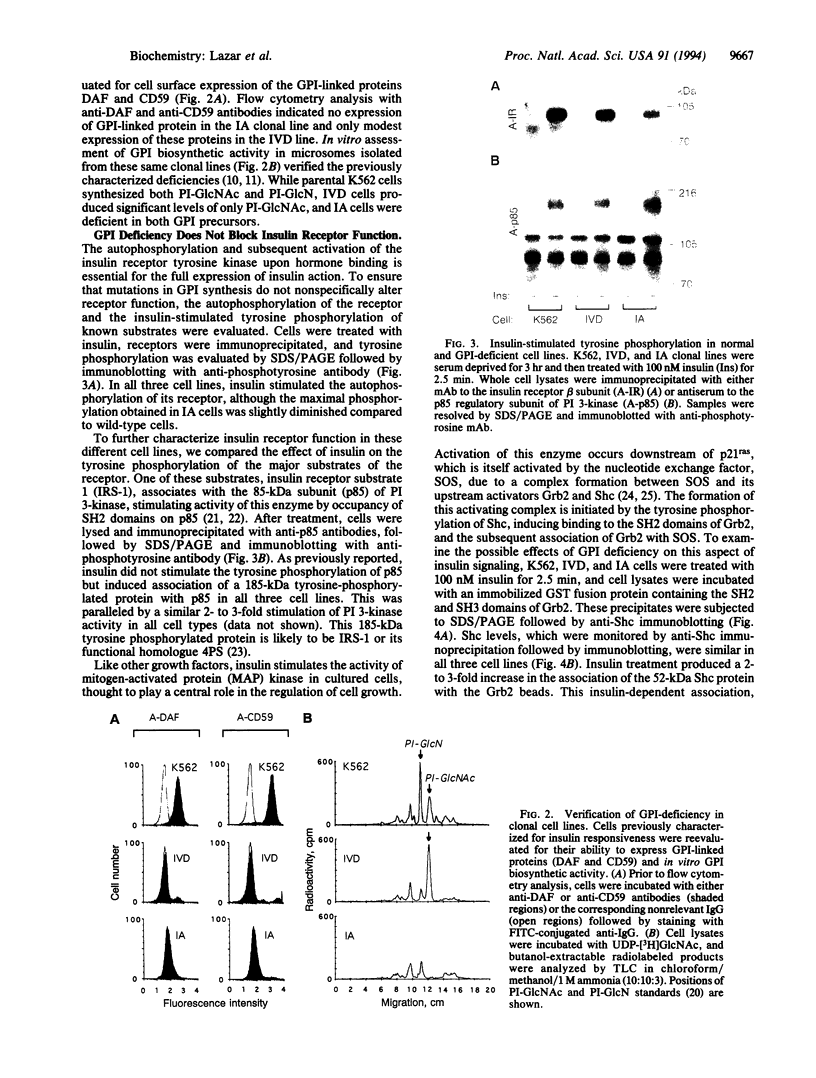
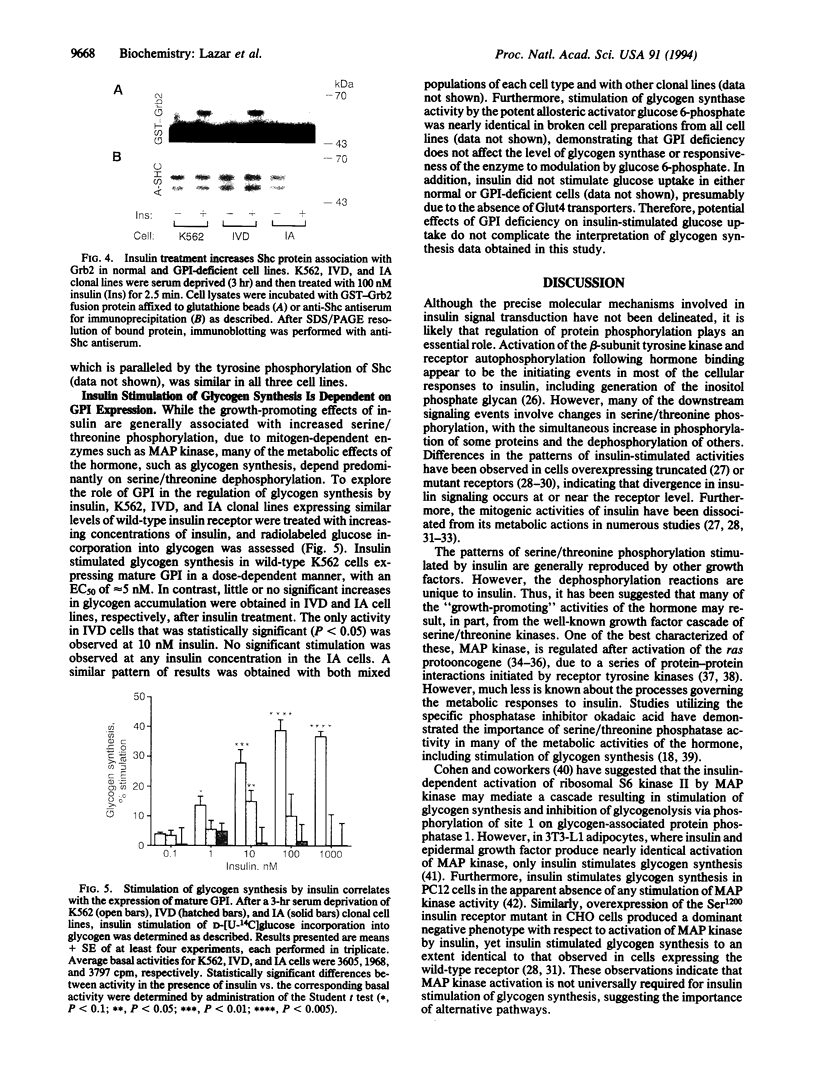
Abstract
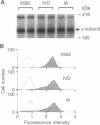
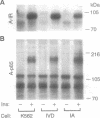
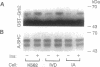
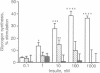
Although the insulin-dependent hydrolysis of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI) may play an important role in insulin action, an absolute requirement for this glycolipid has not been demonstrated. Human K562 cells were mutated to produce a cell line (IA) incapable of the earliest step in PI glycosylation, the formation of PI-GlcNAc. Another cell line (IVD) was deficient in the deacetylation of PI-GlcNAc to form PI-GlcN and subsequent mannosylated species. Each line was transfected with wild-type human insulin receptors. Similar insulin-stimulated receptor autophosphorylation was observed in all three lines, along with a nearly identical increase in the association of phosphorylated insulin receptor substrate 1 with endogenous PI 3-kinase. Both normal and GPI-defective lines also displayed a similar 2- to 3-fold increase in phosphorylation of the Shc protein and its association with growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 in response to insulin. In contrast to these results, striking differences were noted in insulin-stimulated glycogen synthesis. In normal cells, glycogen synthesis was significantly increased by insulin, whereas no insulin stimulation was observed in GPI-deficient IA cells, and only a trace of stimulation was detected in IVD cells. These results indicate that tyrosine phosphorylation produced by insulin is not dependent on GPI synthesis, and this effect is not sufficient to elicit at least some of the metabolic effects of the hormone. In contrast, GPI synthesis is required for the stimulation of glycogen synthesis by insulin in these cells. These findings support the existence of divergent pathways in the action of insulin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alemany S., Mato J. M., Strålfors P. Phospho-dephospho-control by insulin is mimicked by a phospho-oligosaccharide in adipocytes. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):77–79. doi: 10.1038/330077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez J. F., Cabello M. A., Felíu J. E., Mato J. M. A phospho-oligosaccharide mimics insulin action on glycogen phosphorylase and pyruvate kinase activities in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 15;147(2):765–771. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90996-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backer J. M., Myers M. G., Jr, Shoelson S. E., Chin D. J., Sun X. J., Miralpeix M., Hu P., Margolis B., Skolnik E. Y., Schlessinger J. Phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase is activated by association with IRS-1 during insulin stimulation. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3469–3479. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Robbins D. J., Boulton T. G. ERKs, extracellular signal-regulated MAP-2 kinases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;3(6):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90124-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeg M. A., Brass E. P., Rosenberry T. L. Inositol glycan phosphate derived from human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase glycolipid anchor and inositol cyclic 1,2-phosphate antagonize glucagon activation of glycogen phosphorylase. Diabetes. 1993 Sep;42(9):1318–1323. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.9.1318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent P., Lavoinne A., Nakielny S., Caudwell F. B., Watt P., Cohen P. The molecular mechanism by which insulin stimulates glycogen synthesis in mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):302–308. doi: 10.1038/348302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englund P. T. The structure and biosynthesis of glycosyl phosphatidylinositol protein anchors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:121–138. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaulton G. N. Differential regulation of glycosylated phosphatidylinositol subtypes by insulin. Diabetes. 1991 Oct;40(10):1297–1304. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.10.1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori S., Fukuda M., Yamashita T., Nakamura S., Gotoh Y., Nishida E. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and its activator by ras in intact cells and in a cell-free system. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20346–20351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess S. L., Suchin C. R., Saltiel A. R. The specific protein phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid differentially modulates insulin action. J Cell Biochem. 1991 Apr;45(4):374–380. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240450411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose S., Mohney R. P., Mutka S. C., Ravi L., Singleton D. R., Perry G., Tartakoff A. M., Medof M. E. Derivation and characterization of glycoinositol-phospholipid anchor-defective human K562 cell clones. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5272–5278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose S., Ravi L., Hazra S. V., Medof M. E. Assembly and deacetylation of N-acetylglucosaminyl-plasmanylinositol in normal and affected paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3762–3766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamitani T., Chang H. M., Rollins C., Waneck G. L., Yeh E. T. Correction of the class H defect in glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor biosynthesis in Ltk- cells by a human cDNA clone. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):20733–20736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita T., Medof M. E., Silber R., Nussenzweig V. Distribution of decay-accelerating factor in the peripheral blood of normal individuals and patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):75–92. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. C., Jr, Guinovart J. J., Larner J. Activation of rat adipocyte glycogen synthase by insulins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):444–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Bellot F., Honegger A. M., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Zilberstein A. Tyrosine kinase activity is essential for the association of phospholipase C-gamma with the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):435–441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Kelly K. L., Abler A., Jarett L. Identification of a novel insulin-sensitive glycophospholipid from H35 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2131–2137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matuoka K., Shibata M., Yamakawa A., Takenawa T. Cloning of ASH, a ubiquitous protein composed of one Src homology region (SH) 2 and two SH3 domains, from human and rat cDNA libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9015–9019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D. A. Insulin action in cells expressing truncated or kinase-defective insulin receptors. Dissection of multiple hormone-signaling pathways. Diabetes Care. 1990 Mar;13(3):302–316. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.3.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misek D. E., Saltiel A. R. An inositol phosphate glycan derived from a Trypanosoma brucei glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol mimics some of the metabolic actions of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16266–16273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata T., Takeda J., Iida Y., Yamada N., Inoue N., Takahashi M., Maeda K., Kitani T., Kinoshita T. The cloning of PIG-A, a component in the early step of GPI-anchor biosynthesis. Science. 1993 Feb 26;259(5099):1318–1320. doi: 10.1126/science.7680492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohney R. P., Knez J. J., Ravi L., Sevlever D., Rosenberry T. L., Hirose S., Medof M. E. Glycoinositol phospholipid anchor-defective K562 mutants with biochemical lesions distinct from those in Thy-1- murine lymphoma mutants. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6536–6542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller D. E., Benecke H., Flier J. S. Biologic activities of naturally occurring human insulin receptor mutations. Evidence that metabolic effects of insulin can be mediated by a kinase-deficient insulin receptor mutant. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10995–11001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. G., Jr, Backer J. M., Sun X. J., Shoelson S., Hu P., Schlessinger J., Yoakim M., Schaffhausen B., White M. F. IRS-1 activates phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase by associating with src homology 2 domains of p85. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10350–10354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmichi M., Pang L., Ribon V., Saltiel A. R. Divergence of signaling pathways for insulin in PC-12 pheochromocytoma cells. Endocrinology. 1993 Jul;133(1):46–56. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.1.7686484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Harada R., Fujita T., Okada H. Monoclonal antibodies capable of causing hemolysis of neuraminidase-treated human erythrocytes by homologous complement. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2262–2266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson T. S., Lane M. D. Post-translational acquisition of insulin binding activity by the insulin proreceptor. Correlation to recognition by autoimmune antibody. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6816–6822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang L., Lazar D. F., Moller D. E., Flier J. S., Saltiel A. R. The stimulation of pp42mapkinase by insulin does not correlate with its metabolic actions in cells overexpressing mutant insulin receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Oct 15;196(1):301–310. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S. Mitogen-activated protein kinases: versatile transducers for cell signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jun;17(6):233–238. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)80005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendergast A. M., Quilliam L. A., Cripe L. D., Bassing C. H., Dai Z., Li N., Batzer A., Rabun K. M., Der C. J., Schlessinger J. BCR-ABL-induced oncogenesis is mediated by direct interaction with the SH2 domain of the GRB-2 adaptor protein. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):175–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pronk G. J., de Vries-Smits A. M., Buday L., Downward J., Maassen J. A., Medema R. H., Bos J. L. Involvement of Shc in insulin- and epidermal growth factor-induced activation of p21ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1575–1581. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins D. J., Cheng M., Zhen E., Vanderbilt C. A., Feig L. A., Cobb M. H. Evidence for a Ras-dependent extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6924–6928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson L. J., Razzack Z. F., Lawrence J. C., Jr, James D. E. Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation is not sufficient for stimulation of glucose transport or glycogen synthase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26422–26427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolband G. C., Williams J. F., Webster N. J., Olefsky J. M. Deletion of the insulin receptor beta-subunit acidic domain results in enhanced metabolic signaling. Endocrinology. 1993 Sep;133(3):1437–1443. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.3.8396020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero G., Gámez G., Huang L. C., Lilley K., Luttrell L. Anti-inositolglycan antibodies selectively block some of the actions of insulin in intact BC3H1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1476–1480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin stimulates the generation from hepatic plasma membranes of modulators derived from an inositol glycolipid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5793–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Fox J. A., Sherline P., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin-stimulated hydrolysis of a novel glycolipid generates modulators of cAMP phosphodiesterase. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):967–972. doi: 10.1126/science.3016898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R. Insulin generates an enzyme modulator from hepatic plasma membranes: regulation of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase, pyruvate dehydrogenase, and adenylate cyclase. Endocrinology. 1987 Mar;120(3):967–972. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-3-967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Batzer A., Li N., Lee C. H., Lowenstein E., Mohammadi M., Margolis B., Schlessinger J. The function of GRB2 in linking the insulin receptor to Ras signaling pathways. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1953–1955. doi: 10.1126/science.8316835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Taneda Y., Hirai S., Yamamoto-Honda R., Toyota T. Mutated insulin receptor Val996 reduces insulin-dependent generation of inositol glycan and diacylglycerol. Diabetes. 1992 Nov;41(11):1373–1379. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.11.1373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Gutiérrez J. C., Sánchez-Arias J. A., Valle J. C., Guadaño A., Samper B., Mato J. M., Felíu J. E. Insulin resistance in genetically obese (fa/fa) rats: changes in the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol signaling system in isolated hepatocytes. Endocrinology. 1994 Mar;134(3):1485–1492. doi: 10.1210/endo.134.3.8119190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takata Y., Webster N. J., Olefsky J. M. Intracellular signaling by a mutant human insulin receptor lacking the carboxyl-terminal tyrosine autophosphorylation sites. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9065–9070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanti J. F., Grémeaux T., Van Obberghen E., Le Marchand-Brustel Y. Effects of okadaic acid, an inhibitor of protein phosphatases-1 and -2A, on glucose transport and metabolism in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2099–2103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. M., Myers M. G., Jr, Sun X. J., Aaronson S. A., White M., Pierce J. H. IRS-1: essential for insulin- and IL-4-stimulated mitogenesis in hematopoietic cells. Science. 1993 Sep 17;261(5128):1591–1594. doi: 10.1126/science.8372354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Livingston J. N., Backer J. M., Lauris V., Dull T. J., Ullrich A., Kahn C. R. Mutation of the insulin receptor at tyrosine 960 inhibits signal transmission but does not affect its tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):641–649. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilden P. A., Backer J. M., Kahn C. R., Cahill D. A., Schroeder G. J., White M. F. The insulin receptor with phenylalanine replacing tyrosine-1146 provides evidence for separate signals regulating cellular metabolism and growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3358–3362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. W., Sarnecki C., Roberts T. M., Blenis J. ras mediates nerve growth factor receptor modulation of three signal-transducing protein kinases: MAP kinase, Raf-1, and RSK. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1041–1050. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90076-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]