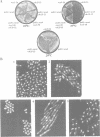
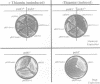
Abstract
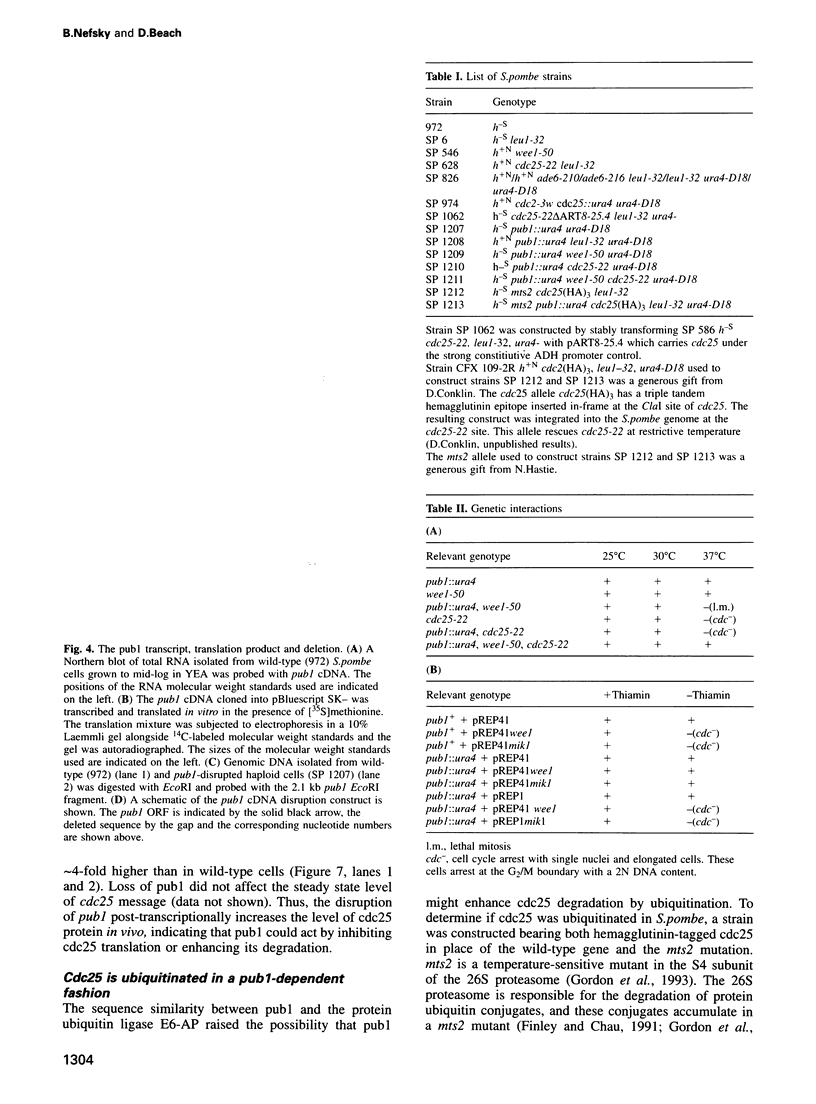
The level of the mitotic activating tyrosine phosphatase cdc25 is regulated by both transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. We have found that cdc25 is ubiquitinated and have cloned pub1, a gene which regulates this event. Pub1 contains a region highly homologous to the putative catalytic domain of the human protein ubiquitin ligase E6-AP. Disruption of pub1 elevates the level of cdc25 protein in vivo rendering cells relatively resistant to the cdc25-opposing tyrosine kinases wee1 and mik1. In addition, loss of wee1 activity in a pub1-disruption background results in a lethal premature entry into mitosis which can be rescued by loss of cdc25 function. A ubiquitin-thioester adduct of pub1 was isolated from fission yeast and disruption of pub1 dramatically reduced ubiquitination of cdc25 in vivo. These results suggest that pub1 directly ubiquitinates cdc25 in vivo.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amon A., Irniger S., Nasmyth K. Closing the cell cycle circle in yeast: G2 cyclin proteolysis initiated at mitosis persists until the activation of G1 cyclins in the next cycle. Cell. 1994 Jul 1;77(7):1037–1050. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90443-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel B., Wünning I., Varshavsky A. The recognition component of the N-end rule pathway. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3179–3189. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07516.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun S., Raymond W. E., Racker E. Synthetic tyrosine polymers as substrates and inhibitors of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2051–2054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnellie J. E. Assay of protein kinases using peptides with basic residues for phosphocellulose binding. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:115–120. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00133-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P., Johnson P., Sommer T., Jentsch S., Hochstrasser M. Multiple ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes participate in the in vivo degradation of the yeast MAT alpha 2 repressor. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90426-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90396-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. D., Lin L. L., Kriz R. W., Ramesha C. S., Sultzman L. A., Lin A. Y., Milona N., Knopf J. L. A novel arachidonic acid-selective cytosolic PLA2 contains a Ca(2+)-dependent translocation domain with homology to PKC and GAP. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90556-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohmen R. J., Madura K., Bartel B., Varshavsky A. The N-end rule is mediated by the UBC2(RAD6) ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7351–7355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Druker B. J., Mamon H. J., Roberts T. M. Oncogenes, growth factors, and signal transduction. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 16;321(20):1383–1391. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911163212007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Kumagai A. The cdc25 protein contains an intrinsic phosphatase activity. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90582-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantes P. Epistatic gene interactions in the control of division in fission yeast. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):428–430. doi: 10.1038/279428a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Chau V. Ubiquitination. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:25–69. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R., Thorner J., Martin G. S. Nucleotidylation, not phosphorylation, is the major source of the phosphotyrosine detected in enteric bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):272–279. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.272-279.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galaktionov K., Lee A. K., Eckstein J., Draetta G., Meckler J., Loda M., Beach D. CDC25 phosphatases as potential human oncogenes. Science. 1995 Sep 15;269(5230):1575–1577. doi: 10.1126/science.7667636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Solomon M. J., Booher R. N., Bazan J. F., Kirschner M. W. cdc25 is a specific tyrosine phosphatase that directly activates p34cdc2. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):197–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90583-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotzer M., Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):132–138. doi: 10.1038/349132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon C., McGurk G., Dillon P., Rosen C., Hastie N. D. Defective mitosis due to a mutation in the gene for a fission yeast 26S protease subunit. Nature. 1993 Nov 25;366(6453):355–357. doi: 10.1038/366355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas A. L., Murphy K. E., Bright P. M. The inactivation of ubiquitin accounts for the inability to demonstrate ATP, ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis in liver extracts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4694–4703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M. Protein kinase catalytic domain sequence database: identification of conserved features of primary structure and classification of family members. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:38–62. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00126-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heald R., McLoughlin M., McKeon F. Human wee1 maintains mitotic timing by protecting the nucleus from cytoplasmically activated Cdc2 kinase. Cell. 1993 Aug 13;74(3):463–474. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80048-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Eytan E., Ciechanover A., Haas A. L. Immunochemical analysis of the turnover of ubiquitin-protein conjugates in intact cells. Relationship to the breakdown of abnormal proteins. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13964–13970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway S. L., Glotzer M., King R. W., Murray A. W. Anaphase is initiated by proteolysis rather than by the inactivation of maturation-promoting factor. Cell. 1993 Jul 2;73(7):1393–1402. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90364-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Scheffner M., Beaudenon S., Howley P. M. A family of proteins structurally and functionally related to the E6-AP ubiquitin-protein ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):2563–2567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.2563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Scheffner M., Howley P. M. A cellular protein mediates association of p53 with the E6 oncoprotein of human papillomavirus types 16 or 18. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4129–4135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04990.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Scheffner M., Howley P. M. Cloning and expression of the cDNA for E6-AP, a protein that mediates the interaction of the human papillomavirus E6 oncoprotein with p53. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):775–784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Scheffner M., Howley P. M. Localization of the E6-AP regions that direct human papillomavirus E6 binding, association with p53, and ubiquitination of associated proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4918–4927. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura K., Nakano Y., Matsuoka K. o-Phosphotyrosyl glutamine synthetase: modification of the nucleotide ligation site of adenylylated glutamine synthetase. J Biochem. 1989 Jan;105(1):84–87. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. W., Jackson P. K., Kirschner M. W. Mitosis in transition. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):563–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90542-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Tomooka Y., Noda M. Identification of a set of genes with developmentally down-regulated expression in the mouse brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jun 30;185(3):1155–1161. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91747-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg R. A., Pasquale E. B. Isolation of cDNA clones that encode active protein-tyrosine kinases using antibodies against phosphotyrosine. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:557–564. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00171-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg R. A., Thompson D. P., Hunter T. Identification of cDNA clones that code for protein-tyrosine kinases by screening expression libraries with antibodies against phosphotyrosine. Oncogene. 1988 Dec;3(6):629–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren K., Walworth N., Booher R., Dembski M., Kirschner M., Beach D. mik1 and wee1 cooperate in the inhibitory tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1111–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madura K., Varshavsky A. Degradation of G alpha by the N-end rule pathway. Science. 1994 Sep 2;265(5177):1454–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.8073290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Jentsch S., Varshavsky A. UBA 1: an essential yeast gene encoding ubiquitin-activating enzyme. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):227–236. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07940.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney J. D., Chang F., Heintz N., Cross F. R. Negative regulation of FAR1 at the Start of the yeast cell cycle. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):833–843. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar J. B., Lenaers G., Russell P. Pyp3 PTPase acts as a mitotic inducer in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4933–4941. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05600.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Nurse P., Russell P. Regulation of mitosis by cyclic accumulation of p80cdc25 mitotic inducer in fission yeast. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):549–552. doi: 10.1038/344549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morla A. O., Draetta G., Beach D., Wang J. Y. Reversible tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2: dephosphorylation accompanies activation during entry into mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):193–203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90415-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Solomon M. J., Kirschner M. W. The role of cyclin synthesis and degradation in the control of maturation promoting factor activity. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):280–286. doi: 10.1038/339280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., Nurse P. Animal cell cycles and their control. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:441–470. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Genetic control of cell size at cell division in yeast. Nature. 1975 Aug 14;256(5518):547–551. doi: 10.1038/256547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Thuriaux P. Regulatory genes controlling mitosis in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Genetics. 1980 Nov;96(3):627–637. doi: 10.1093/genetics/96.3.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker L. L., Atherton-Fessler S., Piwnica-Worms H. p107wee1 is a dual-specificity kinase that phosphorylates p34cdc2 on tyrosine 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2917–2921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racker E. Use of synthetic amino acid polymers for assay of protein-tyrosine and protein-serine kinases. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:107–111. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00131-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. Negative regulation of mitosis by wee1+, a gene encoding a protein kinase homolog. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Huibregtse J. M., Vierstra R. D., Howley P. M. The HPV-16 E6 and E6-AP complex functions as a ubiquitin-protein ligase in the ubiquitination of p53. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):495–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90384-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Münger K., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. The state of the p53 and retinoblastoma genes in human cervical carcinoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5523–5527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Nuber U., Huibregtse J. M. Protein ubiquitination involving an E1-E2-E3 enzyme ubiquitin thioester cascade. Nature. 1995 Jan 5;373(6509):81–83. doi: 10.1038/373081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwob E., Böhm T., Mendenhall M. D., Nasmyth K. The B-type cyclin kinase inhibitor p40SIC1 controls the G1 to S transition in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):233–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seufert W., Futcher B., Jentsch S. Role of a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in degradation of S- and M-phase cyclins. Nature. 1995 Jan 5;373(6509):78–81. doi: 10.1038/373078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Lee T., Kirschner M. W. Role of phosphorylation in p34cdc2 activation: identification of an activating kinase. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):13–27. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swerdlow P. S., Finley D., Varshavsky A. Enhancement of immunoblot sensitivity by heating of hydrated filters. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jul;156(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. The N-end rule. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):725–735. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90285-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vierstra R. D., Langan S. M., Haas A. L. Purification and initial characterization of ubiquitin from the higher plant, Avena sativa. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12015–12021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. W., Goldberg A. R. In vitro phosphorylation of angiotensin analogs by tyrosyl protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1022–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrede D., Tidy J. A., Crook T., Lane D., Vousden K. H. Expression of RB and p53 proteins in HPV-positive and HPV-negative cervical carcinoma cell lines. Mol Carcinog. 1991;4(3):171–175. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940040302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]