Abstract
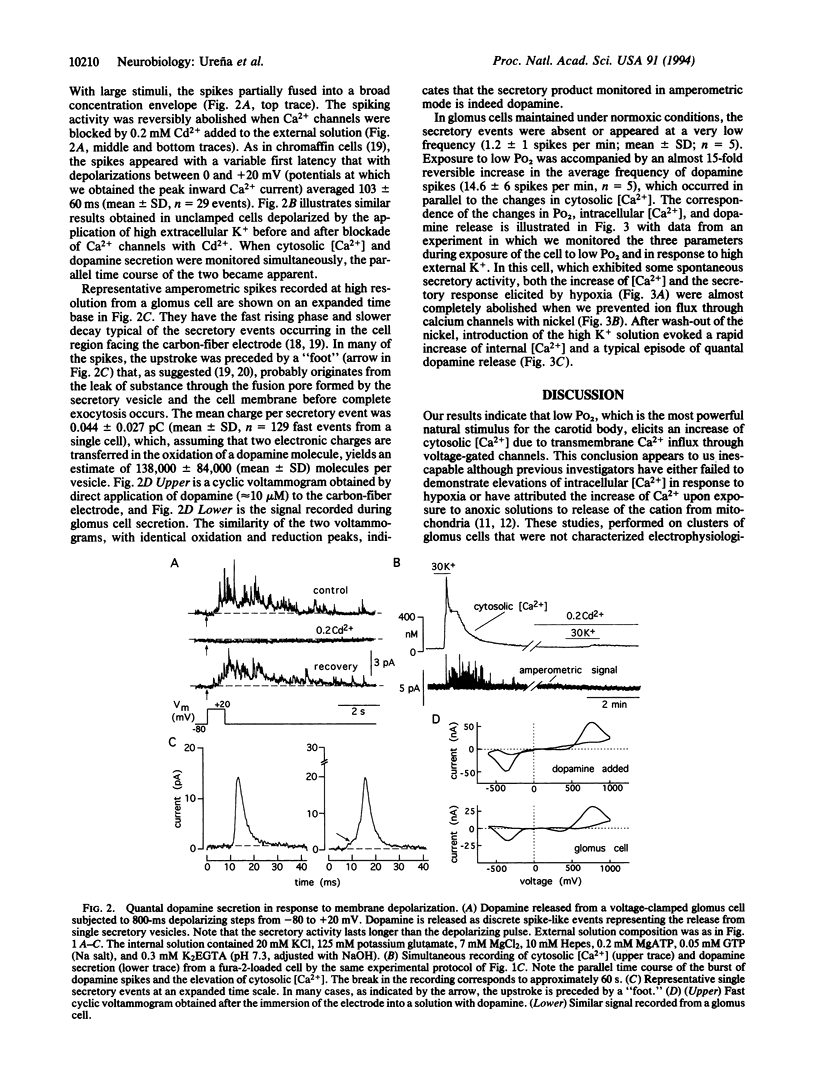
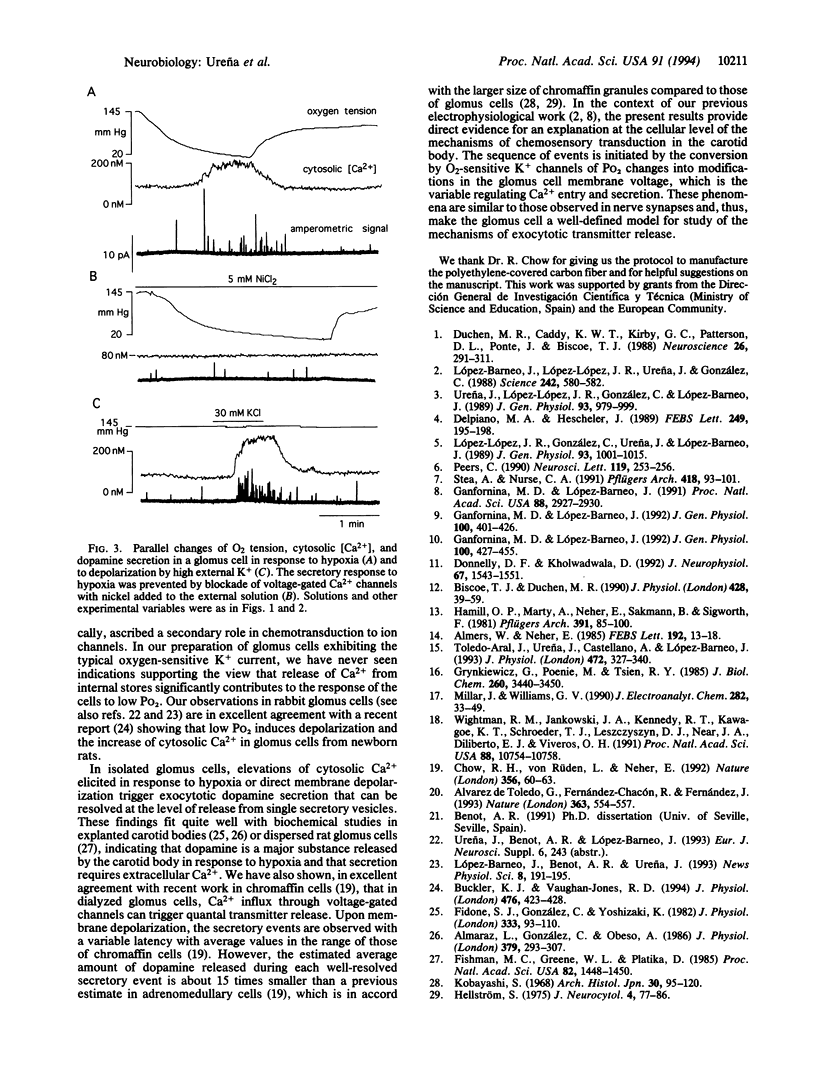
We have investigated the changes of cytosolic [Ca2+] and the secretory activity in single glomus cells dispersed from rabbit carotid bodies during exposure to solutions with variable O2 tension (Po2). In normoxic conditions (Po2 = 145 mmHg; 1 mmHg = 133 Pa), intracellular [Ca2+] was 58 +/- 29 nM, and switching to low Po2 (between 10 and 60 mmHg) led to a reversible increase of [Ca2+] up to 800 nM. The response to hypoxia completely disappeared after removal of external Ca2+ or with the addition of 0.2 mM Cd2+ to the external solution. These same solutions also abolished both the Ca2+ current of the cells and the increase of internal [Ca2+] elicited by high external K+. Elevations of cytosolic [Ca2+] in response to hypoxia or to direct membrane depolarization elicited the release of dopamine, which was detected by amperometric techniques. Dopamine secretion occurred in episodes of spike-like activity that appear to represent the release from single secretory vesicles. From the mean charge of well-resolved secretory events, we estimated the average number of dopamine molecules per vesicle to be approximately 140,000, a value about 15 times smaller than a previous estimate in chromaffin granules of adrenomedullary cells. These results directly demonstrate in a single-cell preparation the secretory response of glomus cells to hypoxia. The data indicate that the enhancement of cellular excitability upon exposure to low Po2 results in Ca2+ entry through voltage-gated channels, which leads to an increase in intracellular [Ca2+] and exocytotic transmitter release.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almaraz L., Gonzalez C., Obeso A. Effects of high potassium on the release of [3H]dopamine from the cat carotid body in vitro. J Physiol. 1986 Oct;379:293–307. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Neher E. The Ca signal from fura-2 loaded mast cells depends strongly on the method of dye-loading. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez de Toledo G., Fernández-Chacón R., Fernández J. M. Release of secretory products during transient vesicle fusion. Nature. 1993 Jun 10;363(6429):554–558. doi: 10.1038/363554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Duchen M. R. Responses of type I cells dissociated from the rabbit carotid body to hypoxia. J Physiol. 1990 Sep;428:39–59. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckler K. J., Vaughan-Jones R. D. Effects of hypoxia on membrane potential and intracellular calcium in rat neonatal carotid body type I cells. J Physiol. 1994 May 1;476(3):423–428. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow R. H., von Rüden L., Neher E. Delay in vesicle fusion revealed by electrochemical monitoring of single secretory events in adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):60–63. doi: 10.1038/356060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delpiano M. A., Hescheler J. Evidence for a PO2-sensitive K+ channel in the type-I cell of the rabbit carotid body. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jun 5;249(2):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80623-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly D. F., Kholwadwala D. Hypoxia decreases intracellular calcium in adult rat carotid body glomus cells. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Jun;67(6):1543–1551. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.67.6.1543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchen M. R., Caddy K. W., Kirby G. C., Patterson D. L., Ponte J., Biscoe T. J. Biophysical studies of the cellular elements of the rabbit carotid body. Neuroscience. 1988 Jul;26(1):291–311. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90146-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidone S., Gonzalez C., Yoshizaki K. Effects of low oxygen on the release of dopamine from the rabbit carotid body in vitro. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:93–110. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman M. C., Greene W. L., Platika D. Oxygen chemoreception by carotid body cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1448–1450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganfornina M. D., López-Barneo J. Gating of O2-sensitive K+ channels of arterial chemoreceptor cells and kinetic modifications induced by low PO2. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Sep;100(3):427–455. doi: 10.1085/jgp.100.3.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganfornina M. D., López-Barneo J. Potassium channel types in arterial chemoreceptor cells and their selective modulation by oxygen. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Sep;100(3):401–426. doi: 10.1085/jgp.100.3.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganfornina M. D., López-Barneo J. Single K+ channels in membrane patches of arterial chemoreceptor cells are modulated by O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2927–2930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellström S. Morphometric studies of dense-cored vesicles in type I cells of rat carotid body. J Neurocytol. 1975 Feb;4(1):77–86. doi: 10.1007/BF01099097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S. Fine structure of the carotid body of the dog. Arch Histol Jpn. 1968 Dec;30(1):95–120. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.30.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Barneo J., López-López J. R., Ureña J., González C. Chemotransduction in the carotid body: K+ current modulated by PO2 in type I chemoreceptor cells. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):580–582. doi: 10.1126/science.2456613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-López J., González C., Ureña J., López-Barneo J. Low pO2 selectively inhibits K channel activity in chemoreceptor cells of the mammalian carotid body. J Gen Physiol. 1989 May;93(5):1001–1015. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.5.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peers C. Hypoxic suppression of K+ currents in type I carotid body cells: selective effect on the Ca2(+)-activated K+ current. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Nov 13;119(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90846-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stea A., Nurse C. A. Whole-cell and perforated-patch recordings from O2-sensitive rat carotid body cells grown in short- and long-term culture. Pflugers Arch. 1991 Mar;418(1-2):93–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00370457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toledo-Aral J., Castellano A., Ureña J., López-Barneo J. Dual modulation of K+ currents and cytosolic Ca2+ by the peptide TRH and its derivatives in guinea-pig septal neurones. J Physiol. 1993 Dec;472:327–340. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ureña J., López-López J., González C., López-Barneo J. Ionic currents in dispersed chemoreceptor cells of the mammalian carotid body. J Gen Physiol. 1989 May;93(5):979–999. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.5.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wightman R. M., Jankowski J. A., Kennedy R. T., Kawagoe K. T., Schroeder T. J., Leszczyszyn D. J., Near J. A., Diliberto E. J., Jr, Viveros O. H. Temporally resolved catecholamine spikes correspond to single vesicle release from individual chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10754–10758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



