Abstract
Background
Listeria (L.) monocytogenes causes fatal infections in many species including ruminants and humans. In ruminants, rhombencephalitis is the most prevalent form of listeriosis. Using multilocus variable number tandem repeat analysis (MLVA) we recently showed that L. monocytogenes isolates from ruminant rhombencephalitis cases are distributed over three genetic complexes (designated A, B and C). However, the majority of rhombencephalitis strains and virtually all those isolated from cattle cluster in MLVA complex A, indicating that strains of this complex may have increased neurotropism and neurovirulence. The aim of this study was to investigate whether ruminant rhombencephalitis strains have an increased ability to propagate in the bovine hippocampal brain-slice model and can be discriminated from strains of other sources. For this study, forty-seven strains were selected and assayed on brain-slice cultures, a bovine macrophage cell line (BoMac) and a human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line (Caco-2). They were isolated from ruminant rhombencephalitis cases (n = 21) and other sources including the environment, food, human neurolisteriosis cases and ruminant/human non-encephalitic infection cases (n = 26).
Results
All but one L. monocytogenes strain replicated in brain slices, irrespectively of the source of the isolate or MLVA complex. The replication of strains from MLVA complex A was increased in hippocampal brain-slice cultures compared to complex C. Immunofluorescence revealed that microglia are the main target cells for L. monocytogenes and that strains from MLVA complex A caused larger infection foci than strains from MLVA complex C. Additionally, they caused larger plaques in BoMac cells, but not CaCo-2 cells.
Conclusions
Our brain slice model data shows that all L. monocytogenes strains should be considered potentially neurovirulent. Secondly, encephalitis strains cannot be conclusively discriminated from non-encephalitis strains with the bovine organotypic brain slice model. The data indicates that MLVA complex A strains are particularly adept at establishing encephalitis possibly by virtue of their higher resistance to antibacterial defense mechanisms in microglia cells, the main target of L. monocytogenes.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12866-015-0454-0) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Listeria monocytogenes, Rhombencephalitis, Neurovirulence, Organotypic brain slice, Plaque test, In vitro model, Ruminant, Microglia, MLVA complex
Background
The Gram + bacterium Listeria (L.) monocytogenes is an opportunistic food-borne pathogen with considerable impact on human and livestock health and food safety. It causes listeriosis [1,2], which may manifest in distinct clinical forms including febrile gastroenteritis, abortions, septicemia, and neurolisteriosis [2,3] and is associated with high mortality [4,5]. In humans, L. monocytogenes is commonly isolated in the context of meningitis [6], and neurolisteriosis is responsible for high fatality rates and chronic sequelae [7–10]. In farmed ruminants, neurolisteriosis is amongst the most common causes of central nervous system (CNS) disorders and characteristically presents as encephalitis, which targets the brainstem (rhombencephalitis) and is often deadly [11–14]. Clinical observations in livestock may indicate differences in organ tropism between L. monocytogenes strains. Different clinical forms of listeriosis rarely overlap in the same ruminant herd or in the same animal during an outbreak [15,16]. Rhombencephalitis generally occurs without involvement of other organs and without inducing abortion in pregnant ruminants [17–19].
The ubiquitous nature of L. monocytogenes as a saprophytic soil inhabitant constitutes a challenge for surveillance and effective disease control [20]. L. monocytogenes is divided into four phylogenetic lineages [21] as determined by various genotypic and phenotypic subtyping tools [22–27] and may differ in virulence and the potential to cause epidemic outbreaks [28–33]. For instance, of the two major phylogenetic lineages I and II, which are associated with human and animal infections, lineage I is overrepresented in clinical isolates [21,22,28,31]. In contrast, lineage II strains are more commonly isolated from food and the environment. The two minor lineages III and IV are rarely isolated and are associated with ruminant infections [21]. From the 13 known serotypes, serotype 4b (belonging to lineage I) is associated with most of the severe clinical cases and the majority of outbreaks [34,35]. Nonetheless, available subtyping methods cannot predict the virulence of a given isolate, and the propensity of certain subtypes to cause sporadic illness, epidemic outbreaks or specific clinical syndromes (e.g. neurolisteriosis) remains poorly understood [36,37].
There have been few systematic investigations of the genetic diversity of L. monocytogenes strains isolated from ruminants [31,38–40]. Using multilocus variable number tandem repeat analysis (MLVA) of 183 isolates, we could show that ruminant rhombencephalitis strains are found predominantly in MLVA complex A and also B, belonging to lineage I, and to a lesser extent to complex C of lineage II [31]. Nearly all rhombencephalitis strains from cattle cluster in MLVA complex A indicating that strains of this genetic complex may have increased neurotropism and neurovirulence [31]. This observation is in line with studies showing that lineage I strains are overrepresented in rhombencephalitis, whereas lineage II strains are equally associated with rhombencephalitis, septicemia and fetal infections [38,39].
The lack of a relevant model hinders experimental determination of neurovirulent potential and neurovirulence mechanisms of L. monocytogenes strains and means that neurovirulence can at present only be defined using data from neurolisteriosis cases [41]. In a previous study, we developed a bovine organotypic hippocampal brain-slice model, which is susceptible to L. monocytogenes [42]. The aim of the present study was to investigate if ruminant rhombencephalitis strains can be discriminated from non-encephalitic strains using the in vitro CNS model. To this end, bovine hippocampal slices were infected with a panel of 47 selected L. monocytogenes strains from various clinical, environmental and food sources. Replication and spread of strains within brain-slice cultures were analyzed by determination of CFU’s and size of infection foci. These results were correlated with the source of the isolate and MLVA–complex of the respective strains and compared to plaque test results in two cell lines.
Results
Infection of organotypic brain-slice cultures with L. monocytogenes strains
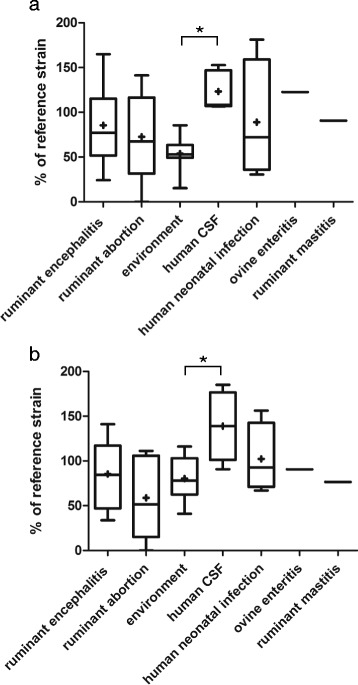
We analyzed replication and capacity to spread in organotypic hippocampal brain-slice cultures of 21 L. monocytogenes strains isolated from ruminant rhombencephalitis cases and 26 strains of ruminant non-encephalitic cases (abortion, mastitis, gastroenteritis), human clinical infections or food/environment (Additional file 1). All but one (bovine abortion, O/D1387/06) replicated in the brain slices (Fig. 1a) and established at least one visible focus of infection at 48 h post inoculation (Fig. 2a). Typically, values between 105 and 107 CFU were recovered from the brain-slices at 48 h post infection, which corresponds to a 103–105 times increase over the incubation period. Recovered CFU numbers were significantly higher in brain-slices infected with L. monocytogenes strains from MLVA complex A than with strains from MLVA complex C (Fig. 1b, p < 0.001). The difference between MLVA complexes was also apparent with encephalitis strains, although as a statistically non-significant tendency (p = 0.055, Fig. 1c). Additionally, strains from complex A spread over a significantly larger area than strains from complex C (Fig. 3a and b, p = 0.03). No differences in CFU counts were detected when comparing strains by host species or source except between human strains isolated from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and environmental strains (Fig. 1d and Fig. 4a). Human CSF strains spread farther than strains isolated from small ruminants (Fig. 3c) and from the environment (Fig. 4b).
Fig. 1.
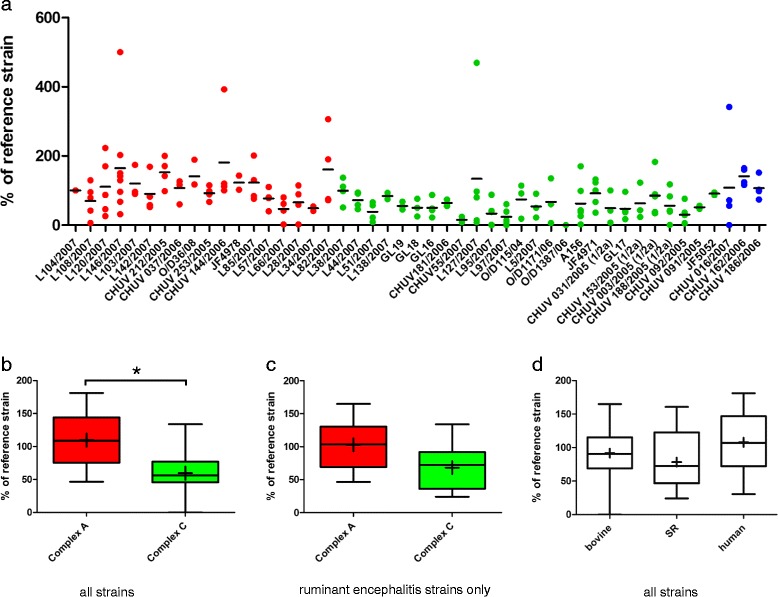
Replication of L. monocytogenes strains in brain-slices. Results are shown relative to the internal control strain L104. a Aligned dot plot of the relative CFU counts of the individual strains. Red: MLVA complex A; green: MLVA complex C; blue: MLVA complex B. The horizontal line indicates the mean. b Box plot comparing relative CFU counts between complex A and C strains. CFU counts are significantly higher in brain-slices infected with complex A strains, * = p < 0.05. c Box plot comparing relative CFU counts between complex A and C strains isolated from ruminant rhombencephalitis. d Box plot comparing relative CFU counts according to host species. Whiskers represent maxima and minima. The horizontal line represents the median, + is the mean
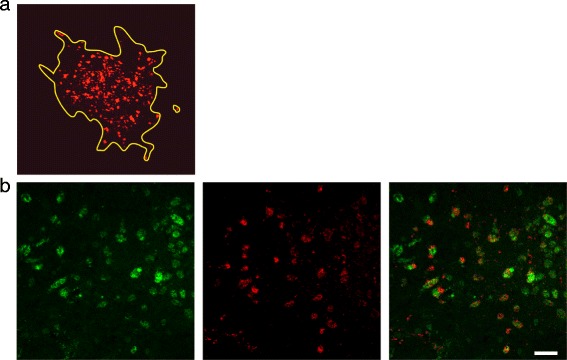
Fig. 2.
Immunofluorescence stained confocal images of bacteria in infected brain-slices. a Delineation of an infection focus (yellow line). L. monocytogenes are stained in red. The surface area covered by L. monocytogenes was drawn and calculated using the Fluoview software (Olympus FV10-ASW Version 03.01.01.09). Magnification 20×. b Representative double-immunofluorescence of a L. monocytogenes infected brain-slice. The vast majority of bacteria are found within microglia. Left: Microglia are stained with CD68 in green. Center: L. monocytogenes in red. Right: Overlay (bar = 40 μm)
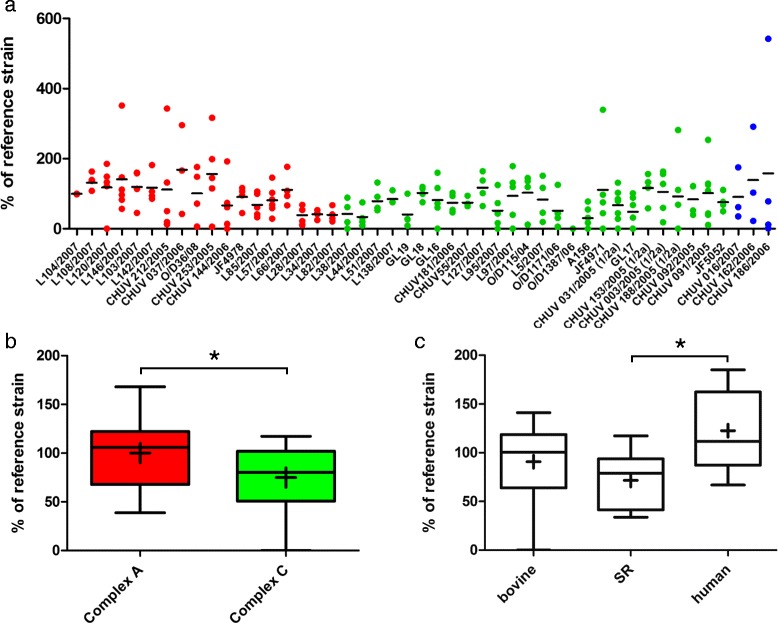
Fig. 3.
Spread of L. monocytogenes strains in brain-slices as determined by size of infection foci. Results are shown relative to the internal control strain L104. a Aligned dot plot analysis of bacterial spread of the individual strains used in this study. Red: MLVA complex A; green: MLVA complex C; blue: MLVA complex B. The horizontal line indicates the mean. b Box plots comparing the total size of foci between complex A and complex C strains. Complex A strains cover a significantly larger area than complex C strains. c Box plot comparing total size of foci according to host species. Human strains caused larger infection foci in brain-slices than strains isolated from small ruminants. Box plots: Whiskers represent maxima and minima. The horizontal line represents the median, + is the mean, * = p < 0.05
Fig. 4.
CFU counts (a) and size of infection foci (b) in organotypic brain-slices infected with L. monocytogenes strains. Results are mapped according to the source and associated clinical infection, respectively. Data are presented as box plots, Whiskers represent maxima and minima. The vertical line represents the median, + is the mean. * = p < 0.05. CFU counts (a) and surface of bacterial spread (b) are shown relative to the internal control strain L104
In agreement with our previous study [42], immunofluorescence with L. monocytogenes antibodies and cell markers revealed that the vast majority of bacteria were located in the cytoplasm of microglia, irrespective of the strain (Fig. 2b). Only a few bacteria were associated with neurofilaments or astrocytes (data not shown).
Plaque forming assays in cell lines
To assess whether the results obtained in the brain-slice infection assay are tissue specific, we performed plaque forming assays [43,44] in two cell lines: BoMac (bovine macrophages) and CaCo-2 (human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line). In parallel to the results in brain-slices, all strains except O/D1387/06 caused plaques in the BoMac cell line (Fig. 5a), and strains from MLVA complex A caused significantly larger plaques than strains from complex C (Fig. 5b). In contrast, plaque assays in CaCo-2 cells demonstrated no correlation between plaque size and MLVA-complex (Fig. 5e). Intriguingly, strain O/D1387/06 caused plaques half the size of the reference strain in this cell line, although it made no plaques in BoMac cells (Fig. 5d). Also, the mean absolute plaque size of L. monocytogenes strains was significantly larger in CaCo-2 cells than in BoMac cells (1.3 vs 0.9 mm, p < 0.001). In the Caco-2 cell line (Fig. 5f), but not in the BoMac cell line (Fig. 5c), human clinical strains produced larger plaques than strains isolated from small ruminants.
Fig. 5.
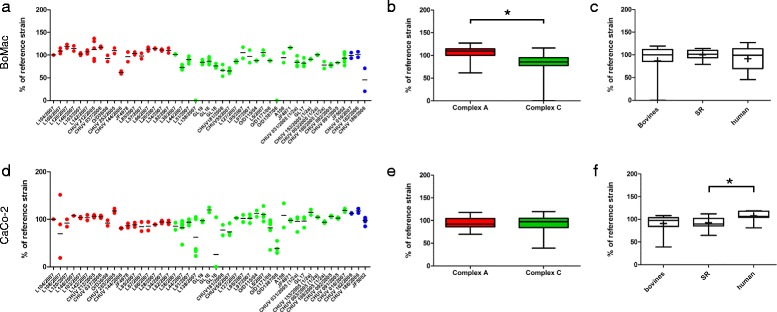
Plaque sizes of L. monocytogenes strains in the BoMac and CaCo-2 cell lines. Results are shown relative to the internal control strain L104. a The relative plaque size in BoMac-cells is shown for each strain as an aligned dot plot. Red: MLVA complex A strains; green: MLVA complex C strains; blue: MLVA complex B strains. The horizontal line indicates the mean. b Box plots comparing plaque size in BoMac cells between complex A and complex C strains. Plaques of complex A strains are significantly larger than those of complex C strains. The horizontal line represents the median, + is the mean. c The host species had no influence on plaque-size in BoMac cells. d CaCo-2 cells: the relative plaque size for each strain is shown as an aligned dot plot. Red: Complex A; green: Complex C; blue: Complex B. The horizontal line indicates the mean. e Box plots comparing plaque size in CaCo-2 cells between complex A and complex C strains. There is no difference in plaque size between complex A and C strains. e Human strains formed larger plaques in CaCo-2 cells than strains isolated from small ruminants. * = p < 0.05. Box plots: Whiskers represent maxima and minima. The horizontal line represents the median, + is the mean
Discussion
Given the ubiquitous presence of L. monocytogenes in the environment, discrimination of neurovirulent subtypes would be highly desirable for surveillance purposes and effective disease control, especially with regard to the high mortality rate [35,45] and the high frequency of persistent neurologic deficits associated with neurolisteriosis [10,41]. In our study, infection assays with L. monocytogenes strains from various sources and MLVA complexes showed that all L. monocytogenes strains except one are able to replicate and spread in bovine brain-slices and that discrimination between rhombencephalitis and non-encephalitic strains is not possible in this system. Hence, based on our results we suggest that all L. monocytogenes strains should be regarded as potentially neurovirulent, independent of their genotype and source of isolation. Brain-slices have the inherent drawback that they only model the intracerebral phase of L. monocytogenes infection and can not mimic invasion barriers (i.e. the blood–brain barrier in hematogenous infection or the cranial nerve in rhombencephalitis). Hence, we cannot exclude that encephalitogenic strains diverge from other L. monocytogenes strains due to their efficiency of brain invasion.
MLVA complex A strains (lineage I) showed a higher replication and spread farther in brain-slices than strains from complex C, indicating that they are better adapted to establish encephalitis. This observation is in accordance with the higher prevalence of lineage I strains in clinical infections and in particular ruminant rhombencephalitis compared to lineage II strains [21,22,31]. Analysis of strains according to their source did not identify significant differences in replication and spread in brain-slices except between human and environmental or small ruminant isolates. However, these observations are likely to be related to the MLVA complex of the strains. All human CSF strains belonged to MLVA complexes A and B (lineage I), whereas all environmental and the majority of small ruminant strains belonged to complex C (lineage II). Microglia, the innate immune cells and resident macrophages of the CNS [46], were the main target cells for all L. monocytogenes strains investigated in hippocampal brain slices. The replication of L. monocytogenes within microglia indicates that these may paradoxically act as a replication niche for L. monocytogenes during encephalitis. In this aspect, our model is consistent with the natural disease, where most bacteria are found within phagocytes of microabscesses [11].
MLVA complex A strains form larger plaques in the bovine macrophage cell line (BoMac) than complex C strains. Interestingly, this difference was not apparent in CaCo-2 cells, where plaques were generally larger than in BoMac cells, indicating a particularly high susceptibility of epithelial cells to L. monocytogenes, which does not allow further differentiation. This notion is further supported by the fact that strain O/D1387/06, a complex C strain that seems to be naturally attenuated, completely failed to replicate and spread in brain-slices and to cause plaques in BoMac cells, but caused small plaques in CaCo-2 cells. Further analysis of this strain revealed a novel PrfA truncation, associated with the attenuated phenotype in vitro [47].
Our data suggests that differences in replication and spread between L. monocytogenes strains are host cell type-specific. Contradictory experimental data on L. monocytogenes virulence from studies using various types of cell lines may support this view [44,48–54]. Unlike CaCo-2 cells, BoMac (derived from bovine macrophages) and microglia share essential features including phagocytic potential and a respiratory burst system [46]. Taken together, the more efficient replication and spread of MLVA complex A vs. complex C strains in microglia and macrophages suggests that complex A strains are more resistant to mononuclear antibacterial defense mechanisms. In this context, it should be noted that listeriolysin S, a virulence factor induced by oxidative stress, has been implicated in L. monocytogenes survival within phagocytes and is specifically expressed by strains of lineage I [55].
Conclusion
Our data demonstrates that all L. monocytogenes strains should be considered potentially neurovirulent and encephalitis strains cannot be conclusively discriminated from non-encephalitis strains using the bovine organotypic brain-slice model. In this CNS model, microglia cells are the main target cells for all tested L. monocytogenes strains, which are able to multiply in these phagocytic cells. Correlation of MLVA data with our in vitro data show that strains from MLVA complex A replicate and spread better in bovine microglia and macrophages possibly by virtue of their higher resistance to mononuclear antibacterial defense mechanisms. These results support the notion that L. monocytogenes strains from MLVA complex A are highly accomplished at establishing encephalitis.
Methods
Bacterial strains
Forty-seven L. monocytogenes strains were investigated in brain-slice cultures and cell lines (Additional file 1). The MLVA-type of 44 strains had been obtained in a previous study [31] and the MLVA-type of three other ruminant isolates (JF4971, JF5052 and JF4978; Additional file 1) were determined during this study by analysis of tandem repeat numbers at eight loci according to Sperry et al. [23]. A minimal spanning tree was created in the BioNumerics software (Version 6.6, Applied Maths Inc., Austin, Texas, USA) in order to define the MLVA complex of the strains [31]. Twenty-one strains isolated from ruminant rhombencephalitis cases were selected based on the following criteria: 1) differences at the 8 MLVA loci and 2) similar numerical representation of the two large MLVA complexes, to which most of the ruminant rhombencephalitis strains belong (MLVA complex A: n = 12; MLVA complex C: n = 9). The ruminant rhombencephalitis strains were compared to a similar number of L. monocytogenes strains from other sources (n = 26) available in our strain collection (Additional file 1). The latter included strains from ruminant non-encephalitic cases including gastroenteritis, mastitis and abortion (n = 7), human clinical cases (n = 9), food and environmental (n = 10) and mainly belonged to MLVA complex C (n = 18). Four strains belonged to MLVA complex A, one strain was a single locus variant associated with MLVA complex A and three strains belonged to MLVA complex B. Non-invasive Listeria innocua type strain CCUG15531T (Culture Collection University of Göteborg) was used as negative control.
Organotypic brain-slice cultures
Hippocampal brain samples from calves under 6 months of age were obtained from the slaughterhouse. A vibratome (Leica VT1000S) was used to cut 350 μm brain-slices and were cultured on membrane inserts (Vitaris, No. 3450 or 3460) as previously described [42].
Infection assays in ruminant organotypic brain-slice cultures
Brain-slices were infected at day 7 in culture. Penicillin and streptomycin were removed from the organotypic brain-slice cultures 1 h prior to inoculation in the first set of experiments and 4 days prior to inoculation in the later experiments due to batch variation of the antibiotics. Medium was changed to a serum-free formula 1 h prior to inoculation. Bacteria were plated on trypticase soy agar (TSA), incubated at 37 °C for 15 h and subsequently diluted using the McFarland optical density standard. One hundred CFU in 0.1 μl NaCl (determined by plating on TSA plates) were focally injected into the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus using a 0.5 μl syringe (Hamilton, 7402 Bonaduz, Switzerland. Model 7000.5 KHOC) and a micromanipulator (made in-house). Brain-slices were incubated with the bacteria for 3 h and subsequently the inoculation medium was substituted with gentamicin-containing medium (final concentration 0.01 mg/ml). All experiments were carried out at least in triplicate and included L. innocua (negative control) and an internal control strain (L104, from bovine rhombencephalitis, MLVA complex A) for normalization. For analysis of bacterial replication CFU’s were determined 48 h post infection by lysing infected brain-slices in 1 ml PBS containing 55 μl Isolator (Wampole, Oxoid) and plating serial dilutions on TSA plates. For analysis of bacterial spread, brain-slices were fixed in 4 % (w/v) paraformaldehyde at 48 h post infection. Following overnight fixation, brain-slices were incubated in 18 % (w/v) sucrose (Sigma, S0389) for 12 h, cut with a cryotome into 4.5 μm-thick sections and stored at −20 °C until further use. Immunofluorescence was performed using the following primary antibodies: anti-Listeria O serotypes 1 and 4 (polyclonal rabbit antibody, No. 223021, Difco, Sparks, MD, USA), neurofilament (monoclonal mouse antibody, No M0762, DAKO, Glostrup, Denmark), GFAP (monoclonal mouse antibody, No. Ab4648, Abcam, Cambridge UK) and CD68 (monoclonal mouse antibody, clone EBM11, DAKO, Glostrup, Denmark). Alexa Fluor 488 and 544 were used as secondary antibodies (No. A21428, Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA,) [42]. Nuclei were stained with TOTO-3 (no T3604, Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA USA), and 10x images were acquired on an Olympus FV1000 confocal microscope. The total area covered by L. monocytogenes was measured on the immunofluorescence labeled cryosections of brain-slices using the Olympus FV10-ASW Version 03.01.01.09 software and expressed in μm2.
Plaque assay in bovine macrophages and CaCo-2 cells
Plaque forming assays were performed according to a previous study [31] in an immortalized bovine macrophage cell line (BoMac, kindly provided by D. Dobbelaere, Department of Clinical Research and Veterinary Public Health, Vetsuisse Faculty Bern) and the human enterocyte-like CaCo-2 cell line (ATCC No. HTB37). Both cell lines were grown in DMEM (Gibco 61965–026) supplemented with penicillin/streptomycin (Gibco, 15140–122, used 1:100) and 10 % fetal calf serum (FCS) (BoMac cells) or 20 % FCS (CaCo-2 cells), respectively. Cells were grown to confluence in a 24-well plate overnight at 37 °C, washed with warm PBS and inoculated with 103 CFU L. monocytogenes (MOI 0.01) in antibiotic free medium supplemented with 2 % FCS. Following 1 h incubation the medium was removed, cells were washed with PBS and overlaid with medium containing 0.7 % agarose and 0.01 mg/ml gentamicin. The size of five randomly chosen plaques per well were measured 72 h post infection. Experiments were carried out in duplicate and the internal control strain L104 was included in all experiments.
Statistical analysis
All results were normalized to the internal control strain L104. Statistical analysis was performed with the Prism Software (Version 5.03, Graph Pad Software Inc.). The Mann–Whitney test was used to determine the p-values where two groups were compared. For comparison of multiple groups, the Kruskal-Wallis test was used with Dunn’s multiple comparisons as post-test. As only three strains belonged to complex B, they were excluded from the statistical analysis comparing complexes.
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by the 3R Research Foundation Switzerland for the promotion of alternative research methods in animal experimentation. Amandine Ruffieux contributed much appreciated help in the laboratory. Stefan Holzer from Metzgerei Holzer in Hindelbank provided us with the brain material. We are very grateful for his willingness to accommodate us and to adjust his schedule to meet our needs.
Additional file
L. monocytogenes strains used in this study. MLVA and serotype data have been either obtained from [31] or were generated in this study (*). SLV Single locus variant, N/a Not applicable, Nd Not determined, CSF Cerebrospinal fluid.
Footnotes
Competing interests
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
AO, TS and AZ conceived and designed the study. CG established the organotypic brain-slices and carried out the majority of the lab work. MB helped preparing the organotypic brain-slices. JF participated in the design of the study and provided valuable input at all stages of the project. CG, AO and TS drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Contributor Information
Claudia Guldimann, Email: cg445@cornell.edu.
Michelle Bärtschi, Email: michelle.baertschi@vetsuisse.unibe.ch.
Joachim Frey, Email: joachim.frey@vetsuisse.unibe.ch.
Andreas Zurbriggen, Email: andreas.zurbriggen@vetsuisse.unibe.ch.
Torsten Seuberlich, Email: torsten.seuberlich@vetsuisse.unibe.ch.
Anna Oevermann, Email: anna.oevermann@vetsuisse.unibe.ch.
References
- 1.Murray EG. A characterization of listeriosis in man and other animals. Can Med Assoc J. 1955;72:99–103. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Low JC, Donachie W. A review of Listeria monocytogenes and listeriosis. Vet J. 1997;153:9–29. doi: 10.1016/S1090-0233(97)80005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Siegman-Igra Y, Levin R, Weinberger M, Golan Y, Schwartz D, Samra Z, Konigsberger H, Yinnon A, Rahav G, Keller N, et al. Listeria monocytogenes infection in Israel and review of cases worldwide. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002;8:305–310. doi: 10.3201/eid0803.010195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Vital signs: Listeria illnesses, deaths, and outbreaks–United States, 2009–2011. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2013;62:448–452. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2011. Euro Surveill. 2013;18:20449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sigurdardottir B, Bjornsson OM, Jonsdottir KE, Erlendsdottir H, Gudmundsson S. Acute bacterial meningitis in adults. A 20-year overview. Arch Intern Med. 1997;157:425–430. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1997.00440250077009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mailles A, Lecuit M, Goulet V, Leclercq A, Stahl JP, National Study on Listeriosis Encephalitis Steering Committee Listeria monocytogenes encephalitis in France. Med Mal Infect. 2011;41:594–601. doi: 10.1016/j.medmal.2011.07.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Arslan F, Meynet E, Sunbul M, Sipahi OR, Kurtaran B, Kaya S, et al. The clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of neuroinvasive listeriosis: a multinational study. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015. doi: 10.1007/s10096-015-2346-5. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 9.Drevets DA, Bronze MS. Listeria monocytogenes: epidemiology, human disease, and mechanisms of brain invasion. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2008;53:151–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2008.00404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Büla CJ, Bille J, Glauser MP. An epidemic of food-borne listeriosis in western Switzerland: description of 57 cases involving adults. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;20:66–72. doi: 10.1093/clinids/20.1.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Oevermann A, Di Palma S, Doherr MG, Abril C, Zurbriggen A, Vandevelde M. Neuropathogenesis of naturally occurring encephalitis caused by Listeria monocytogenes in ruminants. Brain Pathol. 2010;20:378–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2009.00292.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Heim D, Fatzer R, Hornlimann B, Vandevelde M. Frequency of neurologic diseases in cattle. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 1997;139:354–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Miyashita M, Stierstorfer B, Schmahl W. Neuropathological findings in brains of Bavarian cattle clinically suspected of bovine spongiform encephalopathy. J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2004;51:209–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.2004.00755.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Oevermann A, Botteron C, Seuberlich T, Nicolier A, Friess M, Doherr MG, Heim D, Hilbe M, Zimmer K, Zurbriggen A, et al. Neuropathological survey of fallen stock: active surveillance reveals high prevalence of encephalitic listeriosis in small ruminants. Vet Microbiol. 2008;130:320–329. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2008.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ladds PW, Dennis SM, Cooper RF. Sequential studies of experimentally induced ovine listerial abortion: clinical changes and bacteriologic examinations. Am J Vet Res. 1974;35:155–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wilesmith JW, Gitter M. Epidemiology of ovine listeriosis in Great Britain. Vet Rec. 1986;119:467–470. doi: 10.1136/vr.119.19.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wagner M, Melzner D, Bago Z, Winter P, Egerbacher M, Schilcher F, Zangana A, Schoder D. Outbreak of clinical listeriosis in sheep: evaluation from possible contamination routes from feed to raw produce and humans. J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2005;52:278–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.2005.00866.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Killinger AH, Mansfield ME. Epizootiology of listeric infection in sheep. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1970;157:1318–1324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Dreyer M, Thomann A, Böttcher S, Frey J, Oevermann A. Outbreak investigation identifies a single Listeria monocytogenes strain in sheep with different clinical manifestations, soil and water. Vet Microbiol. 2015. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 20.Cartwright EJ, Jackson KA, Johnson SD, Graves LM, Silk BJ, Mahon BE. Listeriosis outbreaks and associated food vehicles, United States, 1998–2008. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19:1–9. doi: 10.3201/eid1901.120393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Orsi RH, den Bakker HC, Wiedmann M. Listeria monocytogenes lineages: genomics, evolution, ecology, and phenotypic characteristics. Int J Med Microbiol. 2011;301:79–96. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2010.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ragon M, Wirth T, Hollandt F, Lavenir R, Lecuit M, Le Monnier A, Brisse S. A new perspective on Listeria monocytogenes evolution. PLoS Pathog. 2008;4:e1000146. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sperry KE, Kathariou S, Edwards JS, Wolf LA. Multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis as a tool for subtyping Listeria monocytogenes strains. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46:1435–1450. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02207-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Liu D. Identification, subtyping and virulence determination of Listeria monocytogenes, an important foodborne pathogen. J Med Microbiol. 2006;55:645–659. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.46495-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Brosch R, Chen J, Luchansky JB. Pulsed-field fingerprinting of listeriae: identification of genomic divisions for Listeria monocytogenes and their correlation with serovar. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994;60:2584–2592. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.7.2584-2592.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Matloob M, Griffiths M. Ribotyping and automated ribotyping of Listeria monocytogenes. Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1157:85–93. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0703-8_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Seeliger HP, Höhne K. Serotyping of Listeria monocytogenes and related species. Methods Microbiol. 1979;13:31–49. doi: 10.1016/S0580-9517(08)70372-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chenal-Francisque V, Lopez J, Cantinelli T, Caro V, Tran C, Leclercq A, Lecuit M, Brisse S. Worldwide distribution of major clones of Listeria monocytogenes. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:1110–1112. doi: 10.3201/eid/1706.101778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.McLauchlin J. Distribution of serovars of Listeria monocytogenes isolated from different categories of patients with listeriosis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990;9:210–213. doi: 10.1007/BF01963840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Schuchat A, Swaminathan B, Broome CV. Epidemiology of human listeriosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991;4:169–183. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.2.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Balandyte L, Brodard I, Frey J, Oevermann A, Abril C. Ruminant rhombencephalitis-associated Listeria monocytogenes alleles linked to a multilocus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis complex. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77:8325–8335. doi: 10.1128/AEM.06507-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Piffaretti JC, Kressebuch H, Aeschbacher M, Bille J, Bannerman E, Musser JM, Selander RK, Rocourt J. Genetic characterization of clones of the bacterium Listeria monocytogenes causing epidemic disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989;86:3818–3822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wiedmann M, Bruce JL, Keating C, Johnson AE, McDonough PL, Batt CA. Ribotypes and virulence gene polymorphisms suggest three distinct Listeria monocytogenes lineages with differences in pathogenic potential. Infect Immun. 1997;65:2707–2716. doi: 10.1128/iai.65.7.2707-2716.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Awofisayo A, Amar C, Ruggles R, Elson R, Adak GK, Mook P, Grant KA. Pregnancy-associated listeriosis in England and Wales. Epidemiol Infect. 2015;143:249–256. doi: 10.1017/S0950268814000594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Swaminathan B, Gerner-Smidt P. The epidemiology of human listeriosis. Microbes Infect. 2007;9:1236–1243. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2007.05.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Datta AR, Laksanalamai P, Solomotis M. Recent developments in molecular sub-typing of Listeria monocytogenes. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2013;30:1437–1445. doi: 10.1080/19440049.2012.728722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.McLauchlin J, Mitchell RT, Smerdon WJ, Jewell K. Listeria monocytogenes and listeriosis: a review of hazard characterisation for use in microbiological risk assessment of foods. Int J Food Microbiol. 2004;92:15–33. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1605(03)00326-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Pohl MA, Wiedmann M, Nightingale KK. Associations among Listeria monocytogenes genotypes and distinct clinical manifestations of listeriosis in cattle. Am J Vet Res. 2006;67:616–626. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.67.4.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Rocha PR, Lomonaco S, Bottero MT, Dalmasso A, Dondo A, Grattarola C, Zuccon F, Iulini B, Knabel SJ, Capucchio MT, et al. Listeria monocytogenes strains from ruminant rhombencephalitis constitute a genetically homogeneous group related to human outbreak strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013;79:3059–3066. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00219-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Jeffers GT, Bruce JL, McDonough PL, Scarlett J, Boor KJ, Wiedmann M. Comparative genetic characterization of Listeria monocytogenes isolates from human and animal listeriosis cases. Microbiology. 2001;147:1095–1104. doi: 10.1099/00221287-147-5-1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Disson O, Lecuit M. Targeting of the central nervous system by Listeria monocytogenes. Virulence. 2012;3:213–221. doi: 10.4161/viru.19586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Guldimann C, Lejeune B, Hofer S, Leib SL, Frey J, Zurbriggen A, Seuberlich T, Oevermann A. Ruminant organotypic brain-slice cultures as a model for the investigation of CNS listeriosis. Int J Exp Pathol. 2012;93:259–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2012.00821.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Sun AN, Camilli A, Portnoy DA. Isolation of Listeria monocytogenes small-plaque mutants defective for intracellular growth and cell-to-cell spread. Infect Immun. 1990;58:3770–3778. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3770-3778.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Roche SM, Velge P, Bottreau E, Durier C, der MN M-v, Pardon P. Assessment of the virulence of Listeria monocytogenes: agreement between a plaque-forming assay with HT-29 cells and infection of immunocompetent mice. Int J Food Microbiol. 2001;68:33–44. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1605(01)00460-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hernandez-Milian A, Payeras-Cifre A. What is new in listeriosis? Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:358051. doi: 10.1155/2014/358051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ransohoff RM, Cardona AE. The myeloid cells of the central nervous system parenchyma. Nature. 2010;468:253–262. doi: 10.1038/nature09615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Rupp S, Aguilar-Bultet L, Jagannathan V, Guldimann C, Drögemüller C, Pfarrer C, et al. A naturally occurring prfA truncation in a Listeria monocytogenes field strain contributes to reduced replication and cell-to-cell spread. Vet Microbiol. 2015. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 48.Bueno VF, Banerjee P, Banada PP, de MA J, Lemes-Marques EG, Bhunia AK. Characterization of Listeria monocytogenes isolates of food and human origins from Brazil using molecular typing procedures and in vitro cell culture assays. Int J Environ Health Res. 2010;20:43–59. doi: 10.1080/09603120903281283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Chatterjee SS, Otten S, Hain T, Lingnau A, Carl UD, Wehland J, Domann E, Chakraborty T. Invasiveness is a variable and heterogeneous phenotype in Listeria monocytogenes serotype strains. Int J Med Microbiol. 2006;296:277–286. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2005.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Van Langendonck N, Bottreau E, Bailly S, Tabouret M, Marly J, Pardon P, Velge P. Tissue culture assays using Caco-2 cell line differentiate virulent from non-virulent Listeria monocytogenes strains. J Appl Microbiol. 1998;85:337–346. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.1998.00515.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Pine L, Kathariou S, Quinn F, George V, Wenger JD, Weaver RE. Cytopathogenic effects in enterocytelike Caco-2 cells differentiate virulent from avirulent Listeria strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1991;29:990–996. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.990-996.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Del Corral F, Buchanan RL, Bencivengo MM, Cooke PH. Quantitative comparison of selected virulence-associated characteristics in food and clinical isolates of Listeria. J Food Prot. 1990;53:1003–1009. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X-53.12.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Roberts AJ, Williams SK, Wiedmann M, Nightingale KK. Some Listeria monocytogenes outbreak strains demonstrate significantly reduced invasion, inlA transcript levels, and swarming motility in vitro. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009;75:5647–5658. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00367-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Werbrouck H, Grijspeerdt K, Botteldoorn N, Van PE, Rijpens N, Van DJ, Uyttendaele M, Herman L, Van CE. Differential inlA and inlB expression and interaction with human intestinal and liver cells by Listeria monocytogenes strains of different origins. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006;72:3862–3871. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02164-05. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Cotter PD, Draper LA, Lawton EM, Daly KM, Groeger DS, Casey PG, Ross RP, Hill C. Listeriolysin S, a novel peptide haemolysin associated with a subset of lineage I Listeria monocytogenes. PLoS Pathog. 2008;4:e1000144. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


