Abstract
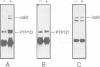
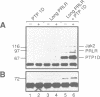
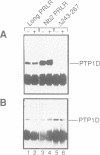
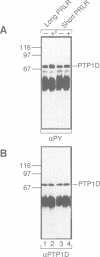
Stimulation of the prolactin receptor (PRLR), a member of the cytokine/growth hormone receptor family, results in activation of the associated Jak2 tyrosine kinase and downstream signaling pathways. We report that PTP1D, a cytoplasmic protein tyrosine phosphatase containing two Src homology 2 (SH2) domains, physically associates with the PRLR-Jak2 complex and is tyrosine-phosphorylated upon stimulation with prolactin. The formation of the trimeric PRLR-Jak2-PTP1D complex is critical for transmission of a lactogenic signal, while PTP1D phosphorylation is necessary, but not sufficient. The dominant negative inhibitory effect of a phosphatase-deficient mutant on expression of a beta-casein promoter-controlled reporter gene is evidence for an essential role of fully functional PTP1D in the regulation of milk protein gene transcription.
Full text
PDF

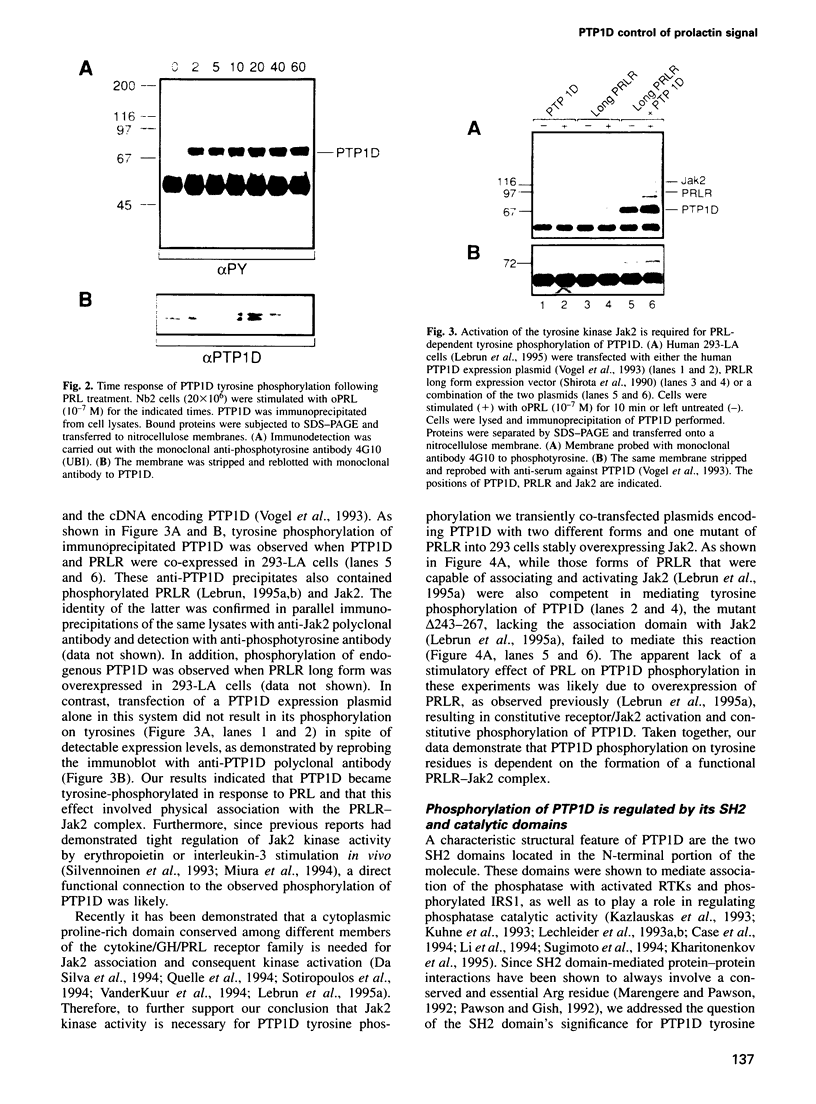

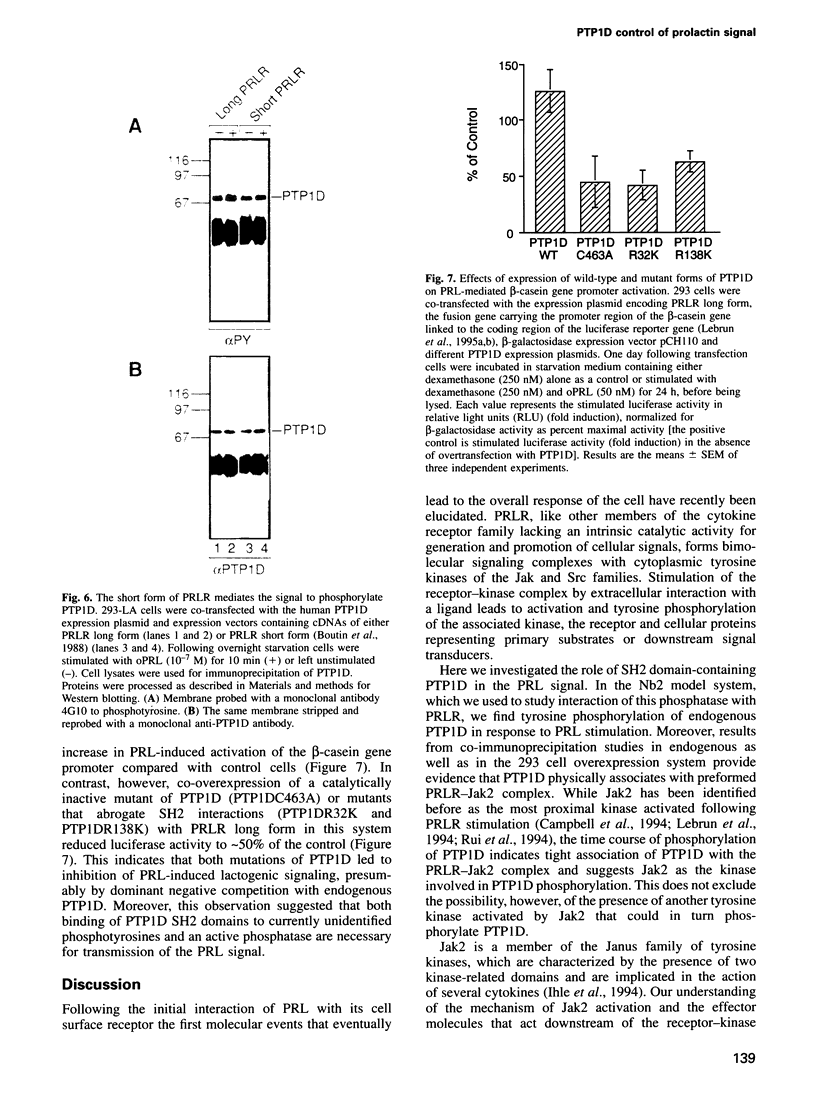



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi M., Sekiya M., Miyachi T., Matsuno K., Hinoda Y., Imai K., Yachi A. Molecular cloning of a novel protein-tyrosine phosphatase SH-PTP3 with sequence similarity to the src-homology region 2. FEBS Lett. 1992 Dec 21;314(3):335–339. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81500-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad S., Banville D., Zhao Z., Fischer E. H., Shen S. H. A widely expressed human protein-tyrosine phosphatase containing src homology 2 domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2197–2201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali S., Edery M., Pellegrini I., Lesueur L., Paly J., Djiane J., Kelly P. A. The Nb2 form of prolactin receptor is able to activate a milk protein gene promoter. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Aug;6(8):1242–1248. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.8.1406702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali S., Pellegrini I., Kelly P. A. A prolactin-dependent immune cell line (Nb2) expresses a mutant form of prolactin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20110–20117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. A novel family of growth factor receptors: a common binding domain in the growth hormone, prolactin, erythropoietin and IL-6 receptors, and the p75 IL-2 receptor beta-chain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 31;164(2):788–795. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91528-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A. M., Tang T. L., Sugimoto S., Walsh C. T., Neel B. G. Protein-tyrosine-phosphatase SHPTP2 couples platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta to Ras. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):7335–7339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Stahl N., Yancopoulos G. D. Ciliary neurotrophic factor/leukemia inhibitory factor/interleukin 6/oncostatin M family of cytokines induces tyrosine phosphorylation of a common set of proteins overlapping those induced by other cytokines and growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11648–11655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutin J. M., Jolicoeur C., Okamura H., Gagnon J., Edery M., Shirota M., Banville D., Dusanter-Fourt I., Djiane J., Kelly P. A. Cloning and expression of the rat prolactin receptor, a member of the growth hormone/prolactin receptor gene family. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90488-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell G. S., Argetsinger L. S., Ihle J. N., Kelly P. A., Rillema J. A., Carter-Su C. Activation of JAK2 tyrosine kinase by prolactin receptors in Nb2 cells and mouse mammary gland explants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5232–5236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case R. D., Piccione E., Wolf G., Benett A. M., Lechleider R. J., Neel B. G., Shoelson S. E. SH-PTP2/Syp SH2 domain binding specificity is defined by direct interactions with platelet-derived growth factor beta-receptor, epidermal growth factor receptor, and insulin receptor substrate-1-derived phosphopeptides. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10467–10474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K. 1002 protein phosphatases? Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:463–493. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DaSilva L., Howard O. M., Rui H., Kirken R. A., Farrar W. L. Growth signaling and JAK2 association mediated by membrane-proximal cytoplasmic regions of prolactin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 15;269(28):18267–18270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doppler W. Regulation of gene expression by prolactin. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1994;124:93–130. doi: 10.1007/BFb0031032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusanter-Fourt I., Muller O., Ziemiecki A., Mayeux P., Drucker B., Djiane J., Wilks A., Harpur A. G., Fischer S., Gisselbrecht S. Identification of JAK protein tyrosine kinases as signaling molecules for prolactin. Functional analysis of prolactin receptor and prolactin-erythropoietin receptor chimera expressed in lymphoid cells. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 1;13(11):2583–2591. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06548.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng G. S., Hui C. C., Pawson T. SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase as a target of protein-tyrosine kinases. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1607–1611. doi: 10.1126/science.8096088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. M., Jr, Plutzky J., Neel B. G. Identification of a human src homology 2-containing protein-tyrosine-phosphatase: a putative homolog of Drosophila corkscrew. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11239–11243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouilleux F., Wakao H., Mundt M., Groner B. Prolactin induces phosphorylation of Tyr694 of Stat5 (MGF), a prerequisite for DNA binding and induction of transcription. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 15;13(18):4361–4369. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06756.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gout P. W., Beer C. T., Noble R. L. Prolactin-stimulated growth of cell cultures established from malignant Nb rat lymphomas. Cancer Res. 1980 Jul;40(7):2433–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Feng G. S., Pawson T., Valius M. The 64-kDa protein that associates with the platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta subunit via Tyr-1009 is the SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase Syp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):6939–6943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.6939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. A., Ali S., Rozakis M., Goujon L., Nagano M., Pellegrini I., Gould D., Djiane J., Edery M., Finidori J. The growth hormone/prolactin receptor family. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1993;48:123–164. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571148-7.50009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingmüller U., Lorenz U., Cantley L. C., Neel B. G., Lodish H. F. Specific recruitment of SH-PTP1 to the erythropoietin receptor causes inactivation of JAK2 and termination of proliferative signals. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):729–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90351-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhné M. R., Pawson T., Lienhard G. E., Feng G. S. The insulin receptor substrate 1 associates with the SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase Syp. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11479–11481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner A. C., David M., Feldman G. M., Igarashi K., Hackett R. H., Webb D. S., Sweitzer S. M., Petricoin E. F., 3rd, Finbloom D. S. Tyrosine phosphorylation of DNA binding proteins by multiple cytokines. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1730–1733. doi: 10.1126/science.8378773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrun J. J., Ali S., Goffin V., Ullrich A., Kelly P. A. A single phosphotyrosine residue of the prolactin receptor is responsible for activation of gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 25;92(9):4031–4035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.9.4031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrun J. J., Ali S., Sofer L., Ullrich A., Kelly P. A. Prolactin-induced proliferation of Nb2 cells involves tyrosine phosphorylation of the prolactin receptor and its associated tyrosine kinase JAK2. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):14021–14026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrun J. J., Ali S., Ullrich A., Kelly P. A. Proline-rich sequence-mediated Jak2 association to the prolactin receptor is required but not sufficient for signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 5;270(18):10664–10670. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.18.10664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechleider R. J., Freeman R. M., Jr, Neel B. G. Tyrosyl phosphorylation and growth factor receptor association of the human corkscrew homologue, SH-PTP2. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13434–13438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechleider R. J., Sugimoto S., Bennett A. M., Kashishian A. S., Cooper J. A., Shoelson S. E., Walsh C. T., Neel B. G. Activation of the SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase SH-PTP2 by its binding site, phosphotyrosine 1009, on the human platelet-derived growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21478–21481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W., Nishimura R., Kashishian A., Batzer A. G., Kim W. J., Cooper J. A., Schlessinger J. A new function for a phosphotyrosine phosphatase: linking GRB2-Sos to a receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):509–517. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marengere L. E., Pawson T. Identification of residues in GTPase-activating protein Src homology 2 domains that control binding to tyrosine phosphorylated growth factor receptors and p62. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):22779–22786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R. J., Bowne D. B., Flores E., Thomas M. L. Characterization of hematopoietic intracellular protein tyrosine phosphatases: description of a phosphatase containing an SH2 domain and another enriched in proline-, glutamic acid-, serine-, and threonine-rich sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2396–2405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milarski K. L., Saltiel A. R. Expression of catalytically inactive Syp phosphatase in 3T3 cells blocks stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by insulin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 19;269(33):21239–21243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura O., Nakamura N., Quelle F. W., Witthuhn B. A., Ihle J. N., Aoki N. Erythropoietin induces association of the JAK2 protein tyrosine kinase with the erythropoietin receptor in vivo. Blood. 1994 Sep 1;84(5):1501–1507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi T., Matozaki T., Horita K., Fujioka Y., Kasuga M. Role of SH-PTP2, a protein-tyrosine phosphatase with Src homology 2 domains, in insulin-stimulated Ras activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6674–6682. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neal K. D., Yu-Lee L. Y. Differential signal transduction of the short, Nb2, and long prolactin receptors. Activation of interferon regulatory factor-1 and cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 21;269(42):26076–26082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Gish G. D. SH2 and SH3 domains: from structure to function. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):359–362. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins L. A., Larsen I., Perrimon N. corkscrew encodes a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase that functions to transduce the terminal signal from the receptor tyrosine kinase torso. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):225–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90098-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plutzky J., Neel B. G., Rosenberg R. D. Isolation of a src homology 2-containing tyrosine phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1123–1127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quelle F. W., Sato N., Witthuhn B. A., Inhorn R. C., Eder M., Miyajima A., Griffin J. D., Ihle J. N. JAK2 associates with the beta c chain of the receptor for granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and its activation requires the membrane-proximal region. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4335–4341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rui H., Djeu J. Y., Evans G. A., Kelly P. A., Farrar W. L. Prolactin receptor triggering. Evidence for rapid tyrosine kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):24076–24081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rui H., Kirken R. A., Farrar W. L. Activation of receptor-associated tyrosine kinase JAK2 by prolactin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 18;269(7):5364–5368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. H., Bastien L., Posner B. I., Chrétien P. A protein-tyrosine phosphatase with sequence similarity to the SH2 domain of the protein-tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):736–739. doi: 10.1038/352736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirota M., Banville D., Ali S., Jolicoeur C., Boutin J. M., Edery M., Djiane J., Kelly P. A. Expression of two forms of prolactin receptor in rat ovary and liver. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1136–1143. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-8-1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Ziemiecki A., Wilks A. F., Harpur A. G., Sadowski H. B., Gilman M. Z., Darnell J. E. Polypeptide signalling to the nucleus through tyrosine phosphorylation of Jak and Stat proteins. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):580–583. doi: 10.1038/366580a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvennoinen O., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Cleveland J. L., Yi T., Ihle J. N. Structure of the murine Jak2 protein-tyrosine kinase and its role in interleukin 3 signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8429–8433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotiropoulos A., Perrot-Applanat M., Dinerstein H., Pallier A., Postel-Vinay M. C., Finidori J., Kelly P. A. Distinct cytoplasmic regions of the growth hormone receptor are required for activation of JAK2, mitogen-activated protein kinase, and transcription. Endocrinology. 1994 Oct;135(4):1292–1298. doi: 10.1210/endo.135.4.7925092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein-Gerlach M., Kharitonenkov A., Vogel W., Ali S., Ullrich A. Protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1D modulates its own state of tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 20;270(42):24635–24637. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.42.24635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto S., Wandless T. J., Shoelson S. E., Neel B. G., Walsh C. T. Activation of the SH2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase, SH-PTP2, by phosphotyrosine-containing peptides derived from insulin receptor substrate-1. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 6;269(18):13614–13622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauchi T., Feng G. S., Marshall M. S., Shen R., Mantel C., Pawson T., Broxmeyer H. E. The ubiquitously expressed Syp phosphatase interacts with c-kit and Grb2 in hematopoietic cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 7;269(40):25206–25211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauchi T., Feng G. S., Shen R., Hoatlin M., Bagby G. C., Jr, Kabat D., Lu L., Broxmeyer H. E. Involvement of SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase Syp in erythropoietin receptor signal transduction pathways. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 10;270(10):5631–5635. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.10.5631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanderKuur J. A., Wang X., Zhang L., Campbell G. S., Allevato G., Billestrup N., Norstedt G., Carter-Su C. Domains of the growth hormone receptor required for association and activation of JAK2 tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 26;269(34):21709–21717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel W., Lammers R., Huang J., Ullrich A. Activation of a phosphotyrosine phosphatase by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1611–1614. doi: 10.1126/science.7681217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakao H., Gouilleux F., Groner B. Mammary gland factor (MGF) is a novel member of the cytokine regulated transcription factor gene family and confers the prolactin response. EMBO J. 1994 May 1;13(9):2182–2191. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06495.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welham M. J., Dechert U., Leslie K. B., Jirik F., Schrader J. W. Interleukin (IL)-3 and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor, but not IL-4, induce tyrosine phosphorylation, activation, and association of SHPTP2 with Grb2 and phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 23;269(38):23764–23768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao S., Rose D. W., Sasaoka T., Maegawa H., Burke T. R., Jr, Roller P. P., Shoelson S. E., Olefsky J. M. Syp (SH-PTP2) is a positive mediator of growth factor-stimulated mitogenic signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 19;269(33):21244–21248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi K., Milarski K. L., Saltiel A. R., Pessin J. E. Protein-tyrosine-phosphatase SHPTP2 is a required positive effector for insulin downstream signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 31;92(3):664–668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi T. L., Cleveland J. L., Ihle J. N. Protein tyrosine phosphatase containing SH2 domains: characterization, preferential expression in hematopoietic cells, and localization to human chromosome 12p12-p13. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):836–846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi T., Mui A. L., Krystal G., Ihle J. N. Hematopoietic cell phosphatase associates with the interleukin-3 (IL-3) receptor beta chain and down-regulates IL-3-induced tyrosine phosphorylation and mitogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7577–7586. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]