Abstract
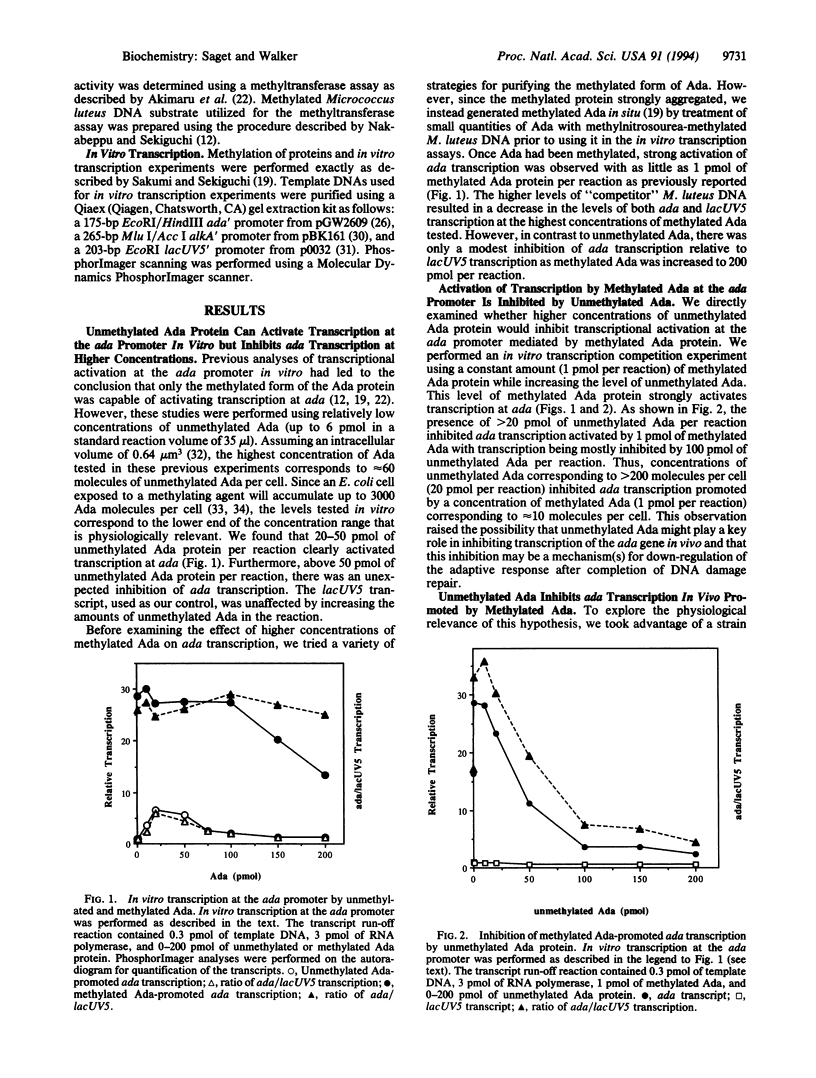
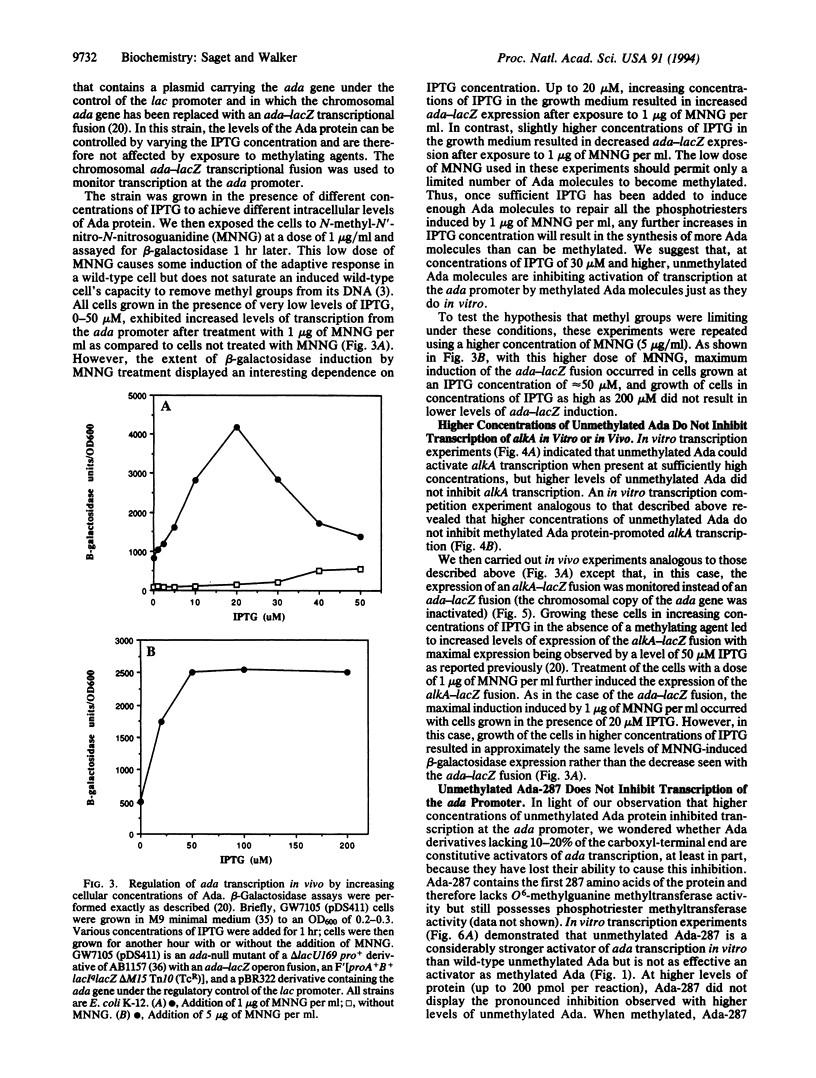
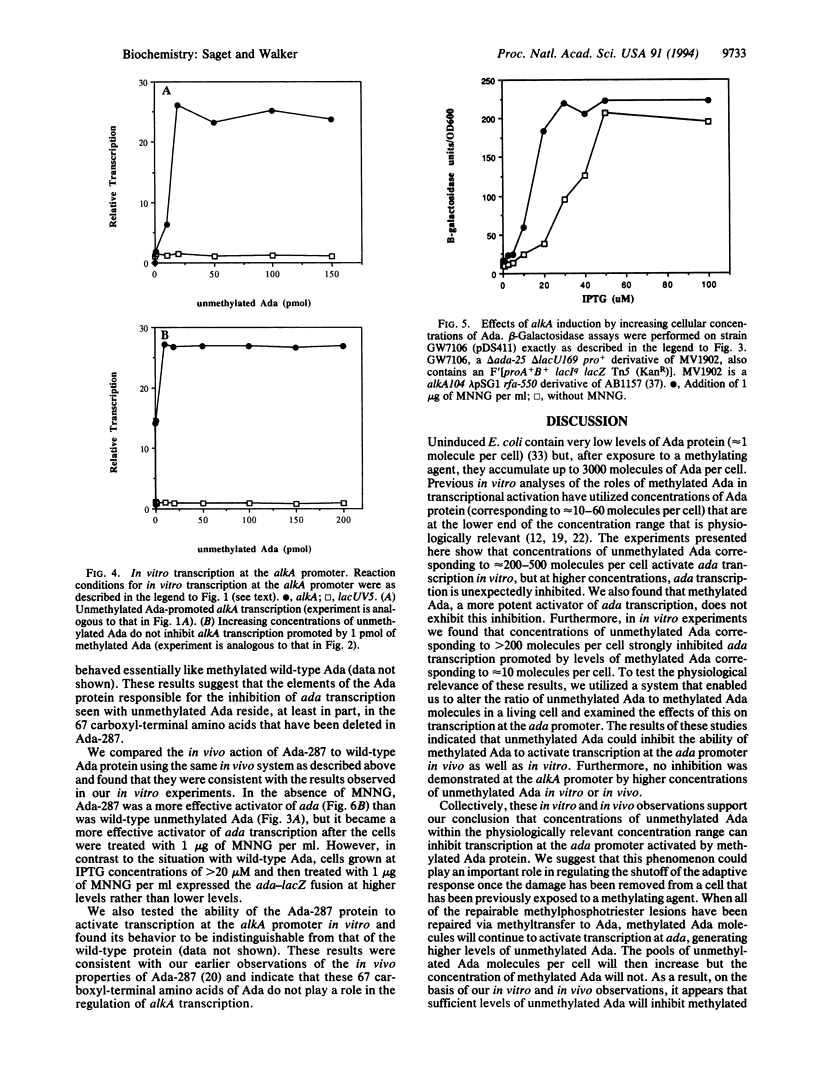
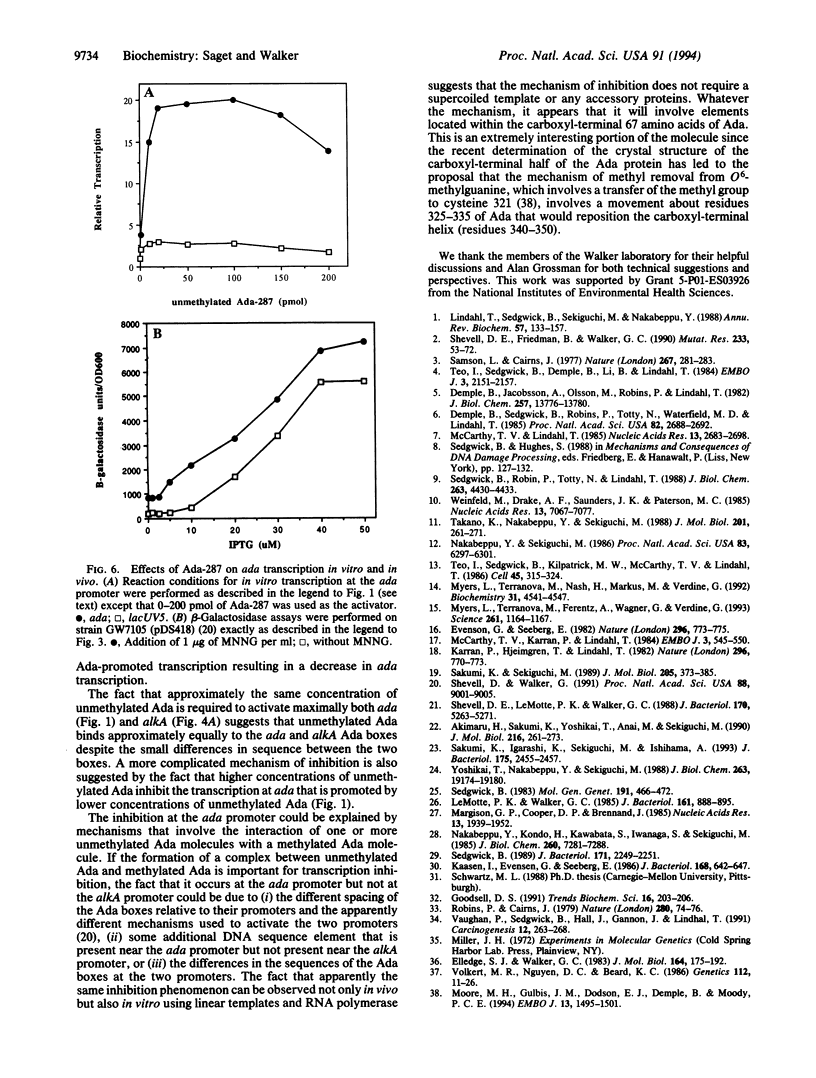
The adaptive response of Escherichia coli protects the cells against the toxic and mutagenic effects of certain alkylating agents. The major effector molecule regulating this response is the 39-kDa Ada protein, which functions as both a DNA repair protein and a transcriptional activator. Ada removes methyl groups from phosphotriester and O6-methylguanine lesions in DNA, irreversibly transferring them to cysteine residues at positions 69 and 321, respectively. When methylated at Cys-69, Ada is converted into a potent activator of ada and alkA transcription and binds to a sequence (Ada box) present in both promoters. We have found that physiologically relevant higher concentrations of unmethylated Ada are able to inhibit the activation of ada transcription by methylated Ada, both in vitro and in vivo. In contrast, the same concentrations of unmethylated Ada do not inhibit the activation of alkA transcription by methylated Ada, either in vitro or in vivo. Deletion of the carboxyl-terminal 67 amino acids of Ada abolished the ability of the unmethylated form of the protein to inhibit activation of ada transcription but not the ability of the methylated form to activate ada or alkA transcription. Our results suggest that the Ada protein plays a pivotal role in the negative modulation of its own synthesis and therefore in the down-regulation of the adaptive response. Elements present in the carboxyl terminus of Ada appear to be necessary for this negative regulatory function.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akimaru H., Sakumi K., Yoshikai T., Anai M., Sekiguchi M. Positive and negative regulation of transcription by a cleavage product of Ada protein. J Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 20;216(2):261–273. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80318-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Jacobsson A., Olsson M., Robins P., Lindahl T. Repair of alkylated DNA in Escherichia coli. Physical properties of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13776–13780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Sedgwick B., Robins P., Totty N., Waterfield M. D., Lindahl T. Active site and complete sequence of the suicidal methyltransferase that counters alkylation mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2688–2692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Walker G. C. Proteins required for ultraviolet light and chemical mutagenesis. Identification of the products of the umuC locus of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 25;164(2):175–192. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evensen G., Seeberg E. Adaptation to alkylation resistance involves the induction of a DNA glycosylase. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):773–775. doi: 10.1038/296773a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodsell D. S. Inside a living cell. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jun;16(6):203–206. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaasen I., Evensen G., Seeberg E. Amplified expression of the tag+ and alkA+ genes in Escherichia coli: identification of gene products and effects on alkylation resistance. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):642–647. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.642-647.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karran P., Hjelmgren T., Lindahl T. Induction of a DNA glycosylase for N-methylated purines is part of the adaptive response to alkylating agents. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):770–773. doi: 10.1038/296770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemotte P. K., Walker G. C. Induction and autoregulation of ada, a positively acting element regulating the response of Escherichia coli K-12 to methylating agents. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):888–895. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.888-895.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Sedgwick B., Sekiguchi M., Nakabeppu Y. Regulation and expression of the adaptive response to alkylating agents. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:133–157. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margison G. P., Cooper D. P., Brennand J. Cloning of the E. coli O6-methylguanine and methylphosphotriester methyltransferase gene using a functional DNA repair assay. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):1939–1952. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy T. V., Karran P., Lindahl T. Inducible repair of O-alkylated DNA pyrimidines in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):545–550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01844.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy T. V., Lindahl T. Methyl phosphotriesters in alkylated DNA are repaired by the Ada regulatory protein of E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):2683–2698. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.2683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. H., Gulbis J. M., Dodson E. J., Demple B., Moody P. C. Crystal structure of a suicidal DNA repair protein: the Ada O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase from E. coli. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 1;13(7):1495–1501. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. C., Terranova M. P., Ferentz A. E., Wagner G., Verdine G. L. Repair of DNA methylphosphotriesters through a metalloactivated cysteine nucleophile. Science. 1993 Aug 27;261(5125):1164–1167. doi: 10.1126/science.8395079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. C., Terranova M. P., Nash H. M., Markus M. A., Verdine G. L. Zinc binding by the methylation signaling domain of the Escherichia coli Ada protein. Biochemistry. 1992 May 19;31(19):4541–4547. doi: 10.1021/bi00134a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Kondo H., Kawabata S., Iwanaga S., Sekiguchi M. Purification and structure of the intact Ada regulatory protein of Escherichia coli K12, O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7281–7288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Sekiguchi M. Regulatory mechanisms for induction of synthesis of repair enzymes in response to alkylating agents: ada protein acts as a transcriptional regulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6297–6301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins P., Cairns J. Quantitation of the adaptive response to alkylating agents. Nature. 1979 Jul 5;280(5717):74–76. doi: 10.1038/280074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakumi K., Igarashi K., Sekiguchi M., Ishihama A. The Ada protein is a class I transcription factor of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(8):2455–2457. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.8.2455-2457.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakumi K., Sekiguchi M. Regulation of expression of the ada gene controlling the adaptive response. Interactions with the ada promoter of the Ada protein and RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 20;205(2):373–385. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90348-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson L., Cairns J. A new pathway for DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1977 May 19;267(5608):281–283. doi: 10.1038/267281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick B. In vitro proteolytic cleavage of the Escherichia coli Ada protein by the ompT gene product. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2249–2251. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2249-2251.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick B. Molecular cloning of a gene which regulates the adaptive response to alkylating agents in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(3):466–472. doi: 10.1007/BF00425764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick B., Robins P., Totty N., Lindahl T. Functional domains and methyl acceptor sites of the Escherichia coli ada protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4430–4433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevell D. E., Friedman B. M., Walker G. C. Resistance to alkylation damage in Escherichia coli: role of the Ada protein in induction of the adaptive response. Mutat Res. 1990 Nov-Dec;233(1-2):53–72. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(90)90151-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevell D. E., LeMotte P. K., Walker G. C. Alteration of the carboxyl-terminal domain of Ada protein influences its inducibility, specificity, and strength as a transcriptional activator. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5263–5271. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5263-5271.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevell D. E., Walker G. C. A region of the Ada DNA-repair protein required for the activation of ada transcription is not necessary for activation of alkA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9001–9005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano K., Nakabeppu Y., Sekiguchi M. Functional sites of the Ada regulatory protein of Escherichia coli. Analysis by amino acid substitutions. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 20;201(2):261–271. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teo I., Sedgwick B., Demple B., Li B., Lindahl T. Induction of resistance to alkylating agents in E. coli: the ada+ gene product serves both as a regulatory protein and as an enzyme for repair of mutagenic damage. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2151–2157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02105.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teo I., Sedgwick B., Kilpatrick M. W., McCarthy T. V., Lindahl T. The intracellular signal for induction of resistance to alkylating agents in E. coli. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):315–324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90396-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan P., Sedgwick B., Hall J., Gannon J., Lindahl T. Environmental mutagens that induce the adaptive response to alkylating agents in Escherichia coli. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Feb;12(2):263–268. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.2.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkert M. R., Nguyen D. C., Beard K. C. Escherichia coli gene induction by alkylation treatment. Genetics. 1986 Jan;112(1):11–26. doi: 10.1093/genetics/112.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinfeld M., Drake A. F., Saunders J. K., Paterson M. C. Stereospecific removal of methyl phosphotriesters from DNA by an Escherichia coli ada+ extract. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):7067–7077. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.7067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikai T., Nakabeppu Y., Sekiguchi M. Proteolytic cleavage of Ada protein that carries methyltransferase and transcriptional regulator activities. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19174–19180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



