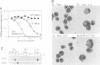
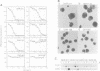
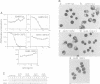
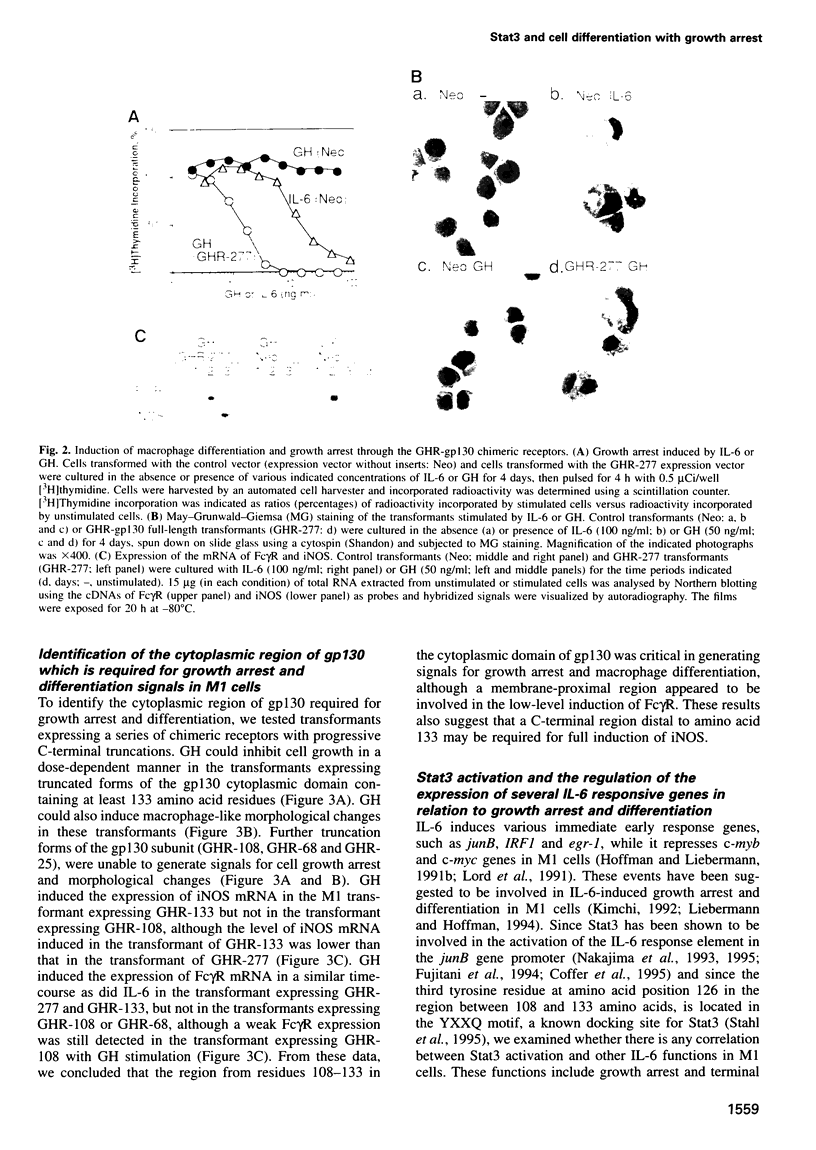
Abstract
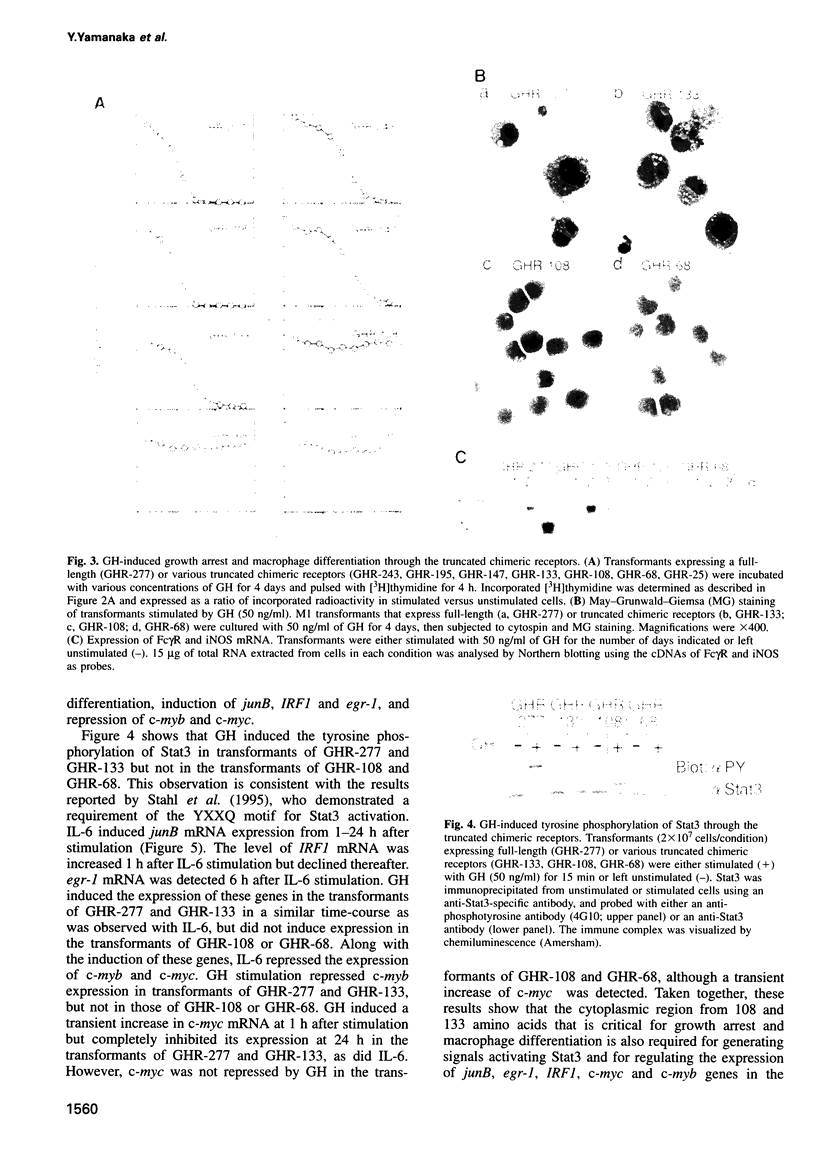
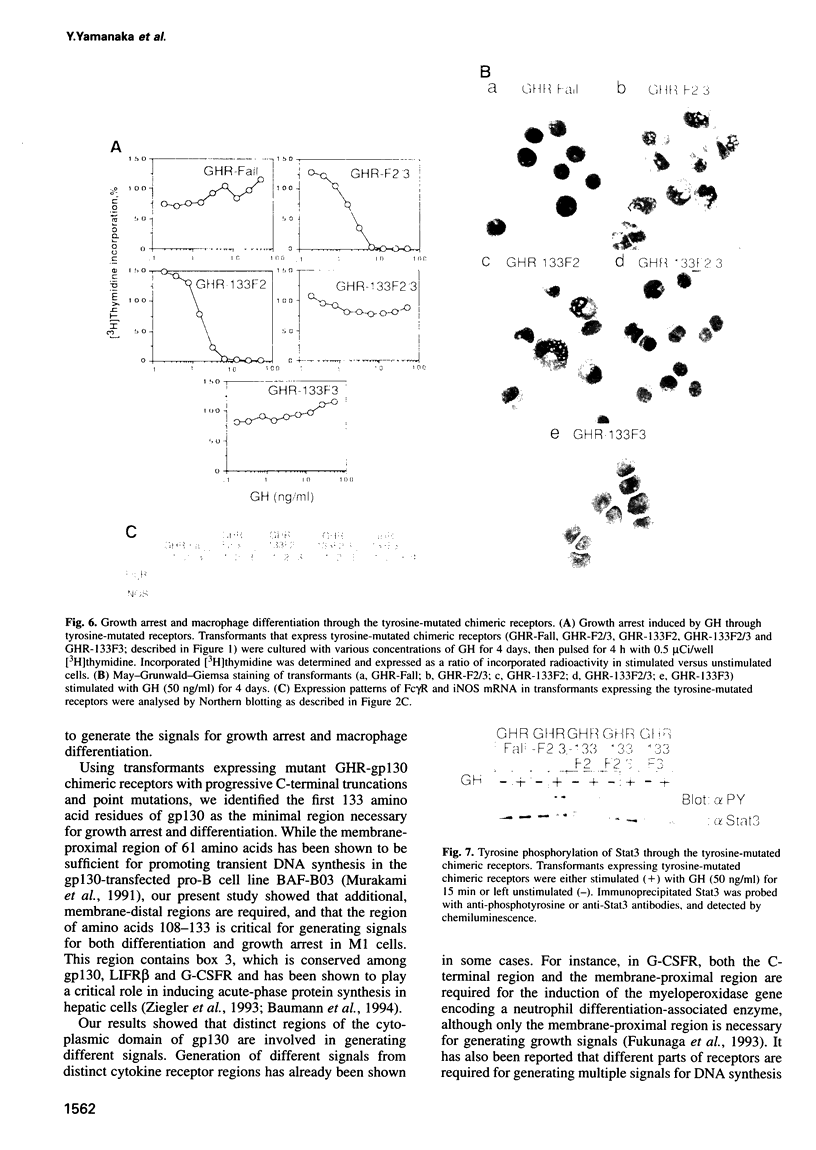
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) induces growth arrest and macrophage differentiation through its receptor in a murine myeloid leukaemic cell line, M1, although it is largely unknown how the IL-6 receptor generates these signals. By using chimeric receptors consisting of the extracellular domain of growth hormone receptor and the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domain of gp130 with progressive C-terminal truncations, we showed that the membrane-proximal 133, but not 108, amino acids of gp130 could generate the signals for growth arrest, macrophage differentiation, down-regulation of c-myc and c-myb, induction of junB and IRF1 and Stat3 activation. Mutational analysis of this region showed that the tyrosine residue with the YXXQ motif was critical not only for Stat3 activation but also for growth arrest and differentiation, accompanied by down-regulation of c-myc and c-myb and immediate early induction of junB and IRF1. The tight correlation between Stat3 activation and other IL-6 functions was further observed in the context of the full-length cytoplasmic region of gp130. The result suggest that Stat3 plays an essential role in the signals for growth arrest and differentiation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Nishio Y., Inoue M., Wang X. J., Wei S., Matsusaka T., Yoshida K., Sudo T., Naruto M., Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning of APRF, a novel IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 p91-related transcription factor involved in the gp130-mediated signaling pathway. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andus T., Geiger T., Hirano T., Northoff H., Ganter U., Bauer J., Kishimoto T., Heinrich P. C. Recombinant human B cell stimulatory factor 2 (BSF-2/IFN-beta 2) regulates beta-fibrinogen and albumin mRNA levels in Fao-9 cells. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 31;221(1):18–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80344-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Symes A. J., Comeau M. R., Morella K. K., Wang Y., Friend D., Ziegler S. F., Fink J. S., Gearing D. P. Multiple regions within the cytoplasmic domains of the leukemia inhibitory factor receptor and gp130 cooperate in signal transduction in hepatic and neuronal cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):138–146. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonni A., Frank D. A., Schindler C., Greenberg M. E. Characterization of a pathway for ciliary neurotrophic factor signaling to the nucleus. Science. 1993 Dec 3;262(5139):1575–1579. doi: 10.1126/science.7504325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Stahl N., Yancopoulos G. D. Ciliary neurotrophic factor/leukemia inhibitory factor/interleukin 6/oncostatin M family of cytokines induces tyrosine phosphorylation of a common set of proteins overlapping those induced by other cytokines and growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11648–11655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Mory Y., Zilberstein A., Revel M. Growth inhibition of human breast carcinoma and leukemia/lymphoma cell lines by recombinant interferon-beta 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8037–8041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffer P., Lutticken C., van Puijenbroek A., Klop-de Jonge M., Horn F., Kruijer W. Transcriptional regulation of the junB promoter: analysis of STAT-mediated signal transduction. Oncogene. 1995 Mar 2;10(5):985–994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. C., Ultsch M., De Vos A. M., Mulkerrin M. G., Clauser K. R., Wells J. A. Dimerization of the extracellular domain of the human growth hormone receptor by a single hormone molecule. Science. 1991 Nov 8;254(5033):821–825. doi: 10.1126/science.1948064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr, Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1415–1421. doi: 10.1126/science.8197455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S., Aldrich T. H., Stahl N., Pan L., Taga T., Kishimoto T., Ip N. Y., Yancopoulos G. D. LIFR beta and gp130 as heterodimerizing signal transducers of the tripartite CNTF receptor. Science. 1993 Jun 18;260(5115):1805–1808. doi: 10.1126/science.8390097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujitani Y., Nakajima K., Kojima H., Nakae K., Takeda T., Hirano T. Transcriptional activation of the IL-6 response element in the junB promoter is mediated by multiple Stat family proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Jul 29;202(2):1181–1187. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga R., Ishizaka-Ikeda E., Nagata S. Growth and differentiation signals mediated by different regions in the cytoplasmic domain of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1079–1087. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90729-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauldie J., Richards C., Harnish D., Lansdorp P., Baumann H. Interferon beta 2/B-cell stimulatory factor type 2 shares identity with monocyte-derived hepatocyte-stimulating factor and regulates the major acute phase protein response in liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7251–7255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halevy O., Novitch B. G., Spicer D. B., Skapek S. X., Rhee J., Hannon G. J., Beach D., Lassar A. B. Correlation of terminal cell cycle arrest of skeletal muscle with induction of p21 by MyoD. Science. 1995 Feb 17;267(5200):1018–1021. doi: 10.1126/science.7863327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harroch S., Revel M., Chebath J. Induction by interleukin-6 of interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1) gene expression through the palindromic interferon response element pIRE and cell type-dependent control of IRF-1 binding to DNA. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 15;13(8):1942–1949. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06463.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley R. G., Lieu F. H., Fong A. Z., Hawley T. S. Versatile retroviral vectors for potential use in gene therapy. Gene Ther. 1994 Mar;1(2):136–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibi M., Murakami M., Saito M., Hirano T., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning and expression of an IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1149–1157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90411-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Matsuda T., Nakajima K. Signal transduction through gp130 that is shared among the receptors for the interleukin 6 related cytokine subfamily. Stem Cells. 1994 May;12(3):262–277. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530120303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T. The biology of interleukin-6. Chem Immunol. 1992;51:153–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Yasukawa K., Harada H., Taga T., Watanabe Y., Matsuda T., Kashiwamura S., Nakajima K., Koyama K., Iwamatsu A. Complementary DNA for a novel human interleukin (BSF-2) that induces B lymphocytes to produce immunoglobulin. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):73–76. doi: 10.1038/324073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D. A. Interleukin-6- and leukemia inhibitory factor-induced terminal differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells is blocked at an intermediate stage by constitutive c-myc. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2375–2381. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D. A. Suppression of c-myc and c-myb is tightly linked to terminal differentiation induced by IL6 or LIF and not growth inhibition in myeloid leukemia cells. Oncogene. 1991 Jun;6(6):903–909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Kerr I. M. Jaks and Stats in signaling by the cytokine receptor superfamily. Trends Genet. 1995 Feb;11(2):69–74. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(00)89000-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., Nye S. H., Boulton T. G., Davis S., Taga T., Li Y., Birren S. J., Yasukawa K., Kishimoto T., Anderson D. J. CNTF and LIF act on neuronal cells via shared signaling pathways that involve the IL-6 signal transducing receptor component gp130. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1121–1132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90634-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawano M., Hirano T., Matsuda T., Taga T., Horii Y., Iwato K., Asaoku H., Tang B., Tanabe O., Tanaka H. Autocrine generation and requirement of BSF-2/IL-6 for human multiple myelomas. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):83–85. doi: 10.1038/332083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimchi A. Cytokine triggered molecular pathways that control cell cycle arrest. J Cell Biochem. 1992 Sep;50(1):1–9. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240500102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita T., Yokota T., Arai K., Miyajima A. Suppression of apoptotic death in hematopoietic cells by signalling through the IL-3/GM-CSF receptors. EMBO J. 1995 Jan 16;14(2):266–275. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner A. C., David M., Feldman G. M., Igarashi K., Hackett R. H., Webb D. S., Sweitzer S. M., Petricoin E. F., 3rd, Finbloom D. S. Tyrosine phosphorylation of DNA binding proteins by multiple cytokines. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1730–1733. doi: 10.1126/science.8378773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord K. A., Abdollahi A., Thomas S. M., DeMarco M., Brugge J. S., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D. A. Leukemia inhibitory factor and interleukin-6 trigger the same immediate early response, including tyrosine phosphorylation, upon induction of myeloid leukemia differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4371–4379. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda T., Yamanaka Y., Hirano T. Interleukin-6-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of multiple proteins in murine hematopoietic lineage cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Apr 29;200(2):821–828. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura Y., Miura O., Ihle J. N., Aoki N. Activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by the erythropoietin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 25;269(47):29962–29969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima A., Mui A. L., Ogorochi T., Sakamaki K. Receptors for granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, interleukin-3, and interleukin-5. Blood. 1993 Oct 1;82(7):1960–1974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyaura C., Onozaki K., Akiyama Y., Taniyama T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Suda T. Recombinant human interleukin 6 (B-cell stimulatory factor 2) is a potent inducer of differentiation of mouse myeloid leukemia cells (M1). FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 4;234(1):17–21. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81293-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki T., Liu Z. J., Kawahara A., Minami Y., Yamada K., Tsujimoto Y., Barsoumian E. L., Permutter R. M., Taniguchi T. Three distinct IL-2 signaling pathways mediated by bcl-2, c-myc, and lck cooperate in hematopoietic cell proliferation. Cell. 1995 Apr 21;81(2):223–231. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90332-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Hibi M., Nakagawa N., Nakagawa T., Yasukawa K., Yamanishi K., Taga T., Kishimoto T. IL-6-induced homodimerization of gp130 and associated activation of a tyrosine kinase. Science. 1993 Jun 18;260(5115):1808–1810. doi: 10.1126/science.8511589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Narazaki M., Hibi M., Yawata H., Yasukawa K., Hamaguchi M., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Critical cytoplasmic region of the interleukin 6 signal transducer gp130 is conserved in the cytokine receptor family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11349–11353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K., Kusafuka T., Takeda T., Fujitani Y., Nakae K., Hirano T. Identification of a novel interleukin-6 response element containing an Ets-binding site and a CRE-like site in the junB promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):3027–3041. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.3027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K., Matsuda T., Fujitani Y., Kojima H., Yamanaka Y., Nakae K., Takeda T., Hirano T. Signal transduction through IL-6 receptor: involvement of multiple protein kinases, stat factors, and a novel H7-sensitive pathway. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995 Jul 21;762:55–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb32314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen H. Q., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D. A. The zinc finger transcription factor Egr-1 is essential for and restricts differentiation along the macrophage lineage. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):197–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90660-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordan R. P., Potter M. A macrophage-derived factor required by plasmacytomas for survival and proliferation in vitro. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):566–569. doi: 10.1126/science.3726549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oritani K., Kaisho T., Nakajima K., Hirano T. Retinoic acid inhibits interleukin-6-induced macrophage differentiation and apoptosis in a murine hematopoietic cell line, Y6. Blood. 1992 Nov 1;80(9):2298–2305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker S. B., Eichele G., Zhang P., Rawls A., Sands A. T., Bradley A., Olson E. N., Harper J. W., Elledge S. J. p53-independent expression of p21Cip1 in muscle and other terminally differentiating cells. Science. 1995 Feb 17;267(5200):1024–1027. doi: 10.1126/science.7863329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski H. B., Shuai K., Darnell J. E., Jr, Gilman M. Z. A common nuclear signal transduction pathway activated by growth factor and cytokine receptors. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1739–1744. doi: 10.1126/science.8397445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamaki K., Miyajima I., Kitamura T., Miyajima A. Critical cytoplasmic domains of the common beta subunit of the human GM-CSF, IL-3 and IL-5 receptors for growth signal transduction and tyrosine phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3541–3549. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05437.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato N., Sakamaki K., Terada N., Arai K., Miyajima A. Signal transduction by the high-affinity GM-CSF receptor: two distinct cytoplasmic regions of the common beta subunit responsible for different signaling. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4181–4189. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06102.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Fu X. Y., Improta T., Aebersold R., Darnell J. E., Jr Proteins of transcription factor ISGF-3: one gene encodes the 91-and 84-kDa ISGF-3 proteins that are activated by interferon alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7836–7839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Shuai K., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of a latent cytoplasmic transcription factor. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):809–813. doi: 10.1126/science.1496401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvakumaran M., Liebermann D. A., Hoffman-Liebermann B. Deregulated c-myb disrupts interleukin-6- or leukemia inhibitory factor-induced myeloid differentiation prior to c-myc: role in leukemogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2493–2500. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvakumaran M., Lin H. K., Sjin R. T., Reed J. C., Liebermann D. A., Hoffman B. The novel primary response gene MyD118 and the proto-oncogenes myb, myc, and bcl-2 modulate transforming growth factor beta 1-induced apoptosis of myeloid leukemia cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2352–2360. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shabo Y., Lotem J., Rubinstein M., Revel M., Clark S. C., Wolf S. F., Kamen R., Sachs L. The myeloid blood cell differentiation-inducing protein MGI-2A is interleukin-6. Blood. 1988 Dec;72(6):2070–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvennoinen O., Schindler C., Schlessinger J., Levy D. E. Ras-independent growth factor signaling by transcription factor tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1736–1739. doi: 10.1126/science.8378775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Boulton T. G., Farruggella T., Ip N. Y., Davis S., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Silvennoinen O., Barbieri G., Pellegrini S. Association and activation of Jak-Tyk kinases by CNTF-LIF-OSM-IL-6 beta receptor components. Science. 1994 Jan 7;263(5143):92–95. doi: 10.1126/science.8272873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Farruggella T. J., Boulton T. G., Zhong Z., Darnell J. E., Jr, Yancopoulos G. D. Choice of STATs and other substrates specified by modular tyrosine-based motifs in cytokine receptors. Science. 1995 Mar 3;267(5202):1349–1353. doi: 10.1126/science.7871433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taga T., Hibi M., Hirata Y., Yamasaki K., Yasukawa K., Matsuda T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Interleukin-6 triggers the association of its receptor with a possible signal transducer, gp130. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):573–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90438-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T. Cytokine signaling through nonreceptor protein tyrosine kinases. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):251–255. doi: 10.1126/science.7716517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teranishi T., Hirano T., Arima N., Onoue K. Human helper T cell factor(s) (ThF). II. Induction of IgG production in B lymphoblastoid cell lines and identification of T cell-replacing factor- (TRF) like factor(s). J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1903–1908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. Interleukin-6: an overview. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:253–278. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegenka U. M., Buschmann J., Lütticken C., Heinrich P. C., Horn F. Acute-phase response factor, a nuclear factor binding to acute-phase response elements, is rapidly activated by interleukin-6 at the posttranslational level. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):276–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki K., Taga T., Hirata Y., Yawata H., Kawanishi Y., Seed B., Taniguchi T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Cloning and expression of the human interleukin-6 (BSF-2/IFN beta 2) receptor. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):825–828. doi: 10.1126/science.3136546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin T., Taga T., Tsang M. L., Yasukawa K., Kishimoto T., Yang Y. C. Involvement of IL-6 signal transducer gp130 in IL-11-mediated signal transduction. J Immunol. 1993 Sep 1;151(5):2555–2561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong Z., Wen Z., Darnell J. E., Jr Stat3: a STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science. 1994 Apr 1;264(5155):95–98. doi: 10.1126/science.8140422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler S. F., Bird T. A., Morella K. K., Mosley B., Gearing D. P., Baumann H. Distinct regions of the human granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor receptor cytoplasmic domain are required for proliferation and gene induction. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2384–2390. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]