Abstract
Barley yellow dwarf virus-GPV (BYDV-GPV) is transmitted by Rhopalosiphum padi and Schizaphis graminum in a persistent nonpropagative manner. To improve our understanding of its transmission mechanism by aphid vectors, we used two approaches, isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ) and yeast two-hybrid (YTH) system, to identify proteins in R. padi that may interact with or direct the spread of BYDV-GPV along the circulative transmission pathway. Thirty-three differential aphid proteins in viruliferous and nonviruliferous insects were identified using iTRAQ coupled to 2DLC-MS/MS. With the yeast two-hybrid system, 25 prey proteins were identified as interacting with the readthrough protein (RTP) and eight with the coat protein (CP), which are encoded by BYDV-GPV. Among the aphid proteins identified, most were involved in primary energy metabolism, synaptic vesicle cycle, the proteasome pathway and the cell cytoskeleton organization pathway. In a systematic comparison of the two methods, we found that the information generated by the two methods was complementary. Taken together, our findings provide useful information on the interactions between BYDV-GPV and its vector R. padi to further our understanding of the mechanisms regulating circulative transmission in aphid vectors.
The Barley yellow dwarf viruses (BYDVs, genus Luteovirus or Polerovirus, family Luteoviridae) are economically important pathogens of wheat, barley, maize, oat and pasture grasses in the world1. They are phloem-limited viruses transmitted by different cereal aphids in a persistent nonpropagative manner2. At least 25 aphid species have been reported as vectors of BYDVs, but each virus is transmitted by only one or few aphid species3,4. In China, four BYDV species have been reported, namely, BYDV-GAV, -GPV, -PAV, and -RMV, respectively5,6,7. Of these four, BYDV-GPV, which is transmitted efficiently by Rhopalosiphum padi and Schizaphis graminum, is treated as an unassigned member of the family Luteoviridae in the most recent ICTV’s Virus Taxonomy Report8. The complete nucleotide sequence of BYDV-GPV was determined in 2009; its genome comprises 5673 nucleotides with six predicted open reading frames (ORFs) and three untranslated regions (UTRs), similar to the genome of poleroviruses9. Comparisons between different open reading frames (ORFs) of the genomes of BYDV-GPV, other poleroviruses and luteoviruses demonstrated that the virus encodes two structural proteins, the major coat protein (CP) and the readthrough protein (RTP), which are responsible for composition of the viral capsid and playing an important role in transmission by the aphids9,10.
Early work on BYDV transmission by aphids focused on the description of primary aphid species based on transmission efficiency and quantitative parameters, such as the time required for virus acquisition by an aphid on an infected plant, the length of time the infectious virus is retained, and the time required for efficient transmission into a new healthy plant3,4. This early work was followed by extensive electron microscopy studies on the transport pathway of the virus within the aphid vectors2,11. The virus crosses the gut epithelium at the posterior midgut and/or hindgut level via transcytosis and exits these cells by exocytosis to enter the hemocoel12,13. Once released from the posterior midgut and/or hindgut, BYDVs are believed to diffuse passively into the hemolymph until they encounter putative receptors located specifically at the basal lamina of the salivary gland cells. They then invade the salivary gland cells, also involving endocytosis and exocytosis, from where they will be introduced into the plant host during insect feeding14,15. So, the viruses must encounter and overcome different barriers in the posterior midgut and/or hindgut and salivary gland cells for successful persistent transmission; thus, specific interactions between components of the virus and its vector are necessary16.
Recent investigations have resulted in a better understanding of the virus and aphid proteins involved in overcoming transmission barriers in the aphid vectors. In the family Luteoviridae, both the CP and RTP have been implicated in aphid transmission17,18. Several proteins of Myzus persicae were found to bind to the virion of Beet western yellows virus, including the receptor for activated C kinase (Rack-1), actin, and glyceradehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH3), which may be involved in the epithelial transcytosis of virus particles in the aphid vectors19. Two proteins, SaM50 and SaM35 from Sitobion avenae and S. graminum showed high affinity for BYDV-MAV or -GAV and contributed to viral transmission specificity20,21. Four aphid proteins, including luciferase and cyclophilin, which have been implicated in macromolecular transport, were found to be specifically associated with the ability of S. graminum to transmit Cereal yellow dwarf virus (CYDV)-RPV22,23. Cilia et al. (2011)24 used 2-D fluorescence difference gel eletrophoresis (DIGE) of proteins from an F2 generation derived from hybrids between clones of S. graminum that differed in transmission efficiency for CYDV-RPV to identify proteins correlated with a transmission phenotype that was stably inherited and expressed in the absence of the virus. They found that the specificity of virus transmission by aphids was due to quantitative and heritable proteomic variation and possibly derived from allele-specific variation in the genetic loci encoding for these proteins24.
Although new advances have been made in our understanding of the transmission mechanism of viruses in the family Luteoviridae by their respective aphid vectors, few studies have focused specifically on the interaction between BYDV-GPV and its insect vector R. padi. In recent years, some new techniques have been used to study the interaction between the host, pathogen and vector. Isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ) is one platform for quantitative proteomics to compare changes in the abundance of specific proteins between different samples25,26. The yeast two-hybrid (YTH) system is also proving to be a powerful tool for proteomic-based investigations and has become a pivotal tool to study uncharacterized protein-protein interactions27,28. In this study, we took advantage of the two approaches to identify proteins in R. padi that may interact with and/or mediate the spread of BYDV-GPV in the aphid vectors. A comparison of the data obtained by two methods could also provide useful information regarding intrinsic merits and constraints of these methods.
Results
Identification of differential proteins in viruliferous and nonviruliferous Rhopalosiphum padi using iTRAQ
Proteins from samples of aphids with 0 h, 12 h, 24 h and 48 h acquisition access period (AAP) on oat plants infected with BYDV-GPV were identified and quantified using 4 plex iTRAQ labeling combined with LC-MS/MS analysis (Fig. 1). In total, we identified 628 proteins, with false discovery rates (FDR) less than 0.01 for the sample sets. These identified proteins were then filtered using population statistics to obtain a list of proteins that differed significantly between the viruliferous and healthy samples. Proteins with a 50% increase or decrease in abundance (iTRAQ ratios greater than 1.5 or less than 0.667) and a significant p-value (p < 0.05) were considered to be significantly differential. A strict cutoff value of a 1.5-fold change resulted in a final set of 33 differential proteins. A complete list of proteins identified in this study, and the details on the proteomic data, including sequence coverage, number of unique peptides, ratios between different samples, and functional pathways, are listed in Table 1.
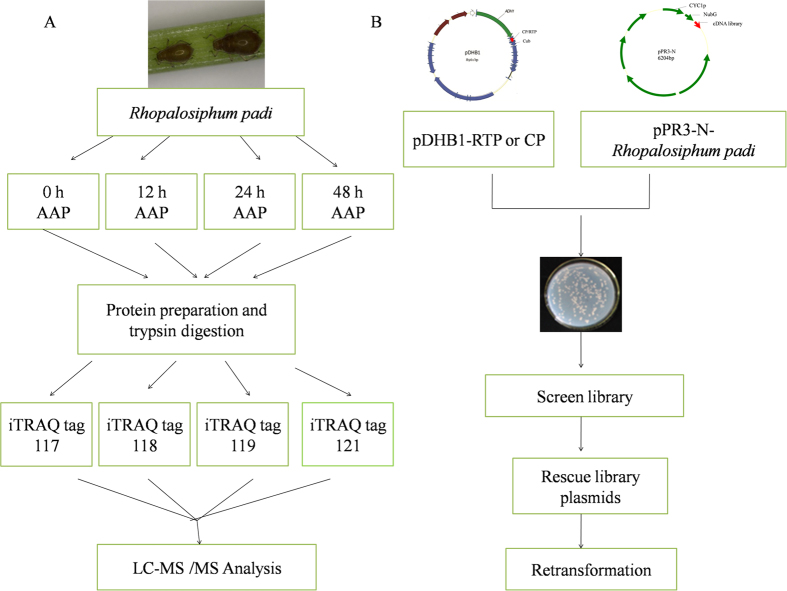
Figure 1. Schematic of iTRAQ design.
(A) and yeast two-hybrid screen design (B). iTRAQ experiment was carried out using the vector aphids Rhopalosiphum padi, which were allowed a 0, 12, 24 or 48 h acquisition access period (AAP) on BYDV-GPV-infected oat plants. Proteins were digested by trypsin, and four iTRAQ labels were used: tag 117 for the 0 h AAP, tag 118 for the 12 h AAP, tag 119 for the 24 h AAP and tag 121 for the 48 h AAP. After labeling, peptides from all four samples were combined and fractionated by chromatography. Each fraction was then analyzed by LC-MS/MS. For yeast two-hybrid screen, the ORFs of BYDV-RTD/BYDV-CP were constructed individually in the yeast expression vector pDHB1, and the cDNA library of R. padi was constructed in prey plasmid pPR3-N. The cDNA library of R. padi was then screened and positive plasmids were rescued. The prey plasmid and bait plasmid were then used to cotransform yeast strain NMY51 to eliminate false positive hits.
Table 1. Differential proteins between healthy and viruliferous Rhopalosiphum padi as identified by iTRAQ.
| 12 h AAPc : 0 h AAP |
24 h AAP : 0 h AAP |
48 h AAP : 0 h AAP |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein and pathway | %Cov (95)a | Peptides (95%)b | Ratiod | Pvale | Ratio | PVal | Ratio | PVal | Accession |
| Metabolic pathways | |||||||||
| PREDICTED: glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial-like isoform 4 | 14.58 | 16 | 4.09 | 0.0204 | 0.92 | 0.7964 | 0.43 | 0.2628 | gi|328709677 |
| PREDICTED: glutamate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial-like | 36.31 | 30 | 3.91 | 0.0004 | 2.11 | 0.0162 | 2.25 | 0.0503 | gi|193582510 |
| ATP synthase subunit beta, mitochondrial | 55.47 | 75 | 3.22 | 0.0204 | 3.56 | 0.0155 | 0.76 | 0.5102 | gi|209915626 |
| putative mitochondrial ATP synthase alpha subunit precursor | 49.00 | 63 | 3.56 | 0.0136 | 3.22 | 0.0204 | 0.96 | 0.3627 | gi|52630965 |
| PREDICTED: probable aconitate hydratase, mitochondrial-like | 21.17 | 23 | 2.99 | 0.0195 | 1.11 | 0.3415 | 0.29 | 0.4397 | gi|328716624 |
| PREDICTED: acetyl-CoA carboxylase-like isoform 4 | 24.69 | 74 | 2.03 | 0.0075 | 2.11 | 0.0035 | 1.53 | 0.0795 | gi|328714419 |
| PREDICTED: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase-like | 42.17 | 32 | 0.25 | 0.0353 | 1.13 | 0.3332 | 0.17 | 0.0047 | gi|193688110 |
| PREDICTED: glucosamine-fructose-6-phosphate aminotransferase [isomerizing] 2-like isoform 1 | 8.09 | 7 | 0.21 | 0.0464 | 0.58 | 0.1816 | 0.36 | 0.0977 | gi|328718712 |
| PREDICTED: elongation factor 2-like | 31.64 | 49 | 0.16 | 0.0001 | 0.94 | 0.3257 | 0.33 | 0.0180 | gi|193690671 |
| ATP citrate lyase | 41.21 | 60 | 1.28 | 0.7255 | 3.16 | 0.0238 | 2.19 | 0.1524 | gi|237874159 |
| peroxiredoxin-6-like | 49.09 | 18 | 2.25 | 0.0613 | 2.29 | 0.0436 | 2.01 | 0.0231 | gi|240848687 |
| PREDICTED: NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] flavoprotein 1, mitochondrial-like | 13.28 | 7 | 0.94 | 0.8571 | 0.44 | 0.1259 | 0.06 | 0.0067 | gi|193587168 |
| Ribosome | |||||||||
| PREDICTED: 40 S ribosomal protein S8-like | 46.15 | 21 | 0.23 | 0.0114 | 0.92 | 0.9471 | 0.69 | 0.5592 | gi|328709805 |
| 40 S ribosomal protein S2-like | 40.38 | 21 | 0.08 | 0.0397 | 1.24 | 0.8129 | 1.45 | 0.9157 | gi|240849555 |
| ribosomal protein S13e-like | 29.14 | 5 | 0.17 | 0.0229 | 0.70 | 0.3303 | 1.29 | 0.7132 | gi|242247489 |
| uncharacterized protein LOC100165190 | 2.79 | 1 | 0.90 | 0.8412 | 1.04 | 0.9312 | 0.01 | 0.0453 | gi|350535082 |
| ACYPI010200 | 31.98 | 17 | 0.21 | 0.0281 | 0.67 | 0.7261 | 0.44 | 0.4620 | gi|239789423 |
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | |||||||||
| PREDICTED: vinculin-like | 18.15 | 17 | 1.42 | 0.0361 | 1.67 | 0.0350 | 1.61 | 0.0497 | gi|193606151 |
| PREDICTED: myosin heavy chain, muscle isoform 1 | 49.72 | 233 | 9.64 | 4.43E-05 | 5.40 | 1.06E-05 | 1.75 | 0.1814 | gi|328702403 |
| Signaling pathway | |||||||||
| PREDICTED: voltage-dependent anion-selective channel-like isoform 1 | 25.27 | 10 | 0.95 | 0.3256 | 1.32 | 0.3841 | 0.17 | 0.0160 | gi|193690508 |
| putative activated protein kinase C receptor | 54.86 | 24 | 0.54 | 0.0629 | 0.58 | 0.0984 | 0.45 | 0.0496 | gi|52630921 |
| Protein processing | |||||||||
| PREDICTED: heat shock protein 83-like | 44.37 | 63 | 0.31 | 0.0867 | 0.58 | 0.0554 | 0.28 | 0.0450 | gi|193652748 |
| PREDICTED: translocon-associated protein subunit gamma-like | 5.95 | 2 | 1.07 | 0.8883 | 1.14 | 0.7876 | 0.01 | 0.0498 | gi|328698093 |
| Synaptic vesicle cycle | |||||||||
| vesicle-associated membrane protein-like | 31.43 | 4 | 0.01 | 0.0478 | 0.86 | 0.7880 | 0.38 | 0.2442 | gi|240848629 |
| RNA degradation | |||||||||
| symbionin symL-pea aphid | 39.05 | 56 | 0.28 | 0.0021 | 0.47 | 0.1640 | 0.13 | 0.0173 | gi|285430 |
| Unknown | |||||||||
| myofilin isoform a | 42.59 | 16 | 5.30 | 0.0365 | 2.78 | 0.2643 | 2.56 | 0.1109 | gi|253735723 |
| PREDICTED: paramyosin, long form-like | 44.71 | 81 | 2.54 | 0.0027 | 1.89 | 0.0377 | 0.63 | 0.9907 | gi|328724595 |
| PREDICTED: staphylococcal nuclease domain-containing protein 1-like | 34.02 | 49 | 0.43 | 0.0047 | 0.65 | 0.2712 | 0.43 | 0.0128 | gi|193688302 |
| cuticular protein 62 precursor | 32.87 | 9 | 2.13 | 0.1359 | 0.44 | 0.0262 | 0.60 | 0.1887 | gi|288558725 |
| PREDICTED: KH domain-containing, RNA-binding, signal transduction-associated protein 3-like | 20.23 | 10 | 0.77 | 0.0560 | 0.85 | 0.6793 | 0.63 | 0.0059 | gi|193688146 |
| putative histone h4-like protein, partial | 52.48 | 23 | 1.20 | 0.4071 | 0.96 | 0.8159 | 0.62 | 0.0376 | gi|604788259 |
| glutathione S-transferase delta 1 | 26.56 | 6 | 0.51 | 0.1068 | 1.64 | 0.3014 | 0.25 | 0.0351 | gi|392584108 |
| PREDICTED: hypothetical protein LOC100164538 | 46.15 | 67 | 0.24 | 0.1818 | 0.74 | 0.6521 | 0.02 | 0.0481 | gi|193706873 |
aPercentage of matching amino acids from identified peptides having confidence ≥95%.
bNumber of distinct wpeptides having at least 95% confidence.
cAcquisition access period (AAP) on BYDV-GPV-infected wheat plants.
dFold-change between two samples, ratio >1 represented up-regulation, ratio <1 represented down-regulation.
fEvaluation of significance of fold-change.
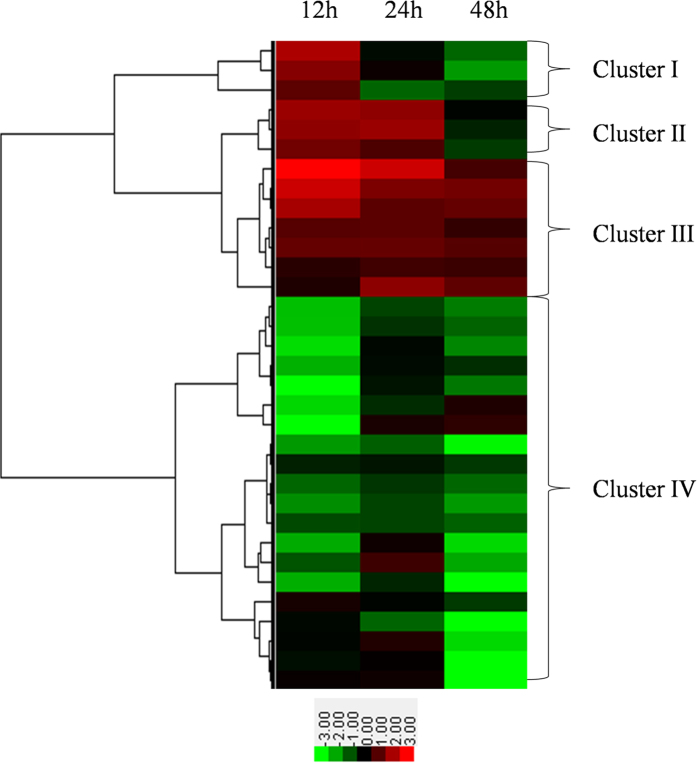
Using the entire set of quantitative data, we further characterized changes in abundance of these differential proteins. We performed cluster analysis by combining the protein abundance data and the sampling time points and using a hierarchical clustering algorithm according to the program instructions. With the proteome of a nonviruliferous aphid as a reference, the 33 differential proteins were clustered into 4 clusters (Fig. 2). Only 3 proteins grouped in cluster I and 3 in cluster II. The abundance of the proteins in cluster I increased after a 12 h acquisition access period (AAP) but subsequently decreased. Proteins in cluster II increased in abundance beginning at 12 h AAP, continued to increase in abundance through 24 h AAP, then decreased. These proteins were likely to be active only during a specific process. Most of the proteins, however, belonged to cluster III and cluster IV. Seven proteins in cluster III were always upregulated in viruliferous aphids compared with nonviruliferous aphids after 12 h, 24 h and 48 h AAP. The largest group was cluster IV, which contained 20 proteins that in general decreased in abundance.
Figure 2. Cluster analysis of differential proteins by hierarchical clustering algorithm.
The three columns from left to right are labeled 12, 24 and 48 h AAP at the top of the heat map. The right braces indicate the four groups classified by cluster analysis. The lower panel is the color key for fold-change. Red represents up-regulation, green represents down-regulation; the brighter the image, the greater the fold-change.
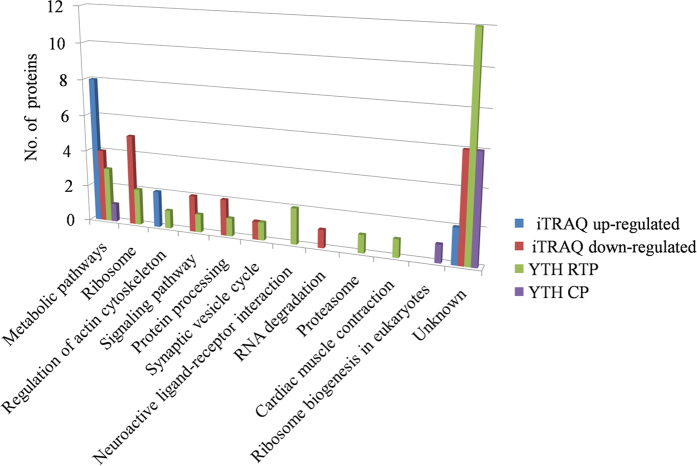
All the differential proteins were also functionally annotated according to biological process, cellular component and molecular function using Uniprot (http://www.uniprot.org) and DAVID (http://david.abcc. ncifcrf.gov/). The prevalent biological processes of the up-regulated proteins were metabolic processes, proton transport and locomotion, while down-regulated proteins, most were in translation, gene silencing and protein refolding. The most up-regulated proteins were cellular components of ATP synthase complex and myosin complex, while down-regulated proteins were assigned to ribosome, membrane and SNARE complex. The molecular functions of up-regulated proteins were motor activity and enzymatic activity, while major functional categories of down-regulated proteins were structural molecule activity, binding activity and dehydrogenase activity. (Fig. 3A,B). The pathways analysis of these differential proteins using the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database (http://www.kegg.jp/kegg/pathway.html) showed that up-regulated proteins basically involved in regulation of actin cytoskeleton and energy and primary metabolism, while down-regulated proteins participated mainly in ribosome, signaling pathway, RNA degradation and synaptic vesicle cycle (Fig. 4).
Figure 3. Functional annotation of.
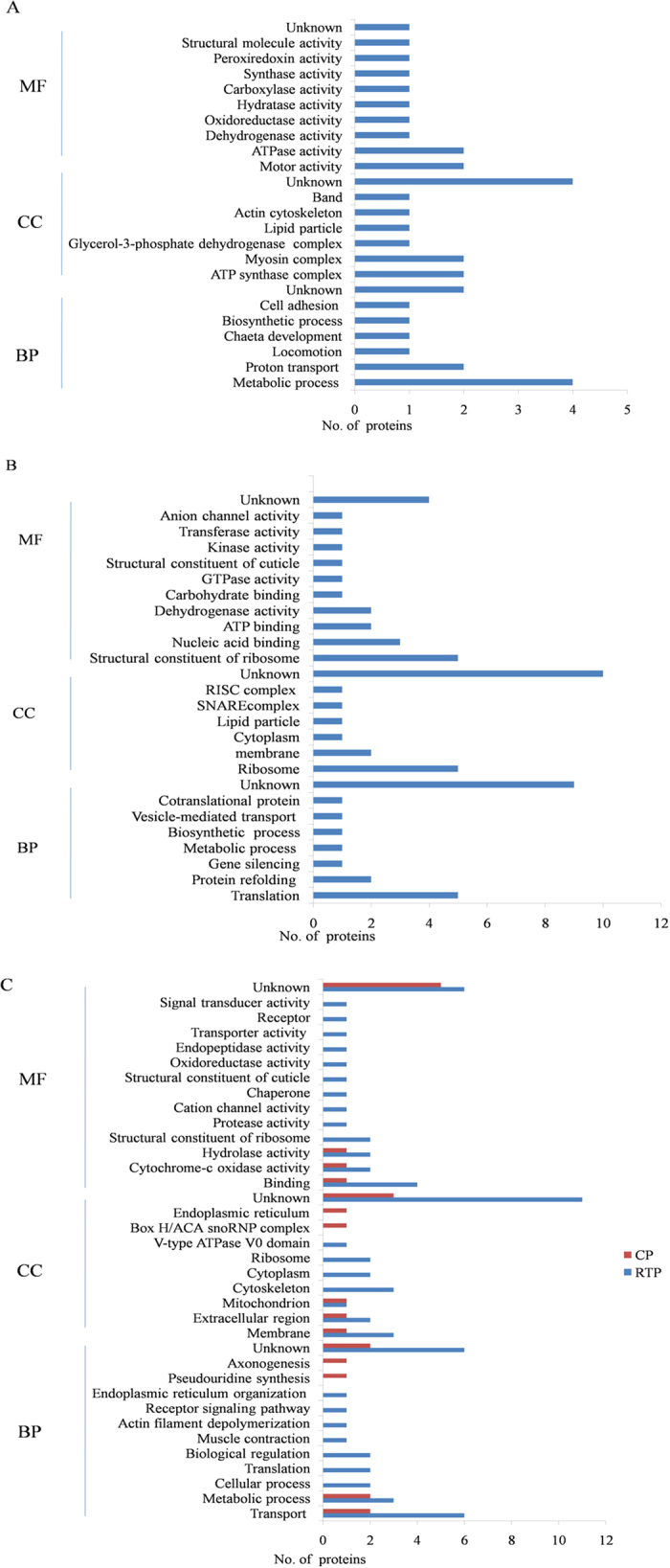
(A) up-regulated proteins, (B) down-regulated proteins identified with iTRAQ and (C) proteins identified from yeast two-hybrid screen. Three main categories were identified: biological process (BP), cellular component (CC) and molecular function (MF). The x-axis represents the number of proteins.
Figure 4. Pathway analysis of proteins identified by iTRAQ and YTH.
The y-axis represents the number of proteins.
Verification of mRNA expression level for three representative proteins (myosin, paramyosin and vinculin) by RT-qPCR
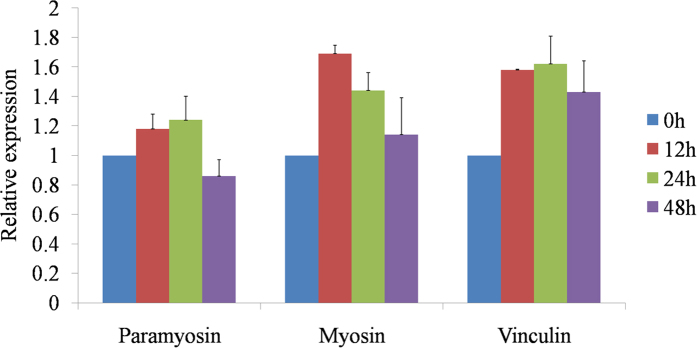
To further confirm the results of iTRAQ and compare the correlation between mRNA transcription level and protein abundances, three representative proteins (myosin, paramyosin and vinculin) were selected based on the functional annotation and verified for mRNA transcription level by RT-qPCR. Myosin and vinculin were always up-regulated after 12, 24 and 48 h AAP. Paramyosin was up-regulated after 12 and 24 h AAP and down-regulated after 48 h AAP. These results for mRNA transcription level for the selected genes showed the same trends as in the results obtained with the iTRAQ analysis (Fig. 5).
Figure 5. RT-qPCR validation at mRNA transcription level of iTRAQ abundance results for three proteins (myosin, paramyosin and vinculin).
Interactions of the proteomes between Barley yellow dwarf virus-GPV and its insect vector, Rhopalosiphum padi, by yeast two-hybrid assay
In the present study, we identified protein interactions between BYDV-GPV using RTP or CP as the bait and the cDNA library of R. padi as the prey in a yeast two-hybrid system (Fig. 1B). To confirm that the bait fusion protein was functionally well expressed in the assay without auto-activation activity, each set of plasmids was used to cotransform NMY51 cells, which were then plated on selective SD medium (synthetic double-dropout medium [DDO: SD/-Leu/-Trp]/synthetic triplex-dropout medium [TDO: SD/-His /-Leu/-Trp]/synthetic quadruple-dropout medium [QDO: SD/−Ade/−His/−Leu/−Trp]). The result of the co-expression (pDHB1-RTP or pDHB1-CP bait vector with the control prey plasmid Ost1-NubI) was the same as the positive control. This set of plasmids enables the expression of reporter genes and thus growth on QDO selective medium. Coexpression of the bait protein with the NubG-nonsense peptide fusion vector (pPR3-N fusion vector) did not result in split ubiquitin formation; thus no yeast transformants grew on QDO plate (Supplementary Figure S1).
In the preliminary library screen of the pDHB1-RTP bait/pPR3-N-R.padi cDNA prey, we obtained 350 yeast colonies from TDO medium and 280 from pDHB1-CP bait/pPR3-N-R.padi cDNA prey. When the potentially positive clones that exhibited bait protein-protein interactions were taken from the TDO medium and streaked onto QDO medium, 87 clones acting as prey proteins grew on QDO medium from the pDHB1-RTP bait, and 46 clones acting as prey proteins grew on QDO medium from the pDHB1-CP bait. All sequences were used to search for reference sequences using BLASTX against the nonredundant (nr) NCBI protein database (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi). We identified 25 prey proteins that interacted with RTP of BYDV-GPV and eight that interacted with the CP of the virus, and five prey proteins that were common to the two bait groups. A complete list of proteins identified in this assay, and the details of BLAST data including e-value, identity and pathway are listed in the Table 2.
Table 2. Putative proteins of Rhopalosiphum padi that interacted with the CP or RTP of Barley yellow dwarf virus-GPV in a yeast two-hybrid assay.
| Protein description and pathway | e-Value | Identity | Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolic pathways | |||
| V-type proton ATPase subunit db | 2.00E-34 | 98% | NP_001191854.1 |
| Pancreatic lipase-related proteinab | 9.70E-02 | 32% | EGI64115.1 |
| Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolaseb | 1.00E-105 | 81% | XP_008186680.1 |
| Ribosome | |||
| ribosomal protein L30-like proteinb | 3.00E-07 | 100% | NP_001119630.1 |
| 60 S ribosomal protein L8-likeb | 2.4 | 100% | NP_001155749.1 |
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | |||
| Twinstarb | 1.00E-46 | 99% | NP_001119642.1 |
| Signaling pathway | |||
| guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(s) subunit alphab | 0.032 | 100% | XP_001944148.1 |
| Protein processing | |||
| t-complex protein 1 subunit theta-likeb | 0.32 | 100% | XP_001944638.1 |
| Synaptic vesicle cycle | |||
| complexinb | 1.00E-25 | 99% | NP_001156645.1 |
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | |||
| neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-7-likeb | 2.00E-35 | 97% | XP_001945224.2 |
| glutamate receptor ionotropic kainate 3-like isoform X3b | 3.00E-56 | 98% | XP_003242706.1 |
| Proteasome | |||
| proteasome beta 3 subunit-likeb | 3.00E-147 | 98% | NP_001155482.1 |
| Cardiac muscle contraction | |||
| tropomyosinb | 6.00E-91 | 85% | XP_008178569.1 |
| Ribosome biogenesis in eukaryotes | |||
| H/ACA ribonucleoproteina | 1.00E-24 | 96% | XP_003248969.1 |
| Unknown | |||
| cytochrome P450 4g15b | 4.00E-31 | 94% | XP_001944205.2 |
| cytochrome c oxidase polypeptide IV-likeab | 5.00E-109 | 93% | NP_001156047.1 |
| nascent polypeptide-associated complex subunit alphaab | 1.00E-94 | 99% | NP_001156301.1 |
| cytochrome c oxidase subunit Va-likeb | 3.00E-97 | 89% | NP_001156232.1 |
| cuticular protein 5 precursorb | 6.00E-40 | 97% | NP_001156154.1 |
| chemosensory protein-like precursorb | 1.00E-58 | 94% | NP_001119652.1 |
| coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix domain containingab | 3.00E-35 | 97% | NP_001155450.1 |
| titin-likeb | 0 | 86% | XP_008188078.1 |
| fibronectin type 3 domainb | 3.00E-05 | 69% | XP_008180552.1 |
| serine/arginine repetitive matrix protein 1ab | 2.00E-10 | 97% | XP_003242057.1 |
| Cu(I)-responsive transcriptional regulatorb | 3.00E-14 | 75% | XP_001948052.2 |
| jagunal homologb | 4.00E-44 | 97% | NP_001155727.1 |
| mitochondrial import inner membrane translocase subunit Tim22 isoform X1a | 9.00E-71 | 95% | XP_003245191.1 |
| EMI domain-containing proteina | 2.00E-60 | 85% | XP_001948474.2 |
aPrey proteins identified by bait BYDV-GPV CP.
bProteins identified by bait BYDV-GPV RTP.
abPrey proteins identified by both bait BYDV-GPV CP and RTP.
For the Gene Ontology (GO) annotation using the same database, 25 proteins screened using the BYDV-GPV RTP bait were assigned to 9 categories of biological process, mainly for transport, metabolic process, muscle contraction and actin filament depolymerization; 7 categories of cellular components, mainly in membranes, extracellular region and cytoskeleton; and 13 categories of molecular function, mainly with binding activity, cytochrome-c oxidase activity and transporter activity (Fig. 3C). In the pathways analysis of these proteins using the KEGG database, the proteins were basically involved in metabolic pathways, ribosome, regulation of actin cytoskeleton and synaptic vesicle cycle (Fig. 4). Eight proteins screened using the BYDV-GPV CP bait were assigned to 4 categories of biological process, mainly for transport and metabolic process; 5 categories of cellular components, mainly in membranes and extracellular region; and 3 categories of molecular function, mainly with binding activity and cytochrome-c oxidase activity (Fig. 3C). They were basically involved in metabolic pathways and ribosome biogenesis in eukaryotes (Fig. 4).
Verification of the yeast two-hybrid results using a retransformation assay and chemiluminescent CO-IP assay
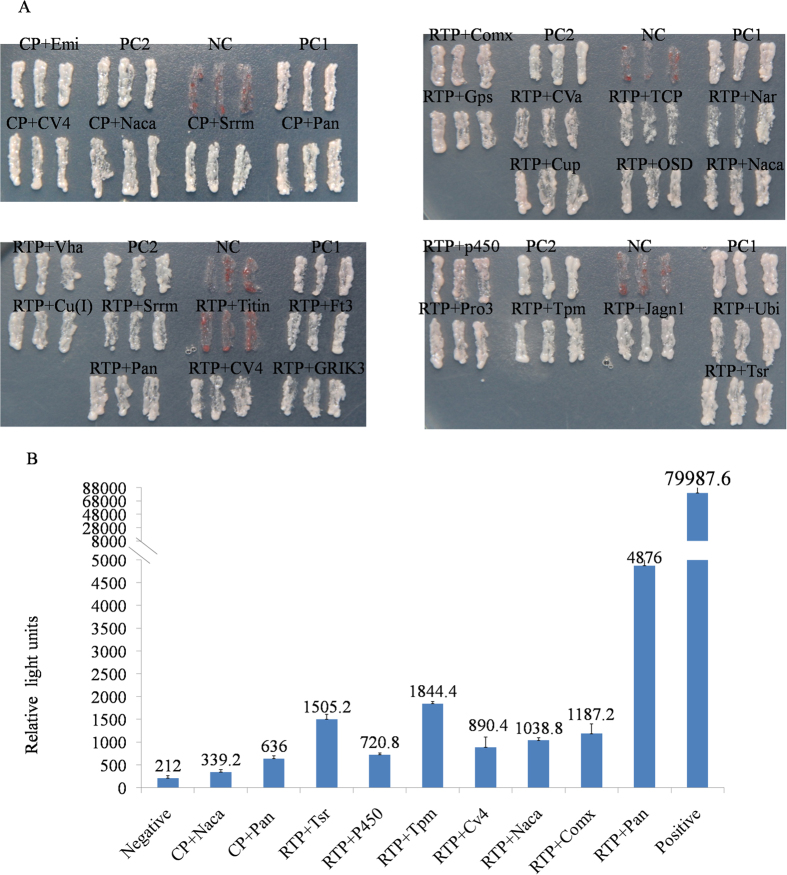
To eliminate false positive hits and retest the specificity of the interactions, we did retransformation confirmation assays. We selected 22 candidate prey plasmids screened with the pDHB1-RTP bait and 5 screened with the pDHB1-CP bait for the interaction analysis. We thus identified 19 proteins that interacted strongly with pDHB1-RTP, 2 prey proteins (T-complex protein 1 subunit theta-like and cytochrome c oxidase subunit Va-like) interacted weakly with pDHB1-RTP, and 1 prey protein (titin) did not interact with pDHB1-RTP. We identified 5 proteins that interacted strongly with pDHB1-CP (Fig. 6A).
Figure 6.
(A) Confirmation of protein-protein interactions by retransformation assay. Bait plasmids (pDHB1-GPV-RTP or pDHB1-GPV-CP bait plasmids) were cotransformed with the prey fusion proteins in yeast strain NMY51. Potential interactions were assessed by plating the transformants on SD/-Ade/-His/-Leu/-Trp (QDO) medium and incubating them for 3-4 days at 30 °C. (B) Confirmation of protein-protein interactions using a chemiluminescent Co-IP assay. We examined the interactions of the BYDV-GPV RTP bait and the BYDV-GPV CP bait with positive prey proteins in HEK293T mammalian cells. After substrate addition, the relative strength and interaction of the resulting signal for pProLabel activity were measured with a GloMax 96 Microplate Luminometer and expressed as relative light units. Protein abbreviations. Emi: EMI domain-containing protein, CV4: cytochrome c oxidase polypeptide IV-like, Naca: nascent polypeptide-associated complex subunit alpha, Srrm: serine/arginine repetitive matrix, Pan: pancreatic lipase-related protein, Comx: complexin, Gps: guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(s) subunit alpha, CVa: cytochrome c oxidase subunit Va-like, TCP: T-complex protein 1 subunit theta-like, Nar: neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-7-like, Cup: cuticular protein 5 precursor, OSD: chemosensory protein-like precursor, Vha: V-type proton ATPase subunit d, Cu(I): Cu(I)-responsive transcriptional regulator, Titin: titin-like, Ft3: fibronectin type 3 domain, GRIK3: glutamate receptor ionotropic kainate 3-like isoform X3, p450: cytochrome P450 4g15, Pro3: proteasome beta 3 subunit-like, Tpm: tropomyosin, Jagn1: jagunal homolog, Ubi: ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase, Tsr : twinstar.
The interaction between BYDV-GPV and positive prey proteins was further assessed in a chemiluminescent Co-IP assay using mammalian cells. In this experiment, combinations of pAcGFP-Lam/pProlabe-T were used as the negative control and pAcGFP-p53/pProLabel-T were used as the positive control. The relative strengths of the interactions between the BYDV-GPV RTP and 7 prey proteins (pancreatic lipase-related protein, tropomyosin, twinstar, complexin, nascent polypeptide-associated complex subunit alpha, cytochrome c oxidase polypeptide IV-like and cytochrome P450 4g15) were 23, 8.7, 7.1, 5.6, 4.9, 4.2, and 3.4 times greater, respectively, than the negative control, and the relative strengths of the interactions between the BYDV-GPV CP and 2 prey proteins (pancreatic lipase-related protein, nascent polypeptide-associated complex subunit alpha) were 3 and 1.6 times, respectively, greater than the negative control. These results confirmed those of the yeast two-hybrid assay and indicated the interaction strength between bait protein and various candidate prey proteins (Fig. 6B).
Comparative proteomics of the data obtained by iTRAQ and yeast two-hybrid system
In this study, we used iTRAQ and YTH to identify various proteins in R. padi that may interact with BYDV-GPV. These methods were compared for their characterization of the proteomes involved in the BYDV-GPV-R. padi interaction for future use in more targeted studies on the mechanisms regulating circulative virus transmission in aphids. In total, we identified 28 potential protein-protein interactions using YTH and 33 differential proteins using iTRAQ. Of all proteins, except two homologous proteins (cuticular protein 5 precursor and cuticular protein 62 precursor) were identified by YTH and iTRAQ, respectively, others are different proteins. The pathways of these proteins are thus the main focus because the proteins may work together for virus transmission. All proteins were distributed among 11 categories of pathways in the KEGG database, and six of these pathways were shared by the 33 proteins that were identified by both methods. Of these 33 proteins, 15 (12 from iTRAQ and three from YTH) were involving in metabolic pathways, seven (five from iTRAQ and two from YTH) in ribosomes, three (two from iTRAQ and one from YTH) in regulation of the actin cytoskeleton, three (two from iTRAQ and one from YTH) in signal pathways, three (two from iTRAQ and one from YTH) in protein processing, and two (one from iTRAQ and one from YTH) in the synaptic vesicle cycle (Fig. 4; Table 1 and 2).
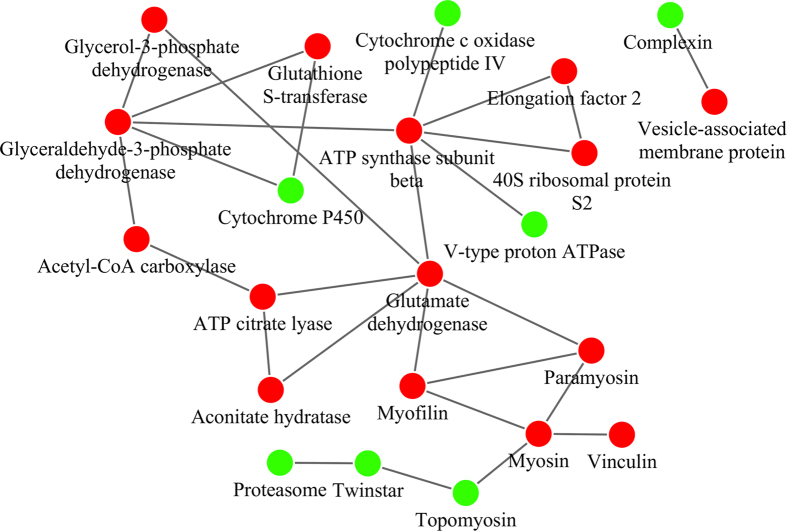
Several proteins related to metabolic pathways, regulation of the actin cytoskeleton and the synaptic vesicle cycle were identified from both iTRAQ and YTH. Thus, we created a network based on known protein-protein interactions using the STRING database (http://string-db.org) and imported the proteomic data into the Cytoscape application v.3.1.1 (http://www.cytoscape.org) (Fig. 7). Among the 61 proteins identified by the two methods, 22 proteins were included in the network (15 identified by iTRAQ, 7 by YTH). Green nodes represent proteins identified by YTH, and red nodes represent proteins identified by iTRAQ. This network suggested that the results of the two methods are complementary. The protein interaction network showed that vesicle-associated membrane protein, which is involved in the synaptic vesicle cycle29, is directly linked to complexin. Complexin positively regulates synaptic vesicle exocytosis by acting on transmembrane regions of syntaxin and vesicle-associated membrane protein30. Overall, the network highlighted particular importance for the host cytoskeleton, including myosin, topomyosin and others, which are implicated in the movement of plant and animal viruses31.
Figure 7. Protein-protein interaction network analysis.
This interaction network for all proteins identified by two methods was created using String. Orphan proteins, i.e., unconnected proteins, were removed, and the network information was exported for visualization in Cytoscape v.3.1.1. Red nodes represent proteins identified by iTRAQ, green nodes represent proteins identified by yeast two-hybrid screen.
Discussion
The circulative transmission pathway through an aphid vector involves complex interactions between viral proteins and vector-associated compounds2,32. Quantitative proteomics has been used to study vector-virus interactions for decades and is still widely used. Vector proteins that interact with a virus have been identified by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and LC/MS24, and a specific interaction between ribosomal protein S2 of M. persicae and Tobacco etch virus HC-Pro was confirmed by 2D electrophoresis separation and far western blotting33. In another study, coupling of differential proteins with the transmission phenotype (S. graminum) was investigated using a 2D electrophoresis quantitative proteomic approach24. However, accurate quantification using 2D electrophoresis is sometimes compromised by comigration or partial comigration of proteins34,35.
iTRAQ is a fairly recent quantitative proteomics technique that is gradually gaining popularity. The iTRAQ technology label isobaric reagents at the N termini and lysine side chains of peptides in a digest mixture and yield reporter ions following MS that can be used to identify and quantify the abundance differences of the proteins in tested samples36,37. This approach simplifies analysis and will potentially increase analytical accuracy and precision38,39. Using this technology, we identified 33 differential proteins between healthy and viruliferous insects. Another frequently-used method in proteomic study, YTH assay has been used extensively to detect protein-protein interactions. When a C-terminal fragment of ubiqultin (Cub) is expressed as a fusion to a reporter protein, the fusion is cleaved and reporter protein expresses only if a N-terminal fragment of ubiquin (Nub) is also expressed in the same cell40. Based on this principle, we linked BYDV-GPV CP/RTP bait to Cub and cDNA library of R. padi to mutationally altered Nub and screened vector proteins that interacted with virus bait directly. Through YTH screening of a rice cDNA library, Kong et al. (2014)41 found that the disease-specific protein of Rice stripe virus (RSV) interacted with rice PsbP (oxygen-evolving complex protein), which plays an important role on symptom development. Vitellogenin (Vg) of Laodelphax striatellus interacts strongly with the nucleocapsid protein of RSV in a YTH assay and was found to play a critical role in carrying the virion into the ovary of the vectors42. We identified 25 prey proteins that interacted with BYDV-GPV RTP and eight prey proteins that interacted with BYDV-GPV CP using YTH assay. Nevertheless, other interactions might not be detected in YTH assay because of the lack of chaperones, assembly factors, post-translational modifications, or other effects43. In addition, the YTH assay may produce false positives if (1) the two proteins are not expressed in the same tissue or at the same time or if (2) the prey protein has a self-activating function43,44.
Using the two methods, we identified 61 proteins that might be involved in the transmission of BYDV-GPV by R. padi. In a previous study using 2D DIGE, Cilia et al. (2011)24 the 50 differential proteins identified in the vector aphid S. graminum may be involved in energy metabolism, membrane trafficking, lipid signaling, and the cytoskeleton and bacterial endosymbiosis. Proteins homologous to those identified by Cilia et al.24 were also identified in our study, including glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, ATP synthase subunit beta, cuticular protein, peroxiredoxin (using iTRAQ) and the cuticular protein and proteasome subunit beta (using the YTH assay).
The proteasome, a large multi-subunit proteinase complex found in the cytoplasm and nucleus of all eukaryotic cells, fulfills vital cellular functions, including elimination of misfolded proteins, generating antigenic peptides, degradation of nuclear and membrane-bound proteins, and regulation of important cellular processes45,46. The tat protein of Human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) can interact with the proteasome in vivo, then block the proteolytic activity of the proteasome, thus contributing directly to virion escape from host immunity47,48. On the basis of our results and published reports, the proteasome of R. padi is strongly implicated as an antiviral immune response against the movement process of BYDV-GPV in the body of its aphid vectors.
In this study, we found that the cuticular protein not only interacted with BYDV-GPV RTP, but it was also differentially expressed between the viruliferous and the healthy aphids. The abundance of this protein changed significantly after uptake of the Pea enation mosaic virus by the pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum) in a transcriptomic analysis of the aphid intestinal genes49. According to a proteomic analysis, several cuticle proteins were also differentially expressed in genotoyes of S. graminum that differed in their ability to transmit CYDV-RPV24, indicating that cuticle proteins may have functions in the hindgut barrier. Recently, our lab found cuticle proteins and pc3 of RSV colocalized in the hemolymph of the small brown planthopper (L. striatellus). When the gene encoding the cuticle protein is silenced by RNAi, the number of viral particles of the virus in the vector insects decreased simultaneously, then virus transmission efficiency by the vector also declined (Liu et al., unpublished manuscript, under review by Mol & Cell Proteomics). Cuticle proteins may aid in the spread of the virus into the hemolymph and protect the virus from degradation by a host immune response.
Vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP) and complexin, which are involved in vesicular trafficking and synaptic vesicle exocytosis50,51 were identified using iTRAQ and YTH assay, respectively. Although receptor-mediated trancytosis (endocytosis/exocytosis) has been proposed as a mechanism for regulating vector-specific transmission of BYDVs by their aphid vectors52, the vector proteins involved in the endocytosis/exocytosis are largely unknown.
The keystone of the vesicle cycle is Ca2+-regulated exocytosis, followed by different routes of endocytosis and recycling29. During the sequential steps of the synaptic vesicle cycle neurotransmitters are first actively transported into synaptic vesicles, which are clustered in front of the active zone. The synaptic vesicles then dock at the active zone, where the vesicles are primed and converted into a state of competence for Ca2+-regulated fusion-pore opening. After the fusion pore opens, the synaptic vesicles undergo endocytosis and are recycled29. It has been shown that soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) proteins, which contain synaptobrevin (vesicle-associated membrane protein) on the vesicular membrane and syntaxin and SNAP-25 on the plasma membrane, play an essential role in Ca2+-regulated synaptic vesicle exocytosis53. The synaptic vesicle membrane and plasma membranes are forced into close proximity, and the fusion pore is opened by the SNARE complex assembly29,30. Human vesicle-associated membrane protein subtype A and subtype B, which participate in the regulation of membrane trafficking, lipid transport and metabolism, and the unfolded protein response, are known to associate with NS5B and NS5A of Hepatitis C virus (HCV)54. Vesicle-associated membrane protein is also essential for two fast synapse specific membrane-trafficking reactions: fast exocytosis for neurotransmitter release and fast endocytosis that mediates rapid reuse of synaptic vesicles by defective mice50.
Complexin, also known as synaphin, is a neuronal cytosolic protein that acts as a positive regulator of synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Complexin binds to a fully assembled SNARE complex strictly in the transmembrane regions of syntaxin and vesicle-associated membrane protein as shown using purified full-length and truncated SNARE proteins and a gel shift assay30. In mast cells, complexin II regulates exocytosis positively through its translocation to the plasma membrane and enhancement of the Ca2+ sensitivity of the fusion machinery51. In light of our results, a direct mechanism based on complexin and vesicle-associated membrane protein involvement in BYDV-GPV movement across the barrier in R. padi is reasonable.
The cytoskeleton, consisting mostly of microtubules, microfilaments and intermediate filaments, has important roles for many viruses in completing their life cycle55. Viruses can induce rearrangements of cytoskeletal filaments to utilize them as tracks or to move them aside when they are barriers31. In the present study, the cytoskeleton component tropomyosin, which interacted with BYDV-GPV RTP according to the YTH assay, and proteins such as myosin and paramyosin that have microfilament motor activity and ATPase activity according to the GO annotation, were up-regulated in viruliferous aphids. In the YTH and Co-IP assays, myosin light chain 2 in the vector Sogatella furcifera interacted with P7-1(a nonstructural protein which is the major component of the tubular structure in vector tissues) of SRBSDV56. The localization of myosin with Pns10 (a nonstructural protein of Rice dwarf virus) was also confirmed in an RDV-infected vector cell monolayer culture; myosin motors were required for the transport of Pns10 containing virus particles to neighboring cells57. Similarly, the vaccinia virus F11 protein interacts with the RhoGAP myosin-9A to inhibit RhoA signaling58. In the absence of myosin-9A experimentally, RhoA signaling is not inhibited, resulting in fewer actin tails and reduced virus release concomitant with the spread of fewer viral particles. Thus, these proteins in the vector may facilitate virions trafficking by binding to BYDV-GPV proteins.
In conclusion, our results suggest that the information generated by the iTRAQ and YTH methods is complementary. These identified proteins may provide useful information on the protein and functional interactions between BYDV-GPV and vector R. padi and will also facilitate our understanding of the molecular mechanism that enables BYDV-GPV to cross the barriers posed by the hindgut and the epithelial cells of the accessory salivary glands in insect vectors. The results obtained with these methods have provided us with exciting directions for future studies on protein function using RNA interference (RNAi) technology and on verifying the involvement of the proteins identified in virus transmission using confocal microscopy.
Methods
Virus maintenance and aphid rearing
Laboratory isolates of BYDV-GPV have been maintained on oat plants (Avena sativa K. Koch cv. Coast-Black) in our laboratory since the 1990s59. A laboratory population of nonviruliferous aphids of R. padi was reared on winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L., cv. Beijing 837), under controlled conditions at 18 °C in a growth chamber60.
Isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ) between viruliferous and nonviruliferous Rhopalosiphum padi
Sample collection
Approximately 240 wingless adult insects of R. padi were picked from wheat with a soft brush, and then released carefully onto oat plants infected with BYDV-GPV for acquisition of viruses. After each feeding duration (0 h, 12 h, 24 h, 48 h), 50 wingless adult aphids were collected.
Sample preparation for proteomics and iTRAQ labeling
The sample was weighed and dissolved in 800 μL of lysis buffer (7 M urea, 2 M thiourea, 0.1% CHAPS), thoroughly resuspended using a vortex mixer, and then incubated at room temperature for 30 min. After centrifugation at 15,000 rpm at 4 °C for 30 min, the supernatant was collected. Protein concentration was determined using the Bradford assay. Each protein sample (200 μg) was digested with 50 μL trypsin solution at 37 °C overnight. iTRAQ proteomics was performed using a 4-plex procedure. The iTRAQ reagents 117, 118, 119 and 121 were used to label the peptides from 0 h, 12 h, 24 h and 48 h respectively (AB Sciex, Foster City, USA).
2DLC-MS/MS analysis
To reduce sample complexity for LC-MS/MS analysis, we separated the mixed peptides using nano-HPLC with the RP analytical column (Durashell-C18, 4.6 mm × 250 mm, 5 μm, 100 Å). Peptides were subsequently eluted using mobile phase A (98% ddH2O, 2% acetonitrile, pH 10) and mobile phase B (98% acetonitrile, 2% ddH2O, pH 10), the flow rate was maintained at 0.7 mL/min. The mixed peptides (desalted with 2% methyl alcohol and 0.1% formic acid) were further separated by nano-HPLC with the secondary RP analytical column (EASY-Spray column, 12 cm × 75 μm, C18, 3 μm). The RP mobile phase A was 100% H2O (with 0.1% formic acid); the RP mobile phase B was 100% acetonitrile (with 0.1% formic acid). The flow rate was maintained at 350 nL/min. Electrospray voltage of 2.1 kV versus the inlet of the mass spectrometer was used. MS was performed using a nano-LC coupled online to a QStar Elite mass spectrometer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, USA), and raw data was collected using Analyst QS 2.0 controlling software (AB Sciex) through a nanospray ion source. ProteinPilot version 3.0 (AB Sciex) was used for processing the raw acquired iTRAQ data files.
Data analysis
ProteinPilot version 3.0 (AB Sciex) was used for processing the raw acquired iTRAQ data files. Proteins were identified using the raw MS data in a search against the Swissprot-Uniprot protein database, with search parameters as follows: iTRAQ labeling at N-terminus and lysine residues, cysteine modification by carboxyamidomethylation and digestion by trypsin. For iTRAQ quantitation, the peptide for quantification was automatically selected by Pro GroupTM algorithm in ProteinPilot to calculate the reporter peak area, error factor (EF) and p-value. The false discovery rate (FDR) for each protein was estimated using a concatenated target-decoy database. The proteins were filtered with a FDR <0.01. The proteins were considered to be differentially expressed if their iTRAQ ratios were >1.5 or <0.666 in the viruliferous aphids compared with the nonviruliferous aphids (p <0.05).
Functional analysis
The protein abundance data from Protein Pilot were further processed using the hierarchical cluster function of Gene Cluster software (http://bonsai.hgc.jp/~mdehoon/software/cluster/software.htm)61 under the default parameters with log-transformation. The functional annotation of identified differential proteins was performed using the information in the Uniprot database (http://www.uniprot.org)62 and DAVID bioinformatic resource (http://david.abcc. ncifcrf.gov/)63. The protein pathway annotations were analyzed using the KEGG database (http://www.kegg.jp/kegg/pathway.html)64.
Verification of differentially expressed genes by RT-qPCR
Total RNAs were extracted using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, California, USA) from four groups of R. padi: collected after 0 h, 12 h, 24 h, or 48 h acquisition access period [AAP] on BYDV-GPV-infected oat plants). First-strand cDNA of each sample was synthesized using the FastQuant RT Kit (Tiangen, Beijing, China) and the kit protocol. Actin was used as the internal reference gene. The obtained cDNAs were used as the template for the q-PCR. The q-PCR reaction mixture comprised 6.4 μL RNase-free ddH2O, 10 μL 2× SuperReal PreMix Plus (SuperReal PreMix Plus kit [SYBR Green I, Tiangen]), 0.6 μL forward primer (10 mM), 0.6 μL reverse primer (10 mM), 0.4 μL 50× ROX Reference Dye, 2 μL diluted cDNA (1:30 dilution of cDNA sample template) or ddH2O (as the no-template control). The reaction program were as follows: 95 °C, 15 min, 1 cycle; followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C 10 s, 59.2 °C 32 s, 60 °C 32 s. Relative gene expression was calculated according to the Livak method (2-ΔΔCt). The experiments were repeated 3 times independently. Primers used in RT-qPCR for validation of differentially expressed genes are shown in Supplementary Table S1.
Yeast two-hybrid (YTH) assay
Construction of BYDV-GPV RTP and CP bait fusion vectors
Total RNA was extracted from virus-infected wheat leaves using Trizol reagent. The genes encoding BYDV-GPV RTP and CP were RT-PCR-amplified respectively with the primer pair CP-pDHB1F/CP-pDHB1R and RTP-pDHB1F/RTD-pDHB1R (Supplementary Table S1), then the amplified products were purified and ligated with pMD19T simple vector (Takara, Dalian, China), and finally used to transform DH5a E. coli cells (Tiangen) according to the instructions. The positive clone was then confirmed by PCR analysis, sequencing and restriction enzyme digestion. The digested sequence was ligated into the SfiI-predigested pDHB1plasmid vector. To test auto-activation of the bait proteins, four sets of plasmid pairs, pDHB1-RTP/pOst1-NubI(pDHB1-CP/pOst1-NubI), pDHB1-RTDP/pPR3-N(pDHB1-CP/pPR3-N), pDHB1-largeT/pDSL-p53, pDHB1-largeT/pPR3-N were used to transform yeast strain NMY51 according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Dualsystems Biotech, Switzerland).
Construction of R. padi cDNA library
The cDNA library of R. padi was constructed in prey plasmid pPR3-N using an EasyClone cDNA library construction kit (Dualsystems Biotech). Total RNA was extracted from R. padi using the Trizol reagent, and first- and double-strand cDNAs were synthesized according to the protocol of the Easy Clone cDNA library construction kit (Dualsystems Biotech). The amplified double-strand cDNA was digested using SfiI. To construct a cDNA library containing as many of the target genes as possible, we collected 200-1000-bp fragments. Then the cDNA fragments were ligated into the complementary sites of pPR3-N plasmid vector.
Library screening
We used a DUAL hunter starter kit (Dualsystems Biotech) to screen R. padi cDNA library. Yeast strain NMY51 was sequentially transformed with the bait fusion vector (pDHB1-RTP or pDHB1-CP) and R. padi cDNA library using the lithium acetate method with single-stranded carrier DNA (ssDNA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The mixture was then spread onto TDO plates and incubated at 30 °C for 4 days. All potential positive hits were restreaked onto higher stringency QDO plates. The prey plasmids in positive clones were isolated using TIANprep yeast plasmid DNA kit (Tiangen).
Positive prey analysis
The positive prey plasmids were further characterized by determining the DNA sequences of the inserts by sequencing. The sequencing results for the positive hits were used to search for reference sequences using BLASTX against the nonredundant (nr) NCBI protein database provided by NCBI (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi) with default parameters. The functional and pathway annotation were done using the Uniprot database, DAVID bioinformatic resource and KEGG database.
Retransformation of prey plasmid for interactors
To distinguish positive from false-positive interactions and further confirm the interaction of bait and prey proteins, we selected 22 positive library plasmids for RTP and 5 for CP based on their molecular function to cotransform yeast strain NMY51 with the prey plasmid and bait plasmid. At the same time, three sets of plasmids, pDHB1-largeT/pDSL-p53, pDHB1-RTD/pOst1-NubI (pDHB1-CP/pOst1-NubI) were respectively used to cotransform yeast strain NMY51 as positive controls, and pDHB1-largeT/pPR3-N were used to cotransformed yeast strain NMY51 as a negative control.
Chemiluminescence Co-IP assay
For constructing the pAcGFP1-bait and pProLabel prey fusion protein expression vectors, the full-length coding sequence of RTP or CP was cloned and fused to pAcGFP1 vector to express the bait fusion protein. Each of the seven potential positive prey genes (pancreatic lipase-related protein, tropomyosin, twinstar, complexin, nascent polypeptide-associated complex subunit alpha, cytochrome c oxidase polypeptide IV-like and cytochrome P450 4g15) derived from the yeast two-hybrid assay was cloned into the pProLabel vector to be expressed as the prey fusion protein. The pAcGFP1-bait plasmid and pProLabel-prey plasmid were used to cotransfect mammalian cells (Human Embryonic Kidney 293 [HEK293] cells) using a CalPhos Mammalian Transfection Kit (Clontech, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. All primers for the Co-IP assay are listed in Supplementary Table S1. Plasmid set pAcGFP1-p53/pProLabel-T was used for the positive control, and set pAcGFP1-Lam/pProLabel-T was used for the negative control. After 48 h, cells were lysed and incubated with anti-GFP polyclonal antibody (Clontech) for 2 h at 4 °C. Protein A/G agarose beads were added to each lysate, and the mixture was incubated with gentle rotation at 4 °C overnight. Beads were collected and washed nine times by centrifugation. Each sample of beads was then resuspended in the lysis/complementation buffer and then transferred to a well in a 96-well solid plate (Costar, USA) to determine the protein-protein interaction strength. To each sample, substrate mix was added, and pProLabel activity was measured using a GloMaxTM 96 Microplate Luminometer (Promega, Wisconsin, USA) after 0, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 and 45 min.
Construction of protein-protein interaction network
The protein-protein interaction network for all proteins identified by iTRAQ and YTH was created using String (http://string-db.org)65. Orphan proteins that were unconnected with other proteins were removed, and the network information was exported for visualization in Cytoscape v.3.1.1 (www.cytoscape.org)66.
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Wang, H. et al. Integrative proteomics to understand the transmission mechanism of Barley yellow dwarf virus-GPV by its insect vector Rhopalosiphum padi. Sci. Rep. 5, 10971; doi: 10.1038/srep10971 (2015).
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Financial support was provided by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (2012CB114004), the Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (201303021), and Natural Science Foundation of China (31272017).
Footnotes
Author Contributions X.W. designed the research. H.W., K.W., Y.L. and Y.W. performed the experiments, H.W. and K.W. analyzed the data, H.W. and X.W. wrote the manuscript.
References
- Miller W. A. & Rasochova L. Barley yellow dwarf viruses. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 35, 167–190 (1997). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray S. & Gildow F. E. Luteovirus-aphid interactions. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 41, 539–566 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochow W. F. The role of aphids in vector-specificity of Barley yellow dwarf virus. Plant Dis. Rep. 42, 905–908 (1958). [Google Scholar]
- Rochow W. F. Biological properties of four isolates of barley yellow dwarf virus. Phytopathology 59, 1580–1589 (1969). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou G. H. et al. Identification and applications of four strains of wheat yellow dwarf virus. Sci. Agri. Sin. 20, 7–12 (1987). [Google Scholar]
- Jin Z. et al. The complete nucleotide sequence and its organization of the genome of Barley yellow dwarf virus-GAV. Sci. China. Life Sci. 47, 175–182 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. et al. A Chinese isolate of barley yellow dwarf virus-PAV represents a third distinct species within the PAV serotype. Arch. Virol. 152, 1365–1373 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. M. Q. et al. Virus taxonomy: ninth report of the international committee on taxonomy of viruses. Elsevier, 1338 pages (2011). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W. W. et al. The complete nucleotide sequence of the barley yellow dwarf GPV isolate from China shows that it is a new member of the genus Polerovirus. Arch. Virol. 154, 1125–1128 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. et al. Two suppressors of RNA silencing encoded by cereal-infecting members of the family Luteoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 93, 1825–1830 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brault V. et al. Electron microscopy studies on luteovirid transmission by aphids. Micron 38, 302–312 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gildow F. E. Evidence for receptor mediated endocytosis regulating luteovirus acquisition by aphids. Phytopathology 83, 270–277 (1993). [Google Scholar]
- Reinbold C. V. et al. Posterior midgut and hindgut are both sites of acquisition of Cucurbit aphid-borne yellows virus in Myzus persicae and Aphis gossypii. J. Gen. Virol. 84, 3473–3484 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gildow F. E. & Gray S. M. The aphid salivary gland basal lamina as a selective barrier associated with vector-specific transmission of barley yellow dwarf luteoviruses. Phytopathology 83, 1293–1302 (1993). [Google Scholar]
- Gildow F. E. & Rochow W. F. Role of accessory salivary glands in aphid transmission of barley yellow dwarf virus. Virology 104, 97–108 (1980). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogenhout S. A. et al. Insect vector interactions with persistently transmitted viruses. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 46, 327–359 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brault V. et al. Effects of point mutations in the readthrough domain of the beet western yellows virus minor capsid protein on virus accumulation in planta and on transmission by aphids. J. Virol. 74, 1140–1148 (2000). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray S. M. Plant virus proteins involved in natural vector transmission. Trends Microbiol. 4, 259–264 (1996). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seddas P. et al. Rack-1, GAPDH3, and actin: proteins of Myzus persicae potentially involved in the transcytosis of beet western yellows virus particles in the aphid. Virology 325, 399–412 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. Y. et al. Vector specificity of barley yellow dwarf virus (BYDV) transmission: Identification of potential cellular receptors binding BYDV-MAV in the aphid, Sitobion avenae. Virology 286, 125–133 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. F. & Zhou G. H. Identification of a protein associated with circulative transmission of Barley yellow dwarf virus from cereal aphids, Schizaphis graminum and Sitobion avenae. Chin. Sci. Bull. 48, 2083–2087 (2003). [Google Scholar]
- Yang X. L. et al. Coupling genetics and proteomics to identify aphid proteins associated with vector-specific transmission of polerovirus (Luteoviridae). J. Virol. 82, 291–299 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamborindeguy C. et al. Genomic and proteomic analysis of Schizaphis graminum reveals cyclophilin proteins are involved in the transmission of cereal yellow dwarf virus. PLoS One 8, e71620 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cilia M. et al. Genetics coupled to quantitative intact proteomics links heritable aphid and endosymbiont protein expression to circulative polerovirus transmission. J. Virol. 85, 2148–2166 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. et al. An insight into iTRAQ: where do we stand now? Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 404, 1011–1027 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lietzen N. et al. Quantitative subcellular proteome and secretome profiling of influenza A virus-infected human primary macrophages. PLoS Pathog. 7, e1001340 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S. & Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature 340, 245–246 (1989). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L. et al. Analysis of vaccinia virus-host protein-protein interactions: validations of yeast two-hybrid screenings. J. Proteome Res. 8, 4311–4318 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudhof T. C. The synaptic vesicle cycle. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 27, 509–547 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu K. A. et al. Action of complexin on SNARE complex. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 41652–41656 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radtke K. et al. Viral interactions with the cytoskeleton: a hitchhiker’s guide to the cell. Cell. Microbiol. 8, 387–400 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray S. M. & Banerjee N. Mechanisms of arthropod transmission of plant and animal viruses. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 63, 128–148 (1999). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Calvino L. et al. The helper-component protease transmission factor of tobacco etch potyvirus binds specifically to an aphid ribosomal protein homologous to the laminin receptor precursor. J. Gen. Virol. 91, 2862–2873 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choe L. H. et al. A comparison of the consistency of proteome quantitation using two-dimensional electrophoresis and shotgun isobaric tagging in Escherichia coli cells. Electrophoresis 26, 2437–2449 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W. W. et al. Comparative study of three proteomic quantitative methods, DIGE, cICAT, and iTRAQ, using 2D gel- or LC-MALDI TOF/TOF. J. Proteome Res. 5, 651–658 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross P. L. et al. Multiplexed protein quantitation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using amine-reactive isobaric tagging reagents. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 3, 1154–1169 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. et al. Quantitative proteomic analysis of meningiomas for the identification of surrogate protein markers. Sci. Rep. 4, 7140; 10.1038/srep07140 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. et al. Comprehensive comparison of iTRAQ and label-free LC-based quantitative proteomics approaches using two Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strains of interest for biofuels engineering. J. Proteome Res. 11, 487–501 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSouza L. et al. Search for cancer markers from endometrial tissues using differentially labeled tags iTRAQ and cICAT with multidimensional liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 4, 377–386 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson N. V. A Split ubiquitin as a sensor of protein interactions in vivo. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 10340–10344 (1994). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong L. F. et al. Interaction between Rice stripe virus disease-specific protein and host PsbP enhances virus symptoms. Mol. Plant 7, 691–708 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huo Y. et al. Transovarial transmission of a plant virus is mediated by vitellogenin of its insect vector. PLoS Pathog. 10, e1003949 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopala S. V. et al. Studying protein complexes by the yeast two-hybrid system. Methods 58, 392–399 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng E. et al. Screening for voltage-gated sodium channel interacting peptides. Sci. Rep. 4, 4569; 10.1038/srep04569 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiller M. M. et al. ER degradation of a misfolded luminal protein by the cytosolic ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Science 273, 1725–1728 (1996). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plemper R. K. & Wolf D. H. Endoplasmic reticulum degradation. Reverse protein transport and its end in the proteasome. Mol. Biol. Rep. 26, 125–130 (1999). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apcher G. S. et al. Human immunodeficiency virus-1 Tat protein interacts with distinct proteasomal α and β subunits. FEBS Lett. 553, 200–204 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang X. H. et al. The RTP site shared by the HIV-1 Tat protein and the 11 S regulator subunit alpha is crucial for their effects on proteasome function including antigen processing. J. Mol. Biol. 323, 771–782 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brault V. et al. Transcriptomic analysis of intestinal genes following acquisition of pea enation mosaic virus by the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. J. Gen. Virol. 91, 802–808 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deak F. et al. Synaptobrevin is essential for fast synaptic-vesicle endocytosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 6, 1102–1108 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadokoro S. et al. Complexin II facilitates exocytotic release in mast cells by enhancing Ca2+ sensitivity of the fusion process. J. Cell Sci. 118, 2239–2246 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochow W. F. A mechanism of vector specificity for circulative aphid-transmitted plant viruses. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 226, 293–301 (1975). [Google Scholar]
- Vivona S. et al. Disassembly of all SNARE complexes by N-Ethylmaleimide-sensitive Factor (NSF) Is initiated by a conserved 1:1 interaction between alpha-Soluble NSF attachment protein (SNAP) and SNARE complex. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 24984–24991 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamamoto I. et al. Human VAP-B is involved in hepatitis C virus replication through interaction with NS5A and NS5B. J. Virol. 79, 13473–13482 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickstead B. & Gull K. The evolution of the cytoskeleton. J. Cell Biol. 194, 513–525 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar T. et al. Proteomic analysis of interaction between P7-1 of Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus and the insect vector reveals diverse insect proteins involved in successful transmission. J. Proteomics 102, 83–97 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei T. Y. et al. Endomembranes and myosin mediate assembly into tubules of Pns10 of Rice dwarf virus and intercellular spreading of the virus in cultured insect vector cells. Virology 372, 349–356 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa Y. et al. Vaccinia Virus F11 promotes viral spread by acting as a PDZ-containing scaffolding protein to bind Myosin-9A and inhibit RhoA signaling. Cell Host Microbe 14, 51–62 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. et al. Three digoxigenin-labeled cDNA probes for specific detection of the natural population of Barley yellow dwarf viruses in China by dot-blot hybridization. J. Virol. Methods 145, 22–29 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu K. K. et al. Sequencing and validation of reference genes to analyze endogenous gene expression and quantify Yellow Dwarf Viruses using RT-qPCR in viruliferous Rhopalosiphum padi. PLoS One 9, e97038 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Hoon M. J. L. et al. Open source clustering software. Bioinformatics 20, 1453–1454 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camon E. et al. The Gene Ontology Annotation (GOA) Database: sharing knowledge in Uniprot with Gene Ontology. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, D262–D266 (2004). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis G. et al. DAVID: Database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4, P3 (2003). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moutselos K. et al. KEGGconverter: a tool for the in-silico modelling of metabolic networks of the KEGG Pathways database. BMC Bioinformatics 10, 324 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franceschini A. et al. STRING v9.1: protein-protein interaction networks, with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, D808–D815 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M. S. et al. Integration of biological networks and gene expression data using Cytoscape. Nat. Protoc. 2, 2366–2382 (2007). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.