Abstract
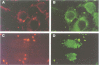
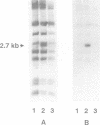
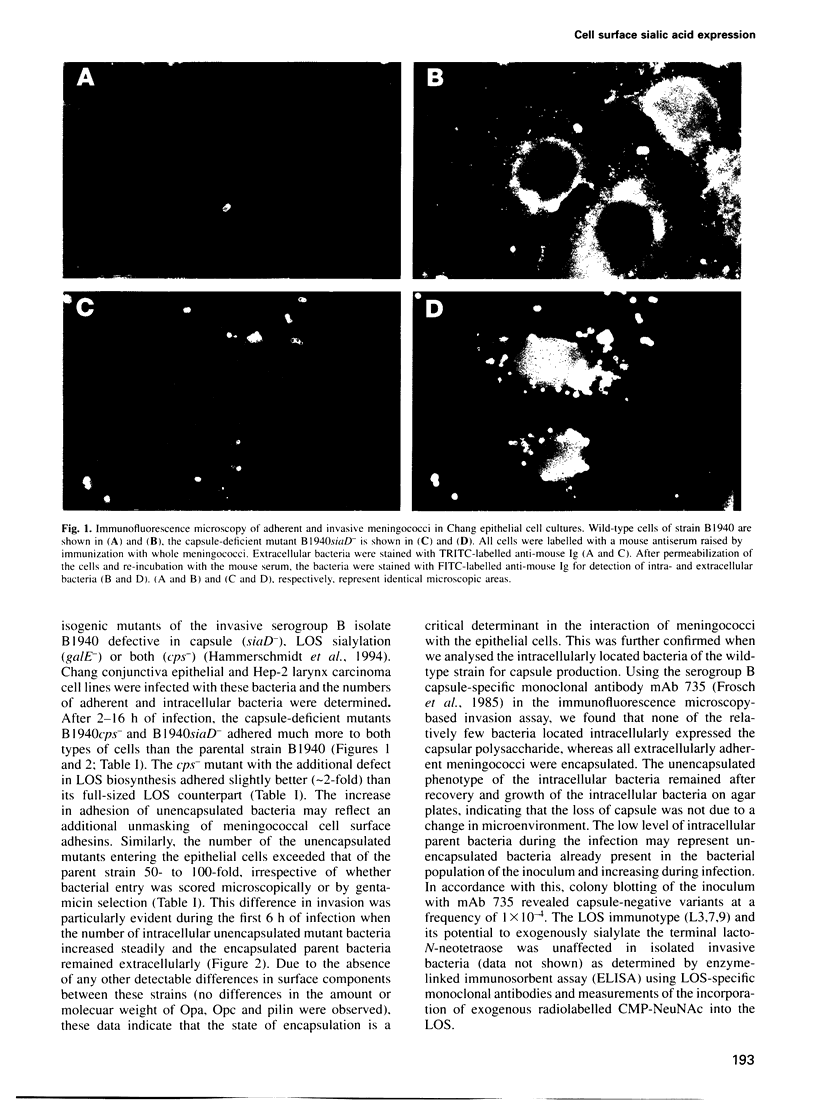
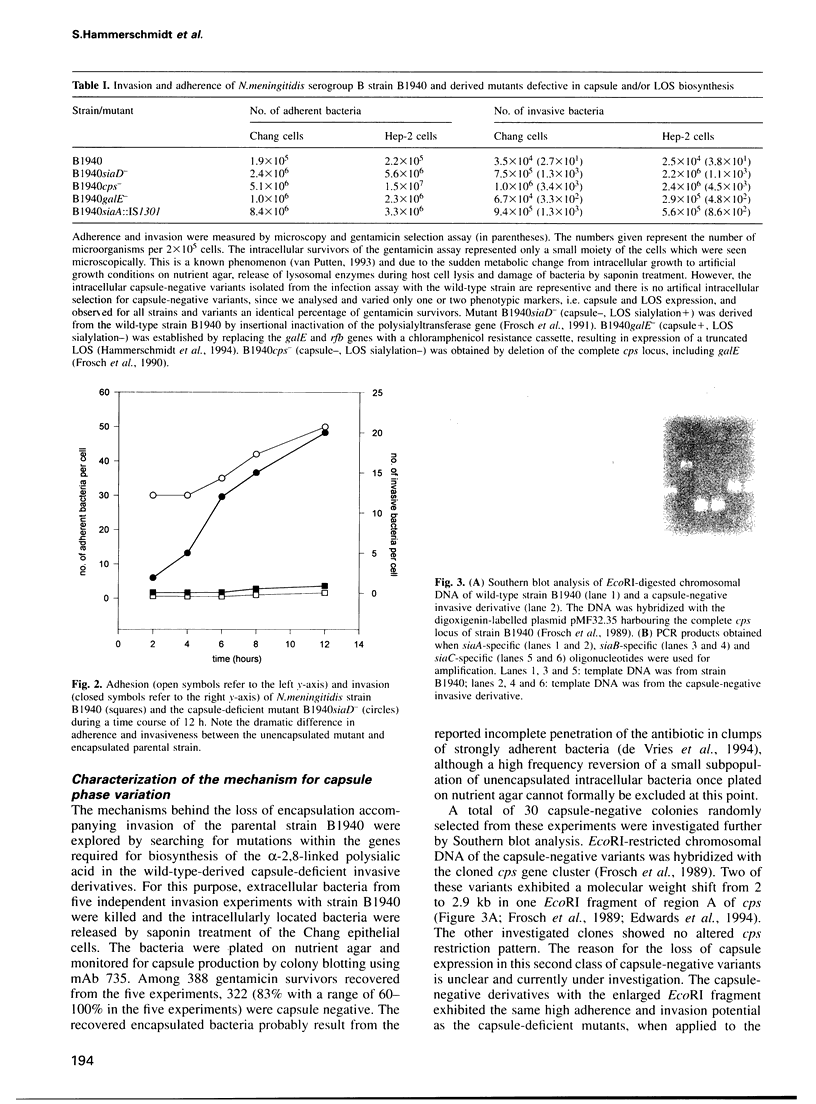
Cell surface-located sialic acids of the capsule and the lipooligosaccharide (LOS) are both pivotal virulence factors in Neisseria meningitidis, promoting survival and dissemination of this pathogen which can cause both sepsis and meningitis. With the aid of a unique set of isogenic meningococcal mutants defective in the expression of cell surface-located sialic acids, we have demonstrated that encapsulation hinders the primary event in the development of the disease, but the spontaneous switching of encapsulated wild-type bacteria to a capsule-negative phenotype promotes meningococcal adherence and invasion into mucosal epithelial cells. Genetic analysis of the capsule-negative, invasive bacteria revealed a unique mechanism for modulation of capsule expression based on the reversible inactivation of an essential sialic acid biosynthesis gene, siaA, by insertion/excision of a naturally occurring insertion sequence element, IS1301. Inactivation of siaA regulates both capsule expression and endogenous LOS sialylation. This is the first example of an insertion sequence element-based genetic switch mechanism in the pathogenic bacterium and is an important step in the understanding of bacterial virulence.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett D. H., Wright M. E., Silverman M. Variable expression of extracellular polysaccharide in the marine bacterium Pseudomonas atlantica is controlled by genome rearrangement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3923–3927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger U., Sonntag H. G., Ulbrich C. Epidemiology of meningococcal infections in the Federal Republic of Germany, 1966-1984. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Mar;268(1):83–102. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards U., Müller A., Hammerschmidt S., Gerardy-Schahn R., Frosch M. Molecular analysis of the biosynthesis pathway of the alpha-2,8 polysialic acid capsule by Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Oct;14(1):141–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frosch M., Edwards U., Bousset K., Krausse B., Weisgerber C. Evidence for a common molecular origin of the capsule gene loci in gram-negative bacteria expressing group II capsular polysaccharides. Mol Microbiol. 1991 May;5(5):1251–1263. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frosch M., Görgen I., Boulnois G. J., Timmis K. N., Bitter-Suermann D. NZB mouse system for production of monoclonal antibodies to weak bacterial antigens: isolation of an IgG antibody to the polysaccharide capsules of Escherichia coli K1 and group B meningococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frosch M., Schultz E., Glenn-Calvo E., Meyer T. F. Generation of capsule-deficient Neisseria meningitidis strains by homologous recombination. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1215–1218. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00697.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frosch M., Weisgerber C., Meyer T. F. Molecular characterization and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene complex encoding the polysaccharide capsule of Neisseria meningitidis group B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1669–1673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halling S. M., Tatum F. M., Bricker B. J. Sequence and characterization of an insertion sequence, IS711, from Brucella ovis. Gene. 1993 Oct 29;133(1):123–127. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90236-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt S., Birkholz C., Zähringer U., Robertson B. D., van Putten J., Ebeling O., Frosch M. Contribution of genes from the capsule gene complex (cps) to lipooligosaccharide biosynthesis and serum resistance in Neisseria meningitidis. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Mar;11(5):885–896. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00367.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbein B. E., Jericho K. W., Likes G. C. Neisseria meningitidis infection in mice: influence of iron, variations in virulence among strains, and pathology. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):545–551. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.545-551.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis G. A. Recognition and control of neisserial infection by antibody and complement. Trends Microbiol. 1995 May;3(5):198–201. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(00)88921-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Bhattacharjee A. K., Bundle D. R., Kenny C. P., Martin A., Smith I. C. Strucutres of the capsular polysaccharides of Neisseria meningitidis as determined by 13C-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S78–S83. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüneberg E., Jensen J. S., Frosch M. Detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae by polymerase chain reaction and nonradioactive hybridization in microtiter plates. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 May;31(5):1088–1094. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.5.1088-1094.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrell R. E., Lesse A. J., Sugai J. V., Shero M., Griffiss J. M., Cole J. A., Parsons N. J., Smith H., Morse S. A., Apicella M. A. In vitro and in vivo modification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipooligosaccharide epitope structure by sialylation. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1649–1664. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrell R. E., Smith H., Jarvis G. A., Griffiss J. M., Cole J. A. Detection and some properties of the sialyltransferase implicated in the sialylation of lipopolysaccharide of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Microb Pathog. 1993 Apr;14(4):307–313. doi: 10.1006/mpat.1993.1030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor J., Fulton S. M., Dobson M. J., Wilson W., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. A retrovirus-like strategy for expression of a fusion protein encoded by yeast transposon Ty1. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):243–246. doi: 10.1038/313243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J. T., Baron L. S., Rubin F. A., Kopecko D. J. Specific insertion and deletion of insertion sequence 1-like DNA element causes the reversible expression of the virulence capsular antigen Vi of Citrobacter freundii in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4402–4405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prère M. F., Chandler M., Fayet O. Transposition in Shigella dysenteriae: isolation and analysis of IS911, a new member of the IS3 group of insertion sequences. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):4090–4099. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.4090-4099.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B. D., Meyer T. F. Genetic variation in pathogenic bacteria. Trends Genet. 1992 Dec;8(12):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90325-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlech W. F., 3rd, Ward J. I., Band J. D., Hightower A., Fraser D. W., Broome C. V. Bacterial meningitis in the United States, 1978 through 1981. The National Bacterial Meningitis Surveillance Study. JAMA. 1985 Mar 22;253(12):1749–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekine Y., Ohtsubo E. Frameshifting is required for production of the transposase encoded by insertion sequence 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4609–4613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens D. S., Farley M. M. Pathogenic events during infection of the human nasopharynx with Neisseria meningitidis and Haemophilus influenzae. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Jan-Feb;13(1):22–33. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens D. S., Spellman P. A., Swartley J. S. Effect of the (alpha 2-->8)-linked polysialic acid capsule on adherence of Neisseria meningitidis to human mucosal cells. J Infect Dis. 1993 Feb;167(2):475–479. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.2.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenzen T., Ohtsubo E. Preferential transposition of an IS630-associated composite transposon to TA in the 5'-CTAG-3' sequence. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6207–6212. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6207-6212.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M., Makepeace K., Ferguson D. J., Achtman M., Moxon E. R. Meningococcal Opa and Opc proteins: their role in colonization and invasion of human epithelial and endothelial cells. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Nov;10(3):499–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00922.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M., Makepeace K., Ferguson D. J., Achtman M., Sarkari J., Moxon E. R. Expression of the Opc protein correlates with invasion of epithelial and endothelial cells by Neisseria meningitidis. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Oct;6(19):2785–2795. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Putten J. P. Phase variation of lipopolysaccharide directs interconversion of invasive and immuno-resistant phenotypes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4043–4051. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]