Abstract
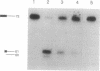
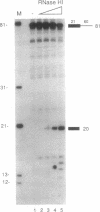
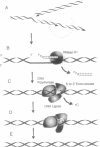
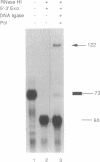
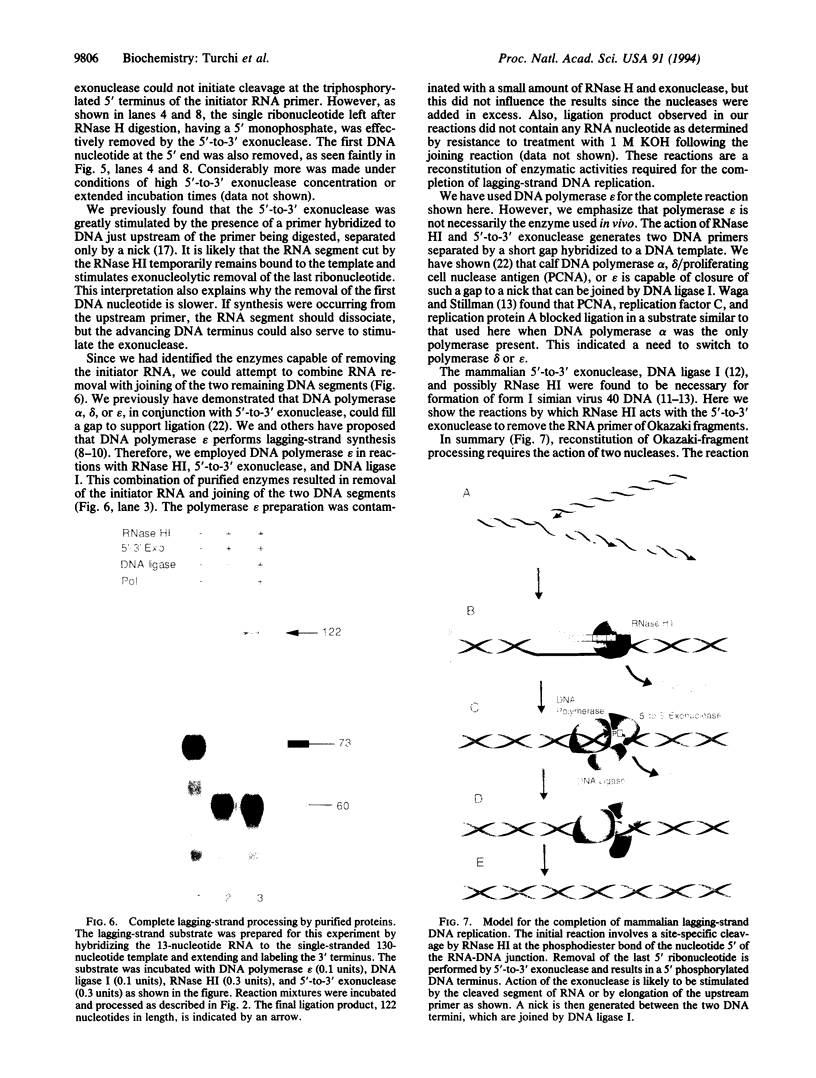
Using purified proteins from calf and a synthetic substrate, we have reconstituted the enzymatic reactions required for mammalian Okazaki fragment processing in vitro. The required reactions are removal of initiator RNA, synthesis from an upstream fragment to generate a nick, and then ligation. With our substrate, RNase H type I (RNase HI) makes a single cut in the initiator RNA, one nucleotide 5' of the RNA-DNA junction. The double strand specific 5' to 3' exonuclease removes the remaining monoribonucleotide. After dissociation of cleaved RNA, synthesis by DNA polymerase generates a nick, which is then sealed by DNA ligase I. The unique specificities of the two nucleases for primers with initiator RNA strongly suggest that they perform the same reactions in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araki H., Ropp P. A., Johnson A. L., Johnston L. H., Morrison A., Sugino A. DNA polymerase II, the probable homolog of mammalian DNA polymerase epsilon, replicates chromosomal DNA in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):733–740. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05106.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bambara R. A., Jessee C. B. Properties of DNA polymerases delta and epsilon, and their roles in eukaryotic DNA replication. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 17;1088(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90147-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulet A., Simon M., Faye G., Bauer G. A., Burgers P. M. Structure and function of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CDC2 gene encoding the large subunit of DNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1849–1854. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgers P. M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae replication factor C. II. Formation and activity of complexes with the proliferating cell nuclear antigen and with DNA polymerases delta and epsilon. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22698–22706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büsen Purification, subunit structure, and serologicai analysis of calf thymus ribonuclease H I. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9434–9443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büsen W., Peters J. H., Hausen P. Ribonuclease H levels during the response of bovine lymphocytes to concanavalin A. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Mar 15;74(1):203–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco R. A., Lehman I. R. Interaction of ribonuclease H from Drosophila melanogaster embryos with DNA polymerase-primase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14764–14770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eder P. S., Walder J. A. Ribonuclease H from K562 human erythroleukemia cells. Purification, characterization, and substrate specificity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6472–6479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eki T., Matsumoto T., Murakami Y., Hurwitz J. The replication of DNA containing the simian virus 40 origin by the monopolymerase and dipolymerase systems. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7284–7294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulian M., Heard C. J. Discrimination between mammalian RNases H-1 and H-2. Anal Biochem. 1991 Feb 1;192(2):398–402. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90555-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulian M., Richards S. H., Heard C. J., Bigsby B. M. Discontinuous DNA synthesis by purified mammalian proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18461–18471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosse F., Krauss G. The primase activity of DNA polymerase alpha from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1881–1888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimi Y., Claude A., Bullock P., Hurwitz J. Complete enzymatic synthesis of DNA containing the SV40 origin of replication. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19723–19733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. M., Snyder M., Chang L. M., Davis R. W., Campbell J. L. Isolation of the gene encoding yeast DNA polymerase I. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogoma T. RNase H-defective mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):361–363. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.361-363.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyamichev V., Brow M. A., Dahlberg J. E. Structure-specific endonucleolytic cleavage of nucleic acids by eubacterial DNA polymerases. Science. 1993 May 7;260(5109):778–783. doi: 10.1126/science.7683443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A., Araki H., Clark A. B., Hamatake R. K., Sugino A. A third essential DNA polymerase in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1143–1151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90391-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murante R. S., Huang L., Turchi J. J., Bambara R. A. The calf 5'- to 3'-exonuclease is also an endonuclease with both activities dependent on primers annealed upstream of the point of cleavage. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1191–1196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nethanel T., Kaufmann G. Two DNA polymerases may be required for synthesis of the lagging DNA strand of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5912–5918. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5912-5918.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegal G., Turchi J. J., Myers T. W., Bambara R. A. A 5' to 3' exonuclease functionally interacts with calf DNA polymerase epsilon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9377–9381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. Initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication in vitro. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:197–245. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turchi J. J., Bambara R. A. Completion of mammalian lagging strand DNA replication using purified proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):15136–15141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waga S., Bauer G., Stillman B. Reconstitution of complete SV40 DNA replication with purified replication factors. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10923–10934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waga S., Stillman B. Anatomy of a DNA replication fork revealed by reconstitution of SV40 DNA replication in vitro. Nature. 1994 May 19;369(6477):207–212. doi: 10.1038/369207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]