Abstract
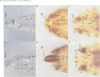
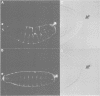
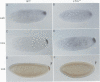
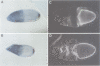
Drosophila encodes five muscle and one cytoskeletal isoform of the actin-binding protein tropomyosin. We have identified a lack-of-function mutation in the cytoskeletal isoform (cTmII). Zygotic mutant embryos show a defect in head morphogenesis, while embryos lacking maternal cTmII are defective in germ cell formation but otherwise give rise to viable adults. oskar mRNA, which is required for both germ cell formation and abdominal segmentation, fails to accumulate at the posterior pole in these embryos. nanos mRNA, however, which is required exclusively for abdominal segmentation, is localized at wild-type levels. These results indicate that head morphogenesis and the accumulation of high levels of oskar mRNA necessary for germ cell formation require tropomyosin-dependent cytoskeleton.
Full text
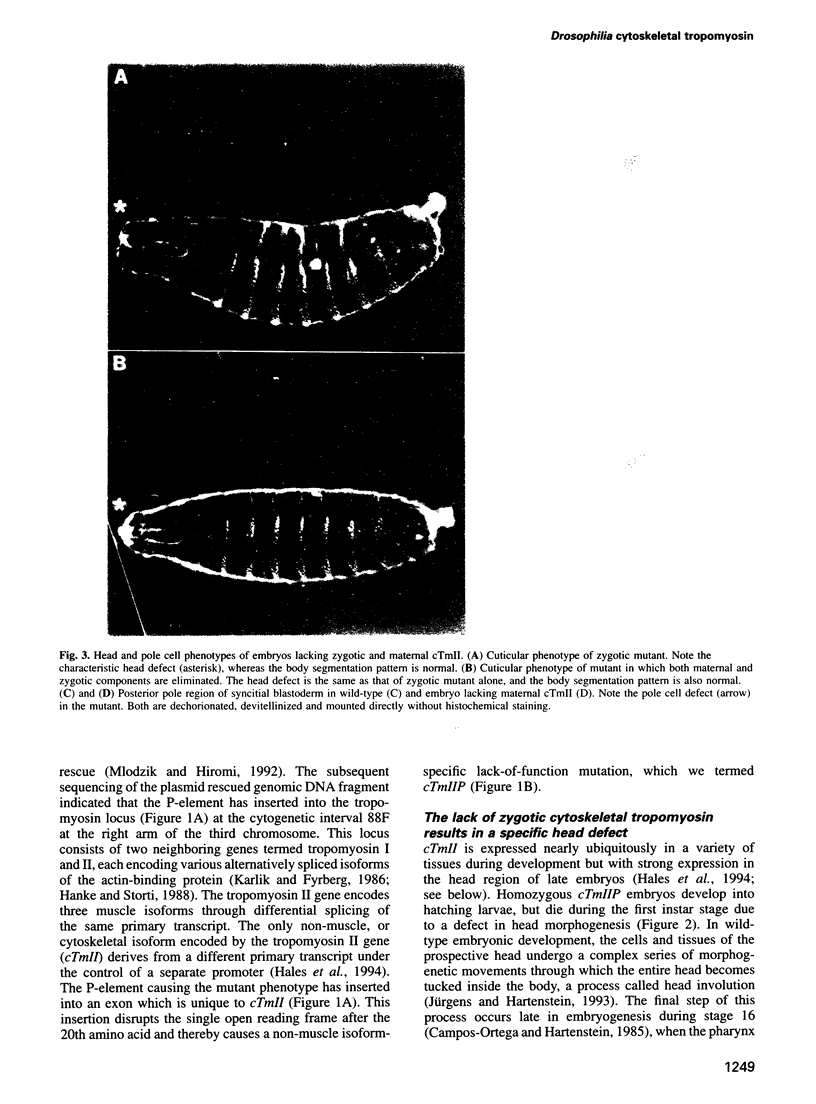
PDF


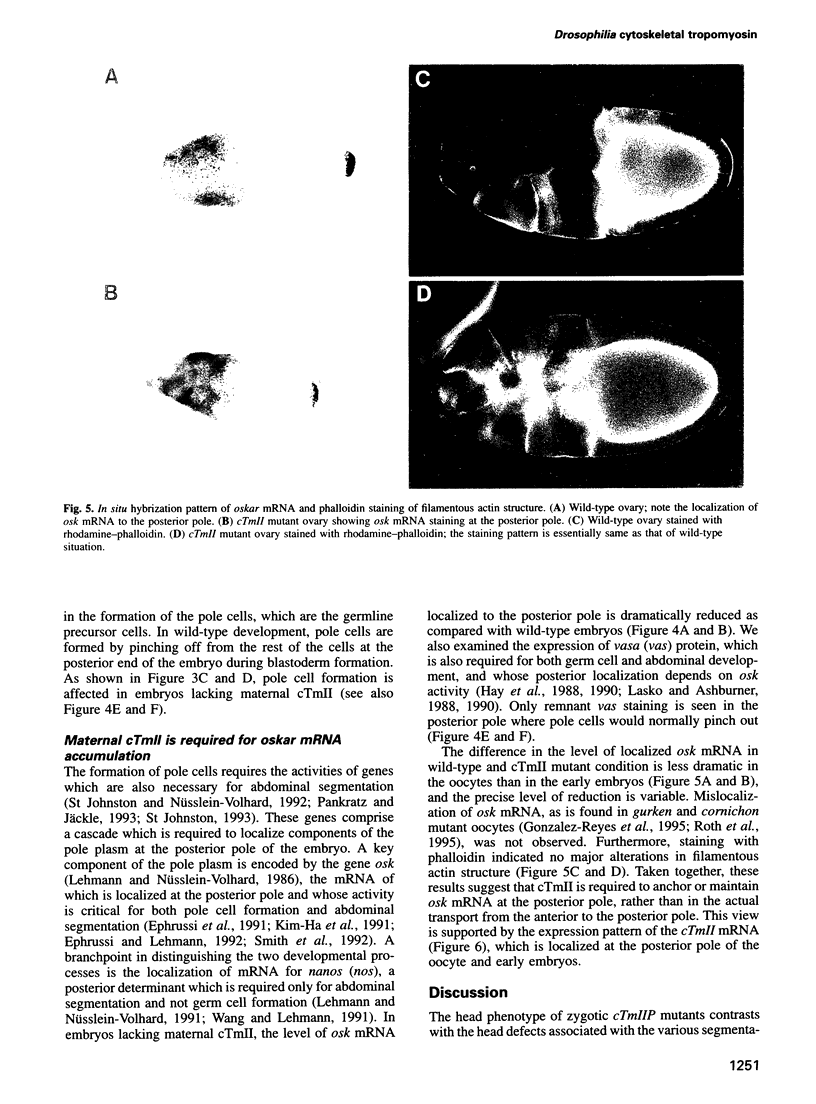


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
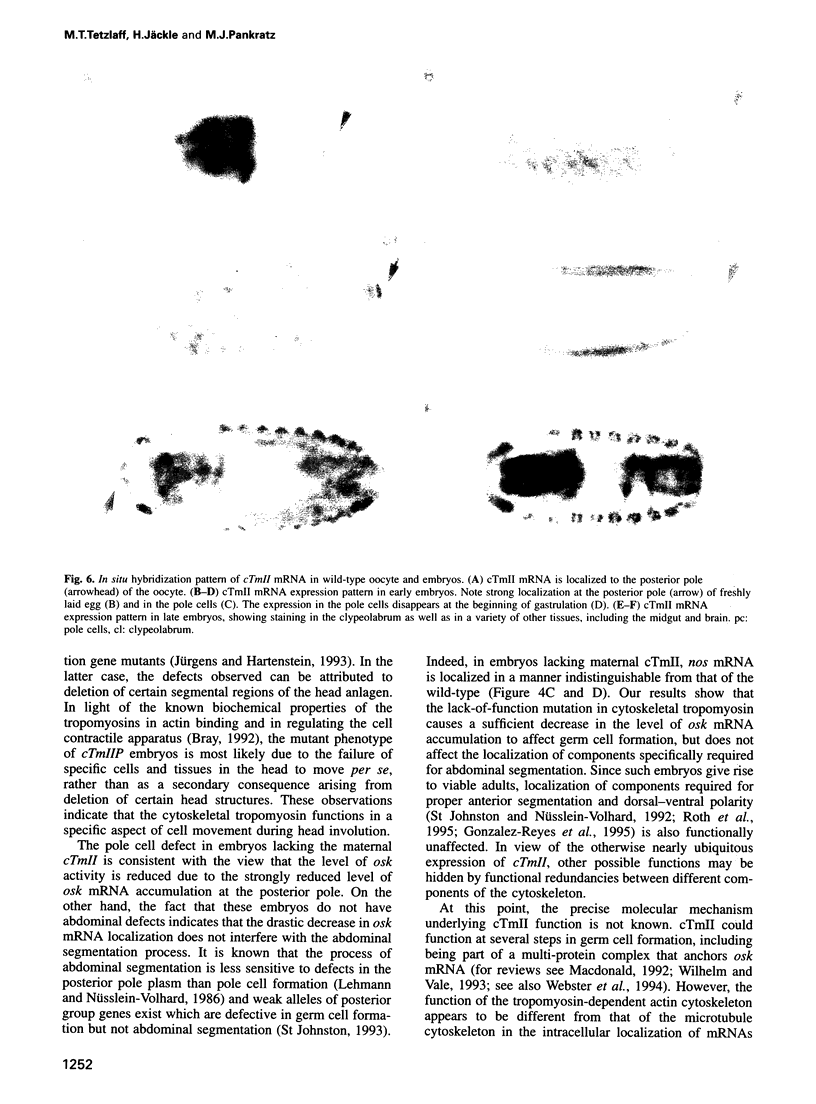
- Balasubramanian M. K., Helfman D. M., Hemmingsen S. M. A new tropomyosin essential for cytokinesis in the fission yeast S. pombe. Nature. 1992 Nov 5;360(6399):84–87. doi: 10.1038/360084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou T. B., Noll E., Perrimon N. Autosomal P[ovoD1] dominant female-sterile insertions in Drosophila and their use in generating germ-line chimeras. Development. 1993 Dec;119(4):1359–1369. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.4.1359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I., Giniger E., Ruohola-Baker H., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Transient posterior localization of a kinesin fusion protein reflects anteroposterior polarity of the Drosophila oocyte. Curr Biol. 1994 Apr 1;4(4):289–300. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooley L., Verheyen E., Ayers K. chickadee encodes a profilin required for intercellular cytoplasm transport during Drosophila oogenesis. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):173–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90128-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Dickinson L. K., Lehmann R. Oskar organizes the germ plasm and directs localization of the posterior determinant nanos. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):37–50. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90137-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Lehmann R. Induction of germ cell formation by oskar. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):387–392. doi: 10.1038/358387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrandon D., Elphick L., Nüsslein-Volhard C., St Johnston D. Staufen protein associates with the 3'UTR of bicoid mRNA to form particles that move in a microtubule-dependent manner. Cell. 1994 Dec 30;79(7):1221–1232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Reyes A., Elliott H., St Johnston D. Polarization of both major body axes in Drosophila by gurken-torpedo signalling. Nature. 1995 Jun 22;375(6533):654–658. doi: 10.1038/375654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales K. H., Meredith J. E., Storti R. V. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of maternal and zygotic cytoskeletal tropomyosin mRNA during Drosophila development correlates with specific morphogenic events. Dev Biol. 1994 Oct;165(2):639–653. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke P. D., Storti R. V. The Drosophila melanogaster tropomyosin II gene produces multiple proteins by use of alternative tissue-specific promoters and alternative splicing. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3591–3602. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay B., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. A protein component of Drosophila polar granules is encoded by vasa and has extensive sequence similarity to ATP-dependent helicases. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):577–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90216-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay B., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Localization of vasa, a component of Drosophila polar granules, in maternal-effect mutants that alter embryonic anteroposterior polarity. Development. 1990 Jun;109(2):425–433. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.2.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karess R. E., Chang X. J., Edwards K. A., Kulkarni S., Aguilera I., Kiehart D. P. The regulatory light chain of nonmuscle myosin is encoded by spaghetti-squash, a gene required for cytokinesis in Drosophila. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1177–1189. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90013-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlik C. C., Fyrberg E. A. An insertion within a variably spliced Drosophila tropomyosin gene blocks accumulation of only one encoded isoform. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlik C. C., Fyrberg E. A. Two Drosophila melanogaster tropomyosin genes: structural and functional aspects. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):1965–1973. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpen G. H., Spradling A. C. Analysis of subtelomeric heterochromatin in the Drosophila minichromosome Dp1187 by single P element insertional mutagenesis. Genetics. 1992 Nov;132(3):737–753. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehart D. P., Feghali R. Cytoplasmic myosin from Drosophila melanogaster. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1517–1525. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim-Ha J., Smith J. L., Macdonald P. M. oskar mRNA is localized to the posterior pole of the Drosophila oocyte. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):23–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90136-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane M. E., Kalderon D. RNA localization along the anteroposterior axis of the Drosophila oocyte requires PKA-mediated signal transduction to direct normal microtubule organization. Genes Dev. 1994 Dec 15;8(24):2986–2995. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.24.2986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasko P. F., Ashburner M. Posterior localization of vasa protein correlates with, but is not sufficient for, pole cell development. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):905–921. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasko P. F., Ashburner M. The product of the Drosophila gene vasa is very similar to eukaryotic initiation factor-4A. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):611–617. doi: 10.1038/335611a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann R., Nüsslein-Volhard C. Abdominal segmentation, pole cell formation, and embryonic polarity require the localized activity of oskar, a maternal gene in Drosophila. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):141–152. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90375-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann R., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The maternal gene nanos has a central role in posterior pattern formation of the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1991 Jul;112(3):679–691. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.3.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H. P., Bretscher A. Disruption of the single tropomyosin gene in yeast results in the disappearance of actin cables from the cytoskeleton. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90961-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald P. M., Struhl G. A molecular gradient in early Drosophila embryos and its role in specifying the body pattern. Nature. 1986 Dec 11;324(6097):537–545. doi: 10.1038/324537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pankratz M. J., Hoch M. Control of epithelial morphogenesis by cell signaling and integrin molecules in the Drosophila foregut. Development. 1995 Jun;121(6):1885–1898. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.6.1885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittenger M. F., Kazzaz J. A., Helfman D. M. Functional properties of non-muscle tropomyosin isoforms. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;6(1):96–104. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pokrywka N. J., Stephenson E. C. Microtubules mediate the localization of bicoid RNA during Drosophila oogenesis. Development. 1991 Sep;113(1):55–66. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., Neuman-Silberberg F. S., Barcelo G., Schüpbach T. cornichon and the EGF receptor signaling process are necessary for both anterior-posterior and dorsal-ventral pattern formation in Drosophila. Cell. 1995 Jun 16;81(6):967–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Ott U., González-Gaitán M., Jäckle H., Technau G. M. Number, identity, and sequence of the Drosophila head segments as revealed by neural elements and their deletion patterns in mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 30;91(18):8363–8367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.18.8363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. L., Wilson J. E., Macdonald P. M. Overexpression of oskar directs ectopic activation of nanos and presumptive pole cell formation in Drosophila embryos. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):849–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90318-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D., Beuchle D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. Staufen, a gene required to localize maternal RNAs in the Drosophila egg. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90138-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D., Driever W., Berleth T., Richstein S., Nüsslein-Volhard C. Multiple steps in the localization of bicoid RNA to the anterior pole of the Drosophila oocyte. Development. 1989;107 (Suppl):13–19. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.Supplement.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The origin of pattern and polarity in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):201–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90466-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D. The intracellular localization of messenger RNAs. Cell. 1995 Apr 21;81(2):161–170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90324-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. On the crawling of animal cells. Science. 1993 May 21;260(5111):1086–1094. doi: 10.1126/science.8493552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suter B., Steward R. Requirement for phosphorylation and localization of the Bicaudal-D protein in Drosophila oocyte differentiation. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):917–926. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90365-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tansey T., Mikus M. D., Dumoulin M., Storti R. V. Transformation and rescue of a flightless Drosophila tropomyosin mutant. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1375–1385. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02378.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theurkauf W. E. Premature microtubule-dependent cytoplasmic streaming in cappuccino and spire mutant oocytes. Science. 1994 Sep 30;265(5181):2093–2096. doi: 10.1126/science.8091233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theurkauf W. E., Smiley S., Wong M. L., Alberts B. M. Reorganization of the cytoskeleton during Drosophila oogenesis: implications for axis specification and intercellular transport. Development. 1992 Aug;115(4):923–936. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.4.923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Lehmann R. Nanos is the localized posterior determinant in Drosophila. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):637–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90110-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster P. J., Suen J., Macdonald P. M. Drosophila virilis oskar transgenes direct body patterning but not pole cell formation or maintenance of mRNA localization in D. melanogaster. Development. 1994 Jul;120(7):2027–2037. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.7.2027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm J. E., Vale R. D. RNA on the move: the mRNA localization pathway. J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;123(2):269–274. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yisraeli J. K., Sokol S., Melton D. A. A two-step model for the localization of maternal mRNA in Xenopus oocytes: involvement of microtubules and microfilaments in the translocation and anchoring of Vg1 mRNA. Development. 1990 Feb;108(2):289–298. doi: 10.1242/dev.108.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young P. E., Richman A. M., Ketchum A. S., Kiehart D. P. Morphogenesis in Drosophila requires nonmuscle myosin heavy chain function. Genes Dev. 1993 Jan;7(1):29–41. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipursky S. L., Venkatesh T. R., Teplow D. B., Benzer S. Neuronal development in the Drosophila retina: monoclonal antibodies as molecular probes. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90069-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]