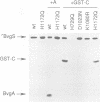
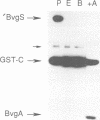
Abstract
BvgS and BvgA, a two-component system, regulate virulence gene expression in Bordetella pertussis. BvgS is a transmembrane sensor protein that can autophosphorylate and phosphorylate BvgA. Phosphorylated BvgA activates transcription of virulence genes. The cytoplasmic region of BvgS contains three domains separated by alanine/proline-rich sequences--the transmitter, receiver and C-terminus. We report that the C-terminal domain, like the transmitter and receiver, is an essential part of the phosphorelay from BvgS to BvgA. The BvgS C-terminal domain is phosphorylated in trans via a phosphotransfer mechanism by the cytoplasmic portion of BvgS, and trans-phosphorylation of the C-terminal domain requires both the transmitter and receiver. We also demonstrate that phosphorylated, purified C-terminal domain alone is sufficient for phosphotransfer to BvgA. A point mutation in the C-terminal domain (His1172-->Gln) abolishes BvgS activity in vivo and eliminates detectable phosphorylation of BvgA in vitro. Activity of BvgS His 1172-->Gln could be restored by providing the wild-type C-terminal domain in trans. Our results indicate an obligatory role for an alternate phosphodonor module in the BvgAS phosphorelay.
Full text
PDF




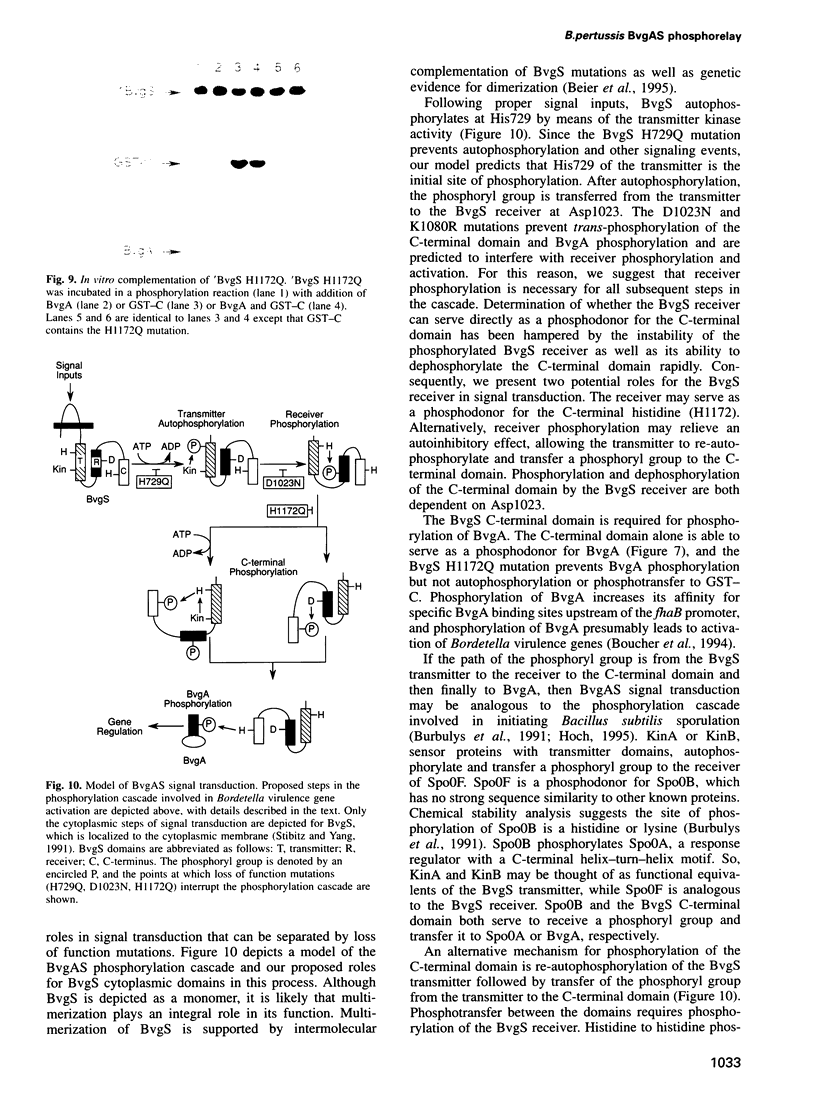



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerley B. J., Cotter P. A., Miller J. F. Ectopic expression of the flagellar regulon alters development of the Bordetella-host interaction. Cell. 1995 Feb 24;80(4):611–620. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90515-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akerley B. J., Monack D. M., Falkow S., Miller J. F. The bvgAS locus negatively controls motility and synthesis of flagella in Bordetella bronchiseptica. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):980–990. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.980-990.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aricó B., Miller J. F., Roy C., Stibitz S., Monack D., Falkow S., Gross R., Rappuoli R. Sequences required for expression of Bordetella pertussis virulence factors share homology with prokaryotic signal transduction proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6671–6675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beier D., Schwarz B., Fuchs T. M., Gross R. In vivo characterization of the unorthodox BvgS two-component sensor protein of Bordetella pertussis. J Mol Biol. 1995 May 5;248(3):596–610. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher P. E., Menozzi F. D., Locht C. The modular architecture of bacterial response regulators. Insights into the activation mechanism of the BvgA transactivator of Bordetella pertussis. J Mol Biol. 1994 Aug 19;241(3):363–377. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burbulys D., Trach K. A., Hoch J. A. Initiation of sporulation in B. subtilis is controlled by a multicomponent phosphorelay. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):545–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90238-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbonetti N. H., Fuchs T. M., Patamawenu A. A., Irish T. J., Deppisch H., Gross R. Effect of mutations causing overexpression of RNA polymerase alpha subunit on regulation of virulence factors in Bordetella pertussis. J Bacteriol. 1994 Dec;176(23):7267–7273. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.23.7267-7273.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Winans S. C. Functional roles assigned to the periplasmic, linker, and receiver domains of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens VirA protein. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(21):7033–7039. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.21.7033-7039.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Kwok S. F., Bleecker A. B., Meyerowitz E. M. Arabidopsis ethylene-response gene ETR1: similarity of product to two-component regulators. Science. 1993 Oct 22;262(5133):539–544. doi: 10.1126/science.8211181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotter P. A., Miller J. F. BvgAS-mediated signal transduction: analysis of phase-locked regulatory mutants of Bordetella bronchiseptica in a rabbit model. Infect Immun. 1994 Aug;62(8):3381–3390. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.8.3381-3390.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giardina P. C., Foster L. A., Musser J. M., Akerley B. J., Miller J. F., Dyer D. W. bvg Repression of alcaligin synthesis in Bordetella bronchiseptica is associated with phylogenetic lineage. J Bacteriol. 1995 Nov;177(21):6058–6063. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.21.6058-6063.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyard S., Bellalou J., Mireau H., Ullmann A. Mutations in the Bordetella pertussis bvgS gene that confer altered expression of the fhaB gene in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1994 Aug;176(16):5163–5166. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.16.5163-5166.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gueirard P., Guiso N. Virulence of Bordetella bronchiseptica: role of adenylate cyclase-hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1993 Oct;61(10):4072–4078. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.10.4072-4078.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. F., Bourret R. B., Simon M. I. Histidine phosphorylation and phosphoryl group transfer in bacterial chemotaxis. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):139–143. doi: 10.1038/336139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. F., Oosawa K., Matsumura P., Simon M. I. Protein phosphorylation is involved in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7609–7613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultquist D. E. The preparation and characterization of phosphorylated derivatives of histidine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 12;153(2):329–340. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(68)90078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishige K., Nagasawa S., Tokishita S., Mizuno T. A novel device of bacterial signal transducers. EMBO J. 1994 Nov 1;13(21):5195–5202. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06850.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Lin E. C. Purification and phosphorylation of the Arc regulatory components of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(17):5617–5623. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.17.5617-5623.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Matsuda Z., Fujiwara T., Lin E. C. The arcB gene of Escherichia coli encodes a sensor-regulator protein for anaerobic repression of the arc modulon. Mol Microbiol. 1990 May;4(5):715–727. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00642.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin S. G., Prusti R. K., Roitsch T., Ankenbauer R. G., Nester E. W. Phosphorylation of the VirG protein of Agrobacterium tumefaciens by the autophosphorylated VirA protein: essential role in biological activity of VirG. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4945–4950. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4945-4950.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin S., Roitsch T., Ankenbauer R. G., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. The VirA protein of Agrobacterium tumefaciens is autophosphorylated and is essential for vir gene regulation. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):525–530. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.525-530.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok J., Trach K. A., Hoch J. A. Effects on Bacillus subtilis of a conditional lethal mutation in the essential GTP-binding protein Obg. J Bacteriol. 1994 Dec;176(23):7155–7160. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.23.7155-7160.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Wurgler-Murphy S. M., Saito H. A two-component system that regulates an osmosensing MAP kinase cascade in yeast. Nature. 1994 May 19;369(6477):242–245. doi: 10.1038/369242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manetti R., Aricò B., Rappuoli R., Scarlato V. Mutations in the linker region of BvgS abolish response to environmental signals for the regulation of the virulence factors in Bordetella pertussis. Gene. 1994 Dec 2;150(1):123–127. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90870-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCleary W. R., Zusman D. R. Purification and characterization of the Myxococcus xanthus FrzE protein shows that it has autophosphorylation activity. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6661–6668. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6661-6668.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton A. R., Weiss A. A. Characterization of environmental regulators of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1993 Mar;61(3):807–815. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.3.807-815.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Johnson S. A., Black W. J., Beattie D. T., Mekalanos J. J., Falkow S. Constitutive sensory transduction mutations in the Bordetella pertussis bvgS gene. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):970–979. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.970-979.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Roy C. R., Falkow S. Analysis of Bordetella pertussis virulence gene regulation by use of transcriptional fusions in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6345–6348. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6345-6348.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa S., Tokishita S., Aiba H., Mizuno T. A novel sensor-regulator protein that belongs to the homologous family of signal-transduction proteins involved in adaptive responses in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Mar;6(6):799–807. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Kofoid E. C. Communication modules in bacterial signaling proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:71–112. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazour G. J., Ta C. N., Das A. Mutants of Agrobacterium tumefaciens with elevated vir gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6941–6945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C. R., Miller J. F., Falkow S. The bvgA gene of Bordetella pertussis encodes a transcriptional activator required for coordinate regulation of several virulence genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6338–6344. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6338-6344.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury S., Sakai K., Chakrabarty A. M. AlgR2 is an ATP/GTP-dependent protein kinase involved in alginate synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2659–2663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr Protein phosphorylation and allosteric control of inducer exclusion and catabolite repression by the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Mar;53(1):109–120. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.1.109-120.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarlato V., Aricò B., Prugnola A., Rappuoli R. Sequential activation and environmental regulation of virulence genes in Bordetella pertussis. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3971–3975. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04967.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz S., Aaronson W., Monack D., Falkow S. Phase variation in Bordetella pertussis by frameshift mutation in a gene for a novel two-component system. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):266–269. doi: 10.1038/338266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz S. Mutations in the bvgA gene of Bordetella pertussis that differentially affect regulation of virulence determinants. J Bacteriol. 1994 Sep;176(18):5615–5621. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.18.5615-5621.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz S., Weiss A. A., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of a region of the Bordetella pertussis chromosome encoding filamentous hemagglutinin and the pleiotropic regulatory locus vir. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2904–2913. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2904-2913.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz S., Yang M. S. Subcellular localization and immunological detection of proteins encoded by the vir locus of Bordetella pertussis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4288–4296. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4288-4296.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson R. V., Bourret R. B., Simon M. I. Intermolecular complementation of the kinase activity of CheA. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(3):435–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl M. A., Miller J. F. Autophosphorylation and phosphotransfer in the Bordetella pertussis BvgAS signal transduction cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):1163–1167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl M. A., Miller J. F. BvgAS is sufficient for activation of the Bordetella pertussis ptx locus in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1995 Nov;177(22):6477–6485. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.22.6477-6485.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsumi R., Katayama S., Taniguchi M., Horie T., Ikeda M., Igaki S., Nakagawa H., Miwa A., Tanabe H., Noda M. Newly identified genes involved in the signal transduction of Escherichia coli K-12. Gene. 1994 Mar 11;140(1):73–77. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90733-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Goodwin M. S. Lethal infection by Bordetella pertussis mutants in the infant mouse model. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3757–3764. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3757-3764.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L., Myers G. A., Falkow S. Tn5-induced mutations affecting virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):33–41. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.33-41.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L. Virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:661–686. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y., Inouye M. Intermolecular complementation between two defective mutant signal-transducing receptors of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11057–11061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]