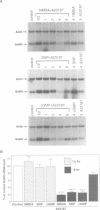
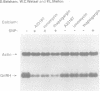
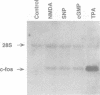
Abstract
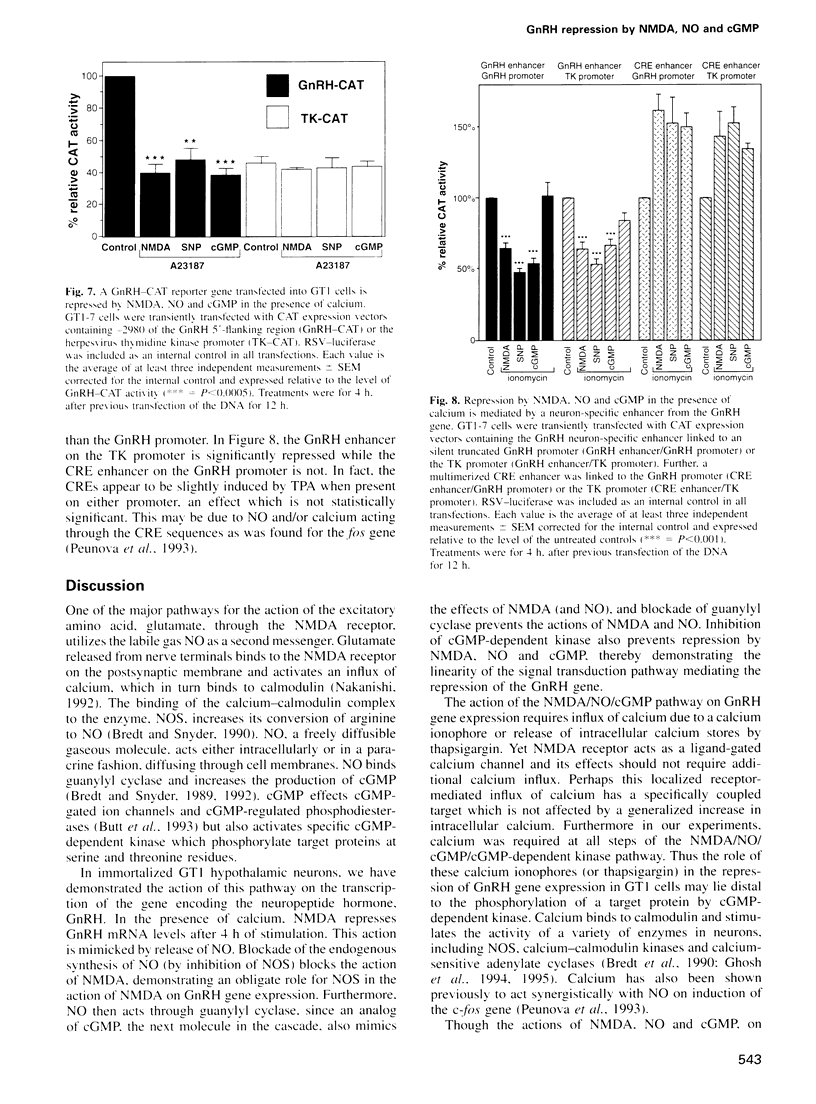
The key roles of the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate and its second messengers, nitric oxide (NO) and cGMP, in long-term potentiation and neural plasticity are well documented. However, complex functions such as memory are likely to require long term changes in synaptic efficacy which require gene expression and protein synthesis. Here we demonstrate that the glutamate receptor agonist, N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA), nitric oxide (NO) and cGMP each repress expression of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) gene in the hypothalamic cell line, GT1. This repression is dependent upon signals from NMDA receptors activating NO synthase to synthesize NO. In turn NO induces guanylyl cyclase to synthesize cGMP, activating cGMP- dependent protein kinase. Repression requires elevation of calcium because it only occurs in the presence of calcium ionophore or with release of intracellular calcium. Repression also requires protein synthesis. Activation of this pathway specifically represses expression of a reporter gene containing the regulatory region of the GnRH gene in transfected GT1 cells, indicating that repression occurs at the transcriptional level. Furthermore the target for transcriptional repression is a 300 bp neuron-specific enhancer found 1.5 kb upstream of the GnRH gene which is sufficient to confer repression to a heterologous promoter. Thus the NMDA/NO/cGMP neurotransmitter signal transduction pathway controls not only synaptic function but also neuron-specific gene expression.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman J. P., Mason A. J., Hayflick J. S., Seeburg P. H. Isolation of the gene and hypothalamic cDNA for the common precursor of gonadotropin-releasing hormone and prolactin release-inhibiting factor in human and rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):179–183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bading H., Ginty D. D., Greenberg M. E. Regulation of gene expression in hippocampal neurons by distinct calcium signaling pathways. Science. 1993 Apr 9;260(5105):181–186. doi: 10.1126/science.8097060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliss T. V., Collingridge G. L. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993 Jan 7;361(6407):31–39. doi: 10.1038/361031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonavera J. J., Sahu A., Kalra P. S., Kalra S. P. Evidence that nitric oxide may mediate the ovarian steroid-induced luteinizing hormone surge: involvement of excitatory amino acids. Endocrinology. 1993 Dec;133(6):2481–2487. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.6.8243268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon J. P., Gerard A., Mathieu J., Simons J., Franchimont P. Pulsatile release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone from hypothalamic explants is restrained by blockade of N-methyl-D,L-aspartate receptors. Endocrinology. 1989 Aug;125(2):1090–1096. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-2-1090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon J. P., Gérard A., Franchimont P. Direct activation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone secretion through different receptors to neuroexcitatory amino acids. Neuroendocrinology. 1989 Apr;49(4):402–408. doi: 10.1159/000125145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourtchuladze R., Frenguelli B., Blendy J., Cioffi D., Schutz G., Silva A. J. Deficient long-term memory in mice with a targeted mutation of the cAMP-responsive element-binding protein. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90400-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Glatt C. E., Hwang P. M., Fotuhi M., Dawson T. M., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide synthase protein and mRNA are discretely localized in neuronal populations of the mammalian CNS together with NADPH diaphorase. Neuron. 1991 Oct;7(4):615–624. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90374-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Snyder S. H. Localization of nitric oxide synthase indicating a neural role for nitric oxide. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):768–770. doi: 10.1038/347768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Isolation of nitric oxide synthetase, a calmodulin-requiring enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):682–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide mediates glutamate-linked enhancement of cGMP levels in the cerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):9030–9033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.9030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide, a novel neuronal messenger. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):3–11. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90104-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruder J. M., Krebs W. D., Nett T. M., Wierman M. E. Phorbol ester activation of the protein kinase C pathway inhibits gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene expression. Endocrinology. 1992 Dec;131(6):2552–2558. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.6.1446598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruder J. M., Wierman M. E. Evidence for transcriptional inhibition of GnRH gene expression by phorbol ester at a proximal promoter region. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1994 Mar;99(2):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(94)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruhwyler J., Chleide E., Liégeois J. F., Carreer F. Nitric oxide: a new messenger in the brain. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1993 Winter;17(4):373–384. doi: 10.1016/s0149-7634(05)80114-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt E., Geiger J., Jarchau T., Lohmann S. M., Walter U. The cGMP-dependent protein kinase--gene, protein, and function. Neurochem Res. 1993 Jan;18(1):27–42. doi: 10.1007/BF00966920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt E., van Bemmelen M., Fischer L., Walter U., Jastorff B. Inhibition of cGMP-dependent protein kinase by (Rp)-guanosine 3',5'-monophosphorothioates. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 9;263(1):47–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80702-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., WATKINS J. C. Acidic amino acids with strong excitatory actions on mammalian neurones. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:1–14. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. E., Mellon P. L. The POU homeodomain transcription factor Oct-1 is essential for activity of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuron-specific enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Nov;15(11):6169–6177. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.11.6169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Singer W. Excitatory amino acid receptors and synaptic plasticity. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jul;11(7):290–296. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90011-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoso A. O., López F. J., Negro-Vilar A. Glutamate receptors of the non-N-methyl-D-aspartic acid type mediate the increase in luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone release by excitatory amino acids in vitro. Endocrinology. 1990 Jan;126(1):414–420. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-1-414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eraly S. A., Mellon P. L. Regulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone transcription by protein kinase C is mediated by evolutionarily conserved promoter-proximal elements. Mol Endocrinol. 1995 Jul;9(7):848–859. doi: 10.1210/mend.9.7.7476968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D. A., Greenberg M. E. CREB: a mediator of long-term memory from mollusks to mammals. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90394-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J., Garthwaite G., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. NMDA receptor activation induces nitric oxide synthesis from arginine in rat brain slices. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Oct 17;172(4-5):413–416. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(89)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh A., Ginty D. D., Bading H., Greenberg M. E. Calcium regulation of gene expression in neuronal cells. J Neurobiol. 1994 Mar;25(3):294–303. doi: 10.1002/neu.480250309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh A., Greenberg M. E. Calcium signaling in neurons: molecular mechanisms and cellular consequences. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):239–247. doi: 10.1126/science.7716515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Yamamoto K. K., Fischer W. H., Karr D., Menzel P., Biggs W., 3rd, Vale W. W., Montminy M. R. A cluster of phosphorylation sites on the cyclic AMP-regulated nuclear factor CREB predicted by its sequence. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):749–752. doi: 10.1038/337749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gore A. C., Roberts J. L. Regulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene expression by the excitatory amino acids kainic acid and N-methyl-D,L-aspartate in the male rat. Endocrinology. 1994 May;134(5):2026–2031. doi: 10.1210/endo.134.5.8156903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haby C., Lisovoski F., Aunis D., Zwiller J. Stimulation of the cyclic GMP pathway by NO induces expression of the immediate early genes c-fos and junB in PC12 cells. J Neurochem. 1994 Feb;62(2):496–501. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62020496.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick J. S., Adelman J. P., Seeburg P. H. The complete nucleotide sequence of the human gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6403–6404. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler J. P., Meyer T. E., Yun Y., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP-responsive DNA-binding protein: structure based on a cloned placental cDNA. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1430–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.2974179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang P. L., Dawson T. M., Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H., Fishman M. C. Targeted disruption of the neuronal nitric oxide synthase gene. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1273–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90615-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Chang B., Kerwin J. F., Jr, Huang Z. J., Murad F. N omega-nitro-L-arginine: a potent inhibitor of endothelium-derived relaxing factor formation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb 6;176(2):219–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90531-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krsmanović L. Z., Stojilković S. S., Merelli F., Dufour S. M., Virmani M. A., Catt K. J. Calcium signaling and episodic secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone in hypothalamic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8462–8466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamas S., Marsden P. A., Li G. K., Tempst P., Michel T. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase: molecular cloning and characterization of a distinct constitutive enzyme isoform. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6348–6352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson M. A., Whyte D. B., Eraly S. A., Mellon P. L. Hypothalamus-specific regulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene expression. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1995;50:459–463. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571150-0.50037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liposits Z., Merchenthaler I., Wetsel W. C., Reid J. J., Mellon P. L., Weiner R. I., Negro-Vilar A. Morphological characterization of immortalized hypothalamic neurons synthesizing luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone. Endocrinology. 1991 Sep;129(3):1575–1583. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-3-1575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein C. J., Glatt C. S., Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Cloned and expressed macrophage nitric oxide synthase contrasts with the brain enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6711–6715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein C. J., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide, a novel biologic messenger. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):705–707. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90301-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López F. J., Donoso A. O., Negro-Vilar A. Endogenous excitatory amino acids and glutamate receptor subtypes involved in the control of hypothalamic luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone secretion. Endocrinology. 1992 Apr;130(4):1986–1992. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.4.1312433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahachoklertwattana P., Black S. M., Kaplan S. L., Bristow J. D., Grumbach M. M. Nitric oxide synthesized by gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons is a mediator of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-induced GnRH secretion. Endocrinology. 1994 Oct;135(4):1709–1712. doi: 10.1210/endo.135.4.7523101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahachoklertwattana P., Sanchez J., Kaplan S. L., Grumbach M. M. N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors mediate the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) by NMDA in a hypothalamic GnRH neuronal cell line (GT1-1). Endocrinology. 1994 Mar;134(3):1023–1030. doi: 10.1210/endo.134.3.8119138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez de la Escalera G., Choi A. L., Weiner R. I. Generation and synchronization of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) pulses: intrinsic properties of the GT1-1 GnRH neuronal cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1852–1855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. W., Johnston M. V. Physiological and pathophysiological roles of excitatory amino acids during central nervous system development. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1990 Jan-Apr;15(1):41–70. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(90)90011-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum B., Garthwaite J. Excitatory amino acid neurotoxicity and neurodegenerative disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Sep;11(9):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90184-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P. L., Clegg C. H., Correll L. A., McKnight G. S. Regulation of transcription by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P. L., Windle J. J., Goldsmith P. C., Padula C. A., Roberts J. L., Weiner R. I. Immortalization of hypothalamic GnRH neurons by genetically targeted tumorigenesis. Neuron. 1990 Jul;5(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90028-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monyer H., Burnashev N., Laurie D. J., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. Developmental and regional expression in the rat brain and functional properties of four NMDA receptors. Neuron. 1994 Mar;12(3):529–540. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90210-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretto M., López F. J., Negro-Vilar A. Nitric oxide regulates luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone secretion. Endocrinology. 1993 Nov;133(5):2399–2402. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.5.8104781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mülsch A., Busse R., Liebau S., Förstermann U. LY 83583 interferes with the release of endothelium-derived relaxing factor and inhibits soluble guanylate cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Oct;247(1):283–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S. Molecular diversity of glutamate receptors and implications for brain function. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):597–603. doi: 10.1126/science.1329206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman C., Runswick M., Pollock R., Treisman R. Isolation and properties of cDNA clones encoding SRF, a transcription factor that binds to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):989–1003. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dell T. J., Huang P. L., Dawson T. M., Dinerman J. L., Snyder S. H., Kandel E. R., Fishman M. C. Endothelial NOS and the blockade of LTP by NOS inhibitors in mice lacking neuronal NOS. Science. 1994 Jul 22;265(5171):542–546. doi: 10.1126/science.7518615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogura T., Yokoyama T., Fujisawa H., Kurashima Y., Esumi H. Structural diversity of neuronal nitric oxide synthase mRNA in the nervous system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jun 30;193(3):1014–1022. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olcese J., Middendorff R., Münker M., Schmidt C., McArdle C. A. Natriuretic peptides stimulate cyclic GMP production in an immortalized LHRH neuronal cell line. J Neuroendocrinol. 1994 Apr;6(2):127–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.1994.tb00562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. GATA-binding transcription factors in hematopoietic cells. Blood. 1992 Aug 1;80(3):575–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen S. L., McCrone S., Keller M., Gardner E. Rapid increase in LHRH mRNA levels following NMDA. Endocrinology. 1991 Sep;129(3):1679–1681. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-3-1679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peunova N., Enikolopov G. Amplification of calcium-induced gene transcription by nitric oxide in neuronal cells. Nature. 1993 Jul 29;364(6436):450–453. doi: 10.1038/364450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilz R. B., Suhasini M., Idriss S., Meinkoth J. L., Boss G. R. Nitric oxide and cGMP analogs activate transcription from AP-1-responsive promoters in mammalian cells. FASEB J. 1995 Apr;9(7):552–558. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.9.7.7737465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettori V., Belova N., Dees W. L., Nyberg C. L., Gimeno M., McCann S. M. Role of nitric oxide in the control of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone release in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10130–10134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambucetti L. C., Schaber M., Kramer R., Crowl R., Curran T. The fos gene product undergoes extensive post-translational modification in eukaryotic but not in prokaryotic cells. Gene. 1986;43(1-2):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H. H., Walter U. NO at work. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):919–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H. The TINS/TiPS Lecture. The molecular biology of mammalian glutamate receptor channels. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Sep;16(9):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Sheen J. Y. A simple phase-extraction assay for chloramphenicol acyltransferase activity. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Greenberg M. E. The regulation and function of c-fos and other immediate early genes in the nervous system. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90106-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sortino M. A., Aleppo G., Scapagnini U., Canonico P. L. Involvement of nitric oxide in the regulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone release from the GT1-1 neuronal cell line. Endocrinology. 1994 Apr;134(4):1782–1787. doi: 10.1210/endo.134.4.7511093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. F. CREB and memory consolidation. Neuron. 1994 Oct;13(4):769–770. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90244-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbanski H. F., Fahy M. M., Daschel M., Meshul C. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor gene expression in the hamster hypothalamus and in immortalized luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone neurones. J Reprod Fertil. 1994 Jan;100(1):5–9. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.1000005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetsel W. C., Eraly S. A., Whyte D. B., Mellon P. L. Regulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone by protein kinase-A and -C in immortalized hypothalamic neurons. Endocrinology. 1993 Jun;132(6):2360–2370. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.6.8504741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetsel W. C., Khan W. A., Merchenthaler I., Rivera H., Halpern A. E., Phung H. M., Negro-Vilar A., Hannun Y. A. Tissue and cellular distribution of the extended family of protein kinase C isoenzymes. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):121–133. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetsel W. C., Liposits Z., Seidah N. G., Collins S. Expression of candidate pro-GnRH processing enzymes in rat hypothalamus and an immortalized hypothalamic neuronal cell line. Neuroendocrinology. 1995 Aug;62(2):166–177. doi: 10.1159/000127001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetsel W. C., Mellon P. L., Weiner R. I., Negro-Vilar A. Metabolism of pro-luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone in immortalized hypothalamic neurons. Endocrinology. 1991 Sep;129(3):1584–1595. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-3-1584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetsel W. C., Valença M. M., Merchenthaler I., Liposits Z., López F. J., Weiner R. I., Mellon P. L., Negro-Vilar A. Intrinsic pulsatile secretory activity of immortalized luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone-secreting neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4149–4153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte D. B., Lawson M. A., Belsham D. D., Eraly S. A., Bond C. T., Adelman J. P., Mellon P. L. A neuron-specific enhancer targets expression of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene to hypothalamic neurosecretory neurons. Mol Endocrinol. 1995 Apr;9(4):467–477. doi: 10.1210/mend.9.4.7659090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray S., Grant P., Gainer H. Evidence that cells expressing luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone mRNA in the mouse are derived from progenitor cells in the olfactory placode. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8132–8136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K. L., Yeo T. T., Dong K. W., Jakubowski M., Lackner-Arkin C., Blum M., Roberts J. L. Second messenger regulation of mouse gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene expression in immortalized mouse hypothalamic GT1-3 cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1994 Jun;102(1-2):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(94)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo M., Hu Y., Schultz C., Kandel E. R., Hawkins R. D. Role of guanylyl cyclase and cGMP-dependent protein kinase in long-term potentiation. Nature. 1994 Apr 14;368(6472):635–639. doi: 10.1038/368635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]