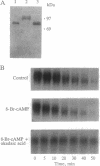
Abstract
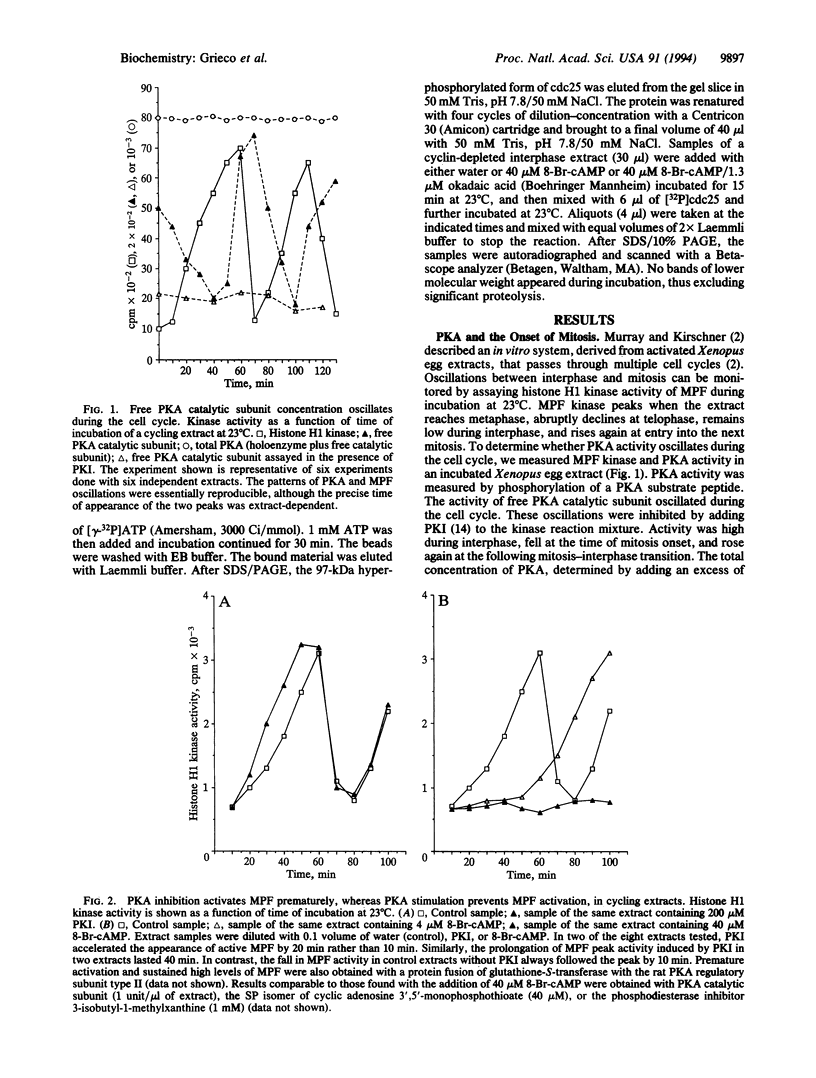
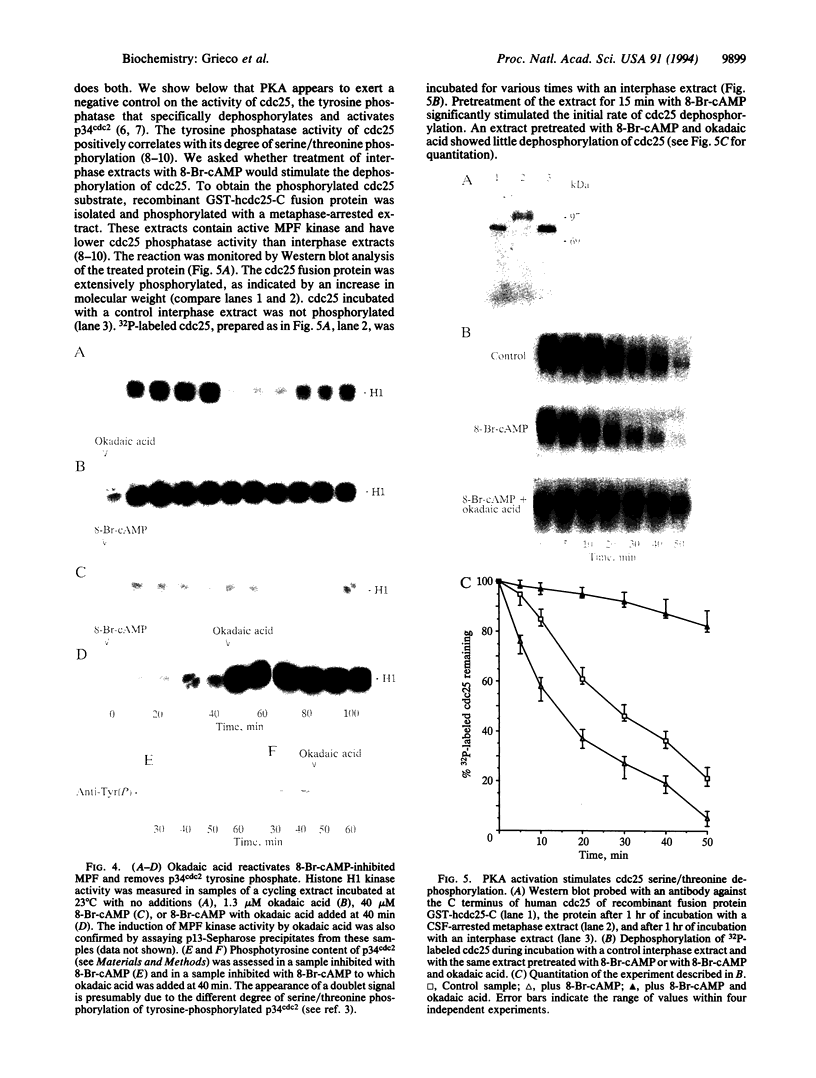
The cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) pathway affects cell cycle progression in "cycling" Xenopus egg extracts. The concentration of free PKA catalytic subunit oscillates during the cell cycle with a peak at the mitosis-interphase transition and a minimum at the onset of mitosis. Inhibition of endogenous PKA in interphase hastens the onset of mitosis. Stimulation of PKA induces interphase arrest, preventing the activation of the M-phase-promoting factor. PKA does not block the accumulation of cyclin or its binding to p34cdc2, but the resultant complex lacks kinase activity and p34cdc2 remains tyrosine-phosphorylated. PKA appears to stimulate an okadaic acid-sensitive serine/threonine phosphatase that acts upon cdc25. In this way PKA could downregulate the p34cdc2 tyrosine phosphatase activity of cdc25 and consequently block the activation of the M-phase-promoting factor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axton J. M., Dombrádi V., Cohen P. T., Glover D. M. One of the protein phosphatase 1 isoenzymes in Drosophila is essential for mitosis. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):33–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90286-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornslaeger E. A., Mattei P., Schultz R. M. Involvement of cAMP-dependent protein kinase and protein phosphorylation in regulation of mouse oocyte maturation. Dev Biol. 1986 Apr;114(2):453–462. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger M. M., Bombik B. M., Breckenridge B. M., Sheppard J. R. Growth control and cyclic alterations of cyclic AMP in the cell cycle. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 11;239(93):161–163. doi: 10.1038/newbio239161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H. C., Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B., Smith A. J., Misconi L., Van Patten S. M., Walsh D. A. A potent synthetic peptide inhibitor of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):989–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke P. R., Hoffmann I., Draetta G., Karsenti E. Dephosphorylation of cdc25-C by a type-2A protein phosphatase: specific regulation during the cell cycle in Xenopus egg extracts. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Apr;4(4):397–411. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.4.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman T. R., Tang Z., Dunphy W. G. Negative regulation of the wee1 protein kinase by direct action of the nim1/cdr1 mitotic inducer. Cell. 1993 Mar 26;72(6):919–929. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90580-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasso M., Newport J. W. Completion of DNA replication is monitored by a feedback system that controls the initiation of mitosis in vitro: studies in Xenopus. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):811–823. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90191-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Kumagai A. The cdc25 protein contains an intrinsic phosphatase activity. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90582-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Félix M. A., Cohen P., Karsenti E. Cdc2 H1 kinase is negatively regulated by a type 2A phosphatase in the Xenopus early embryonic cell cycle: evidence from the effects of okadaic acid. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):675–683. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08159.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Solomon M. J., Booher R. N., Bazan J. F., Kirschner M. W. cdc25 is a specific tyrosine phosphatase that directly activates p34cdc2. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):197–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90583-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann I., Clarke P. R., Marcote M. J., Karsenti E., Draetta G. Phosphorylation and activation of human cdc25-C by cdc2--cyclin B and its involvement in the self-amplification of MPF at mitosis. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):53–63. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumi T., Walker D. H., Maller J. L. Periodic changes in phosphorylation of the Xenopus cdc25 phosphatase regulate its activity. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Aug;3(8):927–939. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.8.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita N., Ohkura H., Yanagida M. Distinct, essential roles of type 1 and 2A protein phosphatases in the control of the fission yeast cell division cycle. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90173-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Nigg E. A. Cell cycle regulation of vertebrate p34cdc2 activity: identification of Thr161 as an essential in vivo phosphorylation site. New Biol. 1992 Apr;4(4):323–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai A., Dunphy W. G. Regulation of the cdc25 protein during the cell cycle in Xenopus extracts. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):139–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90540-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb N. J., Cavadore J. C., Labbe J. C., Maurer R. A., Fernandez A. Inhibition of cAMP-dependent protein kinase plays a key role in the induction of mitosis and nuclear envelope breakdown in mammalian cells. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1523–1533. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07672.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Solomon M. J., Mumby M. C., Kirschner M. W. INH, a negative regulator of MPF, is a form of protein phosphatase 2A. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):415–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90649-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer L., Zarutskie P. Starfish oocyte maturation: 1-methyladenine triggers a drop of cAMP concentration related to the hormone-dependent period. Dev Biol. 1987 Jun;121(2):306–315. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90166-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin synthesis drives the early embryonic cell cycle. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):275–280. doi: 10.1038/339275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkura H., Kinoshita N., Miyatani S., Toda T., Yanagida M. The fission yeast dis2+ gene required for chromosome disjoining encodes one of two putative type 1 protein phosphatases. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):997–1007. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90338-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. cdc25+ functions as an inducer in the mitotic control of fission yeast. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90546-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe C., Newport J. W. Coupling of mitosis to the completion of S phase in Xenopus occurs via modulation of the tyrosine kinase that phosphorylates p34cdc2. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):787–797. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90153-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Glotzer M., Lee T. H., Philippe M., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin activation of p34cdc2. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1013–1024. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]