Figure 4. SUMOylation of K590 at Shp2 promotes ERK activation.
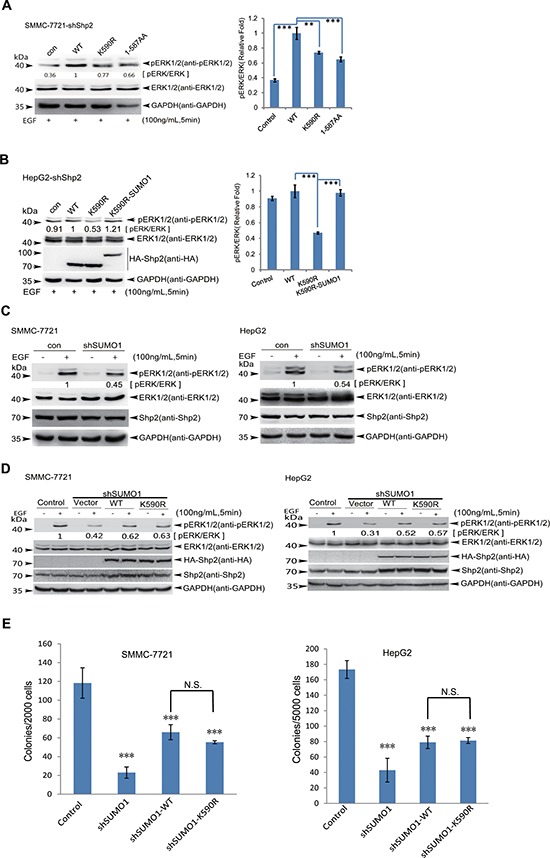
(A) SMMC-7721-shShp2 cells stably re-expressing Shp2WT, Shp2K590R or -truncated form (amino acids 1–587) were starved overnight, and then stimulated by EGF for 5 min. Cell lysates were used for immunoblotting analysis of phospho-ERK1/2, ERK1/2 and GAPDH (left panels). The data are presented as the mean ± s.d. (n = 3) (right panels). (B) HepG2-shShp2 cells stably re-expressing Shp2WT, Shp2K590R or Shp2K590R-SUMO1 (a fusion construct) were stimulated with EGF for 5 min as before, and then the ERK activities were determined by Western blotting (left panels). The data are presented as the mean ± s.d. (n = 3) (right panels). (C) Endogenous SUMO1 in SMMC 7721 and HepG2 was knockdown by a short hairpin RNA targeting 3′-UTR of SUMO1 mRNA (shSUMO1) by using lentiviral vector pLKO.1 system, and the ERK1/2 activities were determined. (D) SMMC-7721-shSUMO1 and HepG2-shSUMO1 stably expressing Shp2WT or Shp2K590R cells were serum-starved, and then stimulated with 100 ng/mL of EGF for 5 min, and the ERK activities were determined by Western blotting. (E) Soft agar colony forming assays, HepG2-shSUMO1 and SMMC-7721-shSUMO1 stably expressing Shp2WT or Shp2K590R cells were seeded in 2 ml of medium containing 5% FBS with 0.35% agar at 1 × 104 and 2 × 103 cells/well, respectively. The photographs were taken 20 days later and the number of colonies was scored. Each value represents the mean ± s.e.m. of three independent experiments with triplicates each.
