Abstract
Galanin, a neuroendocrine peptide of 29 amino acids, binds to Gi/Go-coupled receptors to trigger cellular responses. To determine which amino acids of the recently cloned seven-transmembrane domain-type human galanin receptor are involved in the high-affinity binding of the endogenous peptide ligand, we performed a mutagenesis study. Mutation of the His264 or His267 of transmembrane domain VI to alanine, or of Phe282 of transmembrane domain VII to glycine, results in an apparent loss of galanin binding. The substitution of Glu271 to serine in the extracellular loop III of the receptor causes a 12-fold loss in affinity for galanin. We combined the mutagenesis results with data on the pharmacophores (Trp2, Tyr9) of galanin and with molecular modelling of the receptor using bacteriorhodopsin as a model. Based on these studies, we propose a binding site model for the endogenous peptide ligand in the galanin receptor where the N-terminus of galanin hydrogen bonds with Glu271 of the receptor, Trp2 of galanin interacts with the Zn2+ sensitive pair of His264 and His267 of transmembrane domain VI, and Tyr9 of galanin interacts with Phe282 of transmembrane domain VII, while the C-terminus of galanin is pointing towards the N-terminus of th
Full text
PDF


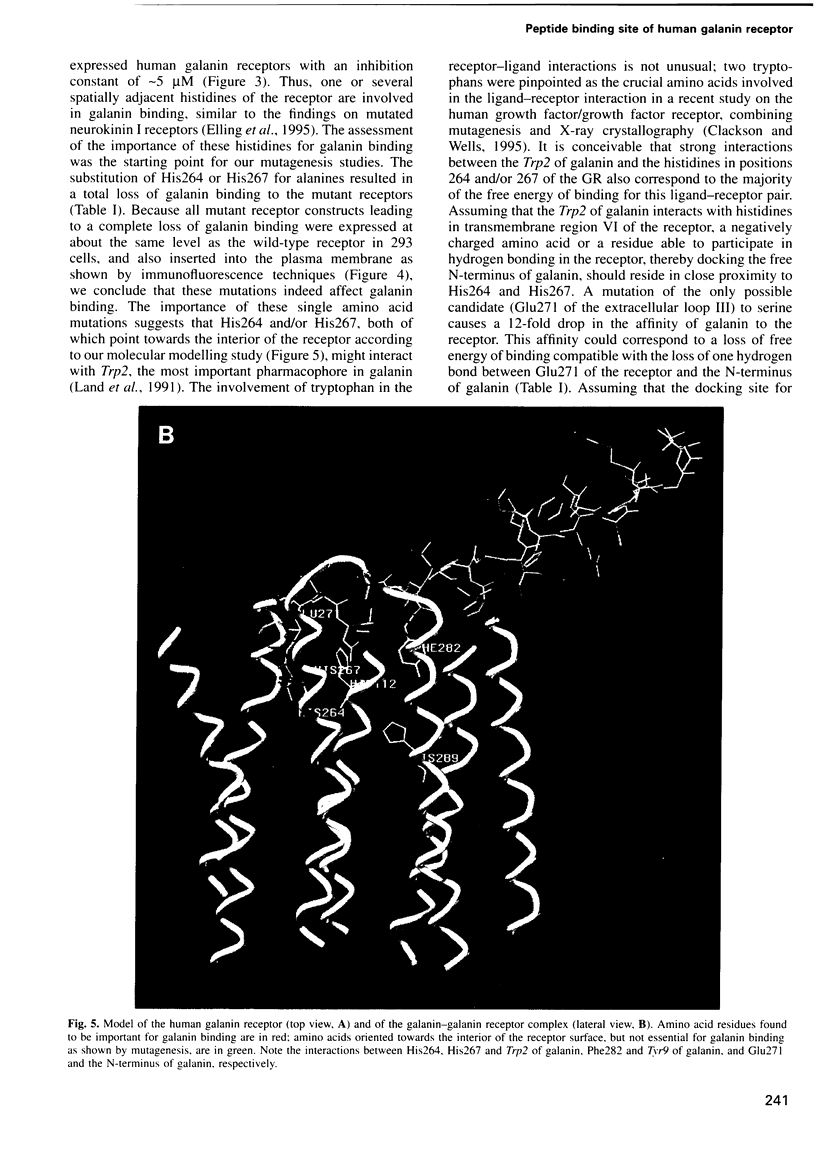



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartfai T., Hökfelt T., Langel U. Galanin--a neuroendocrine peptide. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1993;7(3-4):229–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer F. E., Ginsberg L., Venetikou M., MacKay D. J., Burrin J. M., Bloom S. R. Growth hormone release in man induced by galanin, a new hypothalamic peptide. Lancet. 1986 Jul 26;2(8500):192–195. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92490-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedecs K., Langel U., Bartfai T. Metabolism of galanin and galanin (1-16) in isolated cerebrospinal fluid and spinal cord membranes from rat. Neuropeptides. 1995 Sep;29(3):137–143. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(95)90015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beinborn M., Lee Y. M., McBride E. W., Quinn S. M., Kopin A. S. A single amino acid of the cholecystokinin-B/gastrin receptor determines specificity for non-peptide antagonists. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):348–350. doi: 10.1038/362348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benelli A., Arletti R., Bertolini A., Menozzi B., Basaglia R., Poggioli R. Galantide stimulates sexual behaviour in male rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Aug 1;260(2-3):279–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90352-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clackson T., Wells J. A. A hot spot of binding energy in a hormone-receptor interface. Science. 1995 Jan 20;267(5196):383–386. doi: 10.1126/science.7529940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elling C. E., Nielsen S. M., Schwartz T. W. Conversion of antagonist-binding site to metal-ion site in the tachykinin NK-1 receptor. Nature. 1995 Mar 2;374(6517):74–77. doi: 10.1038/374074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans H. F., Shine J. Human galanin: molecular cloning reveals a unique structure. Endocrinology. 1991 Sep;129(3):1682–1684. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-3-1682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fathi Z., Benya R. V., Shapira H., Jensen R. T., Battey J. F. The fifth transmembrane segment of the neuromedin B receptor is critical for high affinity neuromedin B binding. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14622–14626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisone G., Langel U., Carlquist M., Bergman T., Consolo S., Hökfelt T., Undén A., Andell S., Bartfai T. Galanin receptor and its ligands in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 15;181(1):269–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong T. M., Cascieri M. A., Yu H., Bansal A., Swain C., Strader C. D. Amino-aromatic interaction between histidine 197 of the neurokinin-1 receptor and CP 96345. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):350–353. doi: 10.1038/362350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong T. M., Yu H., Huang R. R., Strader C. D. The extracellular domain of the neurokinin-1 receptor is required for high-affinity binding of peptides. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 1;31(47):11806–11811. doi: 10.1021/bi00162a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gether U., Johansen T. E., Snider R. M., Lowe J. A., 3rd, Nakanishi S., Schwartz T. W. Different binding epitopes on the NK1 receptor for substance P and non-peptide antagonist. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):345–348. doi: 10.1038/362345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habert-Ortoli E., Amiranoff B., Loquet I., Laburthe M., Mayaux J. F. Molecular cloning of a functional human galanin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):9780–9783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.9780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaupmann K., Bruns C., Raulf F., Weber H. P., Mattes H., Lübbert H. Two amino acids, located in transmembrane domains VI and VII, determine the selectivity of the peptide agonist SMS 201-995 for the SSTR2 somatostatin receptor. EMBO J. 1995 Feb 15;14(4):727–735. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07051.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagny-Pourmir I., Lorinet A. M., Yanaihara N., Laburthe M. Structural requirements for galanin interaction with receptors from pancreatic beta cells and from brain tissue of the rat. Peptides. 1989 Jul-Aug;10(4):757–761. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land T., Langel U., Löw M., Berthold M., Undén A., Bartfai T. Linear and cyclic N-terminal galanin fragments and analogs as ligands at the hypothalamic galanin receptor. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1991 Sep;38(3):267–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1991.tb01438.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz S. F., Kim T. Impact of a galanin antagonist on exogenous galanin and natural patterns of fat ingestion. Brain Res. 1992 Dec 18;599(1):148–152. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90863-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorinet A. M., Javoy-Agid F., Laburthe M., Amiranoff B. Galanin receptors in human hypothalamus: biochemical and structural analysis. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Sep 15;269(1):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. J., Dupre J., Tatemoto K., Greenberg G. R., Radziuk J., Mutt V. Galanin inhibits insulin secretion and induces hyperglycemia in dogs. Diabetes. 1985 Feb;34(2):192–196. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.2.192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchenthaler I., López F. J., Negro-Vilar A. Anatomy and physiology of central galanin-containing pathways. Prog Neurobiol. 1993 Jun;40(6):711–769. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(93)90012-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordvall G., Hacksell U. Binding-site modeling of the muscarinic m1 receptor: a combination of homology-based and indirect approaches. J Med Chem. 1993 Apr 16;36(8):967–976. doi: 10.1021/jm00060a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossowski W. J., Rossowski T. M., Zacharia S., Ertan A., Coy D. H. Galanin binding sites in rat gastric and jejunal smooth muscle membrane preparations. Peptides. 1990 Mar-Apr;11(2):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(90)90089-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schambye H. T., Hjorth S. A., Bergsma D. J., Sathe G., Schwartz T. W. Differentiation between binding sites for angiotensin II and nonpeptide antagonists on the angiotensin II type 1 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):7046–7050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schambye H. T., Hjorth S. A., Weinstock J., Schwartz T. W. Interaction between the nonpeptide angiotensin antagonist SKF-108,566 and histidine 256 (HisVI:16) of the angiotensin type 1 receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Mar;47(3):425–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schertler G. F., Villa C., Henderson R. Projection structure of rhodopsin. Nature. 1993 Apr 22;362(6422):770–772. doi: 10.1038/362770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasuka T., Sakurai T., Goto K., Furuichi Y., Watanabe T. Human endothelin receptor ETB. Amino acid sequence requirements for super stable complex formation with its ligand. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7509–7513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Rökaeus A., Jörnvall H., McDonald T. J., Mutt V. Galanin - a novel biologically active peptide from porcine intestine. FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 28;164(1):124–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger V. M., Schertler G. F. Low resolution structure of bovine rhodopsin determined by electron cryo-microscopy. Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):1776–1786. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80354-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. B., Johnson P. S., Wu J. M., Wang W. F., Uhl G. R. Human kappa opiate receptor second extracellular loop elevates dynorphin's affinity for human mu/kappa chimeras. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 21;269(42):25966–25969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennerberg A. B., Cooke R. M., Carlquist M., Rigler R., Campbell I. D. A 1H NMR study of the solution conformation of the neuropeptide galanin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Feb 14;166(3):1102–1109. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90980-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Xu X. J., Langel U., Bedecs K., Hökfelt T., Bartfai T. Galanin-mediated control of pain: enhanced role after nerve injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3334–3337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynick D., Smith D. M., Ghatei M., Akinsanya K., Bhogal R., Purkiss P., Byfield P., Yanaihara N., Bloom S. R. Characterization of a high-affinity galanin receptor in the rat anterior pituitary: absence of biological effect and reduced membrane binding of the antagonist M15 differentiate it from the brain/gut receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4231–4235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y., Song J., Bruno J. F., Berelowitz M. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a human somatostatin receptor, hSSTR4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jun 15;193(2):648–652. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]