Abstract
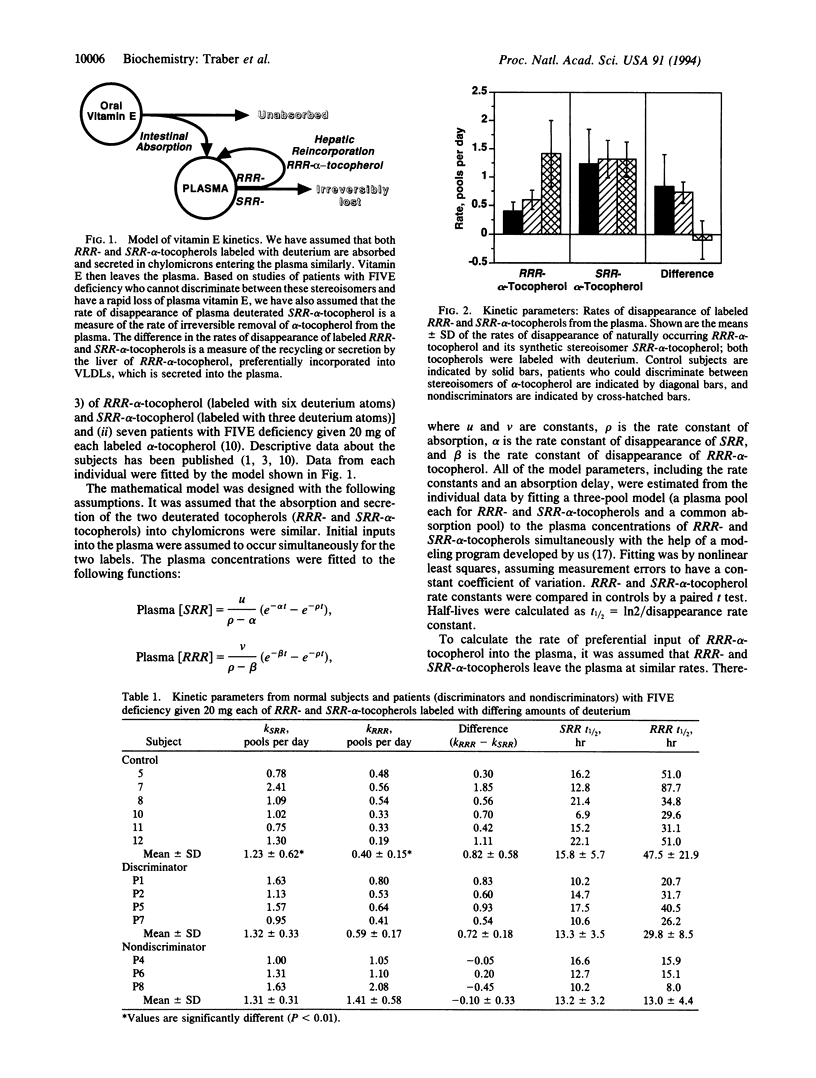
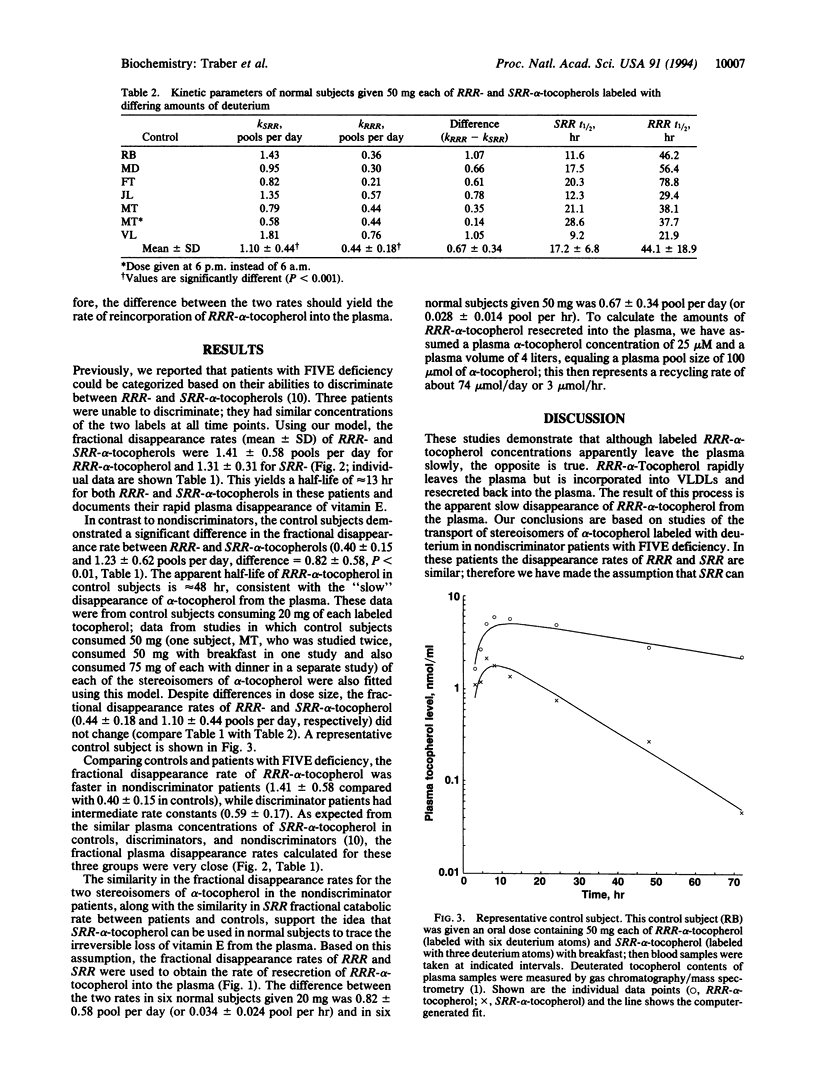
A kinetic model of vitamin E transport in humans is described using data from our studies with deuterium-labeled stereoisomers of alpha-tocopherol (RRR- and SRR-). In normal subjects, both alpha-tocopherols are present at similar concentrations in chylomicrons, but by 24 hr, RRR-alpha-tocopherol is at higher plasma concentrations because RRR-alpha-tocopherol is preferentially incorporated into very low density lipoproteins, which are then secreted into plasma. In three nondiscriminator patients with familial isolated vitamin E deficiency, the fractional disappearance rates (mean +/- SD) of deuterium-labeled RRR- and SRR-alpha-tocopherols in plasma were 1.4 +/- 0.6 and 1.3 +/- 0.3 pools per day, respectively (difference, 0.1 +/- 0.3). In these patients, plasma concentrations of both RRR- and SRR-alpha-tocopherols decreased similarly to SRR-alpha-tocopherol in controls. In six controls, fractional disappearance rates of deuterium-labeled RRR-alpha-tocopherol (0.4 +/- 0.1 pool per day) were significantly (P < 0.01) slower than for SRR- (1.2 +/- 0.6). The differences (0.8 +/- 0.6 pool per day) between these two rates in controls estimate the rate at which RRR-alpha-tocopherol, which had left the plasma, was returned to the plasma. Although plasma labeled RRR-alpha-tocopherol concentrations in controls appear to change slowly, these data show that both RRR- and SRR-alpha-tocopherols leave the plasma rapidly, but only RRR-alpha-tocopherol is returned to the plasma, likely in nascent very low density lipoproteins. This recycling of RRR-alpha-tocopherol accounts for nearly 1 pool of alpha-tocopherol per day.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arad Y., Ramakrishnan R., Ginsberg H. N. Lovastatin therapy reduces low density lipoprotein apoB levels in subjects with combined hyperlipidemia by reducing the production of apoB-containing lipoproteins: implications for the pathophysiology of apoB production. J Lipid Res. 1990 Apr;31(4):567–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben Hamida C., Doerflinger N., Belal S., Linder C., Reutenauer L., Dib C., Gyapay G., Vignal A., Le Paslier D., Cohen D. Localization of Friedreich ataxia phenotype with selective vitamin E deficiency to chromosome 8q by homozygosity mapping. Nat Genet. 1993 Oct;5(2):195–200. doi: 10.1038/ng1093-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjornson L. K., Gniewkowski C., Kayden H. J. Comparison of exchange of alpha-tocopherol and free cholesterol between rat plasma lipoproteins and erythrocytes. J Lipid Res. 1975 Jan;16(1):39–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egusa G., Beltz W. F., Grundy S. M., Howard B. V. Influence of obesity on the metabolism of apolipoprotein B in humans. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):596–603. doi: 10.1172/JCI112011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayden H. J., Traber M. G. Absorption, lipoprotein transport, and regulation of plasma concentrations of vitamin E in humans. J Lipid Res. 1993 Mar;34(3):343–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher J., Losowsky M. S. The absorption of alpha-tocopherol in man. Br J Nutr. 1970 Dec;24(4):1033–1047. doi: 10.1079/bjn19700106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesaniemi Y. A., Beltz W. F., Grundy S. M. Comparison of clofibrate and caloric restriction on kinetics of very low density lipoprotein triglycerides. Arteriosclerosis. 1985 Mar-Apr;5(2):153–161. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.5.2.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlenkamp J., Ronk M., Yusin M., Stolz A., Kaplowitz N. Identification and purification of a human liver cytosolic tocopherol binding protein. Protein Expr Purif. 1993 Oct;4(5):382–389. doi: 10.1006/prep.1993.1050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMahon M. T., Neale G. The absorption of alpha-tocopherol in control subjects and in patients with intestinal malabsorption. Clin Sci. 1970 Feb;38(2):197–210. doi: 10.1042/cs0380197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. J., Mavis R. D. Membrane transfer of alpha-tocopherol. Influence of soluble alpha-tocopherol-binding factors from the liver, lung, heart, and brain of the rat. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10464–10468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimm E. B., Stampfer M. J., Ascherio A., Giovannucci E., Colditz G. A., Willett W. C. Vitamin E consumption and the risk of coronary heart disease in men. N Engl J Med. 1993 May 20;328(20):1450–1456. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199305203282004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Arai H., Miyata A., Tokita S., Yamamoto K., Tanabe T., Inoue K. Primary structure of alpha-tocopherol transfer protein from rat liver. Homology with cellular retinaldehyde-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):17705–17710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Hagiwara K., Arai H., Inoue K. Purification and characterization of the alpha-tocopherol transfer protein from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 19;288(1-2):41–45. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80999-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M. J., Hennekens C. H., Manson J. E., Colditz G. A., Rosner B., Willett W. C. Vitamin E consumption and the risk of coronary disease in women. N Engl J Med. 1993 May 20;328(20):1444–1449. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199305203282003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber M. G., Burton G. W., Hughes L., Ingold K. U., Hidaka H., Malloy M., Kane J., Hyams J., Kayden H. J. Discrimination between forms of vitamin E by humans with and without genetic abnormalities of lipoprotein metabolism. J Lipid Res. 1992 Aug;33(8):1171–1182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber M. G., Burton G. W., Ingold K. U., Kayden H. J. RRR- and SRR-alpha-tocopherols are secreted without discrimination in human chylomicrons, but RRR-alpha-tocopherol is preferentially secreted in very low density lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1990 Apr;31(4):675–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber M. G. Determinants of plasma vitamin E concentrations. Free Radic Biol Med. 1994 Feb;16(2):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(94)90148-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber M. G., Lane J. C., Lagmay N. R., Kayden H. J. Studies on the transfer of tocopherol between lipoproteins. Lipids. 1992 Sep;27(9):657–663. doi: 10.1007/BF02536020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber M. G., Olivecrona T., Kayden H. J. Bovine milk lipoprotein lipase transfers tocopherol to human fibroblasts during triglyceride hydrolysis in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1729–1734. doi: 10.1172/JCI111883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber M. G., Rudel L. L., Burton G. W., Hughes L., Ingold K. U., Kayden H. J. Nascent VLDL from liver perfusions of cynomolgus monkeys are preferentially enriched in RRR- compared with SRR-alpha-tocopherol: studies using deuterated tocopherols. J Lipid Res. 1990 Apr;31(4):687–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber M. G., Sokol R. J., Burton G. W., Ingold K. U., Papas A. M., Huffaker J. E., Kayden H. J. Impaired ability of patients with familial isolated vitamin E deficiency to incorporate alpha-tocopherol into lipoproteins secreted by the liver. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):397–407. doi: 10.1172/JCI114452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber M. G., Sokol R. J., Kohlschütter A., Yokota T., Muller D. P., Dufour R., Kayden H. J. Impaired discrimination between stereoisomers of alpha-tocopherol in patients with familial isolated vitamin E deficiency. J Lipid Res. 1993 Feb;34(2):201–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Yusin M., Ren I., Kuhlenkamp J., Hirano T., Stolz A., Kaplowitz N. Identification, purification, and immunochemical characterization of a tocopherol-binding protein in rat liver cytosol. J Lipid Res. 1992 Mar;33(3):343–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



