Abstract
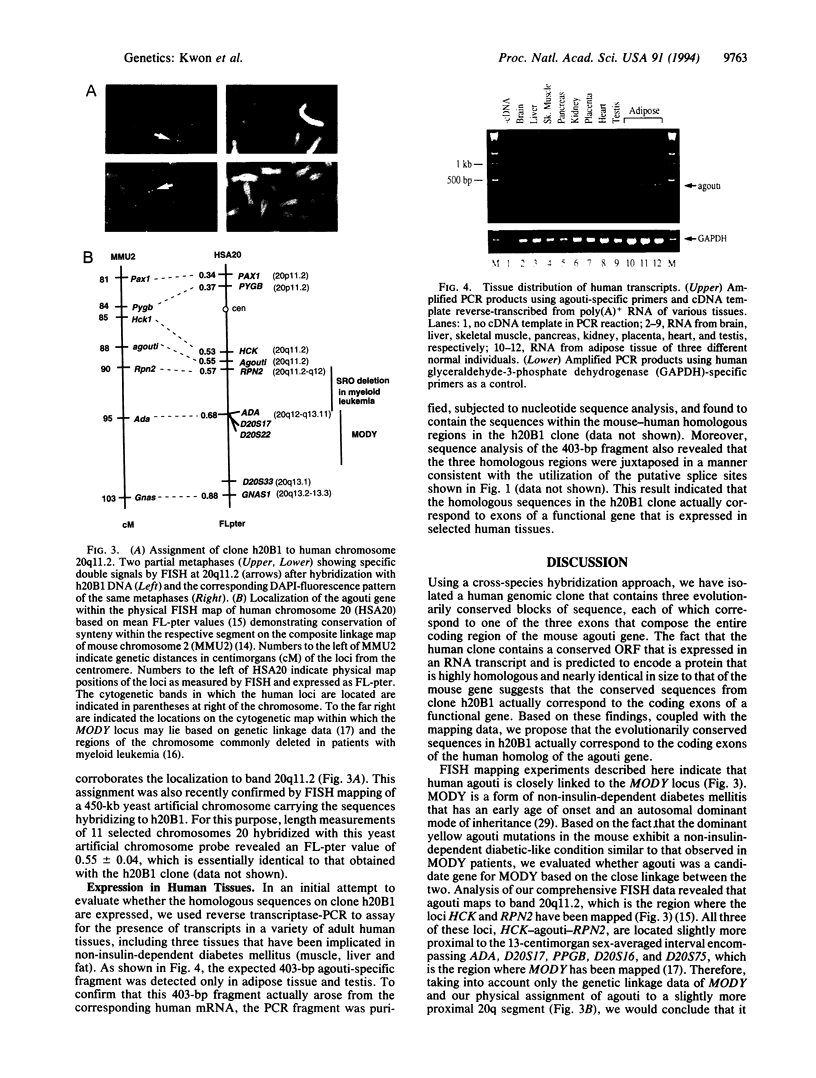
The agouti (a) locus in mouse chromosome 2 normally regulates coat color pigmentation. The mouse agouti gene was recently cloned and shown to encode a distinctive 131-amino acid protein with a consensus signal peptide. Here we describe the cloning of the human homolog of the mouse agouti gene using an interspecies DNA-hybridization approach. Sequence analysis revealed that the coding region of the human agouti gene is 85% identical to the mouse gene and has the potential to encode a protein of 132 amino acids with a consensus signal peptide. Chromosomal assignment using somatic-cell-hybrid mapping panels and fluorescence in situ hybridization demonstrated that the human agouti gene maps to chromosome band 20q11.2. This result revealed that the human agouti gene is closely linked to several traits, including a locus called MODY (for maturity onset diabetes of the young) and another region that is associated with the development of myeloid leukemia. Initial expression studies with RNA from several adult human tissues showed that the human agouti gene is expressed in adipose tissue and testis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bultman S. J., Michaud E. J., Woychik R. P. Molecular characterization of the mouse agouti locus. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1195–1204. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson G. E., Gowen J. W. Hereditary Obesity and Efficient Food Utilization in Mice. Science. 1947 May 9;105(2732):496–498. doi: 10.1126/science.105.2732.496-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drwinga H. L., Toji L. H., Kim C. H., Greene A. E., Mulivor R. A. NIGMS human/rodent somatic cell hybrid mapping panels 1 and 2. Genomics. 1993 May;16(2):311–314. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajans S. S., Bell G. I., Bowden D. W. MODY: a model for the study of the molecular genetics of NIDDM. J Lab Clin Med. 1992 Mar;119(3):206–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELLERSTROM C., HELLMAN B. The Islets of Langerhans in yellow obese mice. Metabolism. 1963 Jun;12:527–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESTON W. E., VLAHAKIS G. Influence of the Ay gene on mammary-gland tumors, hepatomas, and normal growth in mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1961 Apr;26:969–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Cremer T., Borden J., Manuelidis L., Ward D. C. Delineation of individual human chromosomes in metaphase and interphase cells by in situ suppression hybridization using recombinant DNA libraries. Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;80(3):224–234. doi: 10.1007/BF01790090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Tang C. J., Call K., Hermanson G., Evans G. A., Housman D., Ward D. C. High-resolution mapping of human chromosome 11 by in situ hybridization with cosmid clones. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):64–69. doi: 10.1126/science.2294592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaud E. J., Bultman S. J., Klebig M. L., van Vugt M. J., Stubbs L. J., Russell L. B., Woychik R. P. A molecular model for the genetic and phenotypic characteristics of the mouse lethal yellow (Ay) mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2562–2566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaud E. J., Bultman S. J., Stubbs L. J., Woychik R. P. The embryonic lethality of homozygous lethal yellow mice (Ay/Ay) is associated with the disruption of a novel RNA-binding protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1203–1213. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. W., Duhl D. M., Vrieling H., Cordes S. P., Ollmann M. M., Winkes B. M., Barsh G. S. Cloning of the mouse agouti gene predicts a secreted protein ubiquitously expressed in mice carrying the lethal yellow mutation. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):454–467. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao V. V., Löffler C., Wozney J. M., Hansmann I. The gene for bone morphogenetic protein 2A (BMP2A) is localized to human chromosome 20p12 by radioactive and nonradioactive in situ hybridization. Hum Genet. 1992 Nov;90(3):299–302. doi: 10.1007/BF00220084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes. 1988 Dec;37(12):1595–1607. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.12.1595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild C. B., Akots G., Hayworth R., Pettenati M. J., Rao P. N., Wood P., Stolz F. M., Hansmann I., Serino K., Keith T. P. A genetic map of chromosome 20q12-q13.1: multiple highly polymorphic microsatellite and RFLP markers linked to the maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jan;52(1):110–123. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybak J., Tharapel A., Robinett S., Garcia M., Mankinen C., Freeman M. A simple reproducible method for prometaphase chromosome analysis. Hum Genet. 1982;60(4):328–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00569213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siracusa L. D., Abbott C. M. Encyclopedia of the mouse genome III. October 1993. Mouse chromosome 2. Mamm Genome. 1993;4(Spec No):S31–S46. doi: 10.1007/BF00360828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strålfors P., Björgell P., Belfrage P. Hormonal regulation of hormone-sensitive lipase in intact adipocytes: identification of phosphorylated sites and effects on the phosphorylation by lipolytic hormones and insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3317–3321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi T., Kobunai T., Yamamoto H. Genetic control of signal transduction in mouse melanocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 May;92(5 Suppl):239S–242S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep13075730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff G. L., Roberts D. W., Galbraith D. B. Prenatal determination of obesity, tumor susceptibility, and coat color pattern in viable yellow (Avy/a) mice. The yellow mouse syndrome. J Hered. 1986 May-Jun;77(3):151–158. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a110206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]