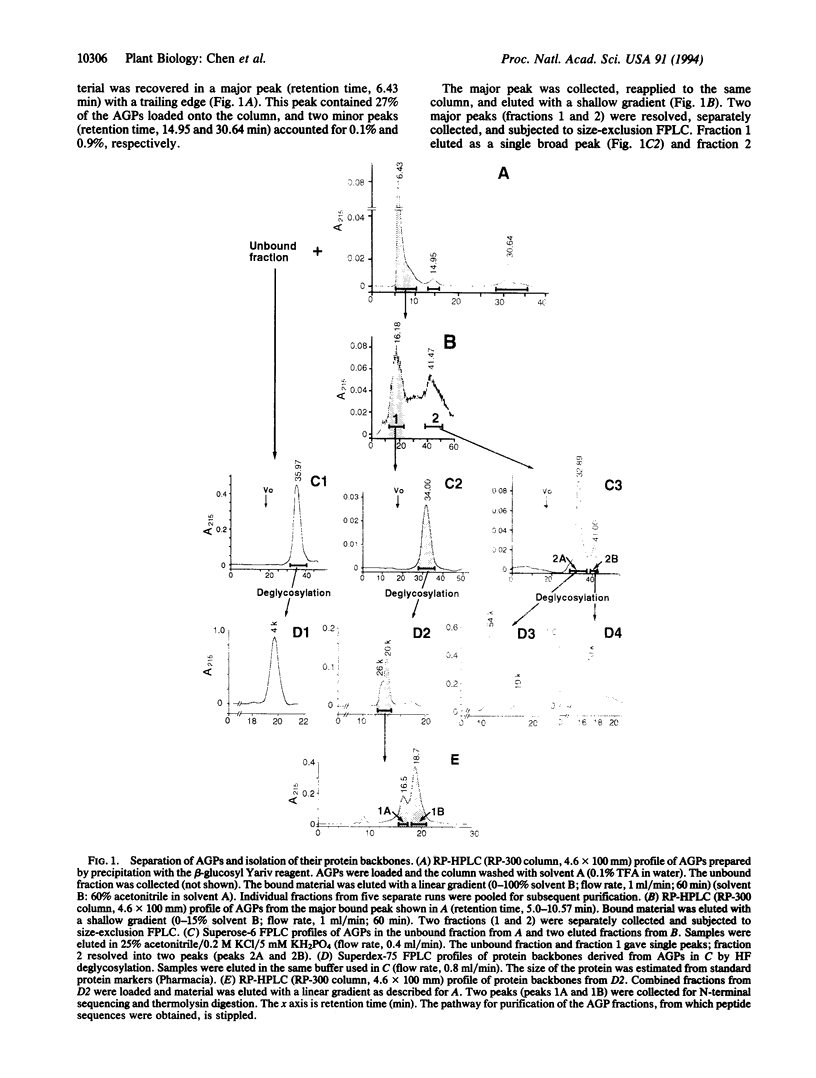
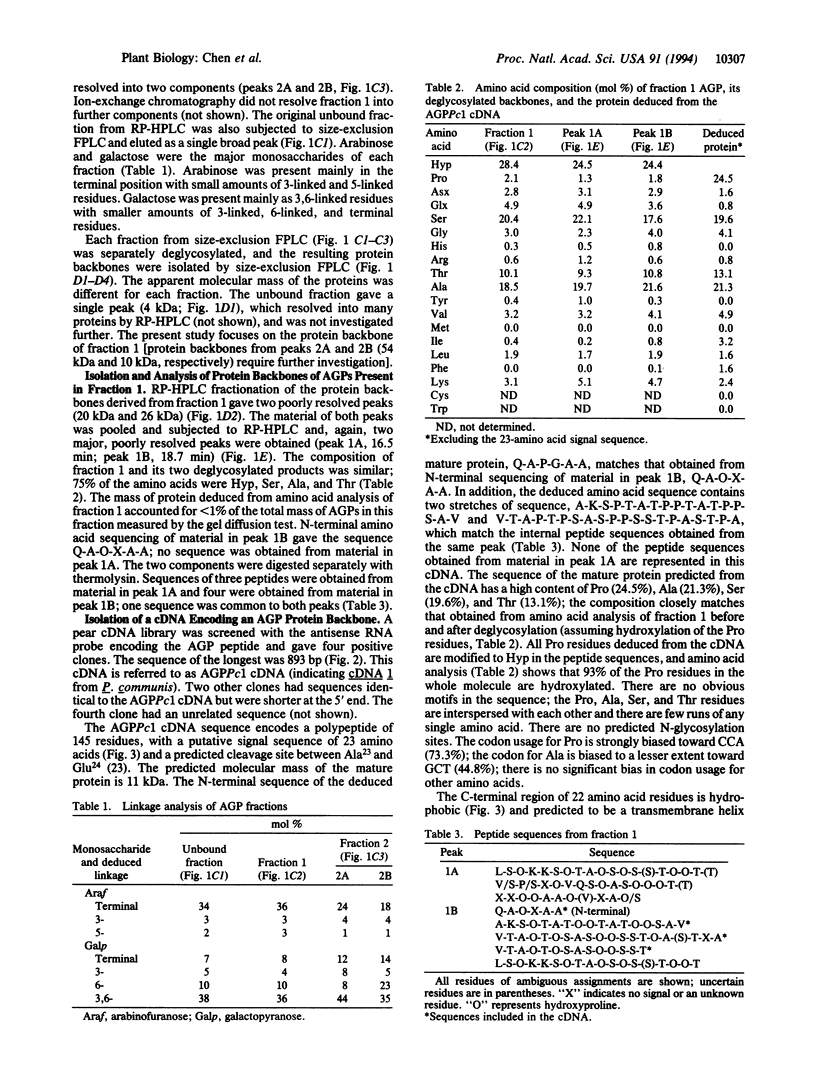
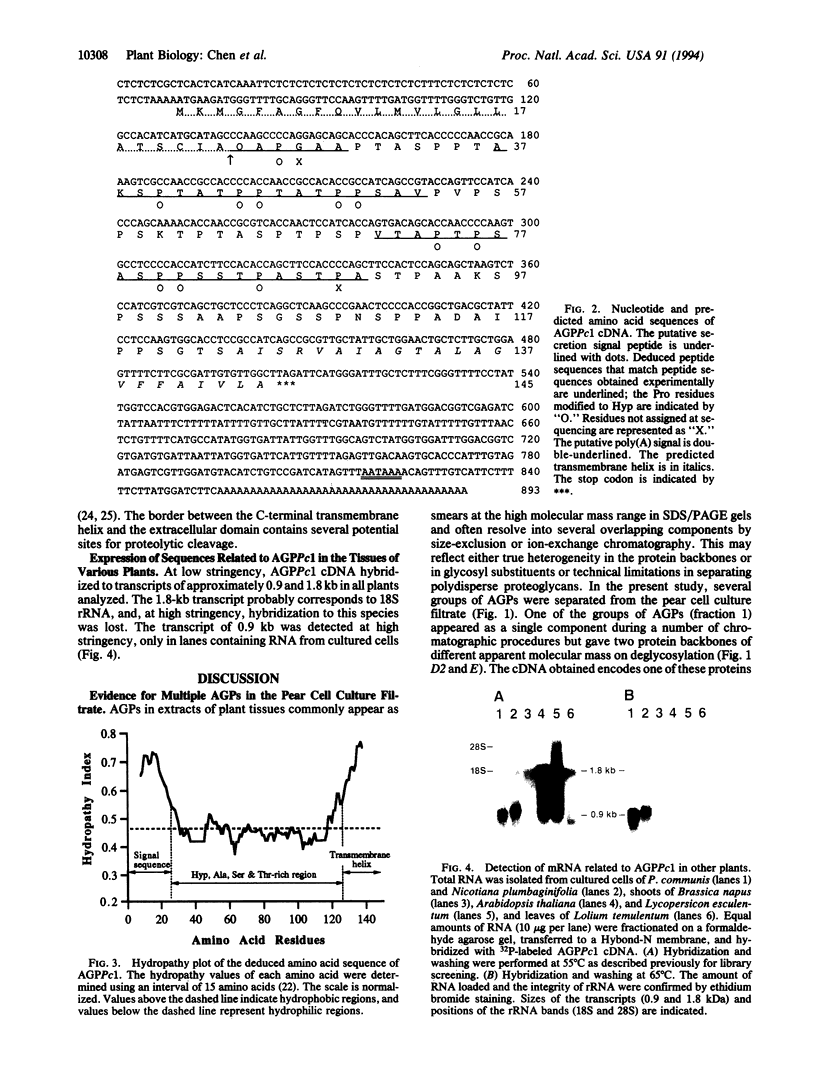
Abstract
Arabinogalactan-proteins (AGPs) are proteoglycans containing a high proportion of carbohydrate (typically > 90%) linked to a protein backbone rich in hydroxyproline (Hyp), Ala, Ser, and Thr. They are widely distributed in plants and may play a role in development. The structure of the carbohydrate of some AGPs is known in detail but information regarding the protein backbone is restricted to a few peptide sequences. Here we report isolation and partial amino acid sequencing of the protein backbone of an AGP. This AGP is a member of one of four major groups of AGPs isolated from the filtrate of pear cell suspension culture. A cDNA encoding this protein backbone (145 amino acids) was cloned; the deduced protein is rich in Hyp, Ala, Ser, and Thr, which together account for > 75% of total residues. It has three domains, an N-terminal secretion signal, a central hydrophilic domain containing all of the Pro residues, and a hydrophobic C-terminal domain that is predicted to be a transmembrane helix. Approximately 93% of the Pro residues are hydroxylated and hence are potential sites for glycosylation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin T. C., McCann M. C., Roberts K. A Novel Hydroxyproline-Deficient Arabinogalactan Protein Secreted by Suspension-Cultured Cells of Daucus carota (Purification and Partial Characterization). Plant Physiol. 1993 Sep;103(1):115–123. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker H. A. Biochemical functions of corrinoid compounds. The sixth Hopkins memorial lecture. Biochem J. 1967 Oct;105(1):1–15. doi: 10.1042/bj1050001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson P. A., McNamara M., Wettenhall R. E., Stone B. A., Fincher G. B. Characterization of the hydroxyproline-rich protein core of an arabinogalactan-protein secreted from suspension-cultured Lolium multiflorum (Italian ryegrass) endosperm cells. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 15;264(3):857–862. doi: 10.1042/bj2640857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grego B., Van Driel I. R., Stearne P. A., Goding J. W., Nice E. C., Simpson R. J. A microbore high-performance liquid chromatography strategy for the purification of polypeptides for gas-phase sequence analysis. Structural studies on the murine transferrin receptor. Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 2;148(3):485–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieliszewski M. J., Kamyab A., Leykam J. F., Lamport D. T. A Histidine-Rich Extensin from Zea mays Is an Arabinogalactan Protein. Plant Physiol. 1992 Jun;99(2):538–547. doi: 10.1104/pp.99.2.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieliszewski M. J., Lamport D. T. Extensin: repetitive motifs, functional sites, post-translational codes, and phylogeny. Plant J. 1994 Feb;5(2):157–172. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1994.05020157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P., Kanehisa M., DeLisi C. The detection and classification of membrane-spanning proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 28;815(3):468–476. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90375-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komalavilas P., Zhu J. K., Nothnagel E. A. Arabinogalactan-proteins from the suspension culture medium and plasma membrane of rose cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15956–15965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohana Rao J. K., Argos P. A conformational preference parameter to predict helices in integral membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 30;869(2):197–214. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90295-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mort A. J., Lamport D. T. Anhydrous hydrogen fluoride deglycosylates glycoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):289–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray E. E., Lotzer J., Eberle M. Codon usage in plant genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):477–498. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennell R. I., Janniche L., Kjellbom P., Scofield G. N., Peart J. M., Roberts K. Developmental Regulation of a Plasma Membrane Arabinogalactan Protein Epitope in Oilseed Rape Flowers. Plant Cell. 1991 Dec;3(12):1317–1326. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.12.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter A. M. Structure and function of plant cell wall proteins. Plant Cell. 1993 Jan;5(1):9–23. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. J., Moritz R. L., Nice E. C., Grego B., Yoshizaki F., Sugimura Y., Freeman H. C., Murata M. Complete amino acid sequence of plastocyanin from a green alga, Enteromorpha prolifera. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jun 16;157(3):497–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09694.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Holst G. J., Clarke A. E. Quantification of arabinogalactan-protein in plant extracts by single radial gel diffusion. Anal Biochem. 1985 Aug 1;148(2):446–450. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90251-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]