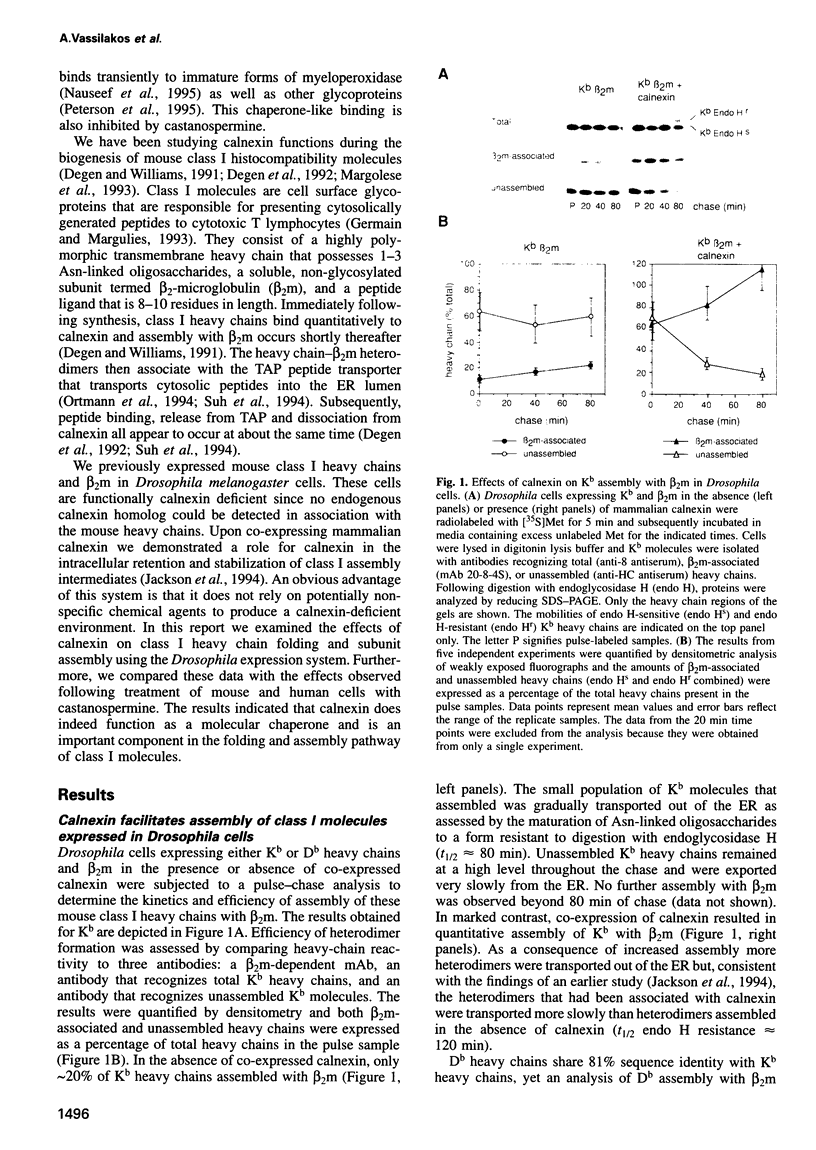
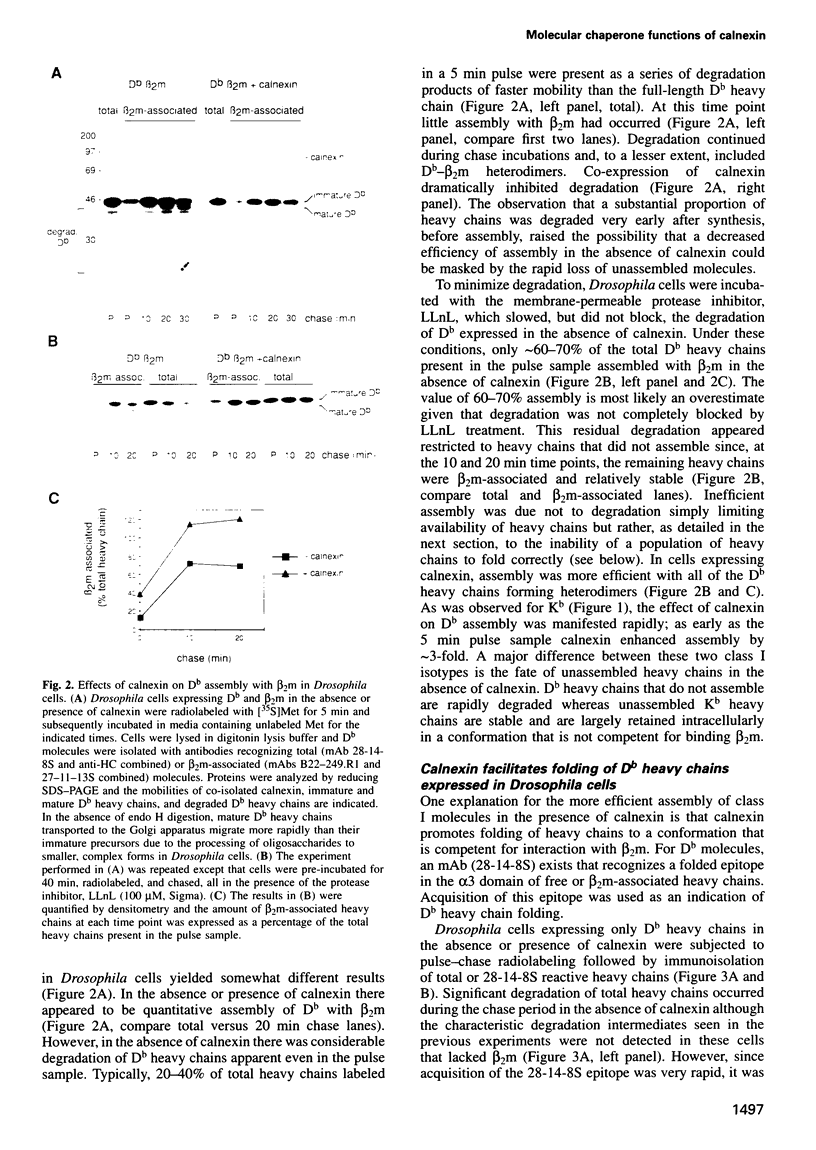
Abstract
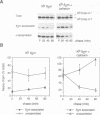
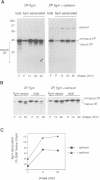
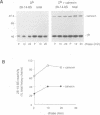
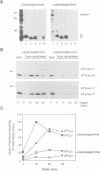
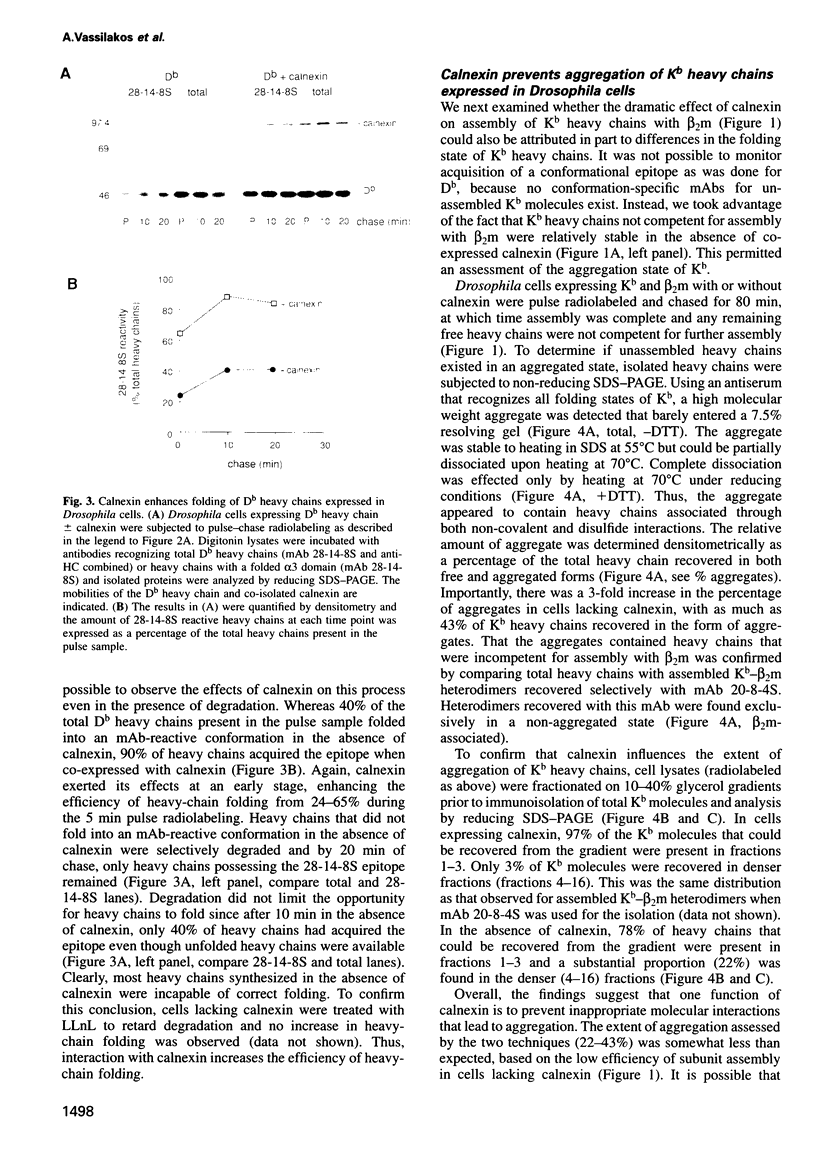
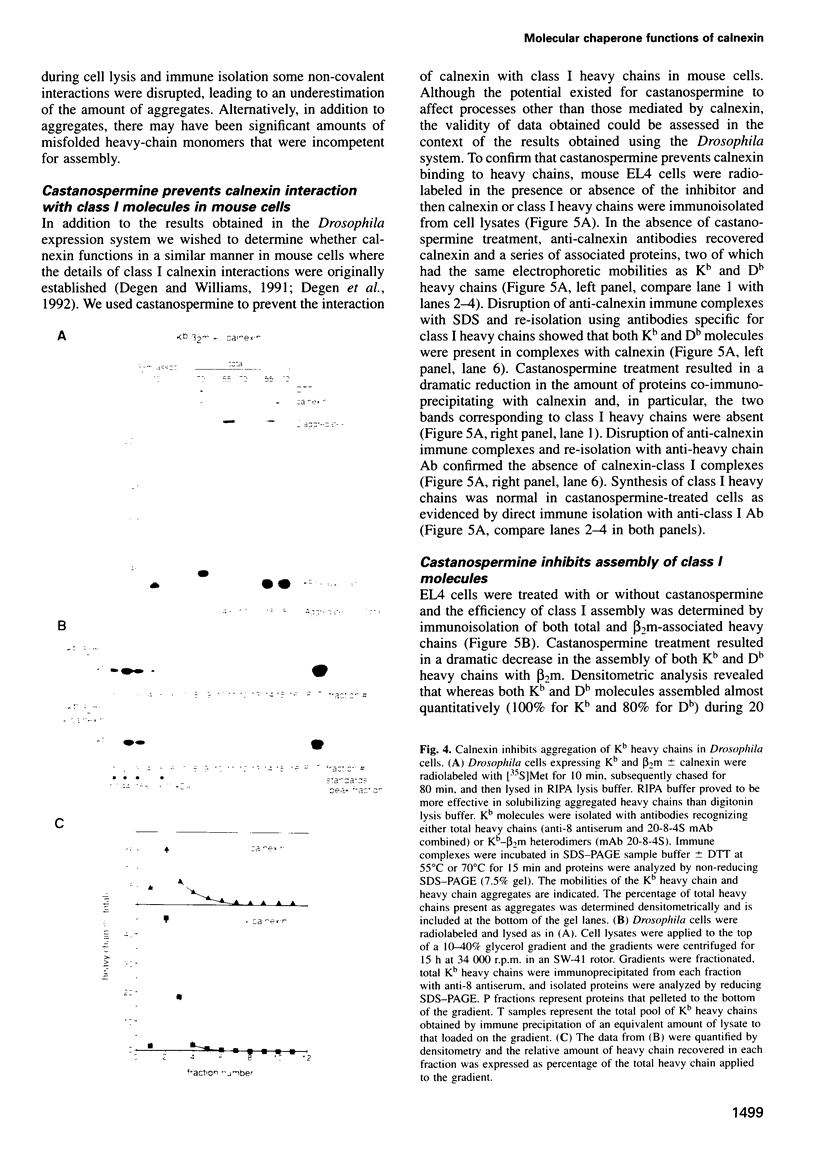
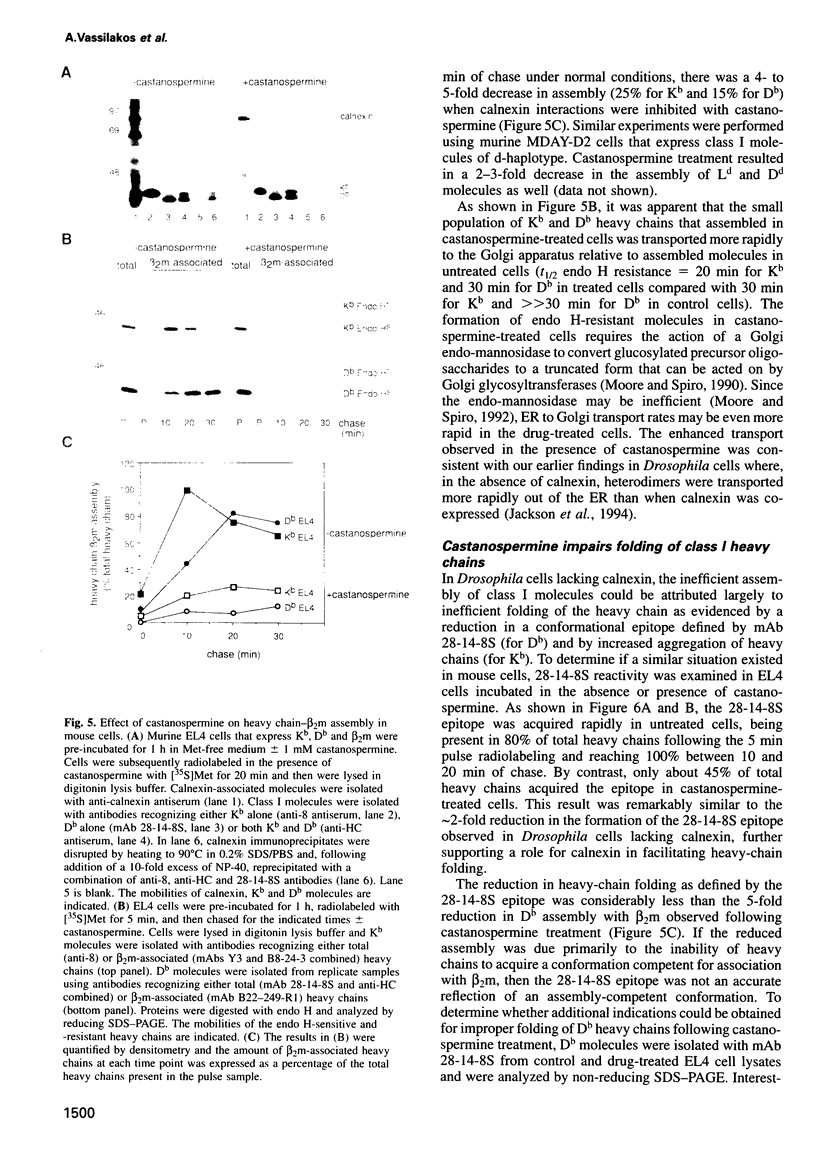
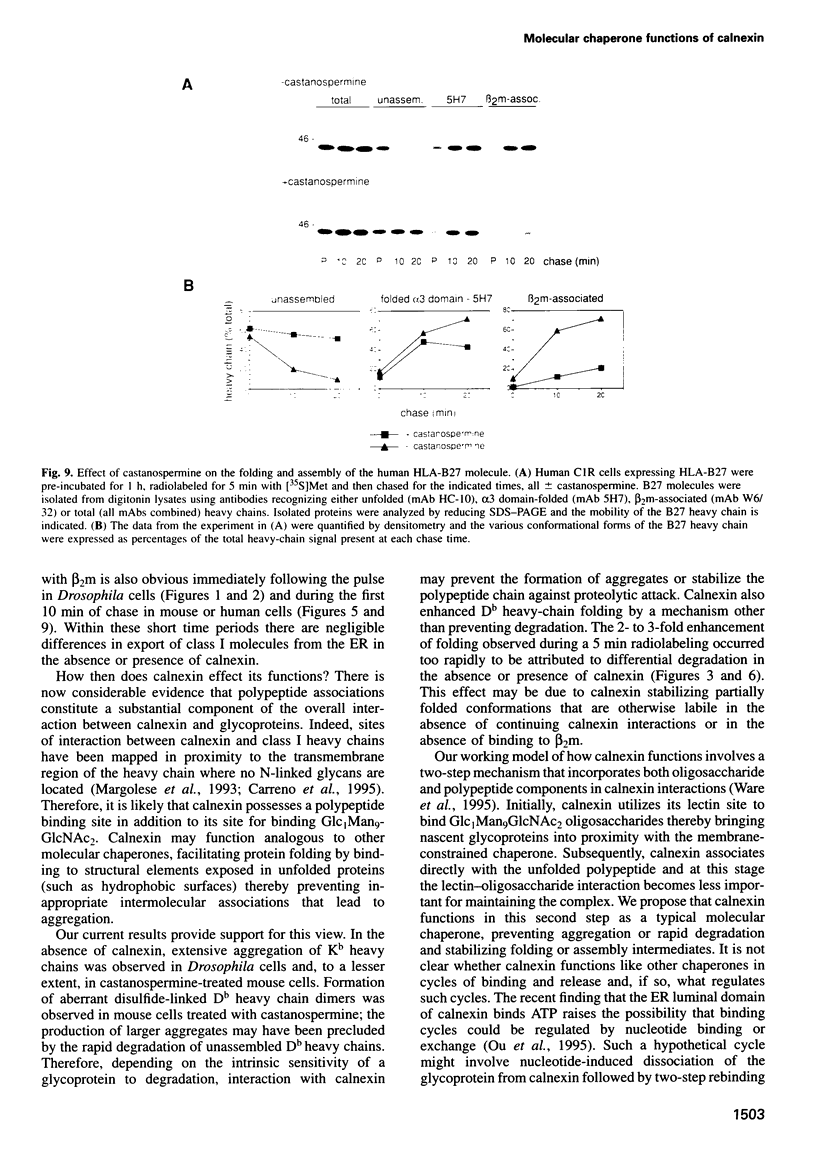
Calnexin, a membrane protein of the endoplasmic reticulum, is generally thought to function as a molecular chaperone, based on indirect or correlative evidence. To examine calnexin's functions more directly, we reconstituted the assembly of class I histocompatibility molecules in the absence or presence of calnexin in Drosophila melanogaster cells. Calnexin enhanced the assembly of class I heavy chains with beta 2-microglobulin as much as 5-fold. The improved assembly appeared largely due to more efficient folding of heavy chains, as evidenced by increased reactivity with a conformation-sensitive monoclonal antibody and by a reduction in the level of aggregates. Similar findings were obtained in mouse or human cells when the interaction of calnexin with class I heavy chains was prevented by treatment with the oligosaccharide processing inhibitor castanospermine. The ability of calnexin to facilitate castanospermine. The ability of calnexin to facilitate heavy chain folding and to prevent the formation of aggregates provides compelling evidence that calnexin functions as a bona fide molecular chaperone.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J., Payne J. A., Murray R., Frelinger J. A., Cresswell P. Differential transport requirements of HLA and H-2 class I glycoproteins. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(6):380–388. doi: 10.1007/BF00375866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen H., Fraser J., Flyer D., Calvin S., Flavell R. Beta 2-microglobulin is not required for cell surface expression of the murine class I histocompatibility antigen H-2Db or of a truncated H-2Db. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7447–7451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arunachalam B., Cresswell P. Molecular requirements for the interaction of class II major histocompatibility complex molecules and invariant chain with calnexin. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 10;270(6):2784–2790. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.6.2784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capps G. G., Robinson B. E., Lewis K. D., Zúiga M. C. In vivo dimeric association of class I MHC heavy chains. Possible relationship to class I MHC heavy chain-beta 2-microglobulin dissociation. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 1;151(1):159–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carreno B. M., Schreiber K. L., McKean D. J., Stroynowski I., Hansen T. H. Aglycosylated and phosphatidylinositol-anchored MHC class I molecules are associated with calnexin. Evidence implicating the class I-connecting peptide segment in calnexin association. J Immunol. 1995 May 15;154(10):5173–5180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen E., Cohen-Doyle M. F., Williams D. B. Efficient dissociation of the p88 chaperone from major histocompatibility complex class I molecules requires both beta 2-microglobulin and peptide. J Exp Med. 1992 Jun 1;175(6):1653–1661. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.6.1653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen E., Williams D. B. Participation of a novel 88-kD protein in the biogenesis of murine class I histocompatibility molecules. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(6):1099–1115. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.6.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. D., Allen H., Flavell R. A., Strominger J. L. Cell-surface expression of H-2Db requires N-linked glycans. Immunogenetics. 1987;26(1-2):31–35. doi: 10.1007/BF00345451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORER P. A. Studies in antibody response of mice to tumour inoculation. Br J Cancer. 1950 Dec;4(4):372–379. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1950.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N., Margulies D. H. The biochemistry and cell biology of antigen processing and presentation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:403–450. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond C., Braakman I., Helenius A. Role of N-linked oligosaccharide recognition, glucose trimming, and calnexin in glycoprotein folding and quality control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):913–917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond C., Helenius A. Folding of VSV G protein: sequential interaction with BiP and calnexin. Science. 1994 Oct 21;266(5184):456–458. doi: 10.1126/science.7939687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert D. N., Foellmer B., Helenius A. Glucose trimming and reglucosylation determine glycoprotein association with calnexin in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1995 May 5;81(3):425–433. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90395-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A. How N-linked oligosaccharides affect glycoprotein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Mar;5(3):253–265. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.3.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Marquardt T., Braakman I. The endoplasmic reticulum as a protein-folding compartment. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;2(8):227–231. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90309-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. R., Cohen-Doyle M. F., Peterson P. A., Williams D. B. Regulation of MHC class I transport by the molecular chaperone, calnexin (p88, IP90). Science. 1994 Jan 21;263(5145):384–387. doi: 10.1126/science.8278813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B., Janeway C. A., Jr Cooperative interaction of B lymphocytes with antigen-specific helper T lymphocytes is MHC restricted. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):547–549. doi: 10.1038/292547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearse K. P., Williams D. B., Singer A. Persistence of glucose residues on core oligosaccharides prevents association of TCR alpha and TCR beta proteins with calnexin and results specifically in accelerated degradation of nascent TCR alpha proteins within the endoplasmic reticulum. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 15;13(16):3678–3686. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06677.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemke H., Hämmerling G. J., Hämmerling U. Fine specificity analysis with monoclonal antibodies of antigens controlled by the major histocompatibility complex and by the Qa/TL region in mice. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:175–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo T. W., Clarke D. M. Prolonged association of temperature-sensitive mutants of human P-glycoprotein with calnexin during biogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 18;269(46):28683–28689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machold R. P., Andrée S., Van Kaer L., Ljunggren H. G., Ploegh H. L. Peptide influences the folding and intracellular transport of free major histocompatibility complex class I heavy chains. J Exp Med. 1995 Mar 1;181(3):1111–1122. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.3.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolese L., Waneck G. L., Suzuki C. K., Degen E., Flavell R. A., Williams D. B. Identification of the region on the class I histocompatibility molecule that interacts with the molecular chaperone, p88 (calnexin, IP90). J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):17959–17966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. E., Spiro R. G. Characterization of the endomannosidase pathway for the processing of N-linked oligosaccharides in glucosidase II-deficient and parent mouse lymphoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8443–8451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. E., Spiro R. G. Demonstration that Golgi endo-alpha-D-mannosidase provides a glucosidase-independent pathway for the formation of complex N-linked oligosaccharides of glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13104–13112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauseef W. M., McCormick S. J., Clark R. A. Calreticulin functions as a molecular chaperone in the biosynthesis of myeloperoxidase. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 3;270(9):4741–4747. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.9.4741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nössner E., Parham P. Species-specific differences in chaperone interaction of human and mouse major histocompatibility complex class I molecules. J Exp Med. 1995 Jan 1;181(1):327–337. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.1.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortmann B., Androlewicz M. J., Cresswell P. MHC class I/beta 2-microglobulin complexes associate with TAP transporters before peptide binding. Nature. 1994 Apr 28;368(6474):864–867. doi: 10.1038/368864a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou W. J., Bergeron J. J., Li Y., Kang C. Y., Thomas D. Y. Conformational changes induced in the endoplasmic reticulum luminal domain of calnexin by Mg-ATP and Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 28;270(30):18051–18059. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.30.18051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou W. J., Cameron P. H., Thomas D. Y., Bergeron J. J. Association of folding intermediates of glycoproteins with calnexin during protein maturation. Nature. 1993 Aug 26;364(6440):771–776. doi: 10.1038/364771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Hansen T. H., Sachs D. H. Monoclonal antibodies to mouse MHC antigens. II. Antibodies to the H-2Ld antigen, the products of a third polymorphic locus of the mouse major histocompatibility complex. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2473–2477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Sachs D. H. Monoclonal antibodies to mouse MHC antigens. III. Hybridoma antibodies reacting to antigens of the H-2b haplotype reveal genetic control of isotype expression. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):317–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahl H. L., Baeuerle P. A. A novel signal transduction pathway from the endoplasmic reticulum to the nucleus is mediated by transcription factor NF-kappa B. EMBO J. 1995 Jun 1;14(11):2580–2588. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07256.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. R., Ora A., Van P. N., Helenius A. Transient, lectin-like association of calreticulin with folding intermediates of cellular and viral glycoproteins. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Sep;6(9):1173–1184. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.9.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopalan S., Brenner M. B. Calnexin retains unassembled major histocompatibility complex class I free heavy chains in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Exp Med. 1994 Jul 1;180(1):407–412. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.1.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopalan S., Xu Y., Brenner M. B. Retention of unassembled components of integral membrane proteins by calnexin. Science. 1994 Jan 21;263(5145):387–390. doi: 10.1126/science.8278814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. E., Dawson J. R. MHC class I expression and transport in a calnexin-deficient cell line. J Immunol. 1995 Jul 1;155(1):143–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. H., Parker J. M., Hodges R. S., Barber B. H. The preparation and characterization of anti-peptide heteroantisera recognizing subregions of the intracytoplasmic domain of class I H-2 antigens. Mol Immunol. 1986 Oct;23(10):1077–1092. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stam N. J., Spits H., Ploegh H. L. Monoclonal antibodies raised against denatured HLA-B locus heavy chains permit biochemical characterization of certain HLA-C locus products. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2299–2306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita M., Brenner M. B. An unstable beta 2-microglobulin: major histocompatibility complex class I heavy chain intermediate dissociates from calnexin and then is stabilized by binding peptide. J Exp Med. 1994 Dec 1;180(6):2163–2171. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.6.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh W. K., Cohen-Doyle M. F., Fruh K., Wang K., Peterson P. A., Williams D. B. Interaction of MHC class I molecules with the transporter associated with antigen processing. Science. 1994 May 27;264(5163):1322–1326. doi: 10.1126/science.8191286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tector M., Salter R. D. Calnexin influences folding of human class I histocompatibility proteins but not their assembly with beta 2-microglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 18;270(33):19638–19642. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.33.19638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada I., Rindress D., Cameron P. H., Ou W. J., Doherty J. J., 2nd, Louvard D., Bell A. W., Dignard D., Thomas D. Y., Bergeron J. J. SSR alpha and associated calnexin are major calcium binding proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19599–19610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware F. E., Vassilakos A., Peterson P. A., Jackson M. R., Lehrman M. A., Williams D. B. The molecular chaperone calnexin binds Glc1Man9GlcNAc2 oligosaccharide as an initial step in recognizing unfolded glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 3;270(9):4697–4704. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.9.4697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. B. The Merck Frosst Award Lecture 1994/La conference Merck Frosst 1994. Calnexin: a molecular chaperone with a taste for carbohydrate. Biochem Cell Biol. 1995 Mar-Apr;73(3-4):123–132. doi: 10.1139/o95-015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Q., Tector M., Salter R. D. Calnexin recognizes carbohydrate and protein determinants of class I major histocompatibility complex molecules. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 24;270(8):3944–3948. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.8.3944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]