Abstract
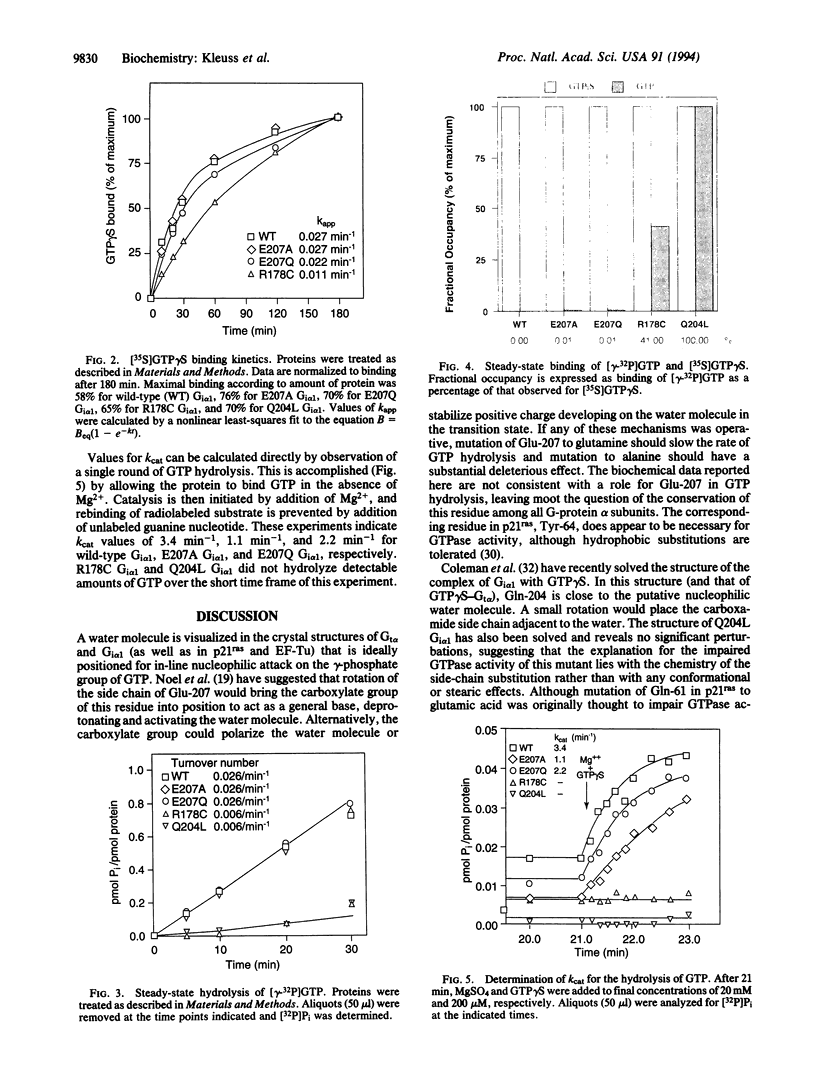
Hydrolysis of GTP by a variety of guanine nucleotide-binding proteins is a crucial step for regulation of these biological switches. Mutations that impair the GTPase activity of certain heterotrimeric signal-transducing G proteins or of p21ras cause tumors in man. A conserved glutamic residue in the alpha subunit of G proteins has been hypothesized to serve as a general base, thereby activating a water molecule for nucleophilic attack on GTP. The results of mutagenesis of this residue (Glu-207) in Gi alpha 1 refute this hypothesis. Based on the structure of the complex of Gi alpha 1 with GDP, Mg2+, and AlF-4, which appears to resemble the transition state for GTP hydrolysis, we believe that Gln-204 of Gi alpha 1, rather than Glu-207, supports catalysis of GTP hydrolysis by stabilization of the transition state.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berchtold H., Reshetnikova L., Reiser C. O., Schirmer N. K., Sprinzl M., Hilgenfeld R. Crystal structure of active elongation factor Tu reveals major domain rearrangements. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):126–132. doi: 10.1038/365126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berstein G., Blank J. L., Jhon D. Y., Exton J. H., Rhee S. G., Ross E. M. Phospholipase C-beta 1 is a GTPase-activating protein for Gq/11, its physiologic regulator. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):411–418. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90165-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigay J., Deterre P., Pfister C., Chabre M. Fluoroaluminates activate transducin-GDP by mimicking the gamma-phosphate of GTP in its binding site. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 28;191(2):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Milburn M. V., Tong L., deVos A. M., Jancarik J., Yamaizumi Z., Nishimura S., Ohtsuka E., Kim S. H. Crystal structure of an active form of RAS protein, a complex of a GTP analog and the HRAS p21 catalytic domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4849–4853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Mechanism of adenylate cyclase activation by cholera toxin: inhibition of GTP hydrolysis at the regulatory site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3307–3311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. E., Lee E., Mixon M. B., Linder M. E., Berghuis A. M., Gilman A. G., Sprang S. R. Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic studies of Gi alpha 1 and mutants of Gi alpha 1 in the GTP and GDP-bound states. J Mol Biol. 1994 May 13;238(4):630–634. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frech M., Darden T. A., Pedersen L. G., Foley C. K., Charifson P. S., Anderson M. W., Wittinghofer A. Role of glutamine-61 in the hydrolysis of GTP by p21H-ras: an experimental and theoretical study. Biochemistry. 1994 Mar 22;33(11):3237–3244. doi: 10.1021/bi00177a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freissmuth M., Gilman A. G. Mutations of GS alpha designed to alter the reactivity of the protein with bacterial toxins. Substitutions at ARG187 result in loss of GTPase activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21907–21914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K., Nash C. R. Characterization of transducin from bovine retinal rod outer segments. II. Evidence for distinct binding sites and conformational changes revealed by limited proteolysis with trypsin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10503–10510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziano M. P., Freissmuth M., Gilman A. G. Expression of Gs alpha in Escherichia coli. Purification and properties of two forms of the protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):409–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziano M. P., Gilman A. G. Synthesis in Escherichia coli of GTPase-deficient mutants of Gs alpha. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15475–15482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler J. R., Gilman A. G. G proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):383–387. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90005-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashijima T., Ferguson K. M., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. The effect of GTP and Mg2+ on the GTPase activity and the fluorescent properties of Go. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):757–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashijima T., Ferguson K. M., Sternweis P. C., Ross E. M., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. The effect of activating ligands on the intrinsic fluorescence of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):752–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashijima T., Graziano M. P., Suga H., Kainosho M., Gilman A. G. 19F and 31P NMR spectroscopy of G protein alpha subunits. Mechanism of activation by Al3+ and F-. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3396–3401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Reed R. R. Molecular cloning of five GTP-binding protein cDNA species from rat olfactory neuroepithelium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14241–14249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurnak F. Structure of the GDP domain of EF-Tu and location of the amino acids homologous to ras oncogene proteins. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):32–36. doi: 10.1126/science.3898365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaziro Y., Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nakafuku M., Satoh T. Structure and function of signal-transducing GTP-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:349–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldgaard M., Nissen P., Thirup S., Nyborg J. The crystal structure of elongation factor EF-Tu from Thermus aquaticus in the GTP conformation. Structure. 1993 Sep 15;1(1):35–50. doi: 10.1016/0969-2126(93)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E., Linder M. E., Gilman A. G. Expression of G-protein alpha subunits in Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1994;237:146–164. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(94)37059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder M. E., Ewald D. A., Miller R. J., Gilman A. G. Purification and characterization of Go alpha and three types of Gi alpha after expression in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8243–8251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons J., Landis C. A., Harsh G., Vallar L., Grünewald K., Feichtinger H., Duh Q. Y., Clark O. H., Kawasaki E., Bourne H. R. Two G protein oncogenes in human endocrine tumors. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):655–659. doi: 10.1126/science.2116665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel J. P., Hamm H. E., Sigler P. B. The 2.2 A crystal structure of transducin-alpha complexed with GTP gamma S. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):654–663. doi: 10.1038/366654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. The guanine nucleotide activating site of the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Identification by ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11416–11423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nur-E-Kamal M. S., Sizeland A., D'Abaco G., Maruta H. Asparagine 26, glutamic acid 31, valine 45, and tyrosine 64 of Ras proteins are required for their oncogenicity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1415–1418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai E. F., Kabsch W., Krengel U., Holmes K. C., John J., Wittinghofer A. Structure of the guanine-nucleotide-binding domain of the Ha-ras oncogene product p21 in the triphosphate conformation. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):209–214. doi: 10.1038/341209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. I., Strathmann M. P., Gautam N. Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):802–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1902986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. Aluminum: a requirement for activation of the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by fluoride. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4888–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





