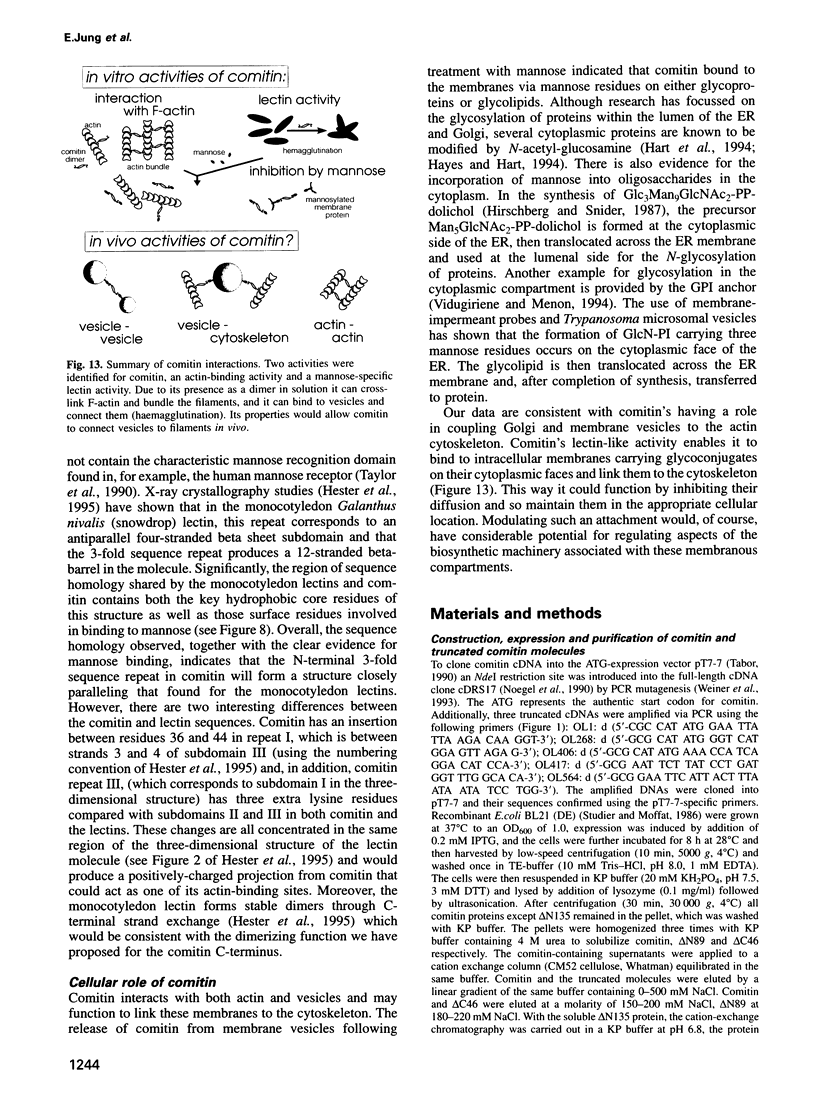
Abstract
Comitin is a 24 kDa actin-binding protein from Dictyostelium discoideum that is located primarily on Golgi and vesicle membranes. We have probed the molecular basis of comitin's interaction with both actin and membranes using a series of truncation mutants obtained by expressing the appropriate cDNA in Escherichia coli. Comitin dimerizes in solution; its principle actin-binding activity is located between residues 90 and 135. The N-terminal 135 'core' residues of comitin contain a 3-fold sequence repeat that is homologous to several monocotyledon lectins and which retains key residues that determine these lectins' three-dimensional structure and mannose binding. These repeats of comitin appear to mediate its interaction with mannose residues in glycoproteins or glycolipids on the cytoplasmic surface of membrane vesicles from D.discoideum, and comitin can be released from membranes with mannose. Our data indicate that comitin binds to vesicle membranes via mannose residues and, by way of its interaction with actin, links these membranes to the cytoskeleton.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams R. J., Pollard T. D. Propulsion of organelles isolated from Acanthamoeba along actin filaments by myosin-I. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):754–756. doi: 10.1038/322754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck K. A., Buchanan J. A., Malhotra V., Nelson W. J. Golgi spectrin: identification of an erythroid beta-spectrin homolog associated with the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;127(3):707–723. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.3.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns A. L., Magendzo K., Shirvan A., Srivastava M., Rojas E., Alijani M. R., Pollard H. B. Calcium channel activity of purified human synexin and structure of the human synexin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3798–3802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claviez M., Pagh K., Maruta H., Baltes W., Fisher P., Gerisch G. Electron microscopic mapping of monoclonal antibodies on the tail region of Dictyostelium myosin. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):1017–1022. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01287.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drickamer K., Taylor M. E. Biology of animal lectins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:237–264. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring V., Schleicher M., Noegel A. A. Dictyostelium annexin VII (synexin). cDNA sequence and isolation of a gene disruption mutant. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17509–17515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichinger L., Schleicher M. Characterization of actin- and lipid-binding domains in severin, a Ca(2+)-dependent F-actin fragmenting protein. Biochemistry. 1992 May 26;31(20):4779–4787. doi: 10.1021/bi00135a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fath K. R., Burgess D. R. Golgi-derived vesicles from developing epithelial cells bind actin filaments and possess myosin-I as a cytoplasmically oriented peripheral membrane protein. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(1):117–127. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hester G., Kaku H., Goldstein I. J., Wright C. S. Structure of mannose-specific snowdrop (Galanthus nivalis) lectin is representative of a new plant lectin family. Nat Struct Biol. 1995 Jun;2(6):472–479. doi: 10.1038/nsb0695-472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschberg C. B., Snider M. D. Topography of glycosylation in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:63–87. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.000431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jia S., Wang J. L. Carbohydrate binding protein 35. Complementary DNA sequence reveals homology with proteins of the heterogeneous nuclear RNP. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6009–6011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung G., Hammer J. A., 3rd The actin binding site in the tail domain of Dictyostelium myosin IC (myoC) resides within the glycine- and proline-rich sequence (tail homology region 2). FEBS Lett. 1994 Apr 4;342(2):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80500-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B. Secretory granule and synaptic vesicle formation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;3(4):654–660. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90037-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov S. A., Langford G. M., Weiss D. G. Actin-dependent organelle movement in squid axoplasm. Nature. 1992 Apr 23;356(6371):722–725. doi: 10.1038/356722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean-Fletcher S. D., Pollard T. D. Viscometric analysis of the gelation of Acanthamoeba extracts and purification of two gelation factors. J Cell Biol. 1980 May;85(2):414–428. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.2.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Modular organization of actin crosslinking proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Mar;16(3):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima N., Creutz C. E., Kretsinger R. H. Polyproline, beta-turn helices. Novel secondary structures proposed for the tandem repeats within rhodopsin, synaptophysin, synexin, gliadin, RNA polymerase II, hordein, and gluten. Proteins. 1990;7(2):125–155. doi: 10.1002/prot.340070204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehul B., Bawumia S., Martin S. R., Hughes R. C. Structure of baby hamster kidney carbohydrate-binding protein CBP30, an S-type animal lectin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 8;269(27):18250–18258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menkel A. R., Kroemker M., Bubeck P., Ronsiek M., Nikolai G., Jockusch B. M. Characterization of an F-actin-binding domain in the cytoskeletal protein vinculin. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(5):1231–1240. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.5.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermall V., McNally J. G., Miller K. G. Transport of cytoplasmic particles catalysed by an unconventional myosin in living Drosophila embryos. Nature. 1994 Jun 16;369(6481):560–562. doi: 10.1038/369560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. K., Aebi U. Bundling of actin filaments by alpha-actinin depends on its molecular length. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2013–2024. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noegel A. A., Gerisch G., Lottspeich F., Schleicher M. A protein with homology to the C-terminal repeat sequence of Octopus rhodopsin and synaptophysin is a member of a multigene family in Dictyostelium discoideum. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 18;266(1-2):118–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81521-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto J. J. Actin-bundling proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;6(1):105–109. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Abdulaev N. G., Zolotarev A. S., Artamonov I. D., Bespalov I. A., Dergachev A. E., Tsuda M. Octopus rhodopsin. Amino acid sequence deduced from cDNA. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 9;232(1):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80388-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Cooper J. A. Actin and actin-binding proteins. A critical evaluation of mechanisms and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:987–1035. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. S., Rener B. The GPQ-rich segment of Dictyostelium myosin IB contains an actin binding site. Biochemistry. 1994 Mar 1;33(8):2322–2328. doi: 10.1021/bi00174a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon N. Lectin-carbohydrate complexes of plants and animals: an atomic view. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jun;18(6):221–226. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90193-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratford C. A., Brown S. S. Isolation of an actin-binding protein from membranes of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):727–735. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. E., Conary J. T., Lennartz M. R., Stahl P. D., Drickamer K. Primary structure of the mannose receptor contains multiple motifs resembling carbohydrate-recognition domains. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12156–12162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towle C. A., Treadwell B. V. Identification of a novel mammalian annexin. cDNA cloning, sequence analysis, and ubiquitous expression of the annexin XI gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5416–5423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsakiridis T., Vranic M., Klip A. Disassembly of the actin network inhibits insulin-dependent stimulation of glucose transport and prevents recruitment of glucose transporters to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 25;269(47):29934–29942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtorta F., Benfenati F., Greengard P. Structure and function of the synapsins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7195–7198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme E. J., Kaku H., Perini F., Goldstein I. J., Peeters B., Yagi F., Decock B., Peumans W. J. Biosynthesis, primary structure and molecular cloning of snowdrop (Galanthus nivalis L.) lectin. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Nov 15;202(1):23–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme E. J., Smeets K., Engelborghs I., Aelbers H., Balzarini J., Pusztai A., van Leuven F., Goldstein I. J., Peumans W. J. Cloning and characterization of the lectin cDNA clones from onion, shallot and leek. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Oct;23(2):365–376. doi: 10.1007/BF00029011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme J. M., Smeets K., Torrekens S., Van Leuven F., Peumans W. J. The mannose-specific lectins from ramsons (Allium ursinum L.) are encoded by three sets of genes. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Oct 1;217(1):123–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidugiriene J., Menon A. K. The GPI anchor of cell-surface proteins is synthesized on the cytoplasmic face of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(2):333–341. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.2.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner O. H., Murphy J., Griffiths G., Schleicher M., Noegel A. A. The actin-binding protein comitin (p24) is a component of the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;123(1):23–34. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Damme E. J., Smeets K., Torrekens S., van Leuven F., Goldstein I. J., Peumans W. J. The closely related homomeric and heterodimeric mannose-binding lectins from garlic are encoded by one-domain and two-domain lectin genes, respectively. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 1;206(2):413–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]