Abstract
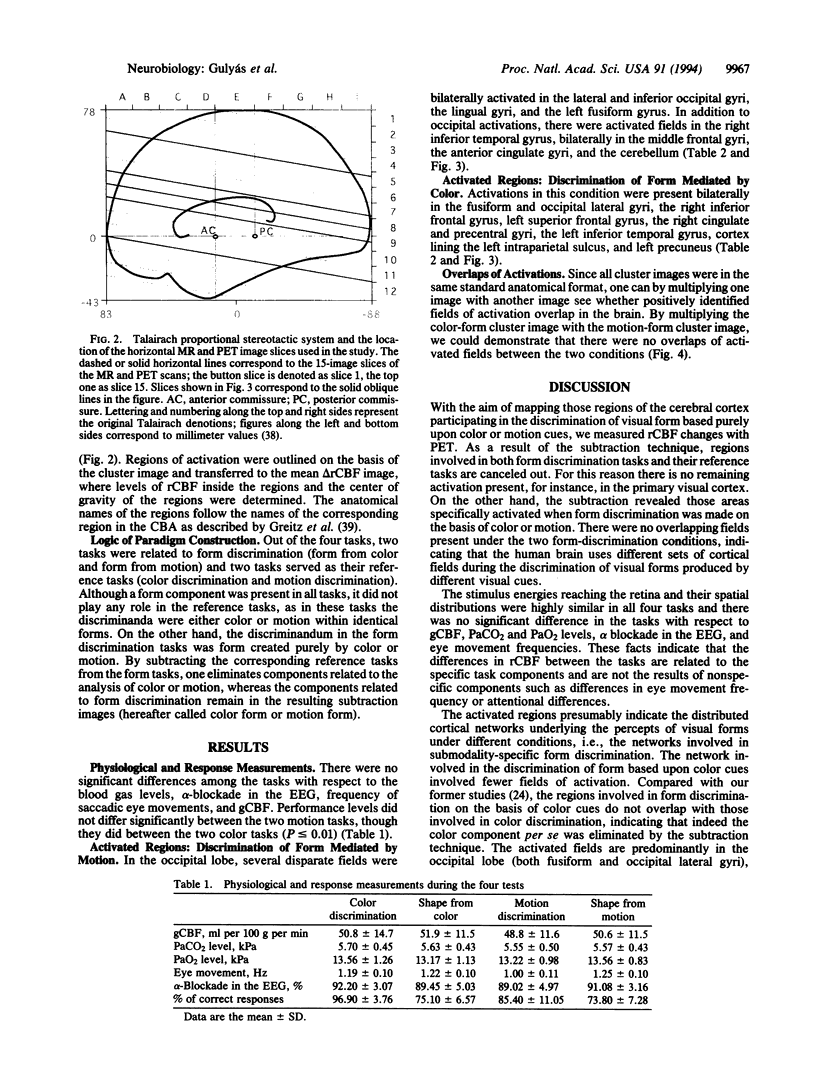
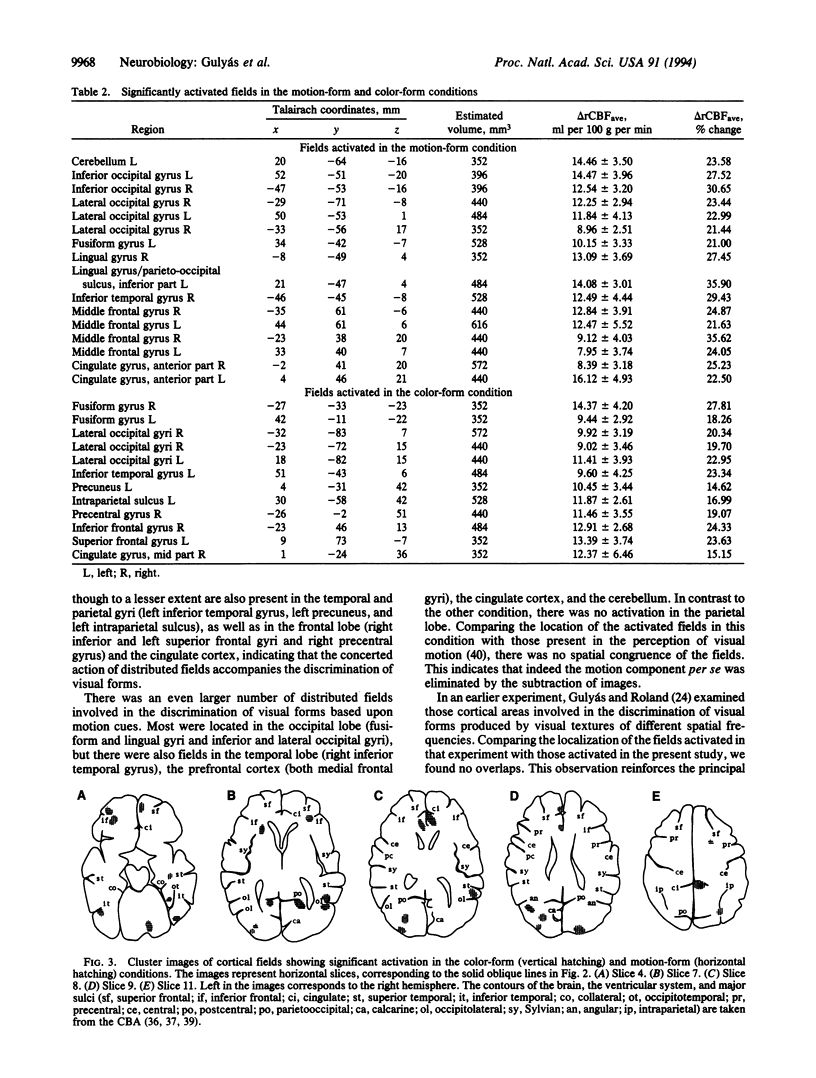
To explore the extent to which various cortical functional pathways are involved in processing and analyzing different types of information that yield the same perceptual entity, we mapped anatomical structures in the human brain participating in the discrimination of visual forms mediated either by motion or color cues. Changes in regional cerebral blood flow were measured in 10 young male volunteers with positron emission tomography and with [15O]butanol. During the measurements, the subjects performed four visual discrimination tasks (form-from-motion, motion alone, form-from-color, and color alone discrimination). The individual regional cerebral blood flow images were standardized in shape and size with the help of a computerized brain atlas. Subtraction images were determined and averaged across data from all subjects. The resulting images were analyzed for statistically significant changes between specific and reference tasks. The discrimination of form by means of motion cues activated functional fields bilaterally in the inferior and lateral occipital gyri, in the lingual, anterior cingulate, middle frontal and orbitofrontal gyri, and in the left fusiform and right inferior temporal gyri. Form discrimination by color cues resulted in activation bilaterally in the inferior temporal, lateral occipital, and orbitofrontal gyri, the left precuneus and intraparietal sulcus, and the right precentral gyrus. The regions engaged in the two kinds of form discrimination did not overlap, demonstrating that differences in visual forms mediated by color or motion cues are processed and analyzed by disparate networks of functional fields in human cerebral cortex.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergström M., Boëthius J., Eriksson L., Greitz T., Ribbe T., Widén L. Head fixation device for reproducible position alignment in transmission CT and positron emission tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1981 Feb;5(1):136–141. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198102000-00027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. S., Adler L. P., Nelson A. D., Cassidy E. H., Muzic R. F., Bednarczyk E. M., Miraldi F. Measurement of human cerebral blood flow with [15O]butanol and positron emission tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1991 Sep;11(5):707–715. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1991.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boussaoud D., Ungerleider L. G., Desimone R. Pathways for motion analysis: cortical connections of the medial superior temporal and fundus of the superior temporal visual areas in the macaque. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Jun 15;296(3):462–495. doi: 10.1002/cne.902960311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten K. H., Newsome W. T., Saunders R. C. Effects of inferotemporal cortex lesions on form-from-motion discrimination in monkeys. Exp Brain Res. 1992;88(2):292–302. doi: 10.1007/BF02259104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney T., Shadlen M., Switkes E. Parallel processing of motion and colour information. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):647–649. doi: 10.1038/328647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh P., Anstis S. The contribution of color to motion in normal and color-deficient observers. Vision Res. 1991;31(12):2109–2148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(91)90169-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbetta M., Miezin F. M., Dobmeyer S., Shulman G. L., Petersen S. E. Selective and divided attention during visual discriminations of shape, color, and speed: functional anatomy by positron emission tomography. J Neurosci. 1991 Aug;11(8):2383–2402. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-08-02383.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeYoe E. A., Van Essen D. C. Concurrent processing streams in monkey visual cortex. Trends Neurosci. 1988 May;11(5):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90130-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greitz T., Bergström M., Boëthius J., Kingsley D., Ribbe T. Head fixation system for integration of radiodiagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Neuroradiology. 1980;19(1):1–6. doi: 10.1007/BF00369080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greitz T., Bohm C., Holte S., Eriksson L. A computerized brain atlas: construction, anatomical content, and some applications. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1991 Jan-Feb;15(1):26–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greitz T., Bohm C., Holte S., Eriksson L. A computerized brain atlas: construction, anatomical content, and some applications. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1991 Jan-Feb;15(1):26–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross C. G., Rocha-Miranda C. E., Bender D. B. Visual properties of neurons in inferotemporal cortex of the Macaque. J Neurophysiol. 1972 Jan;35(1):96–111. doi: 10.1152/jn.1972.35.1.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulyás B., Roland P. E. Cortical fields participating in form and colour discrimination in the human brain. Neuroreport. 1991 Oct;2(10):585–588. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199110000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heywood C. A., Cowey A. The role of the 'face-cell' area in the discrimination and recognition of faces by monkeys. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1992 Jan 29;335(1273):31–38. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1992.0004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone M. S., Hubel D. H. Psychophysical evidence for separate channels for the perception of form, color, movement, and depth. J Neurosci. 1987 Nov;7(11):3416–3468. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-11-03416.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone M., Hubel D. Segregation of form, color, movement, and depth: anatomy, physiology, and perception. Science. 1988 May 6;240(4853):740–749. doi: 10.1126/science.3283936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel A., Bullier J. Anatomical segregation of two cortical visual pathways in the macaque monkey. Vis Neurosci. 1990 Jun;4(6):555–578. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800005769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield R. C. The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia. 1971 Mar;9(1):97–113. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(71)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olesen J., Paulson O. B., Lassen N. A. Regional cerebral blood flow in man determined by the initial slope of the clearance of intra-arterially injected 133Xe. Stroke. 1971 Nov-Dec;2(6):519–540. doi: 10.1161/01.str.2.6.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papathomas T. V., Gorea A., Julesz B. Two carriers for motion perception: color and luminance. Vision Res. 1991;31(11):1883–1892. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(91)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrett D. I., Rolls E. T., Caan W. Visual neurones responsive to faces in the monkey temporal cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1982;47(3):329–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00239352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran V. S., Gregory R. L. Does colour provide an input to human motion perception? Nature. 1978 Sep 7;275(5675):55–56. doi: 10.1038/275055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran V. S. Interaction between colour and motion in human vision. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):645–647. doi: 10.1038/328645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan D., Giaschi D., Sharpe J. A., Hong X. H. Visual processing of motion-defined form: selective failure in patients with parietotemporal lesions. J Neurosci. 1992 Jun;12(6):2198–2210. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-06-02198.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland P. E., Gulyás B., Seitz R. J., Bohm C., Stone-Elander S. Functional anatomy of storage, recall, and recognition of a visual pattern in man. Neuroreport. 1990 Sep;1(1):53–56. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199009000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller P. H., Logothetis N. K., Charles E. R. Functions of the colour-opponent and broad-band channels of the visual system. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):68–70. doi: 10.1038/343068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. L., Desimone R., Albright T. D., Gross C. G. Shape recognition and inferior temporal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5776–5778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz R. J., Bohm C., Greitz T., Roland P. E., Eriksson L., Blomqvist G., Rosenqvist G., Nordell B. Accuracy and precision of the computerized brain atlas programme for localization and quantification in positron emission tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1990 Jul;10(4):443–457. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1990.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sergent J., Ohta S., MacDonald B. Functional neuroanatomy of face and object processing. A positron emission tomography study. Brain. 1992 Feb;115(Pt 1):15–36. doi: 10.1093/brain/115.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sáry G., Vogels R., Orban G. A. Cue-invariant shape selectivity of macaque inferior temporal neurons. Science. 1993 May 14;260(5110):995–997. doi: 10.1126/science.8493538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaina L. M., Lemay M., Bienfang D. C., Choi A. Y., Nakayama K. Intact "biological motion" and "structure from motion" perception in a patient with impaired motion mechanisms: a case study. Vis Neurosci. 1990 Oct;5(4):353–369. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800000444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Essen D. C., Anderson C. H., Felleman D. J. Information processing in the primate visual system: an integrated systems perspective. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):419–423. doi: 10.1126/science.1734518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeki S. M. Functional organization of a visual area in the posterior bank of the superior temporal sulcus of the rhesus monkey. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;236(3):549–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeki S. The representation of colours in the cerebral cortex. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):412–418. doi: 10.1038/284412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeki S., Watson J. D., Lueck C. J., Friston K. J., Kennard C., Frackowiak R. S. A direct demonstration of functional specialization in human visual cortex. J Neurosci. 1991 Mar;11(3):641–649. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-03-00641.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]