Abstract
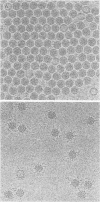
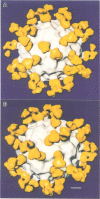
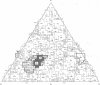
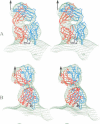
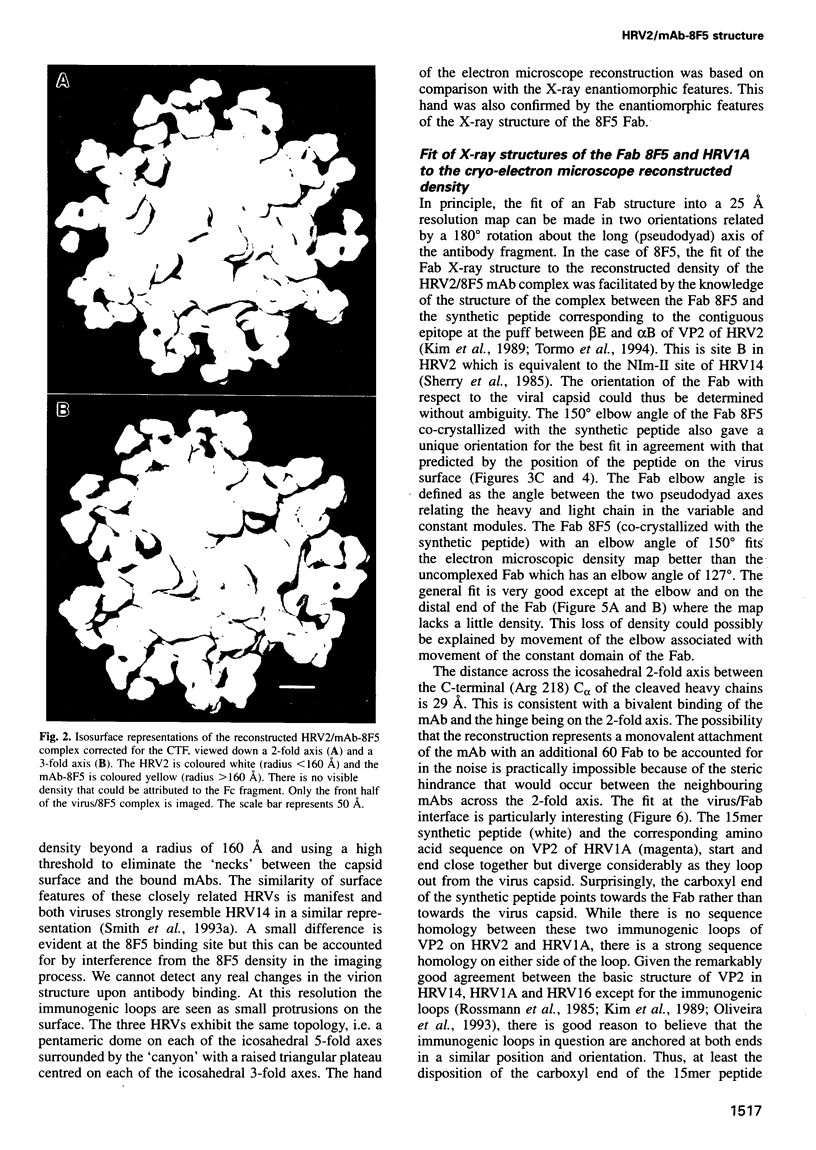
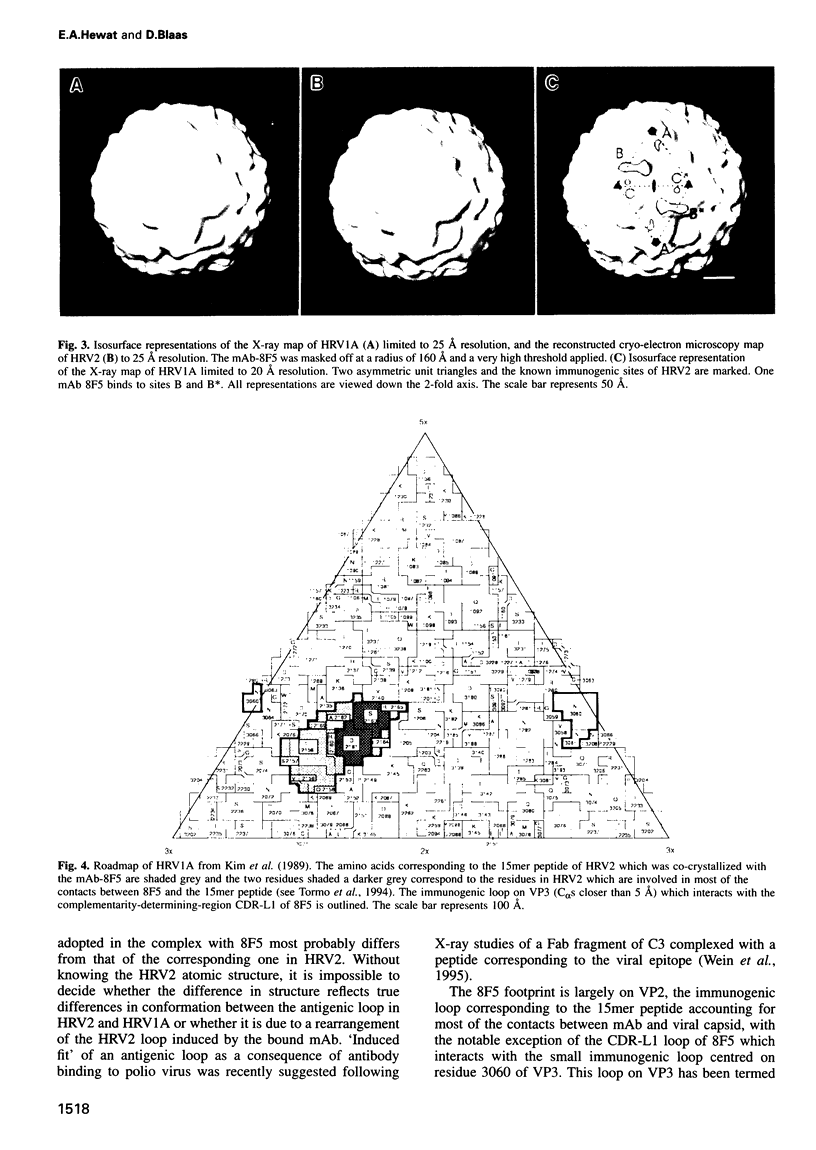
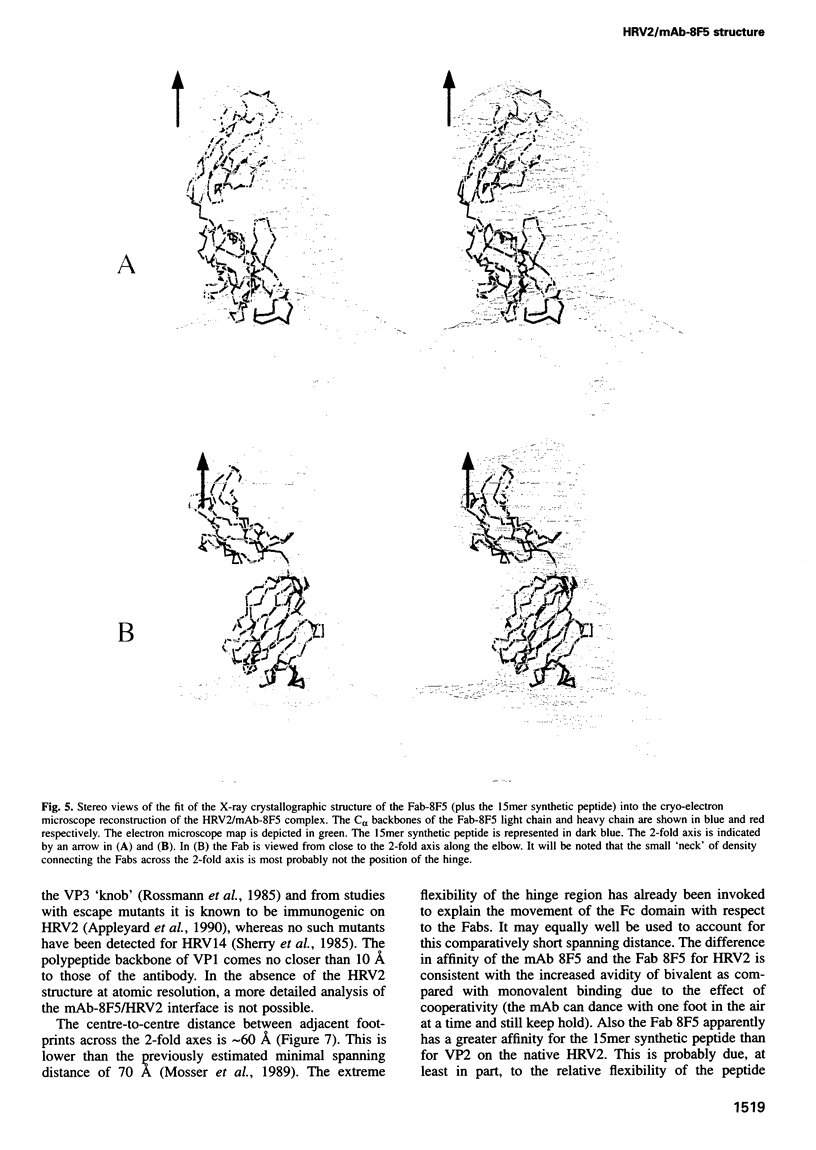
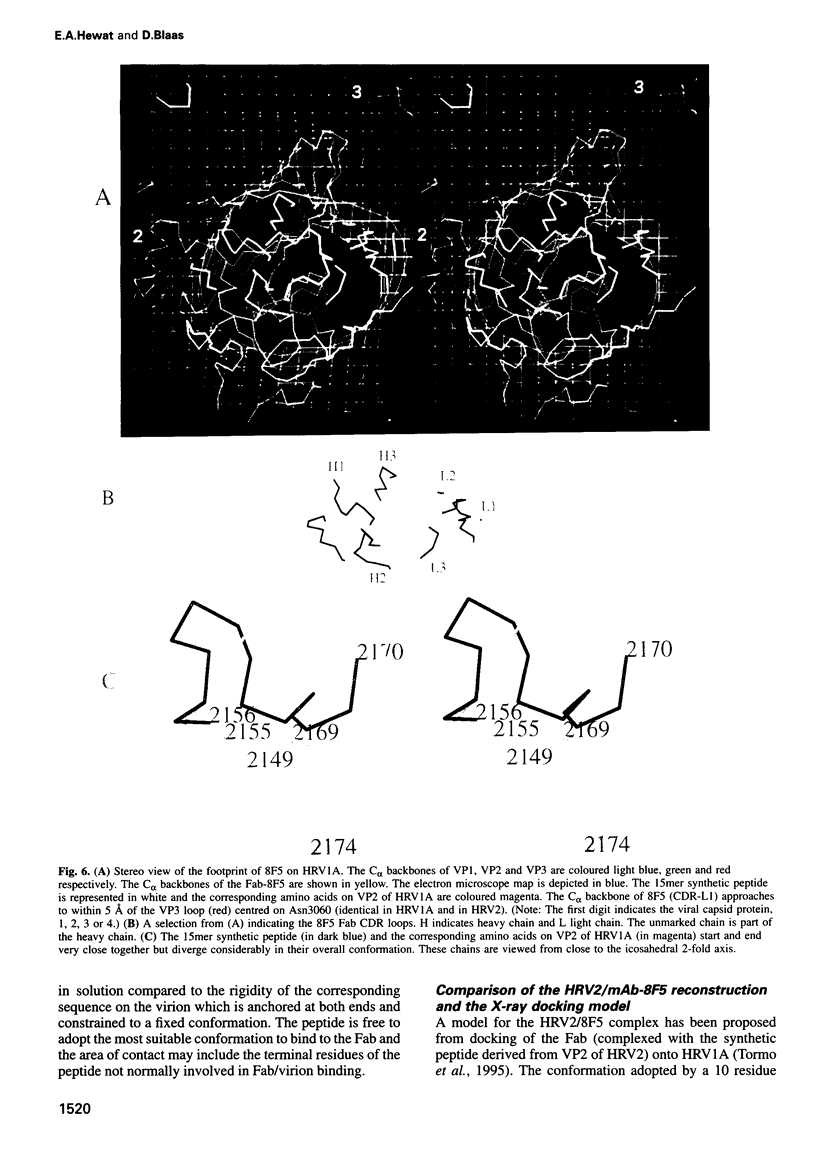
The structure of a complex between human rhinovirus serotype 2 (HRV2) and the weakly neutralizing monoclonal antibody 8F5 has been determined to 25 A resolution by cryo-electron microscopy and 3-D reconstruction techniques. THe antibody is seen to be bound bivalently across the icosahedral 2-fold axis, despite the very short distance of 60 A between the symmetry-related epitopes. The canyon around the 5-fold axis is not obstructed. Due to extreme flexibility of the hinge region the Fc domains occupy random orientations and are not visible in the reconstruction. The atomic coordinates of Fab-8F5 complexes with a synthetic peptide derived from the viral protein 2 (VP2) epitope were fitted to the structure obtained by cryo-electron microscope techniques. The X-ray structure of HRV2 is not unknown, so that of the closely related HRV1A was placed in the electron microscopic density map. The footprint of 8F5 on the viral surface is largely on VP2, but also covers the VP3 loop centred on residue 3060. C alpha atoms of VP1 and 8F5 come no closer than 10 A. Based on the fit of the X-ray coordinates to the electron microscope data, the synthetic 15mer peptide starts and ends in close proximity to the corresponding amino acids of VP2 on HRV1A. However, the respective loops diverge considerably in their overall spatial disposition. It appears from this study that bivalent binding of an antibody directed against a picornavirus exists for a smaller spanning distance than was previously thought possible. Also bivalent binding does not ensure strong neutralization.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleyard G., Russell S. M., Clarke B. E., Speller S. A., Trowbridge M., Vadolas J. Neutralization epitopes of human rhinovirus type 2. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jun;71(Pt 6):1275–1282. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-6-1275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman M. S., Rossmann M. G. Comparison of surface properties of picornaviruses: strategies for hiding the receptor site from immune surveillance. Virology. 1993 Aug;195(2):745–756. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther R. A. Procedures for three-dimensional reconstruction of spherical viruses by Fourier synthesis from electron micrographs. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 May 27;261(837):221–230. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1971.0054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duechler M., Ketter S., Skern T., Kuechler E., Blaas D. Rhinoviral receptor discrimination: mutational changes in the canyon regions of human rhinovirus types 2 and 14 indicate a different site of interaction. J Gen Virol. 1993 Oct;74(Pt 10):2287–2291. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-10-2287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S. D. The T=4 envelope of Sindbis virus is organized by interactions with a complementary T=3 capsid. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):923–934. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90701-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greve J. M., Davis G., Meyer A. M., Forte C. P., Yost S. C., Marlor C. W., Kamarck M. E., McClelland A. The major human rhinovirus receptor is ICAM-1. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90688-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewat E. A., Booth T. F., Loudon P. T., Roy P. Three-dimensional reconstruction of baculovirus expressed bluetongue virus core-like particles by cryo-electron microscopy. Virology. 1992 Jul;189(1):10–20. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90676-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewat E. A., Booth T. F., Roy P. Structure of bluetongue virus particles by cryoelectron microscopy. J Struct Biol. 1992 Jul-Aug;109(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(92)90068-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofer F., Gruenberger M., Kowalski H., Machat H., Huettinger M., Kuechler E., Blaas D. Members of the low density lipoprotein receptor family mediate cell entry of a minor-group common cold virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 1;91(5):1839–1842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.5.1839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. S., Smith T. J., Chapman M. S., Rossmann M. C., Pevear D. C., Dutko F. J., Felock P. J., Diana G. D., McKinlay M. A. Crystal structure of human rhinovirus serotype 1A (HRV1A). J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 5;210(1):91–111. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90293-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H., Smith T. J., Lee W. M., Mosser A. G., Rueckert R. R., Olson N. H., Cheng R. H., Baker T. S. Structure determination of an Fab fragment that neutralizes human rhinovirus 14 and analysis of the Fab-virus complex. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jul 8;240(2):127–137. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira M. A., Zhao R., Lee W. M., Kremer M. J., Minor I., Rueckert R. R., Diana G. D., Pevear D. C., Dutko F. J., McKinlay M. A. The structure of human rhinovirus 16. Structure. 1993 Sep 15;1(1):51–68. doi: 10.1016/0969-2126(93)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson N. H., Kolatkar P. R., Oliveira M. A., Cheng R. H., Greve J. M., McClelland A., Baker T. S., Rossmann M. G. Structure of a human rhinovirus complexed with its receptor molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):507–511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porta C., Wang G., Cheng H., Chen Z., Baker T. S., Johnson J. E. Direct imaging of interactions between an icosahedral virus and conjugate F(ab) fragments by cryoelectron microscopy and X-ray crystallography. Virology. 1994 Nov 1;204(2):777–788. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad B. V., Burns J. W., Marietta E., Estes M. K., Chiu W. Localization of VP4 neutralization sites in rotavirus by three-dimensional cryo-electron microscopy. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):476–479. doi: 10.1038/343476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Arnold E., Erickson J. W., Frankenberger E. A., Griffith J. P., Hecht H. J., Johnson J. E., Kamer G., Luo M., Mosser A. G. Structure of a human common cold virus and functional relationship to other picornaviruses. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):145–153. doi: 10.1038/317145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Johnson J. E. Icosahedral RNA virus structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:533–573. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G. The canyon hypothesis. Hiding the host cell receptor attachment site on a viral surface from immune surveillance. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14587–14590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Mosser A. G., Colonno R. J., Rueckert R. R. Use of monoclonal antibodies to identify four neutralization immunogens on a common cold picornavirus, human rhinovirus 14. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):246–257. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.246-257.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skern T., Neubauer C., Frasel L., Gründler P., Sommergruber W., Zorn M., Kuechler E., Blaas D. A neutralizing epitope on human rhinovirus type 2 includes amino acid residues between 153 and 164 of virus capsid protein VP2. J Gen Virol. 1987 Feb;68(Pt 2):315–323. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-2-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skern T., Sommergruber W., Blaas D., Pieler C., Kuechler E. Relationship of human rhinovirus strain 2 and poliovirus as indicated by comparison of the polymerase gene regions. Virology. 1984 Jul 15;136(1):125–132. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. J., Olson N. H., Cheng R. H., Chase E. S., Baker T. S. Structure of a human rhinovirus-bivalently bound antibody complex: implications for viral neutralization and antibody flexibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7015–7018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. J., Olson N. H., Cheng R. H., Liu H., Chase E. S., Lee W. M., Leippe D. M., Mosser A. G., Rueckert R. R., Baker T. S. Structure of human rhinovirus complexed with Fab fragments from a neutralizing antibody. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1148–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1148-1158.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Merluzzi V. J., Rothlein R., Barton R., Marlin S. D., Springer T. A. A cell adhesion molecule, ICAM-1, is the major surface receptor for rhinoviruses. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):849–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90689-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomassini J. E., Graham D., DeWitt C. M., Lineberger D. W., Rodkey J. A., Colonno R. J. cDNA cloning reveals that the major group rhinovirus receptor on HeLa cells is intercellular adhesion molecule 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4907–4911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tormo J., Blaas D., Parry N. R., Rowlands D., Stuart D., Fita I. Crystal structure of a human rhinovirus neutralizing antibody complexed with a peptide derived from viral capsid protein VP2. EMBO J. 1994 May 15;13(10):2247–2256. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06506.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tormo J., Centeno N. B., Fontana E., Bubendorfer T., Fita I., Blaas D. Docking of a human rhinovirus neutralizing antibody onto the viral capsid. Proteins. 1995 Dec;23(4):491–501. doi: 10.1002/prot.340230404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tormo J., Fita I., Kanzler O., Blaas D. Crystallization and preliminary x-ray diffraction studies of the Fab fragment of a neutralizing monoclonal antibody directed against human rhinovirus serotype 2. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16799–16800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tormo J., Stadler E., Skern T., Auer H., Kanzler O., Betzel C., Blaas D., Fita I. Three-dimensional structure of the Fab fragment of a neutralizing antibody to human rhinovirus serotype 2. Protein Sci. 1992 Sep;1(9):1154–1161. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trus B. L., Newcomb W. W., Booy F. P., Brown J. C., Steven A. C. Distinct monoclonal antibodies separately label the hexons or the pentons of herpes simplex virus capsid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11508–11512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade R. H., Taveau J. C., Lamy J. N. Concerning the axial rotational flexibility of the Fab regions of immunoglobulin G. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 20;206(2):349–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90484-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. J., Porta C., Chen Z. G., Baker T. S., Johnson J. E. Identification of a Fab interaction footprint site on an icosahedral virus by cryoelectron microscopy and X-ray crystallography. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):275–278. doi: 10.1038/355275a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wien M. W., Filman D. J., Stura E. A., Guillot S., Delpeyroux F., Crainic R., Hogle J. M. Structure of the complex between the Fab fragment of a neutralizing antibody for type 1 poliovirus and its viral epitope. Nat Struct Biol. 1995 Mar;2(3):232–243. doi: 10.1038/nsb0395-232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikoff W. R., Wang G., Parrish C. R., Cheng R. H., Strassheim M. L., Baker T. S., Rossmann M. G. The structure of a neutralized virus: canine parvovirus complexed with neutralizing antibody fragment. Structure. 1994 Jul 15;2(7):595–607. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00062-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]