Abstract
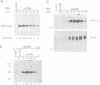
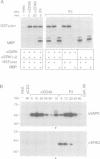
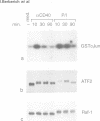
The B cell-associated surface molecule CD40 plays a key role in T cell-dependent B cell maturation, as individuals with defects in either CD40 or its ligand are impaired in immunoglobulin isotype class switching and germinal center formation. CD40 signaling activates downstream effectors, including the tyrosine protein kinase, Lyn, the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI-3 kinase), and the transcription factor, NF-kappa B. In this study, we demonstrate that stress-activated protein kinases (SAPK) are activated after CD40 cross-linking on various B cell lines or human tonsillar B cells. The activation is rapid and transient and is mediated through a cyclosporin A-insensitive pathway. Furthermore, this signaling pathway appears not to rely on protein kinase C. While CD40 ligation strongly activates the SAPKs (up to 25-fold), it does not affect members of the mitogen-activated protein kinase family (MAPK; ERK1 and ERK2). Consistent with these data, CD40 signals up-regulate c-jun but not c-fos mRNA and alter the transcription factor ATF2 but not the Raf-1 protein. In summary, CD40 signaling preferentially induces SAPK but not MAPK.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler V., Franklin C. C., Kraft A. S. Phorbol esters stimulate the phosphorylation of c-Jun but not v-Jun: regulation by the N-terminal delta domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5341–5345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderson M. R., Armitage R. J., Tough T. W., Strockbine L., Fanslow W. C., Spriggs M. K. CD40 expression by human monocytes: regulation by cytokines and activation of monocytes by the ligand for CD40. J Exp Med. 1993 Aug 1;178(2):669–674. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Hattori K., Smeal T., Karin M. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armitage R. J., Fanslow W. C., Strockbine L., Sato T. A., Clifford K. N., Macduff B. M., Anderson D. M., Gimpel S. D., Davis-Smith T., Maliszewski C. R. Molecular and biological characterization of a murine ligand for CD40. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):80–82. doi: 10.1038/357080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banchereau J., Bazan F., Blanchard D., Brière F., Galizzi J. P., van Kooten C., Liu Y. J., Rousset F., Saeland S. The CD40 antigen and its ligand. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:881–922. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.004313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berberich I., Shu G. L., Clark E. A. Cross-linking CD40 on B cells rapidly activates nuclear factor-kappa B. J Immunol. 1994 Nov 15;153(10):4357–4366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird T. A., Kyriakis J. M., Tyshler L., Gayle M., Milne A., Virca G. D. Interleukin-1 activates p54 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase/stress-activated protein kinase by a pathway that is independent of p21ras, Raf-1, and MAP kinase kinase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31836–31844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatta G. S., Spies A. G., Chang S., Mize G. J., Linsley P. S., Ledbetter J. A., Morris D. R. Differential regulation of proto-oncogenes c-jun and c-fos in T lymphocytes activated through CD28. J Immunol. 1994 Dec 15;153(12):5393–5401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng G., Cleary A. M., Ye Z. S., Hong D. I., Lederman S., Baltimore D. Involvement of CRAF1, a relative of TRAF, in CD40 signaling. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1494–1498. doi: 10.1126/science.7533327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi M. S., Brines R. D., Holman M. J., Klaus G. G. Induction of NF-AT in normal B lymphocytes by anti-immunoglobulin or CD40 ligand in conjunction with IL-4. Immunity. 1994 Jun;1(3):179–187. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark E. A., Ledbetter J. A. Activation of human B cells mediated through two distinct cell surface differentiation antigens, Bp35 and Bp50. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4494–4498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark E. A., Ledbetter J. A. How B and T cells talk to each other. Nature. 1994 Feb 3;367(6462):425–428. doi: 10.1038/367425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark E. A., Shu G. L., Lüscher B., Draves K. E., Banchereau J., Ledbetter J. A., Valentine M. A. Activation of human B cells. Comparison of the signal transduced by IL-4 to four different competence signals. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):3873–3880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J. MAPKs: new JNK expands the group. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Nov;19(11):470–473. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du W., Thanos D., Maniatis T. Mechanisms of transcriptional synergism between distinct virus-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90468-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dérijard B., Hibi M., Wu I. H., Barrett T., Su B., Deng T., Karin M., Davis R. J. JNK1: a protein kinase stimulated by UV light and Ha-Ras that binds and phosphorylates the c-Jun activation domain. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1025–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90380-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faris M., Gaskin F., Parsons J. T., Fu S. M. CD40 signaling pathway: anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody induces rapid dephosphorylation and phosphorylation of tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins including protein tyrosine kinase Lyn, Fyn, and Syk and the appearance of a 28-kD tyrosine phosphorylated protein. J Exp Med. 1994 Jun 1;179(6):1923–1931. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.6.1923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis D. A., Karras J. G., Ke X. Y., Sen R., Rothstein T. L. Induction of the transcription factors NF-kappa B, AP-1 and NF-AT during B cell stimulation through the CD40 receptor. Int Immunol. 1995 Feb;7(2):151–161. doi: 10.1093/intimm/7.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galy A. H., Spits H. CD40 is functionally expressed on human thymic epithelial cells. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 1;149(3):775–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gille H., Kortenjann M., Thomae O., Moomaw C., Slaughter C., Cobb M. H., Shaw P. E. ERK phosphorylation potentiates Elk-1-mediated ternary complex formation and transactivation. EMBO J. 1995 Mar 1;14(5):951–962. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07076.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gille H., Sharrocks A. D., Shaw P. E. Phosphorylation of transcription factor p62TCF by MAP kinase stimulates ternary complex formation at c-fos promoter. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):414–417. doi: 10.1038/358414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Campbell D., Dérijard B., Davis R. J. Transcription factor ATF2 regulation by the JNK signal transduction pathway. Science. 1995 Jan 20;267(5196):389–393. doi: 10.1126/science.7824938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart D. N., McKenzie J. L. Isolation and characterization of human tonsil dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):157–170. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath A. W., Chang R., Harada N., Santos-Argumedo L., Gordon J., Hannum C., Campbell D., Shanafelt A. B., Clark E. A., Torres R. Antibodies to murine CD40 stimulate normal B lymphocytes but inhibit proliferation of B lymphoma cells. Cell Immunol. 1993 Dec;152(2):468–480. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1993.1305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibi M., Lin A., Smeal T., Minden A., Karin M. Identification of an oncoprotein- and UV-responsive protein kinase that binds and potentiates the c-Jun activation domain. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2135–2148. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A., Chapel H. X-linked immunodeficiency. The fruits of cooperation. Nature. 1993 Feb 11;361(6412):494–494. doi: 10.1038/361494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu H. M., O'Rourke K., Boguski M. S., Dixit V. M. A novel RING finger protein interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of CD40. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 2;269(48):30069–30072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichiki T., Takahashi W., Watanabe T. The effect of cytokines and mitogens on the induction of C epsilon germline transcripts in a human Burkitt lymphoma B cell line. Int Immunol. 1992 Jul;4(7):747–754. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.7.747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inui S., Kaisho T., Kikutani H., Stamenkovic I., Seed B., Clark E. A., Kishimoto T. Identification of the intracytoplasmic region essential for signal transduction through a B cell activation molecule, CD40. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Aug;20(8):1747–1753. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishigami T., Kim K. M., Horiguchi Y., Higaki Y., Hata D., Heike T., Katamura K., Mayumi M., Mikawa H. Anti-IgM antibody-induced cell death in a human B lymphoma cell line, B104, represents a novel programmed cell death. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 15;148(2):360–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe T., Naka T., Yoshida K., Tanaka T., Fujiwara H., Suematsu S., Yoshida N., Kishimoto T., Kikutani H. The immune responses in CD40-deficient mice: impaired immunoglobulin class switching and germinal center formation. Immunity. 1994 Jun;1(3):167–178. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus S. J., Berberich I., Shu G., Clark E. A. CD40 and its ligand in the regulation of humoral immunity. Semin Immunol. 1994 Oct;6(5):279–286. doi: 10.1006/smim.1994.1036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus S. J., Pinchuk L. M., Ochs H. D., Law C. L., Fanslow W. C., Armitage R. J., Clark E. A. Costimulation through CD28 enhances T cell-dependent B cell activation via CD40-CD40L interaction. J Immunol. 1994 Jun 15;152(12):5643–5652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. A., Gordon J. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation is mandatory for CD40-mediated rescue of germinal center B cells from apoptosis. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Oct;23(10):2578–2584. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830231030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolch W., Heidecker G., Kochs G., Hummel R., Vahidi H., Mischak H., Finkenzeller G., Marmé D., Rapp U. R. Protein kinase C alpha activates RAF-1 by direct phosphorylation. Nature. 1993 Jul 15;364(6434):249–252. doi: 10.1038/364249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruppa G., Thoma B., Machleidt T., Wiegmann K., Krönke M. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated NF-kappa B activation by selective blockade of the human 55-kDa TNF receptor. J Immunol. 1992 May 15;148(10):3152–3157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., Banerjee P., Nikolakaki E., Dai T., Rubie E. A., Ahmad M. F., Avruch J., Woodgett J. R. The stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-Jun kinases. Nature. 1994 May 12;369(6476):156–160. doi: 10.1038/369156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane P., Brocker T., Hubele S., Padovan E., Lanzavecchia A., McConnell F. Soluble CD40 ligand can replace the normal T cell-derived CD40 ligand signal to B cells in T cell-dependent activation. J Exp Med. 1993 Apr 1;177(4):1209–1213. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.4.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G., Gilman M. Dual modes of control of c-fos mRNA induction by intracellular calcium in T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4579–4587. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leprince C., Draves K. E., Geahlen R. L., Ledbetter J. A., Clark E. A. CD22 associates with the human surface IgM-B-cell antigen receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3236–3240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone C., Patel G., Jones N. ATF-2 contains a phosphorylation-dependent transcriptional activation domain. EMBO J. 1995 Apr 18;14(8):1785–1797. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07167.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marais R., Wynne J., Treisman R. The SRF accessory protein Elk-1 contains a growth factor-regulated transcriptional activation domain. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):381–393. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90237-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minden A., Lin A., McMahon M., Lange-Carter C., Dérijard B., Davis R. J., Johnson G. L., Karin M. Differential activation of ERK and JNK mitogen-activated protein kinases by Raf-1 and MEKK. Science. 1994 Dec 9;266(5191):1719–1723. doi: 10.1126/science.7992057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minden A., Lin A., Smeal T., Dérijard B., Cobb M., Davis R., Karin M. c-Jun N-terminal phosphorylation correlates with activation of the JNK subgroup but not the ERK subgroup of mitogen-activated protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6683–6688. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosialos G., Birkenbach M., Yalamanchili R., VanArsdale T., Ware C., Kieff E. The Epstein-Barr virus transforming protein LMP1 engages signaling proteins for the tumor necrosis factor receptor family. Cell. 1995 Feb 10;80(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90489-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noelle R. J., Roy M., Shepherd D. M., Stamenkovic I., Ledbetter J. A., Aruffo A. A 39-kDa protein on activated helper T cells binds CD40 and transduces the signal for cognate activation of B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6550–6554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry S. L., Hasbold J., Holman M., Klaus G. G. Hypercross-linking surface IgM or IgD receptors on mature B cells induces apoptosis that is reversed by costimulation with IL-4 and anti-CD40. J Immunol. 1994 Mar 15;152(6):2821–2829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulie S., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Mellstedt H., Koho H., Ben-Aissa H., Perlmann P. A p50 surface antigen restricted to human urinary bladder carcinomas and B lymphocytes. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1985;20(1):23–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00199769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessara U., Koch N. Tumor necrosis factor alpha regulates expression of the major histocompatibility complex class II-associated invariant chain by binding of an NF-kappa B-like factor to a promoter element. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4146–4154. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinchuk L. M., Polacino P. S., Agy M. B., Klaus S. J., Clark E. A. The role of CD40 and CD80 accessory cell molecules in dendritic cell-dependent HIV-1 infection. Immunity. 1994 Jul;1(4):317–325. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafiee P., Lee J. K., Leung C. C., Raffin T. A. TNF-alpha induces tyrosine phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in adherent human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1995 May 1;154(9):4785–4792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren C. L., Morio T., Fu S. M., Geha R. S. Signal transduction via CD40 involves activation of lyn kinase and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase, and phosphorylation of phospholipase C gamma 2. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):673–680. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe M., Wong S. C., Henzel W. J., Goeddel D. V. A novel family of putative signal transducers associated with the cytoplasmic domain of the 75 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):681–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90532-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluss H. K., Barrett T., Dérijard B., Davis R. J. Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor mediated by JNK protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;14(12):8376–8384. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.12.8376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Farrah T., Goodwin R. G. The TNF receptor superfamily of cellular and viral proteins: activation, costimulation, and death. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):959–962. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su B., Jacinto E., Hibi M., Kallunki T., Karin M., Ben-Neriah Y. JNK is involved in signal integration during costimulation of T lymphocytes. Cell. 1994 Jun 3;77(5):727–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez I., Hughes R. T., Mayer B. J., Yee K., Woodgett J. R., Avruch J., Kyriakis J. M., Zon L. I. Role of SAPK/ERK kinase-1 in the stress-activated pathway regulating transcription factor c-Jun. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):794–798. doi: 10.1038/372794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres R. M., Clark E. A. Differential increase of an alternatively polyadenylated mRNA species of murine CD40 upon B lymphocyte activation. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 15;148(2):620–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsubata T., Wu J., Honjo T. B-cell apoptosis induced by antigen receptor crosslinking is blocked by a T-cell signal through CD40. Nature. 1993 Aug 12;364(6438):645–648. doi: 10.1038/364645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uckun F. M., Schieven G. L., Dibirdik I., Chandan-Langlie M., Tuel-Ahlgren L., Ledbetter J. A. Stimulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation, phosphoinositide turnover, and multiple previously unidentified serine/threonine-specific protein kinases by the Pan-B-cell receptor CD40/Bp50 at discrete developmental stages of human B-cell ontogeny. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17478–17485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu J., Foy T. M., Laman J. D., Elliott E. A., Dunn J. J., Waldschmidt T. J., Elsemore J., Noelle R. J., Flavell R. A. Mice deficient for the CD40 ligand. Immunity. 1994 Aug;1(5):423–431. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan M., Dai T., Deak J. C., Kyriakis J. M., Zon L. I., Woodgett J. R., Templeton D. J. Activation of stress-activated protein kinase by MEKK1 phosphorylation of its activator SEK1. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):798–800. doi: 10.1038/372798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dam H., Duyndam M., Rottier R., Bosch A., de Vries-Smits L., Herrlich P., Zantema A., Angel P., van der Eb A. J. Heterodimer formation of cJun and ATF-2 is responsible for induction of c-jun by the 243 amino acid adenovirus E1A protein. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):479–487. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05680.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dam H., Wilhelm D., Herr I., Steffen A., Herrlich P., Angel P. ATF-2 is preferentially activated by stress-activated protein kinases to mediate c-jun induction in response to genotoxic agents. EMBO J. 1995 Apr 18;14(8):1798–1811. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07168.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]