Abstract
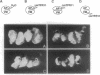
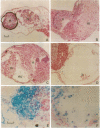
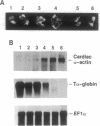
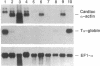
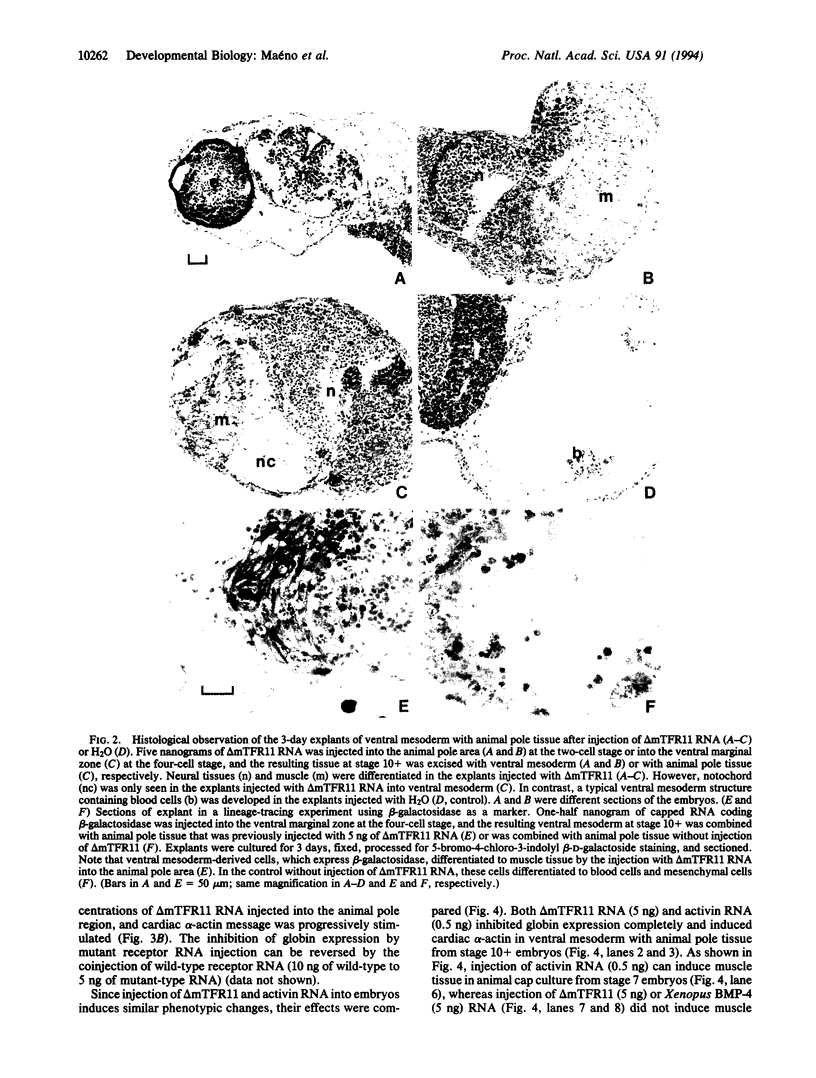
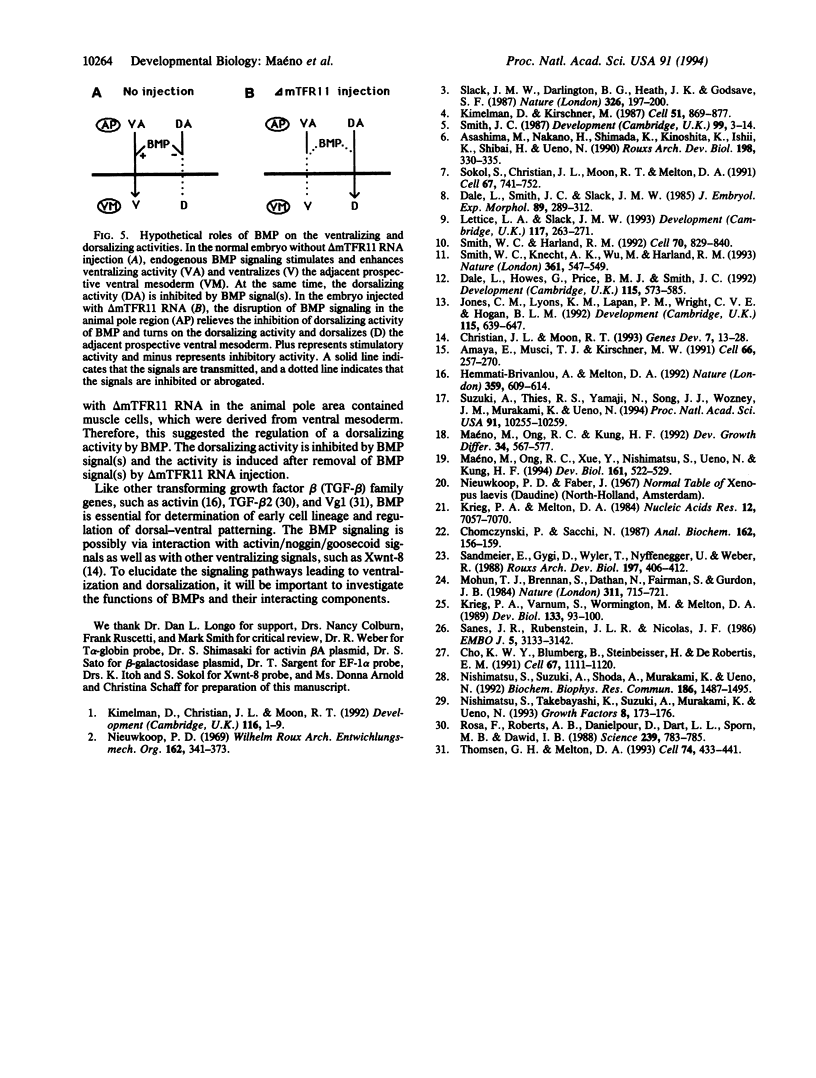
The biological effects of endogenous bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP-4), a member of the transforming growth factor beta family, on embryonic development of Xenopus laevis were investigated by using a functionally defective mutant of the BMP-4 receptor (delta mTFR11), which blocks the BMP signaling pathway. Injection of delta mTFR11 RNA into either the animal pole area or ventral marginal cells at the two-cell stage induced a dorsal phenotype in the explant of ventral mesoderm with animal pole tissue from stage 10+ embryo, even though the normal fate of this explant is a "mesenchymal ball" containing blood cells. These explants with the dorsal phenotype contained muscle, neural tissue, eye capsule, and cement gland. Northern blot analysis showed an increase of cardiac alpha-actin mRNA and a decrease of T alpha-globin mRNA expression, providing further evidence of a conversion from ventral to dorsal phenotype. Although injection of delta mTFR11 RNA did not induce mesoderm in an animal cap culture, the same tissue injected with delta mTFR11 RNA can alter the differentiation fate of uninjected ventral mesodermal explant from ventral to dorsal type, suggesting specific interaction of animal pole tissue and prospective ventral mesoderm in vivo.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amaya E., Musci T. J., Kirschner M. W. Expression of a dominant negative mutant of the FGF receptor disrupts mesoderm formation in Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):257–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90616-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. W., Blumberg B., Steinbeisser H., De Robertis E. M. Molecular nature of Spemann's organizer: the role of the Xenopus homeobox gene goosecoid. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1111–1120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90288-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian J. L., Moon R. T. Interactions between Xwnt-8 and Spemann organizer signaling pathways generate dorsoventral pattern in the embryonic mesoderm of Xenopus. Genes Dev. 1993 Jan;7(1):13–28. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale L., Howes G., Price B. M., Smith J. C. Bone morphogenetic protein 4: a ventralizing factor in early Xenopus development. Development. 1992 Jun;115(2):573–585. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.2.573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale L., Smith J. C., Slack J. M. Mesoderm induction in Xenopus laevis: a quantitative study using a cell lineage label and tissue-specific antibodies. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Oct;89:289–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmati-Brivanlou A., Melton D. A. A truncated activin receptor inhibits mesoderm induction and formation of axial structures in Xenopus embryos. Nature. 1992 Oct 15;359(6396):609–614. doi: 10.1038/359609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. M., Lyons K. M., Lapan P. M., Wright C. V., Hogan B. L. DVR-4 (bone morphogenetic protein-4) as a posterior-ventralizing factor in Xenopus mesoderm induction. Development. 1992 Jun;115(2):639–647. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.2.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelman D., Kirschner M. Synergistic induction of mesoderm by FGF and TGF-beta and the identification of an mRNA coding for FGF in the early Xenopus embryo. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Varnum S. M., Wormington W. M., Melton D. A. The mRNA encoding elongation factor 1-alpha (EF-1 alpha) is a major transcript at the midblastula transition in Xenopus. Dev Biol. 1989 May;133(1):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90300-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lettice L. A., Slack J. M. Properties of the dorsalizing signal in gastrulae of Xenopus laevis. Development. 1993 Jan;117(1):263–271. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.1.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maéno M., Ong R. C., Xue Y., Nishimatsu S., Ueno N., Kung H. F. Regulation of primary erythropoiesis in the ventral mesoderm of Xenopus gastrula embryo: evidence for the expression of a stimulatory factor(s) in animal pole tissue. Dev Biol. 1994 Feb;161(2):522–529. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Brennan S., Dathan N., Fairman S., Gurdon J. B. Cell type-specific activation of actin genes in the early amphibian embryo. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):716–721. doi: 10.1038/311716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimatsu S., Suzuki A., Shoda A., Murakami K., Ueno N. Genes for bone morphogenetic proteins are differentially transcribed in early amphibian embryos. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Aug 14;186(3):1487–1495. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81574-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimatsu S., Takebayashi K., Suzuki A., Murakami K., Ueno N. Immunodetection of Xenopus bone morphogenetic protein-4 in early embryos. Growth Factors. 1993;8(3):173–176. doi: 10.3109/08977199309011020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F., Roberts A. B., Danielpour D., Dart L. L., Sporn M. B., Dawid I. B. Mesoderm induction in amphibians: the role of TGF-beta 2-like factors. Science. 1988 Feb 12;239(4841 Pt 1):783–785. doi: 10.1126/science.3422517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Rubenstein J. L., Nicolas J. F. Use of a recombinant retrovirus to study post-implantation cell lineage in mouse embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. M., Darlington B. G., Heath J. K., Godsave S. F. Mesoderm induction in early Xenopus embryos by heparin-binding growth factors. Nature. 1987 Mar 12;326(6109):197–200. doi: 10.1038/326197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C. A mesoderm-inducing factor is produced by Xenopus cell line. Development. 1987 Jan;99(1):3–14. doi: 10.1242/dev.99.1.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. C., Harland R. M. Expression cloning of noggin, a new dorsalizing factor localized to the Spemann organizer in Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):829–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90316-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. C., Knecht A. K., Wu M., Harland R. M. Secreted noggin protein mimics the Spemann organizer in dorsalizing Xenopus mesoderm. Nature. 1993 Feb 11;361(6412):547–549. doi: 10.1038/361547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol S., Christian J. L., Moon R. T., Melton D. A. Injected Wnt RNA induces a complete body axis in Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90069-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki A., Thies R. S., Yamaji N., Song J. J., Wozney J. M., Murakami K., Ueno N. A truncated bone morphogenetic protein receptor affects dorsal-ventral patterning in the early Xenopus embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10255–10259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen G. H., Melton D. A. Processed Vg1 protein is an axial mesoderm inducer in Xenopus. Cell. 1993 Aug 13;74(3):433–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80045-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]