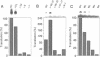Abstract
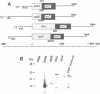
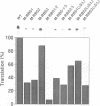
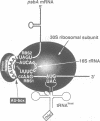
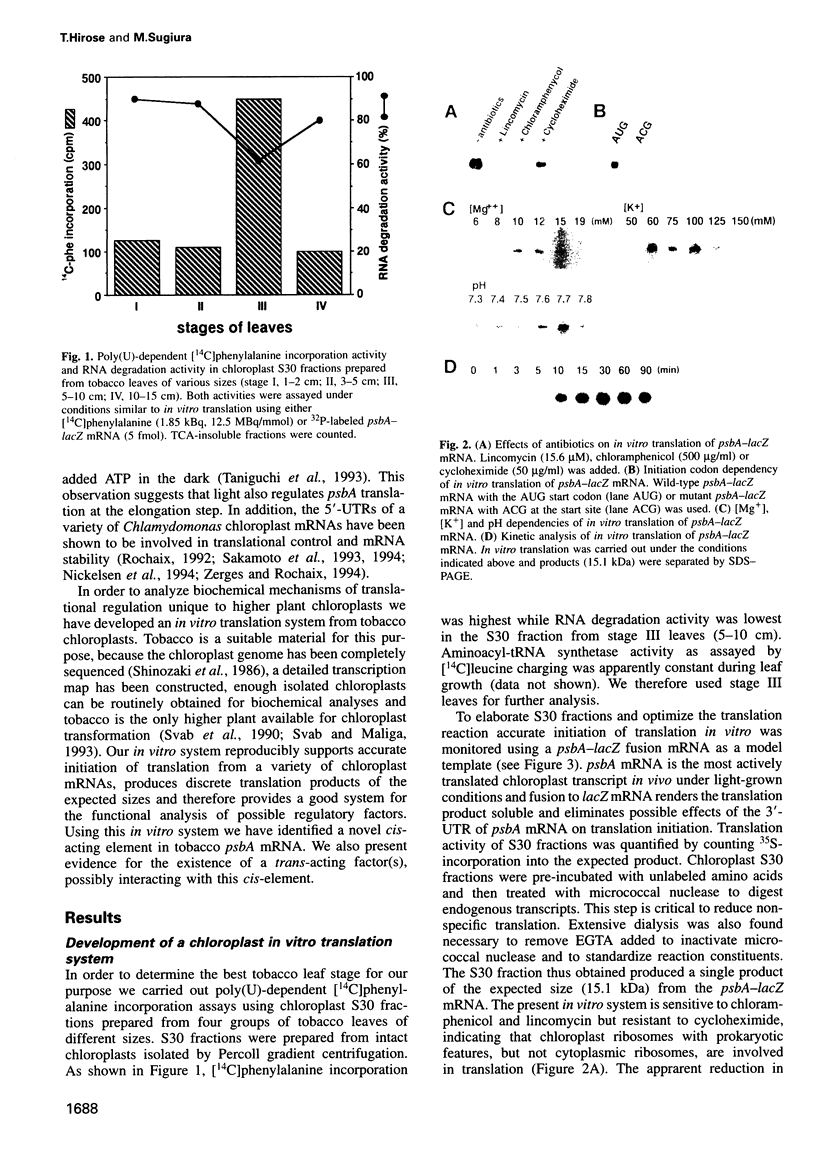
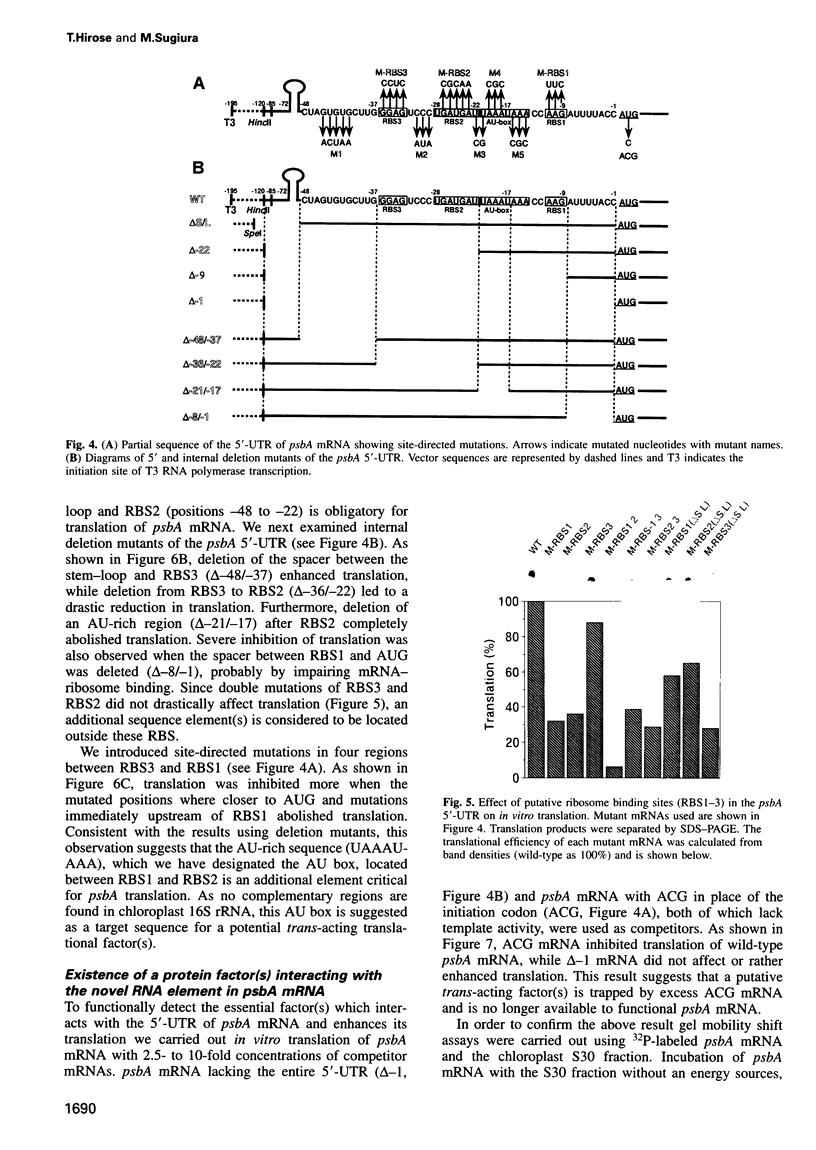
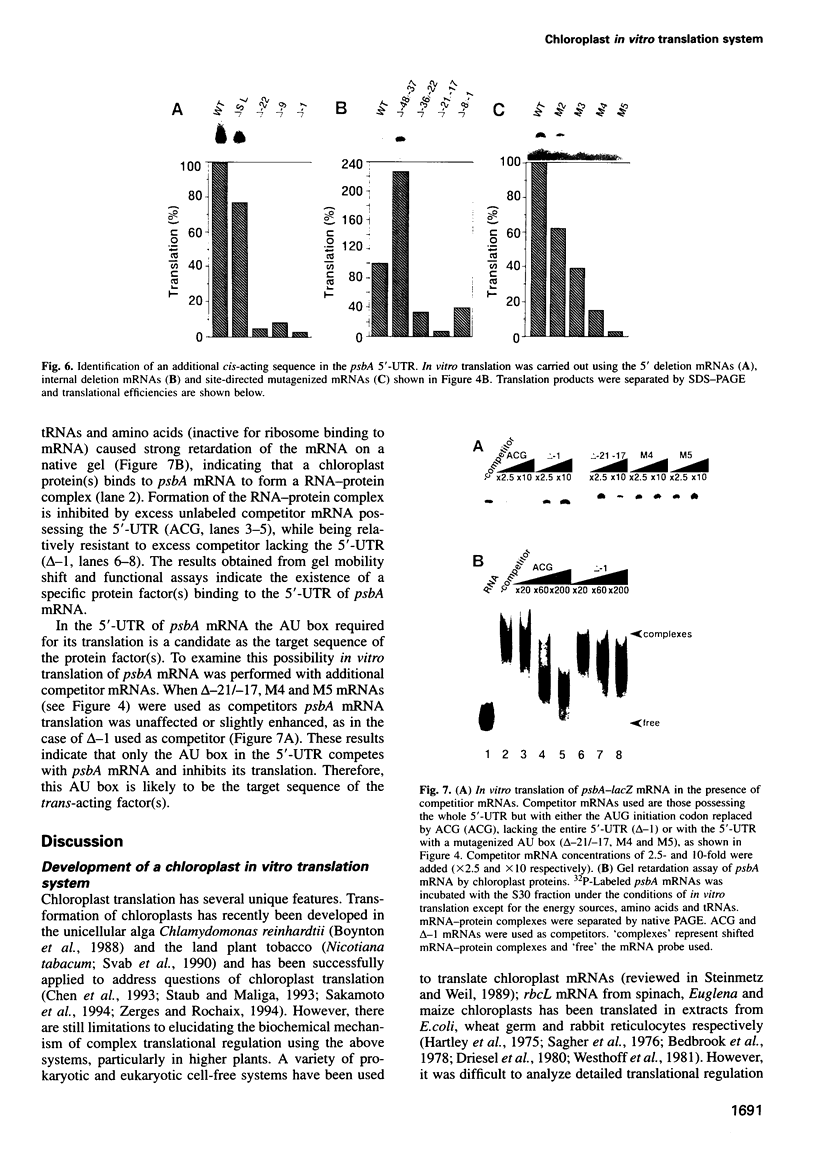
Translational regulation is an important step of gene expression in chloroplasts. To analyze biochemical mechanisms of translational regulation unique to higher plant chloroplasts, an in vitro translation system has been developed from tobacco chloroplasts. Conditions for chloroplast extraction and the in vitro translation reaction have been optimized with a tobacco psbA-lacZ fusion mRNA. The in vitro system supports accurate translation of a variety of chloroplasts mRNAs. Using a series of mutant psbA mRNAs, we showed that three elements within the 5'-untranslated region of the mRNA are required for translation. Two of them are complementary to the 3'-terminus of chloroplast 16S rRNA (termed RBS1 and RBS2) and the other is an AU-rich sequence (UAAAUAAA) located between RBS1 and RBS2 and is termed the AU box. mRNA competition experiments using the in vitro translation reaction and gel mobility shift assays revealed the existence of a trans-acting factor(s) for translation and its possible interaction with the AU box. We propose a model for the initiation of psbA translation whereby RBS1 and RBS2 bind cooperatively to the 3'-end of 16S rRNA resulting in looping out of the AU box, which facilitates the interaction of a trans-acting factor(s).
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bard J., Bourque D. P., Hildebrand M., Zaitlin D. In vitro expression of chloroplast genes in lysates of higher plant chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3983–3987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkan A. Proteins encoded by a complex chloroplast transcription unit are each translated from both monocistronic and polycistronic mRNAs. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2637–2644. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03116.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkan A., Walker M., Nolasco M., Johnson D. A nuclear mutation in maize blocks the processing and translation of several chloroplast mRNAs and provides evidence for the differential translation of alternative mRNA forms. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 1;13(13):3170–3181. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06616.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedbrook J. R., Link G., Coen D. M., Bogorad L. Maize plastid gene expressed during photoregulated development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3060–3064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonham-Smith P. C., Bourque D. P. Translation of chloroplast-encoded mRNA: potential initiation and termination signals. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):2057–2080. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boni I. V., Isaeva D. M., Musychenko M. L., Tzareva N. V. Ribosome-messenger recognition: mRNA target sites for ribosomal protein S1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):155–162. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W., Harris E. H., Hosler J. P., Johnson A. M., Jones A. R., Randolph-Anderson B. L., Robertson D., Klein T. M., Shark K. B. Chloroplast transformation in Chlamydomonas with high velocity microprojectiles. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1534–1538. doi: 10.1126/science.2897716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X., Kindle K., Stern D. Initiation codon mutations in the Chlamydomonas chloroplast petD gene result in temperature-sensitive photosynthetic growth. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3627–3635. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06036.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danon A., Mayfield S. P. ADP-dependent phosphorylation regulates RNA-binding in vitro: implications in light-modulated translation. EMBO J. 1994 May 1;13(9):2227–2235. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06500.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danon A., Mayfield S. P. Light regulated translational activators: identification of chloroplast gene specific mRNA binding proteins. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):3993–4001. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04974.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danon A., Mayfield S. P. Light-regulated translation of chloroplast messenger RNAs through redox potential. Science. 1994 Dec 9;266(5191):1717–1719. doi: 10.1126/science.7992056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Gruissem W. Constitutive transcription and regulation of gene expression in non-photosynthetic plastids of higher plants. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3301–3308. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03200.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driesel A. J., Speirs J., Bohnert H. J. Spinach chloroplast mRNA for a 32 000 dalton polypeptide: size and localization on the physical map of the chloroplast DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 11;610(2):297–310. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzetti B., Carol P., Mache R. Characterization and RNA-binding properties of a chloroplast S1-like ribosomal protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19075–19081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freyer R., Hoch B., Neckermann K., Maier R. M., Kössel H. RNA editing in maize chloroplasts is a processing step independent of splicing and cleavage to monocistronic mRNAs. Plant J. 1993 Oct;4(4):621–629. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1993.04040621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E., Hauser C. R. Translational regulation of gene expression in chloroplasts and mitochondria. Annu Rev Genet. 1994;28:71–93. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.28.120194.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. H., Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W. Chloroplast ribosomes and protein synthesis. Microbiol Rev. 1994 Dec;58(4):700–754. doi: 10.1128/mr.58.4.700-754.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley M. R., Wheeler A., Ellis R. J. Protein synthesis in chloroplasts. V. Translation of messenger RNA for the large subunit of fraction I protein in a heterologous cell-free system. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 5;91(1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90372-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose T., Wakasugi T., Sugiura M., Kössel H. RNA editing of tobacco petB mRNAs occurs both in chloroplasts and non-photosynthetic proplastids. Plant Mol Biol. 1994 Oct;26(1):509–513. doi: 10.1007/BF00039562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Mullet J. E. Ribosome-binding sites on chloroplast rbcL and psbA mRNAs and light-induced initiation of D1 translation. Plant Mol Biol. 1994 Jun;25(3):437–448. doi: 10.1007/BF00043872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo J. S., Spremulli L. L. Analysis of the translational initiation region on the Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (rbcL) messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7494–7500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo J. S., Spremulli L. L. Effect of the secondary structure in the Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase messenger RNA on translational initiation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7501–7508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayfield S. P., Cohen A., Danon A., Yohn C. B. Translation of the psbA mRNA of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii requires a structured RNA element contained within the 5' untranslated region. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(6 Pt 1):1537–1545. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.6.1537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. E., Brimacombe R. Prokaryotic translation: the interactive pathway leading to initiation. Trends Genet. 1994 Nov;10(11):402–407. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickelsen J., van Dillewijn J., Rahire M., Rochaix J. D. Determinants for stability of the chloroplast psbD RNA are located within its short leader region in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 1;13(13):3182–3191. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06617.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinbothe S., Reinbothe C., Heintzen C., Seidenbecher C., Parthier B. A methyl jasmonate-induced shift in the length of the 5' untranslated region impairs translation of the plastid rbcL transcript in barley. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1505–1512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05794.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochaix J. D. Post-transcriptional steps in the expression of chloroplast genes. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:1–28. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruf S., Zeltz P., Kössel H. Complete RNA editing of unspliced and dicistronic transcripts of the intron-containing reading frame IRF170 from maize chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2295–2299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagher D., Grosfeld H., Edelman M. Large subunit ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase messenger RNA from Euglena chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):722–726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto W., Chen X., Kindle K. L., Stern D. B. Function of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii petd 5' untranslated region in regulating the accumulation of subunit IV of the cytochrome b6/f complex. Plant J. 1994 Oct;6(4):503–512. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1994.6040503.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto W., Kindle K. L., Stern D. B. In vivo analysis of Chlamydomonas chloroplast petD gene expression using stable transformation of beta-glucuronidase translational fusions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):497–501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Ohme M., Tanaka M., Wakasugi T., Hayashida N., Matsubayashi T., Zaita N., Chunwongse J., Obokata J., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: its gene organization and expression. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2043–2049. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staub J. M., Maliga P. Accumulation of D1 polypeptide in tobacco plastids is regulated via the untranslated region of the psbA mRNA. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):601–606. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05692.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staub J. M., Maliga P. Translation of psbA mRNA is regulated by light via the 5'-untranslated region in tobacco plastids. Plant J. 1994 Oct;6(4):547–553. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1994.6040547.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian A. R. Molecular genetics of chloroplast ribosomal proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 May;18(5):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura M. The chloroplast genome. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 May;19(1):149–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00015612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svab Z., Hajdukiewicz P., Maliga P. Stable transformation of plastids in higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8526–8530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svab Z., Maliga P. High-frequency plastid transformation in tobacco by selection for a chimeric aadA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):913–917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi M., Kuroda H., Satoh K. ATP-dependent protein synthesis in isolated pea chloroplasts. Evidence for accumulation of a translation intermediate of the D1 protein. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 8;317(1-2):57–61. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81491-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanaraj T. A., Pandit M. W. An additional ribosome-binding site on mRNA of highly expressed genes and a bifunctional site on the colicin fragment of 16S rRNA from Escherichia coli: important determinants of the efficiency of translation-initiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):2973–2985. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.2973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tohdoh N., Sugiura M. The complete nucleotide sequence of 16S ribosomal RNA gene from tobacco chloroplasts. Gene. 1982 Feb;17(2):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. C., Roney W. B., Alston R. L., Spremulli L. L. Initiation complex formation on Euglena chloroplast 30S subunits in the presence of natural mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9735–9747. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerges W., Rochaix J. D. The 5' leader of a chloroplast mRNA mediates the translational requirements for two nucleus-encoded functions in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;14(8):5268–5277. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.8.5268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Deutscher M. P. A uridine-rich sequence required for translation of prokaryotic mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2605–2609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]