Abstract
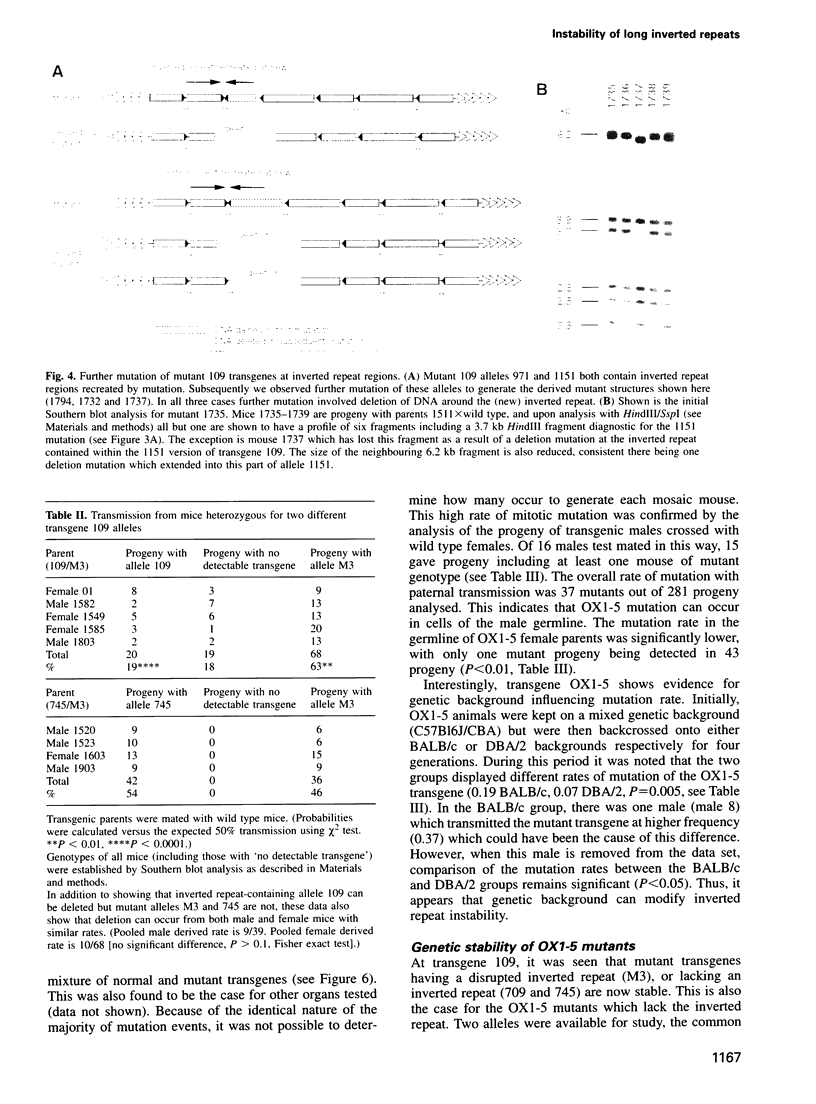
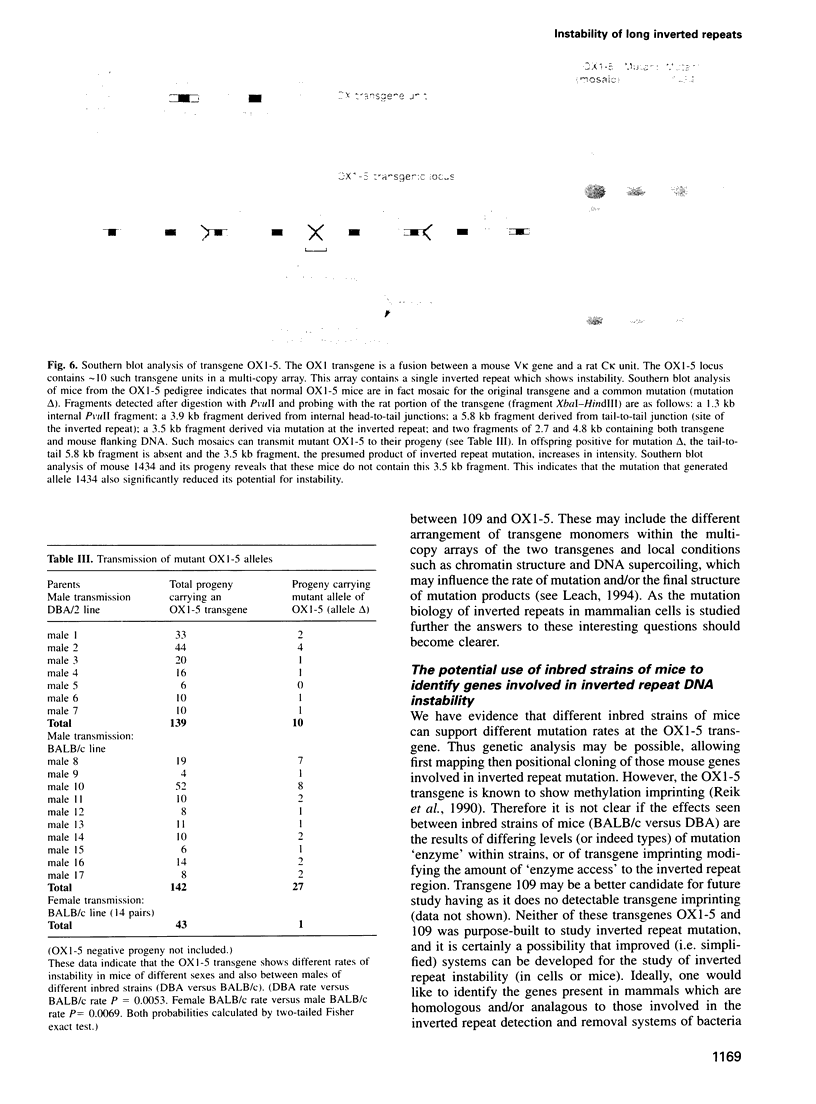
Various sequences in the mammalian genomes are unstable. One class of sequence arrangement is long inverted repeats, which are known to be unstable in bacteria and yeast. While in mammals some evidence suggests that short inverted repeats (<10 bp long) may show instability, nothing is known about the stability of long inverted repeats. Here we describe two unrelated multicopy transgenes in the mouse (loci 109 and OX1-5), each of which contains a long inverted repeat that shows substantial mitotic instability. This instability also occurs in the germline so that mutant transgenes appear within pedigrees at a high frequency. The mutation processes acting at these two inverted repeats are complex and can involve insertion or deletion, and can result in stabilization of the transgene. At transgene 109 mutational events range from very small rearrangements at the centre of the inverted repeat to complete transgene deletion. In addition we show that the rates of mutation at the inverted repeat of transgene OX1-5 can vary between the male and female germlines and between inbred strains of mice, suggesting the possibility of a genetic analysis to identify loci that modulate inverted repeat instability.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen M. J., Jeffreys A. J., Surani M. A., Barton S., Norris M. L., Collick A. Tandemly repeated transgenes of the human minisatellite MS32 (D1S8), with novel mouse gamma satellite integration. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Aug 11;22(15):2976–2981. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.15.2976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett R. J., Dunderdale H. J., West S. C. Resolution of Holliday junctions by RuvC resolvase: cleavage specificity and DNA distortion. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1021–1031. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90724-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biessmann H., Mason J. M. Genetics and molecular biology of telomeres. Adv Genet. 1992;30:185–249. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronner C. E., Baker S. M., Morrison P. T., Warren G., Smith L. G., Lescoe M. K., Kane M., Earabino C., Lipford J., Lindblom A. Mutation in the DNA mismatch repair gene homologue hMLH1 is associated with hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer. Nature. 1994 Mar 17;368(6468):258–261. doi: 10.1038/368258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. M., Schildkraut C. L. A family of moderately repetitive sequences in mouse DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4075–4090. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collick A., Norris M. L., Allen M. J., Bois P., Barton S. C., Surani M. A., Jeffreys A. J. Variable germline and embryonic instability of the human minisatellite MS32 (D1S8) in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 1;13(23):5745–5753. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06912.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishel R., Lescoe M. K., Rao M. R., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Garber J., Kane M., Kolodner R. The human mutator gene homolog MSH2 and its association with hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):1027–1038. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90546-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Feo S., Heard E. The role of inverted duplication in the generation of gene amplification in mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Oct 8;1090(2):143–155. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90095-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordenin D. A., Lobachev K. S., Degtyareva N. P., Malkova A. L., Perkins E., Resnick M. A. Inverted DNA repeats: a source of eukaryotic genomic instability. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5315–5322. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S. T., Petes T. D. Instability of a plasmid-borne inverted repeat in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1993 May;134(1):57–62. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Tamaki K., MacLeod A., Monckton D. G., Neil D. L., Armour J. A. Complex gene conversion events in germline mutation at human minisatellites. Nat Genet. 1994 Feb;6(2):136–145. doi: 10.1038/ng0294-136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach D. R., Lloyd R. G., Coulson A. F. The SbcCD protein of Escherichia coli is related to two putative nucleases in the UvrA superfamily of nucleotide-binding proteins. Genetica. 1992;87(2):95–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00120998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach D. R. Long DNA palindromes, cruciform structures, genetic instability and secondary structure repair. Bioessays. 1994 Dec;16(12):893–900. doi: 10.1002/bies.950161207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach F. S., Nicolaides N. C., Papadopoulos N., Liu B., Jen J., Parsons R., Peltomäki P., Sistonen P., Aaltonen L. A., Nyström-Lahti M. Mutations of a mutS homolog in hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1215–1225. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90330-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. G., Buckman C. Identification and genetic analysis of sbcC mutations in commonly used recBC sbcB strains of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):836–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.836-844.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren A. Development of the mammalian gonad: the fate of the supporting cell lineage. Bioessays. 1991 Apr;13(4):151–156. doi: 10.1002/bies.950130402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris T., Thacker J. Formation of large deletions by illegitimate recombination in the HPRT gene of primary human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1392–1396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalbantoglu J., Hartley D., Phear G., Tear G., Meuth M. Spontaneous deletion formation at the aprt locus of hamster cells: the presence of short sequence homologies and dyad symmetries at deletion termini. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1199–1204. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04347.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Germ-line transformation of mice. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:465–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson C. E., Ruiz M. T., Price G. B., Zannis-Hadjopoulos M. Cruciform DNA binding protein in HeLa cell extracts. Biochemistry. 1994 Nov 29;33(47):14185–14196. doi: 10.1021/bi00251a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reik W., Howlett S. K., Surani M. A. Imprinting by DNA methylation: from transgenes to endogenous gene sequences. Dev Suppl. 1990:99–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Fink G. R. Mutations in POL1 increase the mitotic instability of tandem inverted repeats in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1993 May;134(1):43–56. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandgren E. P., Palmiter R. D., Heckel J. L., Brinster R. L., Degen J. L. DNA rearrangement causes hepatocarcinogenesis in albumin-plasminogen activator transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11523–11527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe M. J., Neuberger M., Pannell R., Surani M. A., Milstein C. Lack of somatic mutation in a kappa light chain transgene. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jun;20(6):1379–1385. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharples G. J., Chan S. N., Mahdi A. A., Whitby M. C., Lloyd R. G. Processing of intermediates in recombination and DNA repair: identification of a new endonuclease that specifically cleaves Holliday junctions. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 15;13(24):6133–6142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06960.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Debatisse M., Giulotto E., Wahl G. M. Recent progress in understanding mechanisms of mammalian DNA amplification. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):901–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90328-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON J. D., CRICK F. H. Molecular structure of nucleic acids; a structure for deoxyribose nucleic acid. Nature. 1953 Apr 25;171(4356):737–738. doi: 10.1038/171737a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaff E., Rouillard P., Willems P. J., Smits A. P., Rousseau F., Oostra B. A. Hotspot for deletions in the CGG repeat region of FMR1 in fragile X patients. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Jan;4(1):45–49. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]