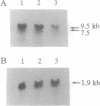
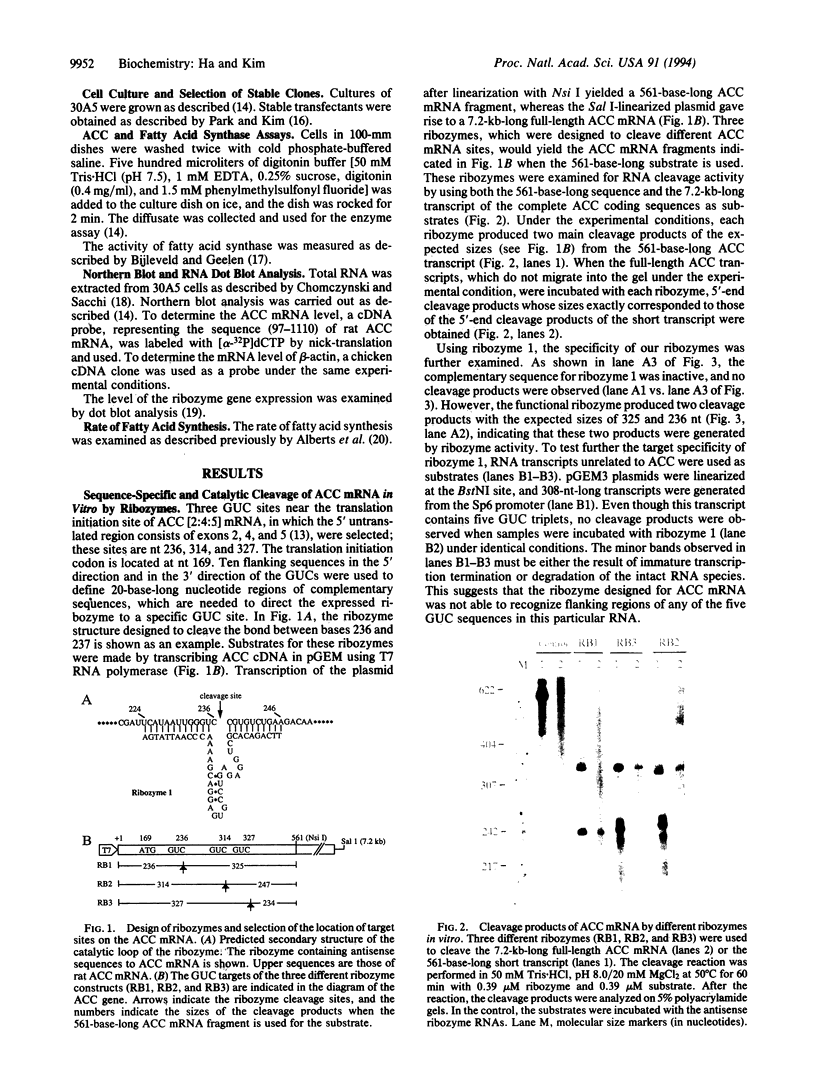
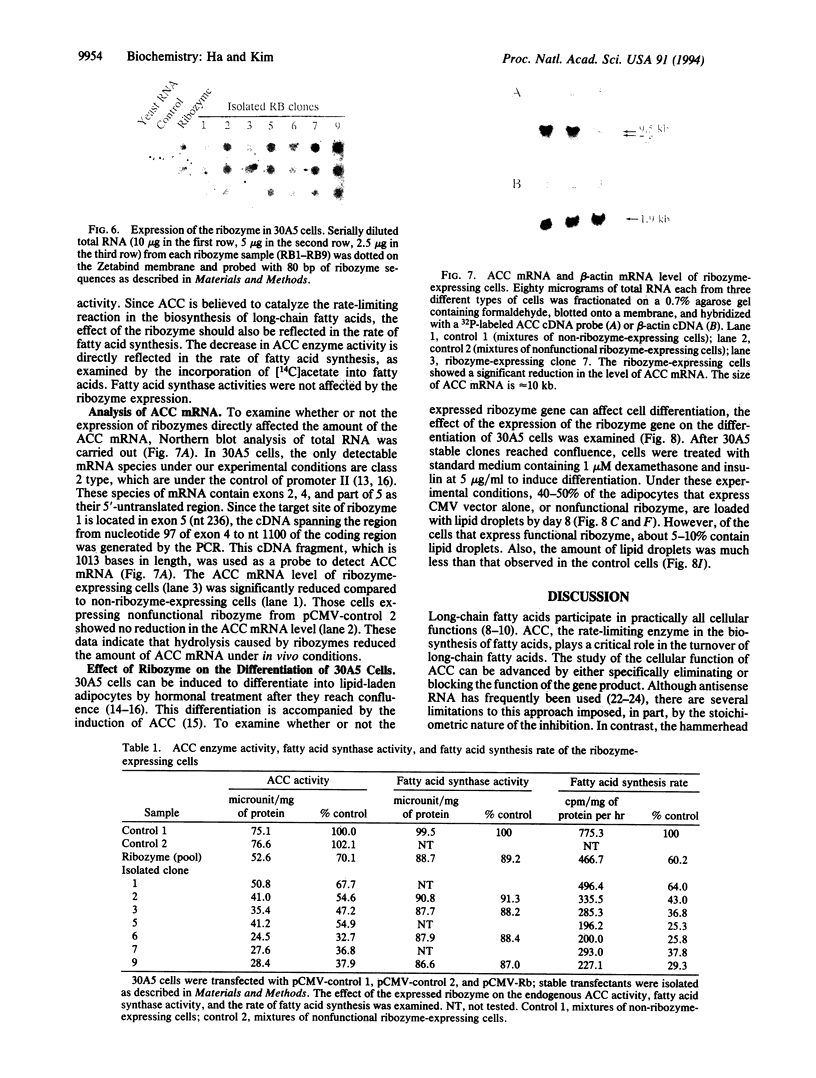
Abstract
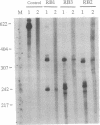
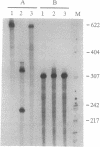
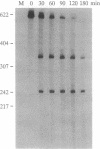
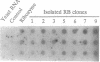
We describe the construction of ribozyme genes that are specific to acetyl-CoA carboxylase [ACC; acetyl-CoA: carbon-dioxide ligase (ADP-forming), EC 6.4.1.2] mRNAs and the effects of their expression on long-chain fatty acid synthesis. In a cell-free system, these ribozymes precisely cleave ACC mRNA at the expected sites. 30A5 preadipocyte cells stably transfected with the ribozyme gene show a substantial reduction in the amount of ACC mRNA as compared to non-ribozyme-expressing cells. The decrease in ACC mRNA was associated with a significant decrease in ACC enzyme activity, and the rate of fatty acid synthesis fell to about 30-70% of the control. When these cells are induced to differentiate into adipocytes, lipid accumulation is very slow in comparison with control cells. The activity of fatty acid synthase and the mRNA level of beta-actin were not affected. These data indicate that ribozymes designed to specifically target ACC mRNA under in vivo conditions act by decreasing the ACC mRNA level, which, in turn, decreases fatty acid synthesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts A. W., Ferguson K., Hennessy S., Vagelos P. R. Regulation of lipid synthesis in cultured animal cells. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5241–5249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bai D. H., Pape M. E., López-Casillas F., Luo X. C., Dixon J. E., Kim K. H. Molecular cloning of cDNA for acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12395–12399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijleveld C., Geelen M. J. Measurement of acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity in isolated hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 24;918(3):274–283. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90231-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron F. H., Jennings P. A. Specific gene suppression by engineered ribozymes in monkey cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9139–9143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Bass B. L. Biological catalysis by RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:599–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. The chemistry of self-splicing RNA and RNA enzymes. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1532–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.2438771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. J., Banerjea A. C., Harmison G. G., Haglund K., Schubert M. Multitarget-ribozyme directed to cleave at up to nine highly conserved HIV-1 env RNA regions inhibits HIV-1 replication--potential effectiveness against most presently sequenced HIV-1 isolates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 11;20(17):4581–4589. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.17.4581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotten M., Birnstiel M. L. Ribozyme mediated destruction of RNA in vivo. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3861–3866. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A. C., Symons R. H. Self-cleavage of plus and minus RNAs of a virusoid and a structural model for the active sites. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90562-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A. C., Symons R. H. Self-cleavage of virusoid RNA is performed by the proposed 55-nucleotide active site. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90657-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodchild J., Agrawal S., Civeira M. P., Sarin P. S., Sun D., Zamecnik P. C. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus replication by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5507–5511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodchild J., Kohli V. Ribozymes that cleave an RNA sequence from human immunodeficiency virus: the effect of flanking sequence on rate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Feb 1;284(2):386–391. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90313-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodridge A. G. Regulation of the activity of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase by palmitoyl coenzyme A and citrate. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6946–6952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Mobile RNA catalysts. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):716–718. doi: 10.1038/336716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha J., Daniel S., Kong I. S., Park C. K., Tae H. J., Kim K. H. Cloning of human acetyl-CoA carboxylase cDNA. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Jan 15;219(1-2):297–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb19941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseloff J., Gerlach W. L. Simple RNA enzymes with new and highly specific endoribonuclease activities. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):585–591. doi: 10.1038/334585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James G., Olson E. N. Fatty acylated proteins as components of intracellular signaling pathways. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 20;29(11):2623–2634. doi: 10.1021/bi00463a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings P. A., Molloy P. L. Inhibition of SV40 replicon function by engineered antisense RNA transcribed by RNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3043–3047. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02610.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht D. A., Loomis W. F. Antisense RNA inactivation of myosin heavy chain gene expression in Dictyostelium discoideum. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1081–1086. doi: 10.1126/science.3576221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo X. C., Kim K. H. An enhancer element in the house-keeping promoter for acetyl-CoA carboxylase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3249–3254. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo X. C., Park K., Lopez-Casillas F., Kim K. H. Structural features of the acetyl-CoA carboxylase gene: mechanisms for the generation of mRNAs with 5' end heterogeneity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4042–4046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Casillas F., Kim K. H. Heterogeneity at the 5' end of rat acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase mRNA. Lipogenic conditions enhance synthesis of a unique mRNA in liver. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7176–7184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., Murray J. M. Antisense RNA of proto-oncogene c-fos blocks renewed growth of quiescent 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):639–649. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape M. E., Kim K. H. Transcriptional regulation of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase gene expression by tumor necrosis factor in 30A-5 preadipocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):974–982. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park K., Kim K. H. Regulation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase gene expression. Insulin induction of acetyl-CoA carboxylase and differentiation of 30A5 preadipocytes require prior cAMP action on the gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12249–12256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarver N., Cantin E. M., Chang P. S., Zaia J. A., Ladne P. A., Stephens D. A., Rossi J. J. Ribozymes as potential anti-HIV-1 therapeutic agents. Science. 1990 Mar 9;247(4947):1222–1225. doi: 10.1126/science.2107573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena S. K., Ackerman E. J. Ribozymes correctly cleave a model substrate and endogenous RNA in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17106–17109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivaram P., Deutscher M. P. Free fatty acids associated with the high molecular weight aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase complex influence its structure and function. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5774–5779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlenbeck O. C. A small catalytic oligoribonucleotide. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):596–600. doi: 10.1038/328596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]