Abstract
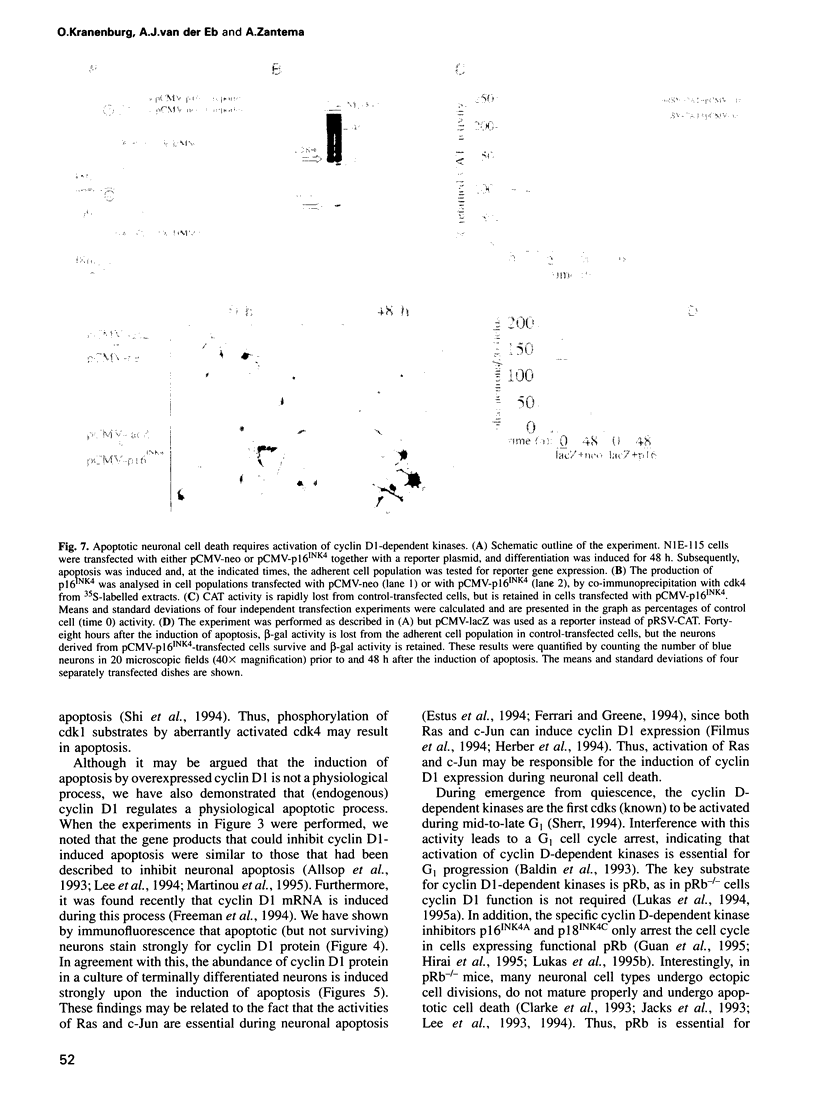
Many neurons in the developing nervous system undergo programmed cell death, or apoptosis. However, the molecular mechanism underlying this phenomenon is largely unknown. In the present report, we present evidence that the cell cycle regulator cyclin D1 is involved in the regulation of neuronal cell death. During neuronal apoptosis, cyclin D1-dependent kinase activity is stimulated, due to an increase in cyclin D1 levels. Moreover, artificial elevation of cyclin D1 levels is sufficient to induce apoptosis, even in non-neural cell types. Cyclin D1-induced apoptosis, like neuronal apoptosis, can be inhibited by 21 kDa E1B, Bcl2 and pRb, but not by 55 kDa E1B. Most importantly, however, overexpression of the cyclin D-dependent kinase inhibitor p16INK4 protects neurons from apoptotic cell death, demonstrating that activation of endogenous cyclin D1-dependent kinases is essential during neuronal apoptosis. These data support a model in which neuronal apoptosis results from an aborted attempt to activate the cell cycle in terminally differentiated neurons.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allsopp T. E., Wyatt S., Paterson H. F., Davies A. M. The proto-oncogene bcl-2 can selectively rescue neurotrophic factor-dependent neurons from apoptosis. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):295–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90230-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almasan A., Yin Y., Kelly R. E., Lee E. Y., Bradley A., Li W., Bertino J. R., Wahl G. M. Deficiency of retinoblastoma protein leads to inappropriate S-phase entry, activation of E2F-responsive genes, and apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 6;92(12):5436–5440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.12.5436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Markowitz S., Fearon E. R., Willson J. K., Vogelstein B. Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell growth by wild-type p53. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):912–915. doi: 10.1126/science.2144057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldin V., Lukas J., Marcote M. J., Pagano M., Draetta G. Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for cell cycle progression in G1. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):812–821. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beijersbergen R. L., Kerkhoven R. M., Zhu L., Carlée L., Voorhoeve P. M., Bernards R. E2F-4, a new member of the E2F gene family, has oncogenic activity and associates with p107 in vivo. Genes Dev. 1994 Nov 15;8(22):2680–2690. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.22.2680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodrug S. E., Warner B. J., Bath M. L., Lindeman G. J., Harris A. W., Adams J. M. Cyclin D1 transgene impedes lymphocyte maturation and collaborates in lymphomagenesis with the myc gene. EMBO J. 1994 May 1;13(9):2124–2130. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06488.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner T., Mogil R. J., LaFace D., Yoo N. J., Mahboubi A., Echeverri F., Martin S. J., Force W. R., Lynch D. H., Ware C. F. Cell-autonomous Fas (CD95)/Fas-ligand interaction mediates activation-induced apoptosis in T-cell hybridomas. Nature. 1995 Feb 2;373(6513):441–444. doi: 10.1038/373441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchou T., Kranenburg O., van Dam H., Roelen D., Zantema A., Hall F. L., van der Eb A. Increased cyclin A and decreased cyclin D levels in adenovirus 5 E1A-transformed rodent cell lines. Oncogene. 1993 Jul;8(7):1765–1773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Maandag E. R., van Roon M., van der Lugt N. M., van der Valk M., Hooper M. L., Berns A., te Riele H. Requirement for a functional Rb-1 gene in murine development. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):328–330. doi: 10.1038/359328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debbas M., White E. Wild-type p53 mediates apoptosis by E1A, which is inhibited by E1B. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):546–554. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhein J., Walczak H., Bäumler C., Debatin K. M., Krammer P. H. Autocrine T-cell suicide mediated by APO-1/(Fas/CD95) Nature. 1995 Feb 2;373(6513):438–441. doi: 10.1038/373438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estus S., Zaks W. J., Freeman R. S., Gruda M., Bravo R., Johnson E. M., Jr Altered gene expression in neurons during programmed cell death: identification of c-jun as necessary for neuronal apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(6 Pt 1):1717–1727. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.6.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Wyllie A. H., Gilbert C. S., Littlewood T. D., Land H., Brooks M., Waters C. M., Penn L. Z., Hancock D. C. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by c-myc protein. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90123-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Sluss H. K., Sherr C. J., Matsushime H., Kato J., Livingston D. M. Functional interactions of the retinoblastoma protein with mammalian D-type cyclins. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):487–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90136-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari G., Greene L. A. Proliferative inhibition by dominant-negative Ras rescues naive and neuronally differentiated PC12 cells from apoptotic death. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 15;13(24):5922–5928. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06937.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filmus J., Robles A. I., Shi W., Wong M. J., Colombo L. L., Conti C. J. Induction of cyclin D1 overexpression by activated ras. Oncogene. 1994 Dec;9(12):3627–3633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. S., Estus S., Johnson E. M., Jr Analysis of cell cycle-related gene expression in postmitotic neurons: selective induction of Cyclin D1 during programmed cell death. Neuron. 1994 Feb;12(2):343–355. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90276-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg D., Vairo G., Chittenden T., Xiao Z. X., Xu G., Wydner K. L., DeCaprio J. A., Lawrence J. B., Livingston D. M. E2F-4, a new member of the E2F transcription factor family, interacts with p107. Genes Dev. 1994 Nov 15;8(22):2665–2679. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.22.2665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich D. W., Wang N. P., Qian Y. W., Lee E. Y., Lee W. H. The retinoblastoma gene product regulates progression through the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):293–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90181-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Jenkins C. W., Li Y., Nichols M. A., Wu X., O'Keefe C. L., Matera A. G., Xiong Y. Growth suppression by p18, a p16INK4/MTS1- and p14INK4B/MTS2-related CDK6 inhibitor, correlates with wild-type pRb function. Genes Dev. 1994 Dec 15;8(24):2939–2952. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.24.2939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas-Kogan D. A., Kogan S. C., Levi D., Dazin P., T'Ang A., Fung Y. K., Israel M. A. Inhibition of apoptosis by the retinoblastoma gene product. EMBO J. 1995 Feb 1;14(3):461–472. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07022.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. Cell death and the cell cycle: a relationship between transformation and neurodegeneration? Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 May;18(5):157–159. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90103-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herber B., Truss M., Beato M., Müller R. Inducible regulatory elements in the human cyclin D1 promoter. Oncogene. 1994 Apr;9(4):1295–1304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P. W., Dowdy S. F., Eaton E. N., Arnold A., Weinberg R. A. Function of a human cyclin gene as an oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):709–713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Roussel M. F., Kato J. Y., Ashmun R. A., Sherr C. J. Novel INK4 proteins, p19 and p18, are specific inhibitors of the cyclin D-dependent kinases CDK4 and CDK6. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2672–2681. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoang A. T., Cohen K. J., Barrett J. F., Bergstrom D. A., Dang C. V. Participation of cyclin A in Myc-induced apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):6875–6879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.6875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houweling A., van den Elsen P. J., van der Eb A. J. Partial transformation of primary rat cells by the leftmost 4.5% fragment of adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1980 Sep;105(2):537–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Fazeli A., Schmitt E. M., Bronson R. T., Goodell M. A., Weinberg R. A. Effects of an Rb mutation in the mouse. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):295–300. doi: 10.1038/359295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalink K., Hordijk P. L., Moolenaar W. H. Growth factor-like effects of lysophosphatidic acid, a novel lipid mediator. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Dec 30;1198(2-3):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(94)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang W., Kahn S. M., Zhou P., Zhang Y. J., Cacace A. M., Infante A. S., Doi S., Santella R. M., Weinstein I. B. Overexpression of cyclin D1 in rat fibroblasts causes abnormalities in growth control, cell cycle progression and gene expression. Oncogene. 1993 Dec;8(12):3447–3457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Matsushime H., Hiebert S. W., Ewen M. E., Sherr C. J. Direct binding of cyclin D to the retinoblastoma gene product (pRb) and pRb phosphorylation by the cyclin D-dependent kinase CDK4. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):331–342. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kranenburg O., de Groot R. P., Van der Eb A. J., Zantema A. Differentiation of P19 EC cells leads to differential modulation of cyclin-dependent kinase activities and to changes in the cell cycle profile. Oncogene. 1995 Jan 5;10(1):87–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. Y., Chang C. Y., Hu N., Wang Y. C., Lai C. C., Herrup K., Lee W. H., Bradley A. Mice deficient for Rb are nonviable and show defects in neurogenesis and haematopoiesis. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):288–294. doi: 10.1038/359288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. Y., Hu N., Yuan S. S., Cox L. A., Bradley A., Lee W. H., Herrup K. Dual roles of the retinoblastoma protein in cell cycle regulation and neuron differentiation. Genes Dev. 1994 Sep 1;8(17):2008–2021. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.17.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovec H., Grzeschiczek A., Kowalski M. B., Möröy T. Cyclin D1/bcl-1 cooperates with myc genes in the generation of B-cell lymphoma in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 1;13(15):3487–3495. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06655.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovec H., Sewing A., Lucibello F. C., Müller R., Möröy T. Oncogenic activity of cyclin D1 revealed through cooperation with Ha-ras: link between cell cycle control and malignant transformation. Oncogene. 1994 Jan;9(1):323–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Ruley H. E. Stabilization of the p53 tumor suppressor is induced by adenovirus 5 E1A and accompanies apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):535–545. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukas J., Bartkova J., Rohde M., Strauss M., Bartek J. Cyclin D1 is dispensable for G1 control in retinoblastoma gene-deficient cells independently of cdk4 activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2600–2611. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukas J., Müller H., Bartkova J., Spitkovsky D., Kjerulff A. A., Jansen-Dürr P., Strauss M., Bartek J. DNA tumor virus oncoproteins and retinoblastoma gene mutations share the ability to relieve the cell's requirement for cyclin D1 function in G1. J Cell Biol. 1994 May;125(3):625–638. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.3.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukas J., Parry D., Aagaard L., Mann D. J., Bartkova J., Strauss M., Peters G., Bartek J. Retinoblastoma-protein-dependent cell-cycle inhibition by the tumour suppressor p16. Nature. 1995 Jun 8;375(6531):503–506. doi: 10.1038/375503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. New light on Myc and Myb. Part I. Myc. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2025–2035. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. P., Schmidt R. E., DiStefano P. S., Lowry O. H., Carter J. G., Johnson E. M., Jr Inhibitors of protein synthesis and RNA synthesis prevent neuronal death caused by nerve growth factor deprivation. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):829–844. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinou I., Fernandez P. A., Missotten M., White E., Allet B., Sadoul R., Martinou J. C. Viral proteins E1B19K and p35 protect sympathetic neurons from cell death induced by NGF deprivation. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jan;128(1-2):201–208. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Quelle D. E., Shurtleff S. A., Shibuya M., Sherr C. J., Kato J. Y. D-type cyclin-dependent kinase activity in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):2066–2076. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.2066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meikrantz W., Gisselbrecht S., Tam S. W., Schlegel R. Activation of cyclin A-dependent protein kinases during apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3754–3758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerson M., Harlow E. Identification of G1 kinase activity for cdk6, a novel cyclin D partner. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):2077–2086. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenbesser S. D., Williams B. O., Jacks T., DePinho R. A. p53-dependent apoptosis produced by Rb-deficiency in the developing mouse lens. Nature. 1994 Sep 1;371(6492):72–74. doi: 10.1038/371072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim R. W. Cell death during development of the nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1991;14:453–501. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.14.030191.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M. Relationship of p53 to the control of apoptotic cell death. Semin Cancer Biol. 1994 Jun;5(3):221–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Theodoras A. M., Tam S. W., Draetta G. F. Cyclin D1-mediated inhibition of repair and replicative DNA synthesis in human fibroblasts. Genes Dev. 1994 Jul 15;8(14):1627–1639. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.14.1627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quelle D. E., Ashmun R. A., Shurtleff S. A., Kato J. Y., Bar-Sagi D., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Overexpression of mouse D-type cyclins accelerates G1 phase in rodent fibroblasts. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1559–1571. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnitzky D., Gossen M., Bujard H., Reed S. I. Acceleration of the G1/S phase transition by expression of cyclins D1 and E with an inducible system. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1669–1679. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano M., Hannon G. J., Beach D. A new regulatory motif in cell-cycle control causing specific inhibition of cyclin D/CDK4. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):704–707. doi: 10.1038/366704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sgonc R., Wick G. Methods for the detection of apoptosis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1994 Dec;105(4):327–332. doi: 10.1159/000236777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. G1 phase progression: cycling on cue. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90540-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi L., Nishioka W. K., Th'ng J., Bradbury E. M., Litchfield D. W., Greenberg A. H. Premature p34cdc2 activation required for apoptosis. Science. 1994 Feb 25;263(5150):1143–1145. doi: 10.1126/science.8108732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh P., Wong S. H., Hong W. Overexpression of E2F-1 in rat embryo fibroblasts leads to neoplastic transformation. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 15;13(14):3329–3338. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06635.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steegenga W. T., Shvarts A., van Laar T., van der Eb A. J., Jochemsen A. G. Altered phosphorylation and oligomerization of p53 in adenovirus type 12-transformed cells. Oncogene. 1995 Jul 6;11(1):49–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. C., Cardiff R. D., Zukerberg L., Lees E., Arnold A., Schmidt E. V. Mammary hyperplasia and carcinoma in MMTV-cyclin D1 transgenic mice. Nature. 1994 Jun 23;369(6482):669–671. doi: 10.1038/369669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X., Levine A. J. p53 and E2F-1 cooperate to mediate apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3602–3606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G., Livingston D. M., Krek W. Multiple members of the E2F transcription factor family are the products of oncogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1357–1361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Laat S. W., van der Saag P. T. The plasma membrane as a regulatory site in growth and differentiation of neuroblastoma cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;74:1–54. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61168-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Heuvel S. J., van Laar T., The I., van der Eb A. J. Large E1B proteins of adenovirus types 5 and 12 have different effects on p53 and distinct roles in cell transformation. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5226–5234. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5226-5234.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Heuvel S., Harlow E. Distinct roles for cyclin-dependent kinases in cell cycle control. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):2050–2054. doi: 10.1126/science.8266103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Eb A. J., Graham F. L. Assay of transforming activity of tumor virus DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):826–839. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]