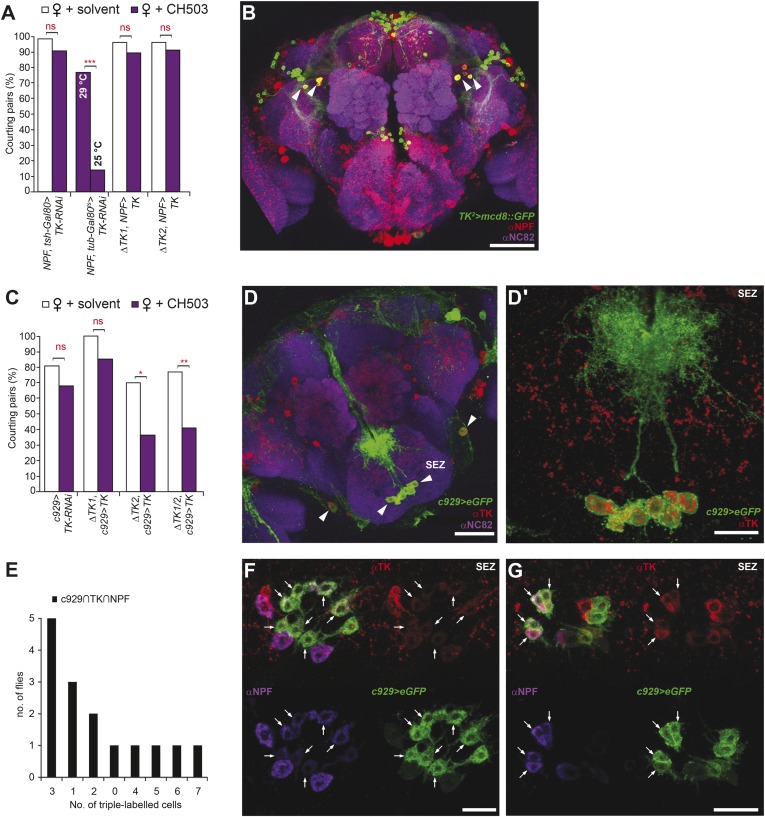
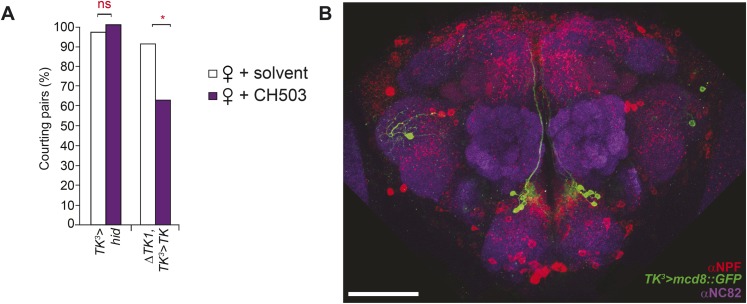
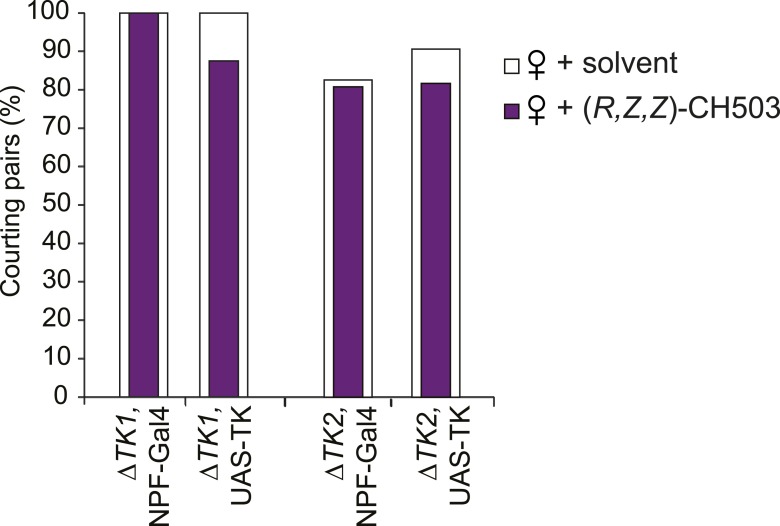
Figure 6. Tachykinin release within the NPF- and c929-defined circuits is required for the processing of CH503.
(A) RNAi-mediated knockdown of TK only in central NPF-Gal4 circuits abrogates the CH503-induced courtship suppression response. Conditional knockdown only from late pupal stage onwards (29°C permissive temperature, TK-RNAi expressed) elicits the same phenotype. At the 25°C restrictive temperature (TK-RNAi not expressed), flies continue to respond to the pheromone. Restoring TK expression only in the NPF-Gal4 circuit is not sufficient to restore sensitivity to CH503. See Figure 6—figure supplement 2 for parental controls. N = 14–23, Fisher's exact probability test, ns: not significant, ***p < 0.001. (B) Co-expression and co-localization of anti-NPF immunostaining with TK2-Gal4 processes is observed only in two pairs of bilateral cells in the ventrolateral protocerebrum (indicated by arrowheads; Pearson's coefficient: 0.7). No co-expression is observed in midline cells—the apparent co-localization observed in some cells (yellow signal) is due to overlapping signals from stacking different optical layers. Image represents a maximum intensity Z-series projection. Scale bar: 50 μm. (C) Silencing TK expression only in the c929-Gal4 circuit removes CH503 sensitivity. Rescuing TK expression only in the c929-Gal4 circuit restores sensitivity. N = 16–24, Fisher's exact probability test, ns: not significant, *p < 0.05. (D) Co-expression of anti-TK immunostaining with c929-Gal4 GFP expression is observed in 10 cell bodies housed in the SEZ (arrowheads; D′). Images represent maximum intensity Z-series projections. Scale bar D: 50 μm; D“: 35 μm. (E) Histogram showing frequency of cells in the SEZ that are triple-labeled with anti-NPF antibody, anti-TK antibody, and c929-Gal4 GFP expression. (F, G) Seven or three triple-labeled cells (arrows) in the SEZ. Images represent maximum intensity Z-series projections. Scale bar: 20 μm.