.
The majority of #9 abnormalities is involving deletions of cell cycle regulatory genes at 9p21.3. The main target to deletions is CDKN2A which encodes for the two transcripts p16/INK4A and p14/ARF (alternative splicing), followed by CDKN2B gene (p15/INK4B); both are tumor suppressor genes. Deletions of CDKN2A/B can be found in 30 and 50 % of B-ALL and T-ALL cases, respectively [23, 25, 27]. In the present study such deletions were only found in 8/34 (24 %) of the studied ALL cases, which is most likely due to low case numbers. CDKN2A/B deletion can be detected at initial diagnosis or acquired at relapse, suggesting that CDKN2A/B deletion is a secondary genetic event. Also, the outcome of cases with CDKN2A/B deletion depends on the status of the second allele, as homozygous deletions are associated with poor outcome and heterozygous deletions represent markers for favorable outcomes [27, 28]. T-ALL-case P61 had such a prognostically adverse homozygous deletion in 9p21.3 together with amplification of 9q34.12 to 9q34.13; the latter contains the ABL1 and NUP214 genes (Fig. 3). NUP214-ABL1 fusion gene amplification was previously mainly observed in T-ALL and associated with poor outcome [6].
Figure 3.
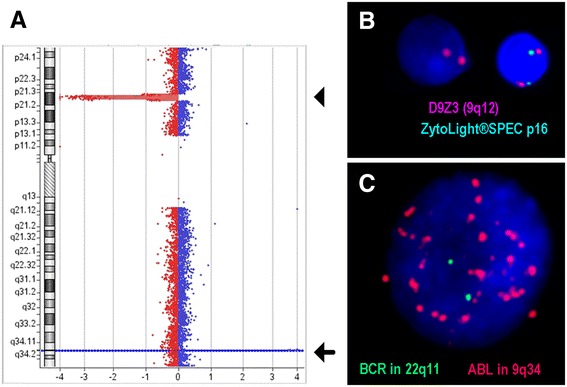
aCGH from case Nr. P61 showed two CNAs in chromosome 9; at 9p21.3 a homozygous deletion (arrowhead) and at 9q34.12 to 9q34.13 an amplification (arrow). a FISH confirmed presence of the homozygous deletion in 9p21.3 in interphase. b An amplification present as double minutes was confirmed using a probe specific for the ABL-gene
Another recurrent deletion in #9 in the studied ALL cases involved the PAX5 gene located in 9p13.2, which encodes for a protein with key roles in lymphoid development. It was found to be deleted in B-ALL (n = 2) and T-ALL (n = 1 showed short arm 9p deleted) in this study. In the literature, deletion of PAX5 was reported in 31.7 % of B-ALL and also it has been involved in several chromosomal translocations [29, 30]. In a recent report, PAX5 deletion was observed in only 10 % and 18 % in children and adult B-ALL, respectively; notably PAX5 deletion was frequently accompanied by deletion of CDKN2A (83.3 % of children and 100.0 % of adults) [28]. Also PAX5 was found to be a common target in leukemogenesis of B-ALL, but not associated with adverse outcome [15]. In future, PAX5 could be used as one of the molecular markers in diagnosis and monitoring of the disease, especially in B-ALL [28–30].
Besides, other CNAs have been identified here, encompassing single or few genes, only. Many of CN losses involve cell cycle regulatory and/or putative tumor suppressor genes like 10q23.3 (PTEN; n = 6), 13q14.2 (RB1; n = 3), and 17p13.1 (TP53; n = 4), or transcriptional regulators and co-activators like 3q26.32 (TBL1XR1; n = 1), 12p13.2 (ETV6; n = 2), 21q22.12 (RUNX1; n = 1) and 21q22.2 (ERG; n = 2), or regulators of chromatin structure and epigenetic regulators like 16p13.3 (CREBBP; n = 2). Although, oncogene overexpression resulting from gene duplication is infrequent in ALL, we found MYB duplication in one case, too. These observations of gene loss of function or overexpression being involved in leukemic transformation [15, 31] underline the heterogeneity of different ALL cases and the potential of molecular approaches to identify new subgroups of this disease.
The present study also highlights, that most likely all CN-ALL cases hold cryptic genomic alterations. DNA sequencing and single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) arrays have been used to detect mutations for a number of target genes that are known to key roles in lymphoid development. Thus, somatic mutations have been identified in both B and T-ALL patients [2]. For instance, mutations in JAK2 were identified in 10 % of high-risk childhood B-ALL and shown to be associated frequently with other abnormalities, including deletions or mutations of IKZF1 and overexpression the CRLF2 gene [23]. In T-ALL, NOTCH1-activating gene mutation has been found in 60 % and FBXW7-inactivating gene mutation occurs in 20 % of pediatric T-ALL [32]. Less commonly, mutations in PTEN, WT1, amplification of MYB and sequence mutations in RAS signaling (NRAS, KRAS, and NF1) and tumor suppression (TP53) have been identified in ALL [8, 31].
Overall, sensitive methods to detect cryptic chromosomal aberrations in CN-ALL are useful and necessary for genetic risk–based classification and correct determination of treatment protocols. The present study highlights that molecular cytogenetic approaches together with molecular methods are suited to identify cryptic rearrangements and potential target genes that involved in leukemogenesis and progression of the disease. Also it could be demonstrated that aCGH is a highly efficient tool for detection of CNAs in CN-ALL. However, while aCGH (and MLPA) provide data on imbalanced genomic alterations, (molecular) cytogenetics additionally detects different leukemic subclones within one sample, as well as balanced translocations leading to tumor-specific fusion genes. It seems to be valid, that there is no leukemia clone without genetic alterations; we just have to use the appropriate techniques to identify them. In conclusion, to obtain a comprehensive picture of all relevant changes in each individual ALL case data from cytogenetics, FISH, MLPA and aCGH needs to be considered and included in diagnostics; however, sometimes such investigations may be hampered by lack of sufficient cellular material, as also in this study, where only 34/61 cases could also be studied on DNA level or other previous studies [16, 33].
Methods
Patients and sample preparation
Cell suspensions were obtained from bone marrow collected from 61 patients diagnosed with ALL (31 with B-ALL, 12 with T-ALL and 18 with undefined ALL; Additional file 1: Table S1). The samples were obtained under informed consent of the corresponding patients and according to institutional ethical committee guidelines (ethical commission of the university clinic Jena, Germany; code 1105-04/03).
GTG-banding
The bone marrow cells were unstimulated cultivated for 24 hours (with and without colchicin) and 48 h, and a standard cytogenetic cell preparation following air drying method was done [34]. GTG-banding was routinely done in each sample following standard procedures. Twenty metaphases were obtained for cytogenetic evolution on a banding level of 250–300 bands per haploid karyotype [35]. Apart from 4 all 61 studied cases had a normal karyotype of 46,XX or 46,XY. In one case the karyotype could not be determined due to low metaphase quality; one case just had (most likely age associated) loss of an X-chromosome in a subset of the cells, one case had a questionable der(19) in all cells, and another one a trisomy 14 in 6/20 studied cells.
Molecular cytogenetics
Fluorescence in situ hybridization was done according to standard procedures and/or according to manufacturer’s instructions.
Homemade were the following probes and probe sets:
24-color-FISH using all human whole chromosome painting (WCP) probes [36];
FISH-banding probe-sets as follows: genome wide multitude multicolor banding (mMCB) and chromosome specific high resolution array-proven multicolor-banding (aMCB) [16, 37, 38];
WCP probes for all chromosomes were homemade [36].
The following commercially available locus-specific probes (LSPs) (Additional file 2: Table S2) were used to validate and possibly confirm the breakpoints found in mMCB, aCGH and/or MLPA: from Abbott/Vysis (Wiesbaden, Germany), Kreatech Diagnostics (Amsterdam, Netherland), ZytoVision (Bremerhaven, Germany), and DNA from bacterial artificial chromosome (BACs) probes obtained from Resources Center (Oakland, USA) were labeled by PCR with SpectrumGreen, SpectrumOrange or TexasRed-dUTP and applied in two- or three-color FISH-approaches. For each interphase FISH analysis to determine the percentage of specific aberrations, at least 200 interphase nuclei were examined per sample and FISH-probe – the applied probes can be found in Additional file 2: Table S2.
Homemade and previously reported chromosome-specific sub-CTM- (= subtelomere -/ subcentromere oriented) probe-sets were applied in selected cases [13] (Additional file 1: Table S1).
DNA isolation
Genomic DNA was extracted from cells fixed in acetic acid-methonal (1:3) by Puregene DNA Purification Kit (Gentra Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA). DNA concentration was determined by a Nanodrop spectrophotometer. The quality of DNA was checked using agarose gel electrophoresis. DNA-samples extracted from fixed cells of 2 healthy males and 2 healthy females by the same method were used as reference samples.
MLPA analysis
SALSA MLPA P377-A1 Hematologic malignancies probemix was used for this study (MRC- Holland, Amsterdam, The Netherlands). This probemix contains probes for 37 genes covered by 54 probes, which have diagnostic or prognostic significant role in hematologic malignancies. MLPA was performed according to the manufacturer’s protocol, which includes three reaction phases: hybridization, ligation, and PCR amplification. Amplified probes and GeneScan LIZ 500 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, USA) standard were separated by capillary electrophoresis using a ABI-PRISM 3130XL Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, USA). GeneMarker (SoftGenetics, USA) was used to analyzeMLPA data. Detection threshold was set at 0.65-1.35; control samples of four healthy donors were included in each run.
Array-comparative genomic Hybridization (aCGH)
aCGH was performed using Agilent SurePrint G3 Human Genome microarray 180 K (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA), an oligonucleotide microarray containing 170,334 probes 60-mer with a ~13 kb overall median probe spacing (11 kb in Refseq-genes). Genomic DNA of patients was co-hybridized with a sex-mismatched control DNA (G1471 or G1521; Promega, Mannheim, Germany). Labeling was performed using Agilent Genomic DNA enzymatic labeling kit (Agilent) according to the manufacturers’ instructions. After hybridization and washing, the aCGH slide was scanned on an Agilent scanner, processed with Feature Extraction software (v12.0.2.2) and results were analyzed using Cytogenomics (v3.0) using ADM2 as aberration algorithm.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in parts by DAAD (fellowship to MAKO and PROBRAL 57054562 to TL) and CAPES (419/14 to MLMS).
Abbreviations
- aCGH
Array-comparative genomic hybridization
- ALL
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- aMCB
Array-proven multicolor-banding
- AML
Acute myelogenous leukemia
- BAC
Bacterial artificial chromosome
- B-ALL
B-cell ALL
- Bp
Basepairs
- CLL
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- CN
Copy number
- CNA
Copy number alteration
- CN-ALL
ALL according to banding cytogenetics with normal karyotype
- CNVs
Copy number variations
- DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- FISH
Fluorescence in situ hybridization
- GTG
G-banding with trypsin-Giemsa
- LSPs
Locus-specific probes
- MLPA
Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification
- mMCB
Multitude multicolor banding
- n.d.
Not determined
- PCR
Polymerase chain reaction
- SNP
Single-nucleotide polymorphism
- sub-CTM
Subtelomere -/ subcentromere oriented
- T-ALL
T-cell ALL
- TPA
2-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate
- WCP
Whole chromosome painting
- Y
Year
Additional files
All 61 CN-ALL cases studied; for each case age, gender and subtype of ALL is given. Also all FISH-probes, probe sets and approaches applied for each case are listed. Abbreviations: n.d. = not determined, y = year.
List of locus specific probes used in the present study for further characterization of acquired aberrations and/or determination of the percentage of deletions or duplications as determined by aCGH or MLPA.
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
MAKO selected the cases, did parts of the FISH-studies and drafted the paper; JBM and IMC performed aCGH analyses and interpretation; MR and MAKO did MLPA analyses and interpretation; AG, BG, BG, KW, MLMS and TdJMS provided ALL-cases including clinical and banding cytogenetic data; KR and BM were involved in FISH-probe generation and application KR did also parts of the FISH-studies; TL planned and organized the study and did final drafting of the paper. All authors read and approved the paper.
References
- 1.Teitell MA, Pandolfi PP. Molecular genetics of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Annu Rev Pathol. 2009;4:175–98. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pathol.4.110807.092227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Faderl S, O'Brien S, Pui CH, Stock W, Wetzler M, Hoelzer D, et al. Adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: concepts and strategies. Cancer. 2010;116:1165–76. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Van Vlierberghe P, Ferrando A. The molecular basis of T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(10):3398–406. doi: 10.1172/JCI61269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zuckerman T, Rowe JM. Pathogenesis and prognostication in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. F1000Prime Rep. 2014;6:59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 5.Perez-Andreu V, Roberts KG, Xu H, Smith C, Zhang H, Yang W, et al. A genome-wide association study of susceptibility to acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adolescents and young adults. Blood. 2015;125:680–6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-09-595744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mrózek K, Harper DP, Aplan PD. Cytogenetics and molecular genetics of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2009;23:991–1010. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2009.07.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Holmfeldt L, Wei L, Diaz-Flores E, Walsh M, Zhang J, Ding L, et al. The genomic landscape of hypodiploid acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat Genet. 2013;45:242–52. doi: 10.1038/ng.2532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mullighan CG. Genomic characterization of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Semin Hematol. 2013;50:314–24. doi: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2013.10.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chilton L, Buck G, Harrison CJ, Ketterling RP, Rowe JM, Tallman MS, et al. High hyperdiploidy among adolescents and adults with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL): cytogenetic features, clinical characteristics and outcome. Leukemia. 2014;28:1511–8. doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Moorman AV, Harrison CJ, Buck GA, Richards SM, Secker-Walker LM, Martineau M, et al. Karyotype is an independent prognostic factor in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): analysis of cytogenetic data from patients treated on the Medical Research Council (MRC) UKALLXII/Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) 2993 trial. Blood. 2007;109:3189–97. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-10-051912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Downing JR, Wilson RK, Zhang J, Mardis ER, Pui CH, Ding L, et al. The pediatric cancer genome project. Nat Genet. 2012;44:619–22. doi: 10.1038/ng.2287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Woo JS, Alberti MO, Tirado CA. Childhood B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a genetic update. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2014;3:16. doi: 10.1186/2162-3619-3-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Karst C, Gross M, Haase D, Wedding U, Höffken K, Liehr T, et al. Novel cryptic chromosomal rearrangements detected in acute lymphoblastic leukemia detected by application of new multicolor fluorescent in situ hybridization approaches. Int J Oncol. 2006;28:891–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Inaba H, Greaves M, Mullighan CG. Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet. 2013;381:1943–55. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)62187-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Roberts KG, Mullighan CG. Genomics in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: insights and treatment implications. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015, in press. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 16.Weise A, Heller A, Starke H, Mrasek K, Kuechler A, Pool-Zobel BL, et al. Multitude multicolor chromosome banding (mMCB) - a comprehensive one-step multicolor FISH banding method. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2003;103:34–9. doi: 10.1159/000076286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Othman MA, Melo JB, Carreira IM, Rincic M, Alhourani E, Wilhelm K, et al. MLLT10 and IL3 rearrangement together with a complex four-way translocation and trisomy 4 in a patient with early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A case report. Oncol Rep. 2015;33:625–30. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Karst C, Heller A, Claussen U, Gebhart E, Liehr T. Detection of cryptic chromosomal aberrations in the in vitro non-proliferating cells of acute myeloid leukemia. Int J Oncol. 2005;27:355–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Carvill GL, Heavin SB, Yendle SC, McMahon JM, O'Roak BJ, Cook J, et al. Targeted resequencing in epileptic encephalopathies identifies de novo mutations in CHD2 and SYNGAP1. Nat Genet. 2013;45:825–30. doi: 10.1038/ng.2646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Derks S, van Engeland M. DCC (deleted in colorectal carcinoma) Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2010;14:945–49. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Alhourani E, Rincic M, Othman MA, Pohle B, Schlie C, Glaser A, et al. Comprehensive chronic lymphocytic leukemia diagnostics by combined multiplex ligation dependent probe amplification (MLPA) and interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization (iFISH) Mol Cytogenet. 2014;7:79. doi: 10.1186/s13039-014-0079-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mullighan CG, Su X, Zhang J, Radtke I, Phillips LA, Miller CB, et al. Deletion of IKZF1 and prognosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:470–80. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0808253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhao Y, Huang H, Wei G. Novel agents and biomarkers for acute lymphoid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2013;6:40. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-6-40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Meyer C, Zur Stadt U, Escherich G, Hofmann J, Binato R, Barbosa Tda C, et al. Refinement of IKZF1 recombination hotspots in pediatric BCP-ALL patients. Am J Blood Res. 2013;3:165–73. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Asai D, Imamura T, Suenobu S, Saito A, Hasegawa D, Deguchi T, et al. IKZF1 deletion is associated with a poor outcome in pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia in Japan. Cancer Med. 2013;2:412–9. doi: 10.1002/cam4.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Placke T, Faber K, Nonami A, Putwain SL, Salih HR, Heidel FH, et al. Requirement for CDK6 in MLL-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2014;124:13–23. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-02-558114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sulong S, Moorman AV, Irving JA, Strefford JC, Konn ZJ, Case MC, et al. A comprehensive analysis of the CDKN2A gene in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia reveals genomic deletion, copy number neutral loss of heterozygosity, and association with specific cytogenetic subgroups. Blood. 2009;113:100–7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-07-166801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kim M, Choi JE, She CJ, Hwang SM, Shin HY, Ahn HS, et al. PAX5 deletion is common and concurrently occurs with CDKN2A deletion in B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2011;47:62–6. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2011.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mullighan CG, Goorha S, Radtke I, Miller CB, Coustan-Smith E, Dalton JD, et al. Genome-wide analysis of genetic alterations in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature. 2007;446:758–64. doi: 10.1038/nature05690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nebral K, Denk D, Attarbaschi A, König M, Mann G, Haas OA, et al. Incidence and diversity of PAX5 fusion genes in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2009;23:134–43. doi: 10.1038/leu.2008.306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Stengel A, Schnittger S, Weissmann S, Kuznia S, Kern W, Kohlmann A, et al. TP53 mutations occur in 15.7 % of ALL and are associated with MYC-rearrangement, low hypodiploidy, and a poor prognosis. Blood. 2014;124:251–8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-02-558833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gallo Llorente L, Luther H, Schneppenheim R, Zimmermann M, Felice M, Horstmann MA. Identification of novel NOTCH1 mutations: increasing our knowledge of the NOTCH signaling pathway. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2014;61:788–96. doi: 10.1002/pbc.24852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Heller A, Loncarevic IF, Glaser M, Gebhart E, Trautmann U, Claussen U, et al. Breakpoint differentiation in chromosomal aberrations of hematological malignancies: Identification of 33 previously unrecorded breakpoints. Int J Oncol. 2004;24:127–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Claussen U, Michel S, Mühlig P, Westermann M, Grummt UW, Kromeyer-Hauschild K, et al. Demystifying chromosome preparation and the implications for the concept of chromosome condensation during mitosis. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2002;98:136–46. doi: 10.1159/000069817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.ISCN. An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Eds: Shaffer LG, McGowan-Jordan J, Schmid M. S. Karger, Basel, 2013.
- 36.Liehr T, Starke H, Weise A, Lehrer H, Claussen U. Multicolor FISH probe sets and their applications. Histol Histopathol. 2004;19:229–37. doi: 10.14670/HH-19.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Liehr T, Heller A, Starke H, Rubtsov N, Trifonov V, Mrasek K, et al. Microdissection based high resolution multicolor banding for all 24 human chromosomes. Int J Mol Med. 2002;9:335–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Weise A, Mrasek K, Fickelscher I, Claussen U, Cheung SW, Cai WW, et al. Molecular definition of high-resolution multicolor banding probes: first within the human DNA sequence anchored FISH banding probe set. J Histochem Cytochem. 2008;56:487–93. doi: 10.1369/jhc.2008.950550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


