Abstract
Metallo-β-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MPPA) is an important nosocomial pathogen that shows resistance to all β-lactam antibiotics except monobactams. There are various types of metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs) in carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa including Imipenemase (IMP), Verona integron-encoded metallo-β-lactamase (VIM), Sao Paulo metallo-β-lactamase (SPM), Germany imipenemase (GIM), New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase (NDM), Florence imipenemase (FIM). Each MBL gene is located on specific genetic elements including integrons, transposons, plasmids, or on the chromosome, in which they carry genes encoding determinants of resistance to carbapenems and other antibiotics, conferring multidrug resistance to P. aeruginosa. In addition, these genetic elements are transferable to other Gram-negative species, increasing the antimicrobial resistance rate and complicating the treatment of infected patients. Therefore, it is essential to understand the epidemiology, resistance mechanism, and molecular characteristics of MPPA for infection control and prevention of a possible global health crisis. Here, we highlight the characteristics of MPPA.
Keywords: Metallo-β-lactamase, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Carbapenem, Epidemiology, Multidrug resistance
Introduction
The continuous emergence, worldwide spread, and increasing prevalence of bacteria resistant to multiple antimicrobial agents are becoming major threats to public health [1,2,3,4,5]. Multidrug and pandrug resistant (MDR or PDR) bacterial infections are closely associated with high mortality, prolonged hospitalization, multiple morbidities, and increased cost due to the limited antimicrobial therapeutic options for infected patients [6,7]. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is one of the primary opportunistic pathogen that causes a variety of nosocomial infections including sepsis, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, and soft-tissue infection [8]. This species is frequently isolated from immunocompromised patients who underwent organ transplantation, invasive procedure, immunosuppressive therapy, or intensive care [9,10,11].
P. aeruginosa is one of the most important bacteria with documented resistance to multiple antimicrobial classes including β-lactams, carbapenems, aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones, and polymyxins [12,13]. Due to its intrinsic and acquired antimicrobial resistance, only limited classes of antibiotics are effective for the treatment of P. aeruginosa infections. Among these antibiotics, carbapenems have been regarded as the most potent β-lactams against MDR Gram-negative bacilli including P. aeruginosa due to their high affinity with penicillin-binding proteins, stability against extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs), and permeability of bacterial outer membranes [14]. Resistance to carbapenems is particularly challenging in clinical settings because they are the mainstays for treatment of multidrug resistance P. aeruginosa. There are few remaining antibiotic options for this strain, and multidrug resistance is much more common for patients infected with carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa [6,15,16].
Among the various antimicrobial resistance mechanisms, the production of carbapenemase is one of the most important mechanisms by which P. aeruginosa acquires carbapenem resistance. Many carbapenemases have been identified in P. aeruginosa, including (1) KPC and GES variants of Ambler class A, (2) IMP-, VIM-, SPM-, GIM-, NDM-, and FIM-type metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs) of Ambler class B, and (3) OXA variant enzymes of Ambler class D [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25].
Here, we overview the epidemiology and molecular characteristics of metallo-β-lactamase-producing P. aeruginosa (MPPA).
Epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa
The global epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa (CRPA) was analyzed based on a careful and thorough literature search of http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed with the combination of key words including the name of each nation, carbapenem, P. aeruginosa, MBL, epidemiology, prevalence, Gram-negative, national survey, and resistance. Countries were grouped by continent in order to show international differences in CRPA prevalence related to geographical distance. We found published reports from a total of 50 countries regarding country of isolation and collection period of clinical isolates, as well as the ratio of CRPA to all P. aeruginosa (Table 1).
Table 1. Carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa report by country.
| Continent | Countrya | Collection period (year) | Resistance rate (%) | Reference or GenBank accession No. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbapenem | Imipenem | Meropenem | Doripenem | Ertapenem | ||||
| East Asia | China | 2003-2011 | 43.4 | 40.9 | [70] | |||
| Japan | 2013 | 28.5 | 22.8 | 12.5 | [71] | |||
| Korea | 2011 | 22 | [61] | |||||
| Taiwan | 2003-2011 | 16 | 19 | [72] | ||||
| Southeast Asia | Philippines | 2010 | 31.1 | [73] | ||||
| Singapore | 2010 | 23.3 | [73] | |||||
| Thailand | 2010 | 28.7 | [73] | |||||
| Vietnam | 2010 | 46.7 | [73] | |||||
| South Asia | India | 2011 | 32 | [74] | ||||
| Iran | 2011-2012 | 31.8 | 13.5 | 74.4 | [75] | |||
| North Asia | Russia | 2008-2010 | 75.3 | [37] | ||||
| Southwest Asia | Israel | 2009-2011 | 24.7 | [76] | ||||
| Saudi Arabia | 2009-2010 | 56 | 34 | [77] | ||||
| Turkey | 2009-2011 | 49.2 | [76] | |||||
| West Europe | Belgium | 2009-2011 | 41.1 | [76] | ||||
| France | 2009-2011 | 18.2 | [76] | |||||
| Germany | 2009-2011 | 24.4 | [76] | |||||
| Greece | 2011 | 50.0 | [78] | |||||
| Ireland | 2009-2011 | 13.8 | [76] | |||||
| Italy | 2009-2011 | 19.9 | [76] | |||||
| Portugal | 2009-2011 | 35.6 | [76] | |||||
| Spain | 2009-2011 | 21.0 | [76] | |||||
| Switzerland | 2009-2011 | 21.7 | [76] | |||||
| North Europe | Poland | 2009-2011 | 70.7 | [76] | ||||
| Sweden | 2009-2011 | 10.9 | [76] | |||||
| Oceania | Australia | 2011 | 16 | [74] | ||||
| New Zealand | 2010 | 10.3 | [73] | |||||
| North Africa | Algeria | 2009-2012 | 39.3 | [79] | ||||
| East Africa | Kenya | 2006-2007 | 13.7 | [80] | ||||
| South Africa | South Africa | 2006 | 45 | 42 | [81] | |||
| North America | Canada | 2009-2010 | 3.3 | [82] | ||||
| Mexico | 2005-2010 | 22 | [83] | |||||
| US | 2012-2013 | 20 | [84] | |||||
| Central America | Costa Rica | Unavailable | 63.1 | [85] | ||||
| Dominica Republic | 2010 | 8 | 8 | [86] | ||||
| El Salvador | 2010 | 25 | 24 | [86] | ||||
| Guatemala | 2010 | 36 | 34 | [86] | ||||
| Honduras | 2010 | 20 | [86] | |||||
| Nicaragua | 2010 | 32 | 40 | [86] | ||||
| Panama | 2010 | 34 | 23 | [86] | ||||
| South America | Argentina | 2010 | 33 | 37 | [86] | |||
| Bolivia | 2010 | 20 | 14 | [86] | ||||
| Brazil | 2005 | 37-57 | 36-52 | [86] | ||||
| Chile | 2005 | 32-40 | 30-33 | [86] | ||||
| Columbia | 2010 | 17 | 19 | [86] | ||||
| Ecuador | 2010 | 21 | 27 | [86] | ||||
| Paraguay | 2010 | 30 | 30 | [86] | ||||
| Peru | 2010 | 66 | 57 | [86] | ||||
| Uruguay | 2010 | 35 | 43 | [86] | ||||
| Venezuela | 2010 | 33 | [86] | |||||
aCountries are listed in alphabetical order.
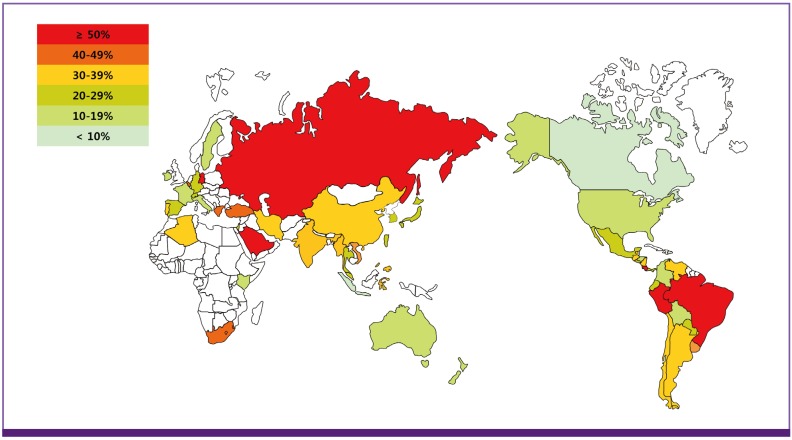
In most countries, the reported CRPA ratio ranged from 10 to 50%. The carbapenem resistance rates in Canada (carbapenem 3.3%) and the Dominican Republic (imipenem and meropenem, both 8%) were the lowest of all countries, with ratios lower than 10%. On the other hand, ratios in Brazil, Peru, Costa Rica, Russia, Greece, Poland, Iran, and Saudi Arabia were higher than 50% in all drugs of the carbapenem class (imipenem, meropenem, doripenem, ertapenem) ranging from 50% to 75.3% (Fig. 1). As shown in Figure 1, Russia, Southwest Asia, and South America were the predominant areas with antimicrobial resistance rates high enough to cause concern for public health to microbiologists and infection specialists.
Figure 1. Geographical distribution of carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Most isolates were collected from 2009 to 2011 with the following exceptions: Chile (2005), Kenya (2006 to 2007), and South Africa (2006). The white colored areas indicate that there was no available published data for that region.
The geographical distribution and ratio of CRPA differed from country to country; many CRPA strains have been identified and their prevalence is increasing gradually. The worldwide emergence of carbepenem-resistant strains with similar mobile genetic elements indicates the dissemination of genes encoding carbapenemases through horizontal gene transfer [26]. The increase in CRPA ratio is known to be driven by both carbapenem use and the application of medical devices, which prompt the selection of resistant organisms [27]. Both factors are related to patient characteristics and clinical practice policies and/or antibiotic prescription patterns of health care facilities in each country.
Resistance mechanisms to carbapenem can be categorized into (1) deficiency of the outer membrane porin OprD, (2) bacterial production of carbapenemases, or (3) overexpression of efflux pump [28,29,30,31,32]. Carbapenem resistance in P. aeruginosa is most often associated with OprD deficiency and less frequently with the release of carbapenemase by the pathogen [33,34,35].
Carbapenemases from each β-lactamase Ambler class have been identified in P. aeruginosa. Of these, Ambler class B β-lactamases are the most clinically significant carbapenemases and are called metallo-β-lactamase (MBL) because a metal ion, such as Zn2+, is essential for their activity, which can be inhibited by metal ion chelators.
Types of metallo-β-lactamases in P. aeruginosa
MBLs efficiently hydrolyze carbapenems and other β-lactams (except monobactams) and are not inhibited by the clinically available β-lactamase inhibitors including clavulanic acid or tazobactam. Except for the SPM-type enzymes, most MBL genes reside within various compositions of integron gene cassettes that are encoded on genes linked to mobile elements, which is a condition that facilitates their spread among different bacterial species and genera through horizontal gene transfer [36,37]. The most notable of the acquired MLBs, the IMP- and VIM-type enzymes, were first detected in the early 1990s [38,39]. Thereafter, many additional types of acquired MBLs have been reported, including the SPM-, GIM-, SIM-, KHM-, NDM-, AIM-, DIM-, SMB-, TMB-, and FIM-type enzymes [40,41]. Since the discovery of IMP-1, which was the first MBL identified in P. aeruginosa, IMP-, VIM-, SPM-, GIM-, NDM- and FIM-type variants in P. aeruginosa have been reported steadily.
Imipenemase (IMP)
In 1988, transferable IMP-1 was first isolated from P. aeruginosa in Japan [38] and was found in a class 1 integron located on a conjugational plasmid. Thereafter, it was identified in many other species suggesting horizontal gene transfer of blaIMP-1 between unrelated Gram-negative species, and also showed predominance of specific IMP type-producing isolates demonstrating clonal expansion [15]. Currently 33 of the 51 known IMP variants have been identified from P. aeruginosa, including the recent detection of IMP-8-producing strains in Germany [42,43] (Table 2). IMP-like enzymes are divided into several subgroups, and the percentage amino acid identity within these subgroups ranges from 90% to 99% showing very similar hydrolytic activities among them [44].
Table 2. Imipenemase-type metallo-β-lactamases found in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
| IMP variant | Frequently identified sequence types | Country of isolation | Reported gene location | Reference(s) or GenBank accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMP-1 | 175, 186, 235, 244, 277, 308, 360, 357, 593, 645, 964, 1,015, 1,070, 1,162 | Japan | C1I | [38, 87] |
| South Korea | C1I | [63] | ||
| Brazil | Unknown | [23] | ||
| China | Unknown | [88] | ||
| Turkey | C1I | [89] | ||
| Singapore | Unknown | [90] | ||
| Thailand | C1I | [91] | ||
| Iran | C1I | [92] | ||
| IMP-2 | NR | Japan | C1I | [93] |
| IMP-4 | NR | Malaysia | Unknown | [94] |
| Australia | C1I | [95] | ||
| China | C1I | [96] | ||
| IMP-5 | NR | Portugal | C1I | [97] |
| IMP-6 | 235, 244, 591, 744, 745, 1,015, 1,162 | South Korea | C1I | [98] |
| China | Unknown | [99] | ||
| IMP-7 | 235, 357, 744, 745 | Canada | C1I | [100] |
| Malaysia | Unknown | [101] | ||
| Slovakia | Unknown | [102] | ||
| Japan | C1I | [103] | ||
| Singapore | Unknown | [90] | ||
| Czech Republic | C1I | [104] | ||
| Denmark | Unknown | [105] | ||
| IMP-8 | 308 | Germany | C1I | [43] |
| IMP-9 | NR | China | C1I | [106] |
| Malaysia | C1I | [107] | ||
| IMP-10 | NR | Japan | C1I | [108] |
| China | C1I | [109] | ||
| IMP-11 | NR | Japan | Unknown | AB074437 |
| IMP-13 | 111, 308, 621 | Austria | C1I | [110] |
| Italy | C1I | [111] | ||
| France | C1I | [112] | ||
| Belgium | C1I | [113] | ||
| IMP-14 | 260 | Thailand | C1I | [114] |
| IMP-15 | 606, 654, 1,446 | Mexico | C1I | [115] |
| Spain | C1I | [116] | ||
| Germany | Unknown | [76] | ||
| IMP-16 | NR | Brazil | C1I | [117] |
| IMP-18 | NR | USA | Unknown | [118] |
| Mexico | C1I | [119] | ||
| Puerto Rico | C1I | [120] | ||
| IMP-19 | 235 | Japan | Unknown | AB184876 |
| Italy | C1I | [121] | ||
| IMP-20 | NR | Japan | C1I | AB196988 |
| IMP-21 | NR | Japan | C1I | AB204557 |
| IMP-22 | 175, 620 | Austria | C1I | [110] |
| Italy | C1I | [122] | ||
| IMP-25 | China | C1I | EU352796 | |
| IMP-26 | 235, 654 | Malaysia | C1I | [123] |
| Singapore | Unknown | [31] | ||
| IMP-29 | 235 | France | C1I | [124] |
| IMP-30 | NR | Russia | Unknown | [125] |
| IMP-31 | 235 | Germany | Unknown | [126] |
| IMP-33 | NR | Italy | C1I | [127] |
| IMP-35 | 622 | Germany | C1I | [128] |
| IMP-37 | 111, 308, 621 | France | Unknown | JX131372 |
| IMP-40 | NR | Japan | Unknown | AB753457 |
| IMP-41 | NR | Japan | Unknown | AB753458 |
| IMP-43 | 235, 357 | Japan | C1I | [129] |
| IMP-44 | 357 | Japan | C1I | [129] |
| IMP-45 | 308 | China | C1I | [130] |
| IMP-48 | NR | USA | Unknown | KM087857 |
IMP, imipenemase; C1I, Class 1 integron; NR, not reported.
Verona integron-encoded metallo-β-lactamase (VIM)
VIM enzymes share the same hydrolytic spectrum the IMP-type enzymes, with less than 40% amino acid identity [45]. VIM-1 was identified first in P. aeruginosa in 1999, and after that, has also been reported in other Gram-negative species from several countries [39]. Currently, VIM-2 is the most widespread MBL in P. aeruginosa and has been the source of multiple outbreaks [44]. Twenty-four of the 46 VIM variants, including VIM-43 found in the USA (GenBank accession number KP096412), have been identified in P. aeruginosa (Table 3).
Table 3. Verona integron-encoded metallo-β-lactamases found in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
| VIM type MBL | Frequently identified sequence type | Country of isolation | Reported gene location | Reference(s) or GenBank accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIM-1 | 17, 111, 227, 228, 235 | Italy | C1I | [39] |
| France | C1I | [131] | ||
| Greece | C1I | [132] | ||
| Germany | Unknown | [76] | ||
| Italy | C1I | [121] | ||
| VIM-2 | 17, 111, 155, 175, 179, 229, 233, 235, 244, 309, 364, 639, 640, 654, 773, 811, 973, 1,020, 1,074, 1,699, 1,700 | Tunisia | C1I | [133] |
| Thailand | Unknown | [114] | ||
| Austria | C1I | [110] | ||
| Mexico | C1I | [115] | ||
| India | Unknown | [134] | ||
| Kenya | Unknown | [80] | ||
| Hungary | C1I | [135] | ||
| Malaysia | C1I | [136] | ||
| South Korea | C1I | [19] | ||
| Japan | C1I | [137] | ||
| France | C1I | [138] | ||
| Greece | C1I | [139] | ||
| Italy | C1I | [140] | ||
| Portugal | C1I | [141] | ||
| Spain | Unknown | [142] | ||
| Croatia | C1I | [143] | ||
| Poland | C1I | [144] | ||
| Chile | C1I | [44] | ||
| Venezuela | C1I | [44] | ||
| Argentina | Unknown | [44] | ||
| USA | C1I | [44] | ||
| Belgium | Unknown | [76] | ||
| Germany | Unknown | [76] | ||
| Turkey | Unknown | [76] | ||
| Egypt | C1I | [145] | ||
| VIM-3 | 298 | Taiwan | Unknown | [146] |
| VIM-4 | 111, 229, 230, 235, 313 | Greece | C1I | [44] |
| Sweden | Unknown | [44] | ||
| Poland | C1I | [44] | ||
| Hungary | C1I | [135, 147] | ||
| France | Unknown | [76] | ||
| VIM-5 | 85, 534 | India | Unknown | [134] |
| Turkey | C1I | [44] | ||
| VIM-6 | 85, 746 | India | C1I | [134] |
| Indonesia | C1I | [148] | ||
| South Korea | C1I | [148] | ||
| Philippines | C1I | [148] | ||
| VIM-7 | NR | USA | C1I | [149] |
| VIM-8 | NR | Columbia | Unknown | [150] |
| VIM-9 | NR | UK | Unknown | AY524988 |
| VIM-10 | NR | UK | Unknown | [151] |
| VIM-11 | NR | India | C1I | [134] |
| Argentina | Unknown | [152] | ||
| Italy | Unknown | AY635904 | ||
| Malaysia | C1I | [136] | ||
| VIM-13 | 235 | Spain | C1I | [153] |
| VIM-14 | 260 | Spain | Unknown | EF055455 |
| Italy | C1I | [154] | ||
| VIM-15 | NR | Bulgaria | C1I | [155] |
| VIM-16 | NR | Germany | C1I | [155] |
| VIM-17 | NR | Greece | C1I | [156] |
| VIM-18 | NR | India | C1I | [134] |
| VIM-20 | NR | Spain | Unknown | [157] |
| VIM-28 | NR | Egypt | C1I | [158] |
| VIM-30 | NR | France | C1I | JN129451 |
| VIM-36 | 111 | Belgium | Unknown | [76] |
| VIM-37 | NR | Poland | Unknown | [76] |
| VIM-38 | NR | Turkey | C1I | [159] |
| VIM-43 | NR | USA | Unknown | KP096412 |
VIM, Verona-integron-encoded metallo-β-lactamase; MBL, metallo-β-lactamase; C1I, Class 1 integron; NR, not reported.
Sao Paulo metallo-β-lactamase (SPM)
SPM-1 was first isolated in Brazil in 1997 from a P. aeruginosa clinical isolate that was resistant to all available antibiotics except colistin [46] (Table 4). SPM is quite different from VIM and IMP, presenting the highest amino acid identity to IMP-1 (35.5%), and represents a new subfamily of MBLs. Dissemination of MDR P. aeruginosa producing SPM-1 was demonstrated in distinct regions of Brazil; however, these strains have not yet spread to other countries, with only one exception of a single isolate identified in a Swiss patient who had previously been hospitalized in Brazil [47,48]. The blaSPM-1 gene has been reported in Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter spp. isolated from various hospitals in Brazil, and its product is a major contributor to the high level carbapenem resistance observed in South America. Currently, the ratio of carbapenem resistance in South America is among the highest in the world [49]. The blaSPM-1 gene is either chromosomal or plasmid-encoded. In addition, it is associated with the insertion sequence common region 4 (ISCR4) at the origin of its acquisition and expression and is likely transposed through a rolling-circle replication mechanism [50].
Table 4. Other metallo-β-lactamases found in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
| MBL enzymes | Frequently identified sequence type | Country of isolation | Reported gene location | Reference(s) or GenBank accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDM-1 | 235 | Serbia | Chromosome | [20] |
| France | Chromosome | [54, 55] | ||
| India | Plasmid | [56] | ||
| Italy | Chromosome | [57] | ||
| Egypt | Unknown | [58] | ||
| Slovakia | Unknown | [59] | ||
| SPM-1 | NR | Brazil | ISCR4 | [160] |
| Switzerland | ISCR4 | [48] | ||
| GIM-1 | NR | Germany | Class 1 Integron, Plasmid | [51, 52] |
| FIM-1 | 235 | Italy | Chromosome | [60] |
MBL, metallo-β-lactamase; NDM, New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase; SPM, Sao Paulo metallo-β-lactamase; NR, not reported; ISCR4, insertion sequence common region 4; GIM, Germany imipenemase; FIM, Florence imipenemase.
Germany imipenemase (GIM)
In 2002, GIM-1 was identified in P. aeruginosa isolates from Germany (Table 4). Molecular analysis revealed that the amino acid sequence identity of GIM-1 with other clinically significant MBL genes, including IMP and VIM variants, was less than 45%, indicating that GIM-1 is a new phylogenetic subclass of MBLs. Initially, this enzyme was not predicted to be mobile because the 22-kb plasmid carrying In77 is nonconjugative and has a restricted host range [51]; however, GIM-1 has also been found in Enterobacter cloacae, Pseudomonas putida, Serratia marcescens, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella oxytoca, and Citrobacter freundii [52]. Molecular analysis of class 1 integron arrays showed that most blaGIM-1 gene cassettes shared identical elements (aacA4, aadA1, and blaOXA-2), which demonstrates horizontal gene transfer of a large block of genetic information [52]. To date, there have been no reports of GIM-1-producing strains outside of Germany.
New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase (NDM)
NDM-1 was first isolated in Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli recovered from a patient who was previously admitted to a hospital in New Delhi, India, in 2009 [53]. Since then, additional six NDM variants (NDM-2 to NDM-7) have been identified in P. aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, and E. coli. NDM-1-producing P. aeruginosa strains were first reported in 2011, with two isolates recovered from Serbia [20] (Table 4). In 2012, NDM-1-producing P. aeruginosa sequence type 235 (ST235) strain was isolated in France from a patient previously hospitalized in Serbia [54,55]. Since then, NDM-1-positive P. aeruginosa isolates have been recovered throughout the world including India, Italy, Egypt, and Slovakia [56,57,58,59].
Florence imipenemase (FIM-1)
In 2012, a novel FIM-1 MBL was isolated from a MDR P. aeruginosa in Florence (Italy) that showed highest similarity (40% amino acid identity) with NDM-type enzymes [60] (Table 4). This isolate belonged to the ST235 epidemic clonal lineage. Anaylsis of the kinetic parameters showed that FIM-1 has a broad substrate specificity, especially with penicillins and carbapenems. The blaFIM-1 gene was chromosomally located and was associated with ISCR19-like elements that were likely involved in its capture and mobilization; its origin remains unknown [60].
Metallo-β-lactamase-producing P. aeruginosa in Korea
VIM-2 was first described in P. aeruginosa isolated from the blood culture of a woman treated with imipenem in Marseilles, France, in 1996 [62]. The first reported MBL in Korea was a VIM-2-producing P. aeruginosa isolated in 2002 [19]. Since then, many MBL enzymes including VIM-2 have been detected in P. aeruginosa, Acinetobacter spp., and Enterobacteriaceae isolates. The prevalence of dominant MBL types has changed with time. In 2003, more than 10% of imipenem-resistant P. aeruginosa produced VIM-2 type MBL, but the ratio of VIM-2 carriage decreased to 7.7% according to a study in 2005, which was followed by IMP-1 at 2.4% and IMP-6 at 0.7% [63,64,65]. In 2011, the ratio of imipenem-resistant P. aeruginosa was 22% among 15,032 clinical isolates in Korea, and IMP-6 became the dominant MBL enzyme in Korea, representing 7.8% of all P. aeruginosa clinical isolates, followed by VIM-2 at 0.3% [66]. This trend in MPPA was also found in 2015; although the prevalence of MPPA in P. aeruginosa clinical isolates slightly decreased from 8.0% (31/386) to 6.4% (21/329), IMP-6 was still the most frequently detected MBL type in P. aeruginosa in Korea, followed by VIM-2 at 1.2% (4/329), which is different from the worldwide prevalence of VIM-2 [66,67,68]. IMP-6 was first identified in Japan in 1996 in plasmid pKU501 from Serratia marcescens KU383. It showed very similar amino acid identity with IMP-1 MBL, differing by only one Ser196Gly amino acid substitution, resulting in augmented hydrolytic activity for meropenem [69].
Molecular analysis demonstrated that ST235 is the most dominant MPPA in Korea [67]. Association of ST235-like strains with MBL genes has been reported in several European countries, with VIM-1-producers in Italy; VIM-4-producers in Greece, Sweden, Hungary and Belgium; VIM-13-producers in Spain; and IMP-29-producers in France [42]. This clone might therefore possess some specific traits enhancing its clonal dissemination. The combination of prevalent sequence types and specific MBL enzymes might suggest the keys to understand the proliferation of resistant strains and mechanisms of gene transfer. Given that MPPA ST235 was the only strain detected in Korea five years ago, it is also worthy to note that MPPA ST309 and ST463 have emerged along with the prevalent MPPA ST235 strain because this clonal diversity might be a sign of alarm for additional dissemination of MPPA in Korea.
Conclusion
The emergence and dissemination of MPPA is a global concern threatening not only immunocompromised patients, but also healthy members of the community. MPPA is an important bacteria due to the antimicrobial resistance characteristics as well as its pathogenicity. It contains multiple antimicrobial resistance genes and has the potential to transfer these to other strains, which is a major clinical problem because of limited treatment options for patients infected with MPPA. There are many obstacles to overcome regarding bacterial resistance. These can be broadly categorized into issues of emergence, spread, and clonal expansion with diversity. These factors are related to each other and are very difficult to control. Several factors are already well known to cause the proliferation of resistant strains, which include natural genetic diversification caused by mutation, horizontal gene transfer among other species, an increase of international travel and patient transfer between countries raising the possibility for further dissemination of resistant strains, and greater antibiotic selective pressure especially in immunocompromised patients who received aggressive and invasive treatment. Further studies on epidemiology, antimicrobial resistance mechanisms, proper antibiotic stewardship, and rapid diagnostic methods for detection of MPPA are recommended in order to develop strategies that contain the dissemination and limit the transmission of MPPA.
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by a grant of the Korean Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (A120843).
Footnotes
Conflicts of Interest: No conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Fischbach MA, Walsh CT. Antibiotics for emerging pathogens. Science. 2009;325:1089–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.1176667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.McDonald LC, Killgore GE, Thompson A, Owens RC, Jr, Kazakova SV, Sambol SP, Johnson S, Gerding DN. An epidemic, toxin gene-variant strain of Clostridium difficile. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2433–2441. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa051590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dorman SE, Chaisson RE. From magic bullets back to the magic mountain: the rise of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Nat Med. 2007;13:295–298. doi: 10.1038/nm0307-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Munoz-Price LS, Weinstein RA. Acinetobacter infection. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1271–1281. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra070741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Oliver A, Canton R, Campo P, Baquero F, Blázquez J. High frequency of hypermutable Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis lung infection. Science. 2000;288:1251–1254. doi: 10.1126/science.288.5469.1251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lautenbach E, Synnestvedt M, Weiner MG, Bilker WB, Vo L, Schein J, Kim M. Imipenem resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: emergence, epidemiology, and impact on clinical and economic outcomes. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2010;31:47–53. doi: 10.1086/649021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Garner MJ, Carson C, Lingohr EJ, Fazil A, Edge VL, Trumble Waddell J. An assessment of antimicrobial resistant disease threats in Canada. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0125155. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rosenthal VD, Bijie H, Maki DG, Mehta Y, Apisarnthanarak A, Medeiros EA, Leblebicioglu H, Fisher D, Álvarez-Moreno C, Khader IA, Del Rocío González Martínez M, Cuellar LE, Navoa-Ng JA, Abouqal R, Guanche Garcell H, Mitrev Z, Pirez García MC, Hamdi A, Dueñas L, Cancel E, Gurskis V, Rasslan O, Ahmed A, Kanj SS, Ugalde OC, Mapp T, Raka L, Yuet Meng C, Thu le TA, Ghazal S, Gikas A, Narváez LP, Mejía N, Hadjieva N, Gamar Elanbya MO, Guzmán Siritt ME, Jayatilleke K INICC members. International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium (INICC) report, data summary of 36 countries, for 2004-2009. Am J Infect Control. 2012;40:396–407. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2011.05.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schneider H, Geginat G, Hogardt M, Kramer A, Dürken M, Schroten H, Tenenbaum T. Pseudomonas aeruginosa outbreak in a pediatric oncology care unit caused by an errant water jet into contaminated siphons. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012;31:648–650. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e31824d1a11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nagao M, Iinuma Y, Igawa J, Saito T, Yamashita K, Kondo T, Matsushima A, Takakura S, Takaori-Kondo A, Ichiyama S. Control of an outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a haemato-oncology unit. J Hosp Infect. 2011;79:49–53. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2011.04.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Caselli D, Cesaro S, Ziino O, Zanazzo G, Manicone R, Livadiotti S, Cellini M, Frenos S, Milano GM, Cappelli B, Licciardello M, Beretta C, Aricò M, Castagnola E Infection Study Group of the Associazione Italiana Ematologia Oncologia Pediatrica (AIEOP) Multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in children undergoing chemotherapy and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica. 2010;95:1612–1615. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2009.020867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bergen PJ, Bulitta JB, Forrest A, Tsuji BT, Li J, Nation RL. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic investigation of colistin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa using an in vitro model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54:3783–3789. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00903-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Johansen HK, Moskowitz SM, Ciofu O, Pressler T, Høiby N. Spread of colistin resistant non-mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa among chronically infected Danish cystic fibrosis patients. J Cyst Fibros. 2008;7:391–397. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2008.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zavascki AP, Carvalhaes CG, Picão RC, Gales AC. Multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii: resistance mechanisms and implications for therapy. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2010;8:71–93. doi: 10.1586/eri.09.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Queenan AM, Bush K. Carbapenemases: the versatile beta-lactamases. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2007;20:440–458. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00001-07. table of contents. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kitao T, Tada T, Tanaka M, Narahara K, Shimojima M, Shimada K, Miyoshi-Akiyama T, Kirikae T. Emergence of a novel multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain producing IMP-type metallo-beta-lactamases and AAC(6')-Iae in Japan. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012;39:518–521. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2012.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Poirel L, Nordmann P, Lagrutta E, Cleary T, Munoz-Price LS. Emergence of KPC-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54:3072. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00513-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wang C, Cai P, Chang D, Mi Z. A Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolate producing the GES-5 extended-spectrum beta-lactamase. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006;57:1261–1262. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkl116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lee K, Lim JB, Yum JH, Yong D, Chong Y, Kim JM, Livermore DM. blaVIM-2 cassette-containing novel integrons in metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas putida isolates disseminated in a Korean hospital. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002;46:1053–1058. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.4.1053-1058.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jovcic B, Lepsanovic Z, Suljagic V, Rackov G, Begovic J, Topisirovic L, Kojic M. Emergence of NDM-1 metallo-beta-lactamase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates from Serbia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011;55:3929–3931. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00226-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Potron A, Poirel L, Nordmann P. Plasmid-mediated transfer of the blaNDM-1 gene in Gram-negative rods. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2011;324:111–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2011.02392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yezli S, Shibl AM, Memish ZA. The molecular basis of beta-lactamase production in Gram-negative bacteria from Saudi Arabia. J Med Microbiol. 2015;64:127–136. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.077834-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Martins AF, Zavascki AP, Gaspareto PB, Barth AL. Dissemination of Pseudomonas aeruginosa producing SPM-1-like and IMP-1-like metallo-beta-lactamases in hospitals from southern Brazil. Infection. 2007;35:457–460. doi: 10.1007/s15010-007-6289-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sevillano E, Gallego L, García-Lobo JM. First detection of the OXA-40 carbapenemase in P. aeruginosa isolates, located on a plasmid also found in A. baumannii. Pathol Biol (Paris) 2009;57:493–495. doi: 10.1016/j.patbio.2008.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.El Garch F, Bogaerts P, Bebrone C, Galleni M, Glupczynski Y. OXA-198, an acquired carbapenem-hydrolyzing class D beta-lactamase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011;55:4828–4833. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00522-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Mendes RE, Bell JM, Turnidge JD, Castanheira M, Jones RN. Emergence and widespread dissemination of OXA-23, -24/40 and -58 carbapenemases among Acinetobacter spp. in Asia-Pacific nations: report from the SENTRY Surveillance Program. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009;63:55–59. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkn434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Voor In 't Holt AF, Severin JA, Lesaffre EM, Vos MC. A systematic review and meta-analyses show that carbapenem use and medical devices are the leading risk factors for carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58:2626–2637. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01758-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yoneyama H, Nakae T. Mechanism of efficient elimination of protein D2 in outer membrane of imipenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993;37:2385–2390. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.11.2385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Borgianni L, Prandi S, Salden L, Santella G, Hanson ND, Rossolini GM, Docquier JD. Genetic context and biochemical characterization of the IMP-18 metallo-beta-lactamase identified in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolate from the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011;55:140–145. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00858-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hocquet D, Plésiat P, Dehecq B, Mariotte P, Talon D, Bertrand X ONERBA. Nationwide investigation of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases, metallo-beta-lactamases, and extended-spectrum oxacillinases produced by ceftazidime-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains in France. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54:3512–3515. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01646-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Koh TH, Khoo CT, Tan TT, Arshad MA, Ang LP, Lau LJ, Hsu LY, Ooi EE. Multilocus sequence types of carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Singapore carrying metallo-beta-lactamase genes, including the novel blaIMP-26 gene. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48:2563–2564. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01905-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Quale J, Bratu S, Gupta J, Landman D. Interplay of efflux system, ampC, and oprD expression in carbapenem resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50:1633–1641. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.5.1633-1641.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bradford PA. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases in the 21st century: characterization, epidemiology, and detection of this important resistance threat. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2001;14:933–951. doi: 10.1128/CMR.14.4.933-951.2001. table of contents. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jacoby GA, Munoz-Price LS. The new beta-lactamases. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:380–391. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra041359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Walsh TR. Clinically significant carbapenemases: an update. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2008;21:367–371. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0b013e328303670b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Partridge SR, Tsafnat G, Coiera E, Iredell JR. Gene cassettes and cassette arrays in mobile resistance integrons. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2009;33:757–784. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Edelstein MV, Skleenova EN, Shevchenko OV, D'Souza JW, Tapalski DV, Azizov IS, Sukhorukova MV, Pavlukov RA, Kozlov RS, Toleman MA, Walsh TR. Spread of extensively resistant VIM-2-positive ST235 Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Russia: a longitudinal epidemiological and clinical study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13:867–876. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70168-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Watanabe M, Iyobe S, Inoue M, Mitsuhashi S. Transferable imipenem resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991;35:147–151. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lauretti L, Riccio ML, Mazzariol A, Cornaglia G, Amicosante G, Fontana R, Rossolini GM. Cloning and characterization of blaVIM, a new integron-borne metallo-beta-lactamase gene from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999;43:1584–1590. doi: 10.1128/aac.43.7.1584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wachino J, Yoshida H, Yamane K, Suzuki S, Matsui M, Yamagishi T, Tsutsui A, Konda T, Shibayama K, Arakawa Y. SMB-1, a novel subclass B3 metallo-beta-lactamase, associated with ISCR1 and a class 1 integron, from a carbapenem-resistant Serratia marcescens clinical isolate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011;55:5143–5149. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05045-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.El Salabi A, Borra PS, Toleman MA, Samuelsen Ø, Walsh TR. Genetic and biochemical characterization of a novel metallo-beta-lactamase, TMB-1, from an Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain isolated in Tripoli, Libya. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012;56:2241–2245. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05640-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Potron A, Poirel L, Nordmann P. Emerging broad-spectrum resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii: Mechanisms and epidemiology. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2015;45:568–585. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2015.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Willmann M, Bezdan D, Zapata L, Susak H, Vogel W, Schröppel K, Liese J, Weidenmaier C, Autenrieth IB, Ossowski S, Peter S. Analysis of a long-term outbreak of XDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a molecular epidemiological study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2015;70:1322–1330. doi: 10.1093/jac/dku546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Walsh TR, Toleman MA, Poirel L, Nordmann P. Metallo-beta-lactamases: the quiet before the storm? Clin Microbiol Rev. 2005;18:306–325. doi: 10.1128/CMR.18.2.306-325.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nordmann P, Poirel L. Emerging carbapenemases in Gram-negative aerobes. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2002;8:321–331. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-0691.2002.00401.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Toleman MA, Simm AM, Murphy TA, Gales AC, Biedenbach DJ, Jones RN, Walsh TR. Molecular characterization of SPM-1, a novel metallo-beta-lactamase isolated in Latin America: report from the SENTRY antimicrobial surveillance programme. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2002;50:673–679. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkf210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Gales AC, Menezes LC, Silbert S, Sader HS. Dissemination in distinct Brazilian regions of an epidemic carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa producing SPM metallo-beta-lactamase. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003;52:699–702. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkg416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Salabi AE, Toleman MA, Weeks J, Bruderer T, Frei R, Walsh TR. First report of the metallo-beta-lactamase SPM-1 in Europe. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54:582. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00719-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Jones RN, Biedenbach DJ, Sader HS, Fritsche TR, Toleman MA, Walsh TR. Emerging epidemic of metallo-beta-lactamase-mediated resistances. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2005;51:77–84. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2004.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Toleman MA, Bennett PM, Walsh TR. ISCR elements: novel gene-capturing systems of the 21st century? Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006;70:296–316. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00048-05. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Castanheira M, Toleman MA, Jones RN, Schmidt FJ, Walsh TR. Molecular characterization of a beta-lactamase gene, blaGIM-1, encoding a new subclass of metallo-beta-lactamase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48:4654–4661. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.12.4654-4661.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Wendel AF, Brodner AH, Wydra S, Ressina S, Henrich B, Pfeffer K, Toleman MA, Mackenzie CR. Genetic characterization and emergence of the metallo-beta-lactamase GIM-1 in Pseudomonas spp. and Enterobacteriaceae during a long-term outbreak. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57:5162–5165. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00118-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Yong D, Toleman MA, Giske CG, Cho HS, Sundman K, Lee K, Walsh TR. Characterization of a new metallo-beta-lactamase gene, blaNDM-1, and a novel erythromycin esterase gene carried on a unique genetic structure in Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 14 from India. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53:5046–5054. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00774-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Flateau C, Janvier F, Delacour H, Males S, Ficko C, Andriamanantena D, Jeannot K, Merens A, Rapp C. Recurrent pyelonephritis due to NDM-1 metallo-beta-lactamase producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a patient returning from Serbia, France, 2012. Euro Surveill. 2012;17:pii: 20311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Janvier F, Jeannot K, Tessé S, Robert-Nicoud M, Delacour H, Rapp C, Mérens A. Molecular characterization of blaNDM-1 in a sequence type 235 Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolate from France. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57:3408–3411. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02334-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Khajuria A, Praharaj AK, Kumar M, Grover N. Emergence of NDM - 1 in the clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in India. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013;7:1328–1331. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2013/5509.3137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Carattoli A, Fortini D, Galetti R, Garcia-Fernandez A, Nardi G, Orazi D, Capone A, Majolino I, Proia A, Mariani B, Parisi G, Morrone A, Petrosillo N. Isolation of NDM-1-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa sequence type ST235 from a stem cell transplant patient in Italy, May 2013. Euro Surveill. 2013;18:pii: 20633. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.es2013.18.46.20633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Zafer MM, Amin M, El Mahallawy H, Ashour MS, Al Agamy M. First report of NDM-1-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Egypt. Int J Infect Dis. 2014;29:80–81. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2014.07.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kulkova N, Babalova M, Sokolova J, Krcmery V. First report of New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase-1-producing strains in Slovakia. Microb Drug Resist. 2015;21:117–120. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2013.0162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Pollini S, Maradei S, Pecile P, Olivo G, Luzzaro F, Docquier JD, Rossolini GM. FIM-1, a new acquired metallo-beta-lactamase from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolate from Italy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57:410–416. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01953-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Yong D, Shin HB, Kim YK, Cho J, Lee WG, Ha GY, Choi TY, Jeong SH, Lee K, Chong Y KONSAR group. Increase in the prevalence of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter isolates and ampicillin-resistant non-typhoidal Salmonella species in Korea: A KONSAR study conducted in 2011. Infect Chemother. 2014;46:84–93. doi: 10.3947/ic.2014.46.2.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Poirel L, Naas T, Nicolas D, Collet L, Bellais S, Cavallo JD, Nordmann P. Characterization of VIM-2, a carbapenem-hydrolyzing metallo-beta-lactamase and its plasmid- and integron-borne gene from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolate in France. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000;44:891–897. doi: 10.1128/aac.44.4.891-897.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Lee K, Lee WG, Uh Y, Ha GY, Cho J, Chong Y Korean Nationwide Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance Group. VIM- and IMP-type metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas spp and Acinetobacter spp. in Korean hospitals. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:868–871. doi: 10.3201/eid0907.030012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Lee K, Ha GY, Shin BM, Kim JJ, Kang JO, Jang SJ, Yong D, Chong Y Korean Nationwide Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance (KONSAR) group. Metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Gram-negative bacilli in Korean Nationwide Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance group hospitals in 2003: continued prevalence of VIM-producing Pseudomonas spp. and increase of IMP-producing Acinetobacter spp. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2004;50:51–58. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2004.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Lee K, Park AJ, Kim MY, Lee HJ, Cho JH, Kang JO, Yong D, Chong Y KONSAR group. Metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas spp. in Korea: high prevalence of isolates with VIM-2 type and emergence of isolates with IMP-1 type. Yonsei Med J. 2009;50:335–339. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.3.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Seok Y, Bae IK, Jeong SH, Kim SH, Lee H, Lee K. Dissemination of IMP-6 metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa sequence type 235 in Korea. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66:2791–2796. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Hong JS, Kim JO, Lee H, Bae IK, Jeong SH, Lee K. Characteristics of metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Korea. Infect Chemother. 2015;47:33–40. doi: 10.3947/ic.2015.47.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Valenza G, Joseph B, Elias J, Claus H, Oesterlein A, Engelhardt K, Turnwald D, Frosch M, Abele-Horn M, Schoen C. First survey of metallo-beta-lactamases in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a German university hospital. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54:3493–3497. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00080-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Yano H, Kuga A, Okamoto R, Kitasato H, Kobayashi T, Inoue M. Plasmid-encoded metallo-beta-lactamase (IMP-6) conferring resistance to carbapenems, especially meropenem. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001;45:1343–1348. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.5.1343-1348.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Xu J, Duan X, Wu H, Zhou Q. Surveillance and correlation of antimicrobial usage and resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a hospital population-based study. PLoS One. 2013;8:e78604. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Kakeya H, Yamada K, Nakaie K, Takizawa E, Okada Y, Fujita A, Nakamura Y, Abe J, Hirose A, Kaneko Y, Hino M. A comparison of susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates to carbapenem antibiotics in our hospital. Jpn J Antibiot. 2014;67:241–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Lee HS, Loh YX, Lee JJ, Liu CS, Chu C. Antimicrobial consumption and resistance in five Gram-negative bacterial species in a hospital from 2003 to 2011. J Microbiol ImmunolInfect. 2014 doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2014.04.009. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Kiratisin P, Chongthaleong A, Tan TY, Lagamayo E, Roberts S, Garcia J, Davies T. Comparative in vitro activity of carbapenems against major Gram-negative pathogens: results of Asia-Pacific surveillance from the COMPACT II study. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012;39:311–316. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2012.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Mendes RE, Mendoza M, Banga Singh KK, Castanheira M, Bell JM, Turnidge JD, Lin SS, Jones RN. Regional resistance surveillance program results for 12 Asia-Pacific nations (2011) Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57:5721–5726. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01121-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Farajzadeh Sheikh A, Rostami S, Jolodar A, Tabatabaiefar MA, Khorvash F, Saki A, Shoja S, Sheikhi R. Detection of metallo-beta lactamases among carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2014;7:e12289. doi: 10.5812/jjm.12289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Castanheira M, Deshpande LM, Costello A, Davies TA, Jones RN. Epidemiology and carbapenem resistance mechanisms of carbapenem-non-susceptible Pseudomonas aeruginosa collected during 2009-11 in 14 European and Mediterranean countries. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014;69:1804–1814. doi: 10.1093/jac/dku048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Mansour SA, Eldaly O, Jiman-Fatani A, Mohamed ML, Ibrahim EM. Epidemiological characterization of P. aeruginosa isolates of intensive care units in Egypt and Saudi Arabia. East Mediterr Health J. 2013;19:71–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Liakopoulos A, Mavroidi A, Katsifas EA, Theodosiou A, Karagouni AD, Miriagou V, Petinaki E. Carbapenemase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa from central Greece: molecular epidemiology and genetic analysis of class I integrons. BMC Infect Dis. 2013;13:505. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Sefraoui I, Berrazeg M, Drissi M, Rolain JM. Molecular epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical strains isolated from western Algeria between 2009 and 2012. Microb Drug Resist. 2014;20:156–161. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2013.0161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Pitout JD, Revathi G, Chow BL, Kabera B, Kariuki S, Nordmann P, Poirel L. Metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from a large tertiary centre in Kenya. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2008;14:755–759. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2008.02030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Brink A, Moolman J, da Silva MC, Botha M National Antibiotic Surveillance Forum. Antimicrobial susceptibility profile of selected bacteraemic pathogens from private institutions in South Africa. S Afr Med J. 2007;97:273–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Mataseje LF, Bryce E, Roscoe D, Boyd DA, Embree J, Gravel D, Katz K, Kibsey P, Kuhn M, Mounchili A, Simor A, Taylor G, Thomas E, Turgeon N, Mulvey MR Canadian Nosocomial Infection Surveillance Program. Carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacilli in Canada 2009-10: results from the Canadian Nosocomial Infection Surveillance Program (CNISP) J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012;67:1359–1367. doi: 10.1093/jac/dks046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Morfin-Otero R, Tinoco-Favila JC, Sader HS, Salcido-Gutierrez L, Perez-Gomez HR, Gonzalez-Diaz E, Petersen L, Rodriguez-Noriega E. Resistance trends in gram-negative bacteria: surveillance results from two Mexican hospitals, 2005-2010. BMC Res Notes. 2012;5:277. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-5-277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Perez F, Hujer AM, Marshall SH, Ray AJ, Rather PN, Suwantarat N, Dumford D, 3rd, O'Shea P, Domitrovic TN, Salata RA, Chavda KD, Chen L, Kreiswirth BN, Vila AJ, Haussler S, Jacobs MR, Bonomo RA. Extensively drug-resistant pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates containing blaVIM-2 and elements of Salmonella genomic island 2: a new genetic resistance determinant in Northeast Ohio. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58:5929–5935. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02372-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Toval F, Guzmán-Marte A, Madriz V, Somogyi T, Rodríguez C, García F. Predominance of carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates carrying blaIMP and blaVIM metallo-beta-lactamases in a major hospital in Costa Rica. J Med Microbiol. 2015;64:37–43. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.081802-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Labarca JA, Salles MJ, Seas C, Guzmán-Blanco M. Carbapenem resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii in the nosocomial setting in Latin America. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2014 doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2014.940494. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Mano Y, Saga T, Ishii Y, Yoshizumi A, Bonomo RA, Yamaguchi K, Tateda K. Molecular analysis of the integrons of metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates collected by nationwide surveillance programs across Japan. BMC Microbiol. 2015;15:41. doi: 10.1186/s12866-015-0378-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Qu TT, Zhang JL, Wang J, Tao J, Yu YS, Chen YG, Zhou JY, Li LJ. Evaluation of phenotypic tests for detection of metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains in China. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:1136–1142. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01592-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Ozgumus OB, Caylan R, Tosun I, Sandalli C, Aydin K, Koksal I. Molecular epidemiology of clinical Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates carrying IMP-1 metallo-beta-lactamase gene in a University Hospital in Turkey. Microb Drug Resist. 2007;13:191–198. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2007.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Koh TH, Wang GC, Sng LH. Clonal spread of IMP-1-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa in two hospitals in Singapore. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:5378–5380. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.11.5378-5380.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Boonkerd N, Pibalpakdi P, Tiloklurs M, Niumsup PR. Class 1 integron containing metallo beta-lactamase gene blaIMP-1 in carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Thailand. J Infect Chemother. 2009;15:257–261. doi: 10.1007/s10156-009-0684-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Fallah F, Borhan RS, Hashemi A. Detection of blaIMP and blaVIM metallo-beta-lactamases genes among Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. Int J Burns Trauma. 2013;3:122–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Shibata N, Doi Y, Yamane K, Yagi T, Kurokawa H, Shibayama K, Kato H, Kai K, Arakawa Y. PCR typing of genetic determinants for metallo-beta-lactamases and integrases carried by gram-negative bacteria isolated in Japan, with focus on the class 3 integron. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41:5407–5413. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.12.5407-5413.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Bert F, Vanjak D, Leflon-Guibout V, Mrejen S, Delpierre S, Redondo A, Nicolas-Chanoine MH. IMP-4-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a French patient repatriated from Malaysia: impact of early detection and control measures. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44:764–765. doi: 10.1086/511693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Peleg AY, Franklin C, Bell JM, Spelman DW. Dissemination of the metallo-beta-lactamase gene blaIMP-4 among gram-negative pathogens in a clinical setting in Australia. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41:1549–1556. doi: 10.1086/497831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Hawkey PM, Xiong J, Ye H, Li H, M'Zali FH. Occurrence of a new metallo-beta-lactamase IMP-4 carried on a conjugative plasmid in Citrobacter youngae from the People's Republic of China. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2001;194:53–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2001.tb09445.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Brízio A, Conceição T, Pimentel M, Da Silva G, Duarte A. High-level expression of IMP-5 carbapenemase owing to point mutation in the -35 promoter region of class 1 integron among Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2006;27:27–31. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2005.08.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Ryoo NH, Lee K, Lim JB, Lee YH, Bae IK, Jeong SH. Outbreak by meropenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa producing IMP-6 metallo-beta-lactamase in a Korean hospital. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009;63:115–117. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2008.08.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Chen Y, Sun M, Wang M, Lu Y, Yan Z. Dissemination of IMP-6-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa ST244 in multiple cities in China. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014;33:1181–1187. doi: 10.1007/s10096-014-2063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Gibb AP, Tribuddharat C, Moore RA, Louie TJ, Krulicki W, Livermore DM, Palepou MF, Woodford N. Nosocomial outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa with a new blaIMP allele, blaIMP-7. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002;46:255–258. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.1.255-258.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Ho SE, Subramaniam G, Palasubramaniam S, Navaratnam P. Carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in malaysia producing IMP-7 beta-lactamase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002;46:3286–3287. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.10.3286-3287.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Ohlasova D, Kmet V, Niks M. First report of the carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa producing IMP-7 metallo-beta-lactamase in Slovakia. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2007;30:370–371. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2007.06.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Kouda S, Kuwahara R, Ohara M, Shigeta M, Fujiwara T, Komatsuzawa H, Usui T, Sugai M. First isolation of blaIMP-7 in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Japan. J Infect Chemother. 2007;13:276–277. doi: 10.1007/s10156-007-0520-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Hrabák J, Fridrichová M, Stolbová M, Bergerová T, Zemlickova H, Urbaskova P. First identification of metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the Czech Republic. Euro Surveill. 2009;14:pii: 19102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Hammerum AM, Jakobsen L, Hansen F, Stegger M, Sørensen LA, Andersen PS, Wang M. Characterisation of an IMP-7-producing ST357 Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolate detected in Denmark using whole genome sequencing. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2015;45:200–201. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2014.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Xiong J, Hynes MF, Ye H, Chen H, Yang Y, M'Zali F, Hawkey PM. blaIMP-9 and its association with large plasmids carried by Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from the People's Republic of China. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50:355–358. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.1.355-358.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Lim KT, Yasin RM, Yeo CC, Puthucheary SD, Balan G, Maning N, Wahab ZA, Ismail N, Tan EA, Mustaffa A, Thong KL. Genetic fingerprinting and antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa hospital isolates in Malaysia. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2009;42:197–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Iyobe S, Kusadokoro H, Takahashi A, Yomoda S, Okubo T, Nakamura A, O'Hara K. Detection of a variant metallo-beta-lactamase, IMP-10, from two unrelated strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and an alcaligenes xylosoxidans strain. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002;46:2014–2016. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.6.2014-2016.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Zhao WH, Chen G, Ito R, Hu ZQ. Relevance of resistance levels to carbapenems and integron-borne blaIMP-1, blaIMP-7, blaIMP-10 and blaVIM-2 in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Med Microbiol. 2009;58:1080–1085. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.010017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Duljasz W, Gniadkowski M, Sitter S, Wojna A, Jebelean C. First organisms with acquired metallo-beta-lactamases (IMP-13, IMP-22, and VIM-2) reported in Austria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53:2221–2222. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01573-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Pagani L, Colinon C, Migliavacca R, Labonia M, Docquier JD, Nucleo E, Spalla M, Li Bergoli M, Rossolini GM. Nosocomial outbreak caused by multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa producing IMP-13 metallo-beta-lactamase. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43:3824–3828. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.8.3824-3828.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Fournier D, Jeannot K, Robert-Nicoud M, Muller E, Cholley P, van der Mee-Marquet N, Plésiat P. Spread of the blaIMP-13 gene in French Pseudomonas aeruginosa through sequence types ST621, ST308 and ST111. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012;40:571–573. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2012.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Naas T, Bogaerts P, Kostyanev T, Cuzon G, Huang TD, Ozsu S, Nordmann P, Glupczynski Y. Silent spread of IMP-13-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa belonging to sequence type 621 in Belgium. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66:2178–2179. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Piyakul C, Tiyawisutsri R, Boonbumrung K. Emergence of metallo-beta-lactamase IMP-14 and VIM-2 in Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates from a tertiary-level hospital in Thailand. Epidemiol Infect. 2012;140:539–541. doi: 10.1017/S0950268811001294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Quinones-Falconi F, Galicia-Velasco M, Marchiaro P, Mussi MA, Ballerini V, Vila AJ, Viale AM, Bermejo-Morales K, Limansky AS. Emergence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains producing metallo-beta-lactamases of the IMP-15 and VIM-2 types in Mexico. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010;16:126–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02780.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Gilarranz R, Juan C, Castillo-Vera J, Chamizo FJ, Artiles F, Álamo I, Oliver A. First detection in Europe of the metallo-beta-lactamase IMP-15 in clinical strains of Pseudomonas putida and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013;19:E424–E427. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Mendes RE, Toleman MA, Ribeiro J, Sader HS, Jones RN, Walsh TR. Integron carrying a novel metallo-beta-lactamase gene, blaIMP-16, and a fused form of aminoglycoside-resistant gene aac(6')-30/aac(6')-Ib': report from the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48:4693–4702. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.12.4693-4702.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Hanson ND, Hossain A, Buck L, Moland ES, Thomson KS. First occurrence of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolate in the United States producing an IMP metallo-beta-lactamase, IMP-18. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50:2272–2273. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01440-05. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Garza-Ramos U, Tinoco P, Silva-Sanchez J, Morfin-Otero R, Rodriguez-Noriega E, Leon-Garnica G, Sader HS, Jones RN. Metallo-beta-lactamase IMP-18 is located in a class 1 integron (In96) in a clinical isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Mexico. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2008;31:78–80. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2007.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Wolter DJ, Khalaf N, Robledo IE, Vázquez GJ, Santé MI, Aquino EE, Goering RV, Hanson ND. Surveillance of carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from Puerto Rican Medical Center Hospitals: dissemination of KPC and IMP-18 beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53:1660–1664. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01172-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Pollini S, Antonelli A, Venturelli C, Maradei S, Veggetti A, Bracco S, Rumpianesi F, Luzzaro F, Rossolini GM. Acquisition of plasmid-borne blaIMP-19 gene by a VIM-1-positive Pseudomonas aeruginosa of the sequence type 235 epidemic lineage. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013;68:722–724. doi: 10.1093/jac/dks440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Pellegrini C, Mercuri PS, Celenza G, Galleni M, Segatore B, Sacchetti E, Volpe R, Amicosante G, Perilli M. Identification of blaIMP-22 in Pseudomonas spp. in urban wastewater and nosocomial environments: biochemical characterization of a new IMP metallo-enzyme variant and its genetic location. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009;63:901–908. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkp061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Kim MJ, Bae IK, Jeong SH, Kim SH, Song JH, Choi JY, Yoon SS, Thamlikitkul V, Hsueh PR, Yasin RM, Lalitha MK, Lee K. Dissemination of metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa of sequence type 235 in Asian countries. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013;68:2820–2824. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkt269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Jeannot K, Poirel L, Robert-Nicoud M, Cholley P, Nordmann P, Plésiat P. IMP-29, a novel IMP-type metallo-beta-lactamase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012;56:2187–2190. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05838-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Pegg KM, Liu EM, Lacuran AE, Oelschlaeger P. Biochemical characterization of IMP-30, a metallo-beta-lactamase with enhanced activity toward ceftazidime. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57:5122–5126. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02341-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Pfennigwerth N, Geis G, Gatermann SG, Kaase M. Description of IMP-31, a novel metallo-beta-lactamase found in an ST235 Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain in Western Germany. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2015 doi: 10.1093/jac/dkv079. [Epub ahed of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Deshpande LM, Davies TA, Blandino G, Nicoletti G, Jones RN, Castanheira M. IMP-33, a New IMP variant detected in Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Sicily. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57:6401–6403. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02532-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Pournaras S, Köck R, Mossialos D, Mellmann A, Sakellaris V, Stathopoulos C, Friedrich AW, Tsakris A. Detection of a phylogenetically distinct IMP-type metallo-beta-lactamase, IMP-35, in a CC235 Pseudomonas aeruginosa from the Dutch-German border region (Euregio) J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013;68:1271–1276. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkt004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Tada T, Miyoshi-Akiyama T, Shimada K, Shimojima M, Kirikae T. IMP-43 and IMP-44 metallo-beta-lactamases with increased carbapenemase activities in multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57:4427–4432. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00716-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Wang Y, Wang X, Schwarz S, Zhang R, Lei L, Liu X, Lin D, Shen J. IMP-45-producing multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa of canine origin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014;69:2579–2581. doi: 10.1093/jac/dku133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Corvec S, Poirel L, Decousser JW, Allouch PY, Drugeon H, Nordmann P. Emergence of carbapenem-hydrolysing metallo-beta-lactamase VIM-1 in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates in France. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006;12:941–942. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.1532_1.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Tsakris A, Pournaras S, Woodford N, Palepou MF, Babini GS, Douboyas J, Livermore DM. Outbreak of infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa producing VIM-1 carbapenemase in Greece. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:1290–1292. doi: 10.1128/jcm.38.3.1290-1292.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Mansour W, Poirel L, Bettaieb D, Bouallegue O, Boujaafar N, Nordmann P. Metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates in Tunisia. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009;64:458–461. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2009.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Castanheira M, Bell JM, Turnidge JD, Mathai D, Jones RN. Carbapenem resistance among Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains from India: evidence for nationwide endemicity of multiple metallo-beta-lactamase clones (VIM-2, -5, -6, and -11 and the newly characterized VIM-18) Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53:1225–1227. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01011-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Libisch B, Watine J, Balogh B, Gacs M, Muzslay M, Szabó G, Füzi M. Molecular typing indicates an important role for two international clonal complexes in dissemination of VIM-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates in Hungary. Res Microbiol. 2008;159:162–168. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2007.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Khosravi Y, Tee Tay S, Vadivelu J. Metallo-beta-lactamase-producing imipenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates in a university teaching hospital in Malaysia: detection of IMP-7 and first identification of IMP-4, VIM-2, and VIM-11. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010;67:294–296. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2010.02.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Yatsuyanagi J, Saito S, Harata S, Suzuki N, Ito Y, Amano K, Enomoto K. Class 1 integron containing metallo-beta-lactamase gene blaVIM-2 in Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical strains isolated in Japan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48:626–628. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.2.626-628.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Poirel L, Collet L, Nordmann P. Carbapenem-hydrolyzing metallo-beta-lactamase from a nosocomial isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in France. Emerg Infect Dis. 2000;6:84–85. doi: 10.3201/eid0601.000117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Poole K. Overcoming multidrug resistance in gram-negative bacteria. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2003;4:128–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Pallecchi L, Riccio ML, Docquier JD, Fontana R, Rossolini GM. Molecular heterogeneity of blaVIM-2-containing integrons from Pseudomonas aeruginosa plasmids encoding the VIM-2 metallo-beta-lactamase. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2001;195:145–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2001.tb10512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Cardoso O, Leitão R, Figueiredo A, Sousa JC, Duarte A, Peixe LV. Metallo-beta-lactamase VIM-2 in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Portugal. Microb Drug Resist. 2002;8:93–97. doi: 10.1089/107662902760190635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Prats G, Miro E, Mirelis B, Poirel L, Bellais S, Nordmann P. First isolation of a carbapenem-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Spain. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002;46:932–933. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.3.932-933.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Sardelic S, Pallecchi L, Punda-Polic V, Rossolini GM. Carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa-carrying VIM-2 metallo-beta-lactamase determinants, Croatia. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:1022–1023. doi: 10.3201/eid0908.020373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Walsh TR, Toleman MA, Hryniewicz W, Bennett PM, Jones RN. Evolution of an integron carrying blaVIM-2 in Eastern Europe: report from the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003;52:116–119. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkg299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Zafer MM, Al-Agamy MH, El-Mahallawy HA, Amin MA, El Din Ashour S. Dissemination of VIM-2 producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa ST233 at tertiary care hospitals in Egypt. BMC Infect Dis. 2015;15:122. doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-0861-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Yan JJ, Hsueh PR, Ko WC, Luh KT, Tsai SH, Wu HM, Wu JJ. Metallo-beta-lactamases in clinical Pseudomonas isolates in Taiwan and identification of VIM-3, a novel variant of the VIM-2 enzyme. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001;45:2224–2228. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.8.2224-2228.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Libisch B, Gacs M, Csiszár K, Muzslay M, Rókusz L, Füzi M. Isolation of an integron-borne blaVIM-4 type metallo-beta-lactamase gene from a carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolate in Hungary. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48:3576–3578. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.9.3576-3578.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Castanheira M, Bell JM, Turnidge JD, Mendes RE, Jones RN. Dissemination and genetic context analysis of blaVIM-6 among Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates in Asian-Pacific Nations. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010;16:186–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Toleman MA, Rolston K, Jones RN, Walsh TR. blaVIM-7, an evolutionarily distinct metallo-beta-lactamase gene in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolate from the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48:329–332. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.1.329-332.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Crespo MP, Woodford N, Sinclair A, Kaufmann ME, Turton J, Glover J, Velez JD, Castañeda CR, Recalde M, Livermore DM. Outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa producing VIM-8, a novel metallo-beta-lactamase, in a tertiary care center in Cali, Colombia. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:5094–5101. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.11.5094-5101.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Woodford N, Zhang J, Kaufmann ME, Yarde S, Tomas Mdel, M, Faris C, Vardhan MS, Dawson S, Cotterill SL, Livermore DM. Detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates producing VEB-type extended-spectrum beta-lactamases in the United Kingdom. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008;62:1265–1268. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkn400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Marchiaro P, Tomatis PE, Mussi MA, Pasteran F, Viale AM, Limansky AS, Vila AJ. Biochemical characterization of metallo-beta-lactamase VIM-11 from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical strain. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008;52:2250–2252. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01025-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Juan C, Beceiro A, Gutiérrez O, Albertí S, Garau M, Pérez JL, Bou G, Oliver A. Characterization of the new metallo-beta-lactamase VIM-13 and its integron-borne gene from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolate in Spain. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008;52:3589–3596. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00465-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Mazzariol A, Mammina C, Koncan R, Di Gaetano V, Di Carlo P, Cipolla D, Corsello G, Cornaglia G. A novel VIM-type metallo-beta-lactamase (VIM-14) in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolate from a neonatal intensive care unit. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011;17:722–724. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Schneider I, Keuleyan E, Rasshofer R, Markovska R, Queenan AM, Bauernfeind A. VIM-15 and VIM-16, two new VIM-2-like metallo-beta-lactamases in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from Bulgaria and Germany. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008;52:2977–2979. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00175-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Siarkou VI, Vitti D, Protonotariou E, Ikonomidis A, Sofianou D. Molecular epidemiology of outbreak-related Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains carrying the novel variant blaVIM-17 metallo-beta-lactamase gene. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53:1325–1330. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01230-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Riera E, Cabot G, Mulet X, García-Castillo M, del Campo R, Juan C, Cantón R, Oliver A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa carbapenem resistance mechanisms in Spain: impact on the activity of imipenem, meropenem and doripenem. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66:2022–2027. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.El-Mahdy TS. Identification of a novel metallo-beta-lactamase VIM-28 located within unusual arrangement of class 1 integron structure in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from Egypt. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2014;67:382–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Iraz M, Duzgun AO, Cicek AC, Bonnin RA, Ceylan A, Saral A, Nordmann P, Sandalli C. Characterization of novel VIM carbapenemase, VIM-38, and first detection of GES-5 carbapenem-hydrolyzing beta-lactamases in Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Turkey. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014;78:292–294. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2013.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Poirel L, Magalhaes M, Lopes M, Nordmann P. Molecular analysis of metallo-beta-lactamase gene blaSPM-1-surrounding sequences from disseminated Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates in Recife, Brazil. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48:1406–1409. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.4.1406-1409.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]