Abstract
Introduction Wegener granulomatosis is a systemic vasculitis affecting small and medium-sized vessels of the upper and lower respiratory tract and kidneys.
Objective To describe a case of Wegener disease with atypical manifestation.
Resumed Report We describe the case of a 50-year-old woman with chronic otitis media and sensorineural hearing loss as the primary symptoms, without other manifestations.
Conclusion In cases of acute ear manifestations with or without hearing loss and with poor response to usual treatments, Wegener granulomatosis should be included among the possible etiologies. After adequate diagnoses and treatment of this rare disease, there was favorable evolution.
Keywords: Wegener granulomatosis, otitis media, hearing loss
Introduction
Wegener granulomatosis (WG) is a rare multisystem autoimmune disease of unknown etiology.1 2 It is a systemic vasculitis, affecting small and medium-sized vessels of the upper and lower respiratory tract and kidneys, including necrotizing granulomatous inflammation.2 3 WG has a spectrum of clinical presentations that includes recurrent respiratory infection, renal manifestations, and nonspecific systemic symptoms. Otologic manifestations are occasionally the first to appear in 20 to 60% of cases of WG, and serous otitis media is the most common presentation in ear disease.4 5 6 However, WG is not a common diagnosis in ear, nose, and throat (ENT) practice. We describe a case of a 50-year-old woman with severe bilateral hearing loss as the first symptom of the disease.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of WG with otologic manifestations may include tuberculous otitis media, cholesteatoma, Langerhans cell histiocytosis, neoplastic diseases, and other forms of vasculitis, sarcoidosis, and systemic lupus erythematosus.
Tuberculous otitis media is characterized by painless otorrhea that fails to respond to the usual antimicrobial treatment in a patient with evidence of tubercle infection elsewhere, followed by multiple tympanic membrane perforations, abundant granulation tissue, bone necrosis, and preauricular lymphadenopathy. Deafness is out of proportion with the apparent degree of development of disease seen in the otoscopy.
An ear exam may show a pocket or perforation in the eardrum often with drainage when cholesteatoma occurs.
Sarcoidosis is an idiopathic disease that presents in anatomic areas of concern to otorhinolaryngologists. It can cause dysfunction of both auditory and vestibular systems. In patients known previously to have sarcoidosis, this disease should be seriously considered. In patients presenting with otologic disorders and associated facial nerve paralysis or other neuropathies, uveitis, granulomatous meningitis, or diabetes insipidus, sarcoidosis should be suspected. An examination of the eyes as well as a chest X-ray is imperative. Sudden and fluctuating neurosensory hearing loss has been reported.
Case Report
The patient presented with complaints of severe and progressive bilateral hearing loss with onset 6 months previously. Symptoms evolved with otorrhea and pain refractory to broad-spectrum antibiotics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. During ENT examination, otoscopy showed bilateral thickening and retraction of the tympanic membrane and fluid in the middle ear, with no other clinical findings. After carrying out the audiometry (Fig. 1) and emittanciometry, ventilation tubes were placed bilaterally.
Fig. 1.
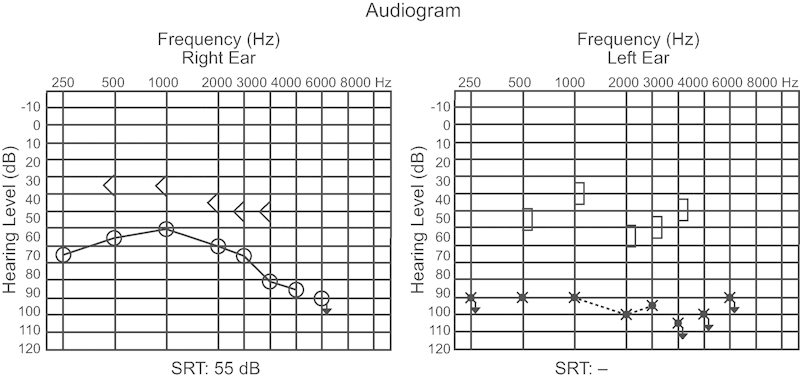
Audiogram before treatment. Abbreviation: SRT, speech reception threshold.
After 1 month, the patient complained of weight loss (7 kg/mo), lack of appetite, fevers, night sweats, asthenia, and dry cough. Laboratory findings revealed mild normochromic normocytic anemia, Westergren erythrocyte sedimentation elevated rate, elevated C-reactive protein, nonreactive Mantoux tuberculin skin test, negative sputum smear, and negative HIV antibody.
Computed tomography of the temporal bone (Fig. 2) and audiometry were performed. Chest computed tomography showed the presence of pulmonary nodules and masses with excavation areas in the left upper and lower lobes, with moderate pericardial effusion (Fig. 3). Bronchoscopy with transbronchial biopsy showed inconclusive pathologic result, with the presence of discrete fibrous thickening and septal fibrosis nodular focus.
Fig. 2.
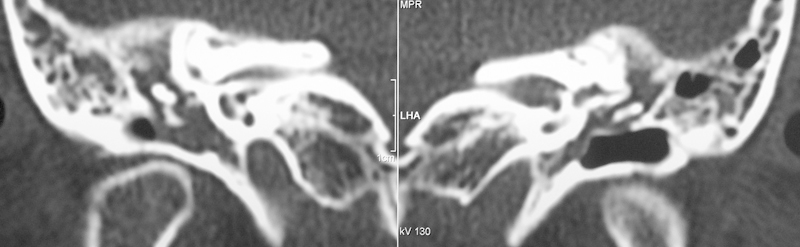
Computed tomography of the temporal bone.
Fig. 3.
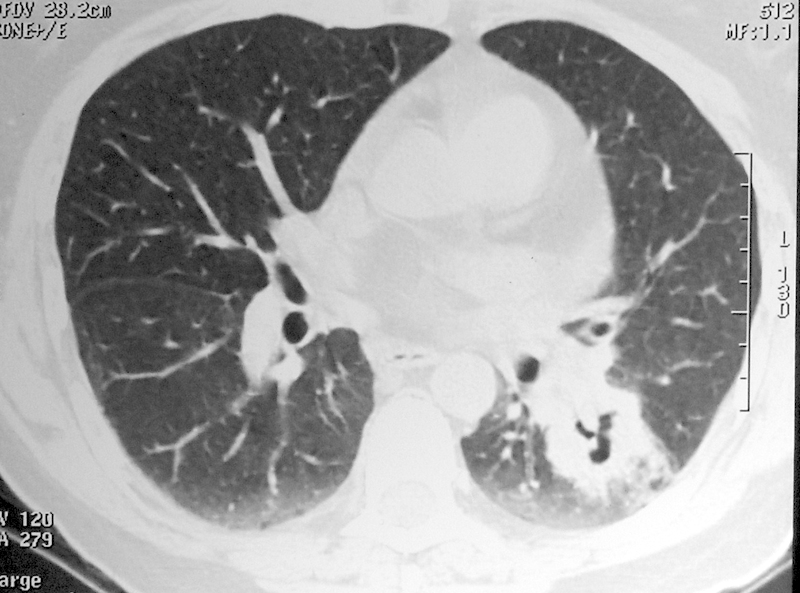
Chest computed tomography showed the presence of pulmonary nodules and masses with excavation areas in the left upper and lower lobes and moderate pericardial effusion.
The patient was also referred to the Department of Rheumatology for antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies testing, which was positive, and then antiproteinase 3 antibody testing, which was also positive, confirming the diagnosis.
With the onset of steroid (prednisone 60 mg/d), the patient's symptoms improved and hearing thresholds recovered significantly after 1 week of treatment (Fig. 4). The patient currently uses cyclophosphamide monthly and corticosteroids daily with good clinical and laboratory control.
Fig. 4.
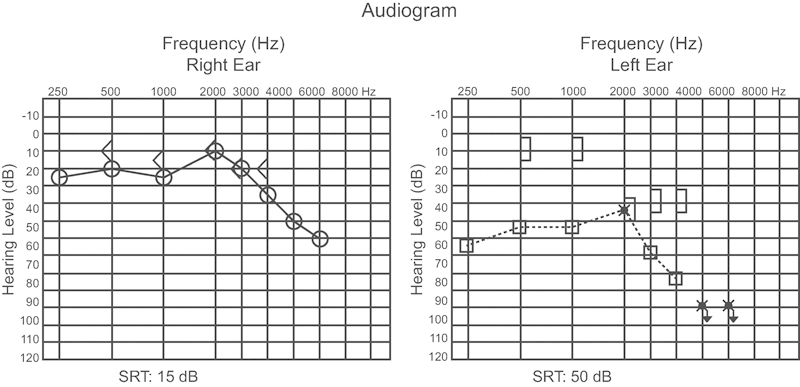
Audiogram performed after treatment. Abbreviation: SRT, speech reception threshold.
Discussion
WG is a rare idiopathic disease, immunologically mediated, which affects the small arteries of the upper and lower respiratory tracts and the kidneys, causing inflammation with necrosis, granuloma formation, and vasculitis in these organs.1 2 3 4 The average age of diagnosis is usually between 20 and 40 years, and males are affected more than females (1.5:1.0).5 Otologic manifestation varies widely, occurring in ∼20 to 60% of the affected patients, and includes serous otitis media, chronic otitis media, sensorineural hearing loss, vertigo, tinnitus, and facial palsy.4 6 Treatment should be started early for a better hearing outcome.7 Pulmonary manifestations occur in 45% of cases at initial presentation and 87% during the course of the disease.8 9 Ocular involvement in WG can be part of the initial presentation of the disease in 8 to 16% of cases. The majority of studies have reported initial manifestations in ENT, followed by lung, skin, and kidneys.3 10 Immunosuppressive drugs are the first-line therapy.1 2 5
Final Comments
In cases of acute ear manifestations with or without hearing loss and with poor response to usual treatments, WG should be included among the possible etiologies. As the prognosis depends on early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, the otolaryngologist plays a decisive role in reducing the morbidity and mortality rate in this disease.
References
- 1.Rossini B AA, Bogaz E A, Yonamine F K, Testa J RG, Penido NdeO. Refractory otitis media as the first manifestation of Wegener's granulomatosis. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2010;76(4):541. doi: 10.1590/S1808-86942010000400024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Scalcon M RR, Pereira I A, Rachid Filho A, Paiva E S. Manifestação otológica localizada em paciente com granulomatose de Wegener. Rev Bras Reumatol. 2008;48(4):253–255. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Antunes T, Barbas C SV. Granulomatose de Wegener. J Bras Pneumol. 2005;31 01:S21–S26. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pires A PBA, Sousa N JA, Sousa R CA. et al. Wegener's granulomatosis presenting with bilateral facial nerve palsy. Acta ORL. 2008;26(4):209–259. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rezende C EB, Rodrigues R EC, Yoshimura R, Uvo I P, Rapoport P B. Wegener's granulomatosis: a case report. Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol. 2003;69:261–265. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cahali S, Souza M MA, Silveira M C, Cabali M B, Cahali R B. Wegener's granulomatosis—case report with otological manifestation as first symptom. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 1997;63(1):72–74. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Takagi D, Nakamaru Y, Maguchi S, Furuta Y, Fukuda S. Otologic manifestations of Wegener's granulomatosis. Laryngoscope. 2002;112(9):1684–1690. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200209000-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Fauci A S, Haynes B F, Katz P, Wolff S M. Wegener's granulomatosis: prospective clinical and therapeutic experience with 85 patients for 21 years. Ann Intern Med. 1983;98(1):76–85. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-1-76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cordier J F, Valeyre D, Guillevin L, Loire R, Brechot J M. Pulmonary Wegener's granulomatosis. A clinical and imaging study of 77 cases. Chest. 1990;97(4):906–912. doi: 10.1378/chest.97.4.906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Correa J C, Azevedo A G, Rubens J, Rocha G. Granulomatose de Wegener: análise de dois casos. J Bras Med. 1985;48(6):34–38. [Google Scholar]


