Abstract
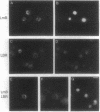
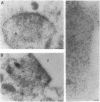
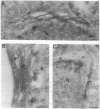
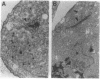
We have expressed human lamin B and the chicken lamin B receptor (LBR), either separately or together, in yeast and have monitored the subcellular location of the expressed proteins by immunofluorescence microscopy, immunoelectron microscopy, and cell fractionation. At the light microscopic level, the heterologous lamin B localized to the yeast nuclear rim and at electron microscopic resolution was found subjacent to the yeast inner nuclear membrane. These data indicate that vertebrate lamin B was correctly targeted in yeast. Expression of the heterologous LBR, either alone or together with the heterologous lamin B, resulted in the formation of membrane stacks primarily adjacent to the nuclear envelope, but also projecting from the nuclear envelope into the cytoplasm or under the plasma membrane. Double immunoelectron microscopy showed colocalization of the heterologous lamin B and LBR in the yeast nuclear envelope and in the LBR-induced membrane stacks. Cell fractionation showed the presence of the heterologous lamin B and LBR in a subnuclear fraction enriched in nuclear envelopes. The heterologous lamin B was extracted at 8 M urea, but not at 4 M urea, thus behaving as a peripheral membrane protein and indistinguishable from assembled lamins. The heterologous LBR was not extracted by 8 M urea, indicating that it was integrated into the membrane. The observed colocalization and cofractionation are consistent with previously reported in vitro binding data and suggest that heterologous lamin B and LBR interact with each other when coexpressed in yeast.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailer S. M., Eppenberger H. M., Griffiths G., Nigg E. A. Characterization of A 54-kD protein of the inner nuclear membrane: evidence for cell cycle-dependent interaction with the nuclear lamina. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(3):389–400. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.3.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck L. A., Hosick T. J., Sinensky M. Isoprenylation is required for the processing of the lamin A precursor. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1489–1499. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary N., Courvalin J. C. Stepwise reassembly of the nuclear envelope at the end of mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(2):295–306. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. N., Capieaux E., Balzi E., Goffeau A. The YGL022 gene encodes a putative transport protein. Yeast. 1991 Apr;7(3):305–308. doi: 10.1002/yea.320070313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courvalin J. C., Lassoued K., Worman H. J., Blobel G. Identification and characterization of autoantibodies against the nuclear envelope lamin B receptor from patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):961–967. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch T., Peter M., Nurse P., Nigg E. A. p34cdc2 acts as a lamin kinase in fission yeast. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(5):797–807. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.5.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnsworth C. C., Wolda S. L., Gelb M. H., Glomset J. A. Human lamin B contains a farnesylated cysteine residue. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20422–20429. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. Z., Chaudhary N., Blobel G. cDNA sequencing of nuclear lamins A and C reveals primary and secondary structural homology to intermediate filament proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6450–6454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foisner R., Gerace L. Integral membrane proteins of the nuclear envelope interact with lamins and chromosomes, and binding is modulated by mitotic phosphorylation. Cell. 1993 Jul 2;73(7):1267–1279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90355-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgatos S. D., Maroulakou I., Blobel G. Lamin A, lamin B, and lamin B receptor analogues in yeast. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2069–2082. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Blobel G. The nuclear envelope lamina is reversibly depolymerized during mitosis. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Blum A., Blobel G. Immunocytochemical localization of the major polypeptides of the nuclear pore complex-lamina fraction. Interphase and mitotic distribution. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):546–566. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Simons K., Warren G., Tokuyasu K. T. Immunoelectron microscopy using thin, frozen sections: application to studies of the intracellular transport of Semliki Forest virus spike glycoproteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:466–485. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Yocum R. R., Gifford P. A GAL10-CYC1 hybrid yeast promoter identifies the GAL4 regulatory region as an upstream site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höger T. H., Krohne G., Franke W. W. Amino acid sequence and molecular characterization of murine lamin B as deduced from cDNA clones. Eur J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;47(2):283–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. H., Bard M., Pierson C. A., Alexander J. F., Goebl M., Carter G. T., Kirsch D. R. The identification of a gene family in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ergosterol biosynthesis pathway. Gene. 1994 Mar 11;140(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90728-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz R. T., Parks L. W. Cloning, sequencing, and disruption of the gene encoding sterol C-14 reductase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;11(9):685–692. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz R. J., Trujillo M. A., Denham K. S., Wenger L., Sinensky M. Nucleoplasmic localization of prelamin A: implications for prenylation-dependent lamin A assembly into the nuclear lamina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3000–3004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon F. D., Kirschner M. W., Caput D. Homologies in both primary and secondary structure between nuclear envelope and intermediate filament proteins. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):463–468. doi: 10.1038/319463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard K. M., Chan E. K., Grant B. J., Sullivan K. F., Tan E. M., Glass C. A. In vitro posttranslational modification of lamin B cloned from a human T-cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2164–2175. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. R., Adams A. E., Drubin D. G., Haarer B. K. Immunofluorescence methods for yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:565–602. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94043-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radu A., Blobel G., Wozniak R. W. Nup155 is a novel nuclear pore complex protein that contains neither repetitive sequence motifs nor reacts with WGA. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(1):1–9. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts C. J., Raymond C. K., Yamashiro C. T., Stevens T. H. Methods for studying the yeast vacuole. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:644–661. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94047-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rout M. P., Kilmartin J. V. Components of the yeast spindle and spindle pole body. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):1913–1927. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.1913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severs N. J., Jordan E. G., Williamson D. H. Nuclear pore absence from areas of close association between nucleus and vacuole in synchronous yeast cultures. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Mar;54(3):374–387. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimanuki M., Goebl M., Yanagida M., Toda T. Fission yeast sts1+ gene encodes a protein similar to the chicken lamin B receptor and is implicated in pleiotropic drug-sensitivity, divalent cation-sensitivity, and osmoregulation. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Mar;3(3):263–273. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.3.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small G. M., Imanaka T., Shio H., Lazarow P. B. Efficient association of in vitro translation products with purified stable Candida tropicalis peroxisomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1848–1855. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S., Blobel G. The first membrane spanning region of the lamin B receptor is sufficient for sorting to the inner nuclear membrane. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(3):631–637. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T. A technique for ultracryotomy of cell suspensions and tissues. J Cell Biol. 1973 May;57(2):551–565. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.2.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Niman H. L., Houghten R. A., Cherenson A. R., Connolly M. L., Lerner R. A. The structure of an antigenic determinant in a protein. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90412-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worman H. J., Evans C. D., Blobel G. The lamin B receptor of the nuclear envelope inner membrane: a polytopic protein with eight potential transmembrane domains. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1535–1542. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worman H. J., Yuan J., Blobel G., Georgatos S. D. A lamin B receptor in the nuclear envelope. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8531–8534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R. Insights from inducible membranes. Curr Biol. 1993 Dec 1;3(12):870–873. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90221-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]