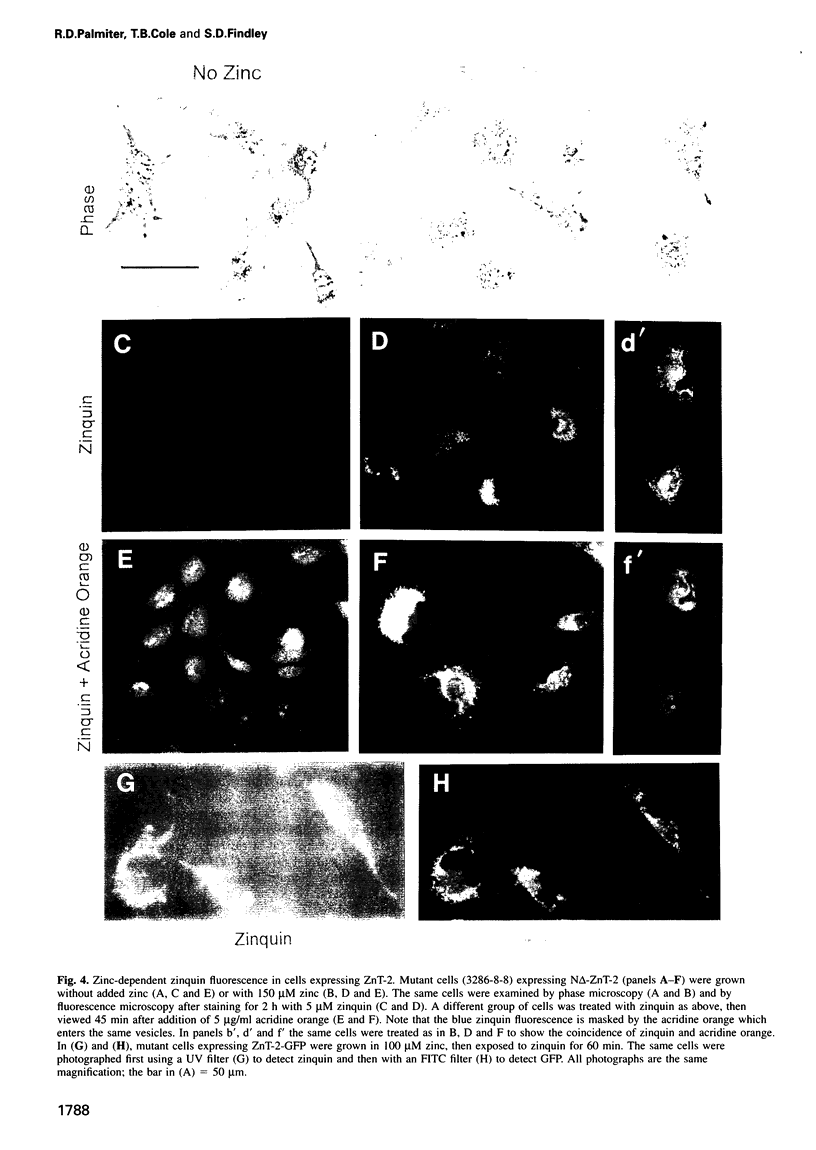
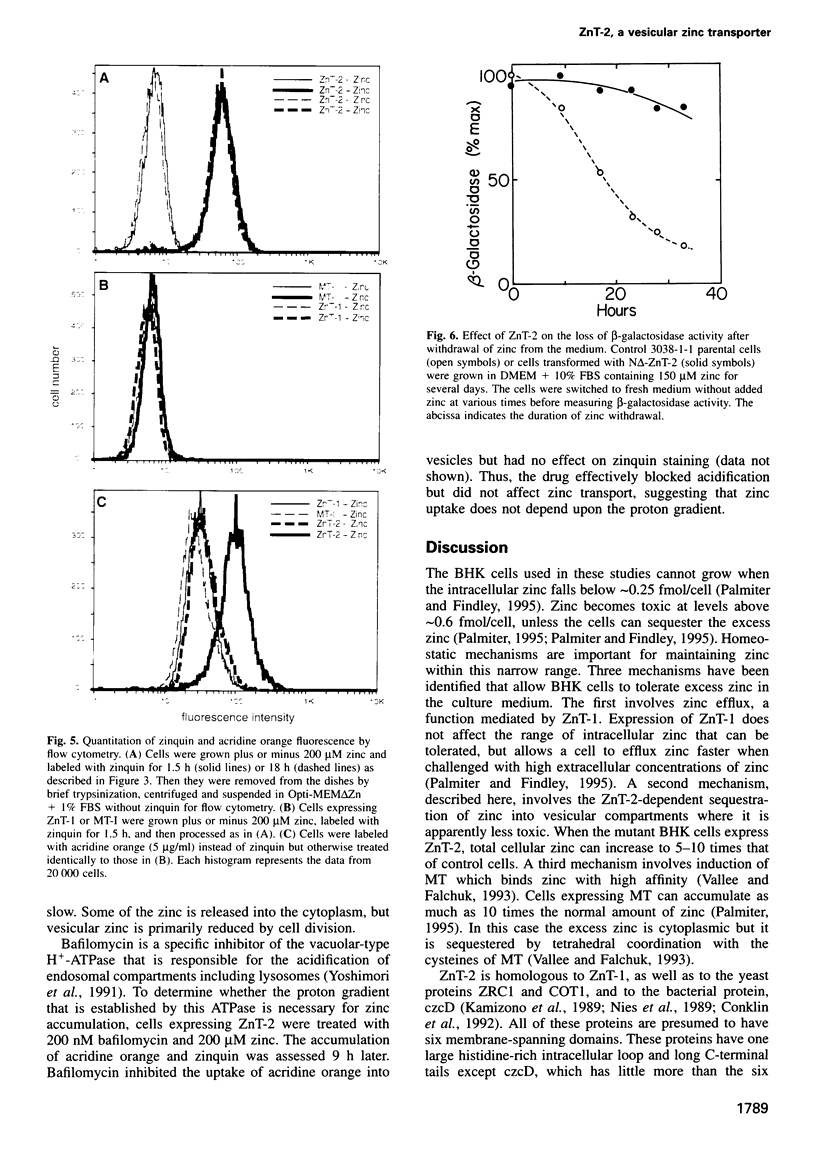
Abstract
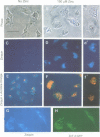
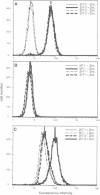
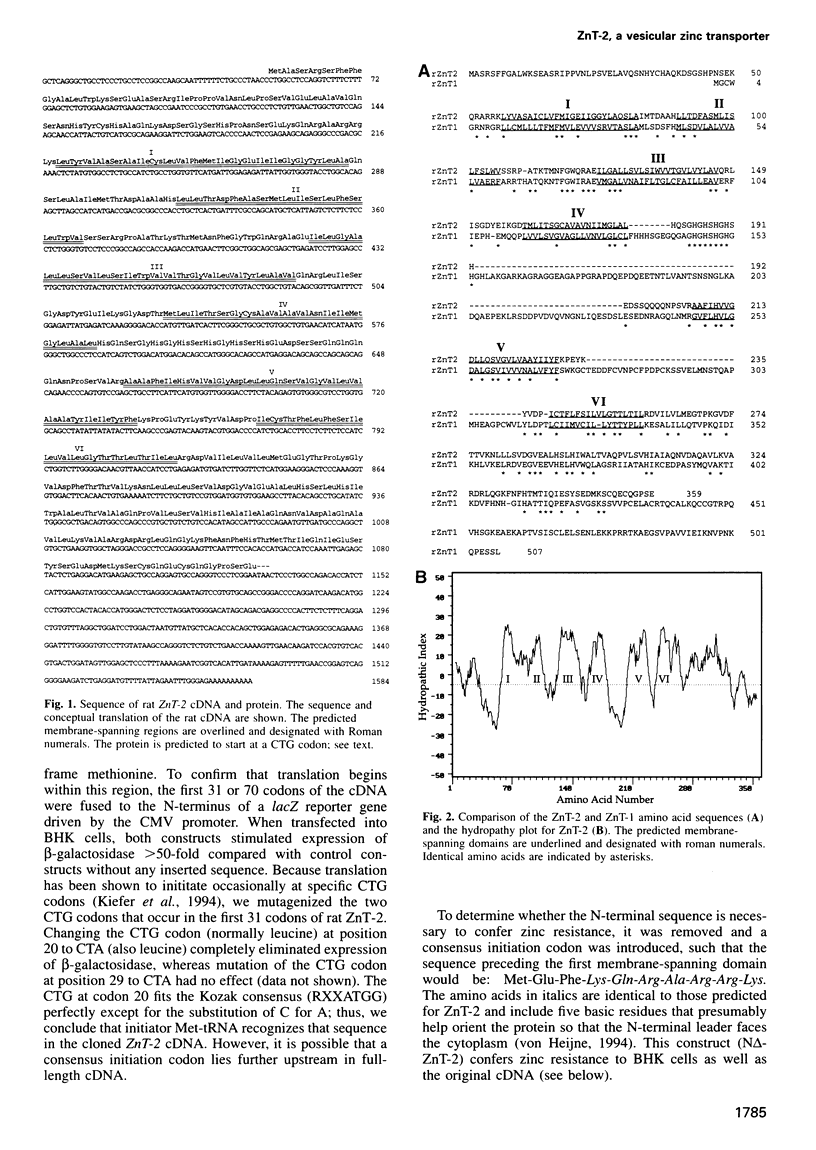
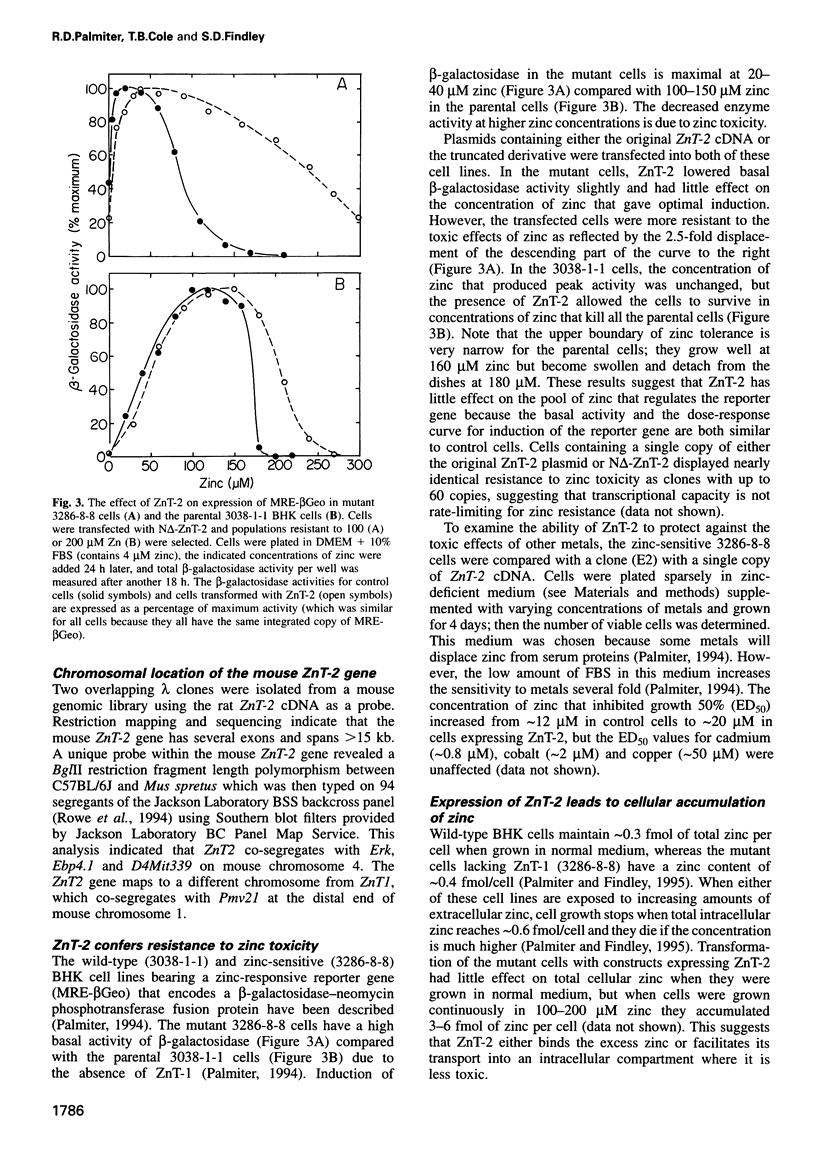
A cDNA encoding a second zinc transporter (ZnT-2) was isolated from a rat kidney cDNA expression library by complementation of a zinc-sensitive BHK cell line. The protein predicted from the open reading frame of ZnT-2 cDNA has 359 amino acids and initiates with a CTG codon. It resembles ZnT-1 (a plasma membrane protein that stimulates zinc efflux) in overall topology in that it has six membrane-spanning domains, a histidine-rich intracellular loop and a long C-terminal tail; however, the overall amino acid identity is only 26%. Unlike ZnT-1, which is in the plasma membrane and lowers cellular zinc by stimulating zinc efflux, ZnT-2 is localized on vesicles and allows the zinc-sensitive BHK cells to accumulate zinc to levels that are much higher than non-transformed cells can tolerate. Zinc was visualized within these vesicles with zinquin, a zinc-specific fluorescent probe. The intracellular compartment that accumulates zinc is acidic as revealed by staining with acridine orange or LysoTracker. Prolonged exposure of cells expressing ZnT-2 to zinc causes an accretion of intracellular vesicles. We suggest that ZnT-2 protects these cells from zinc toxicity by facilitating zinc transport into an endosomal/lysosomal compartment.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conklin D. S., Culbertson M. R., Kung C. Interactions between gene products involved in divalent cation transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1994 Aug 2;244(3):303–311. doi: 10.1007/BF00285458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin D. S., McMaster J. A., Culbertson M. R., Kung C. COT1, a gene involved in cobalt accumulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3678–3688. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danscher G. Histochemical demonstration of heavy metals. A revised version of the sulphide silver method suitable for both light and electronmicroscopy. Histochemistry. 1981;71(1):1–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00592566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederickson C. J., Moncrieff D. W. Zinc-containing neurons. Biol Signals. 1994 May-Jun;3(3):127–139. doi: 10.1159/000109536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heim R., Cubitt A. B., Tsien R. Y. Improved green fluorescence. Nature. 1995 Feb 23;373(6516):663–664. doi: 10.1038/373663b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamizono A., Nishizawa M., Teranishi Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Identification of a gene conferring resistance to zinc and cadmium ions in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Oct;219(1-2):161–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00261172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer P., Acland P., Pappin D., Peters G., Dickson C. Competition between nuclear localization and secretory signals determines the subcellular fate of a single CUG-initiated form of FGF3. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 1;13(17):4126–4136. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nies D. H. CzcR and CzcD, gene products affecting regulation of resistance to cobalt, zinc, and cadmium (czc system) in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(24):8102–8110. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.24.8102-8110.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nies D. H., Nies A., Chu L., Silver S. Expression and nucleotide sequence of a plasmid-determined divalent cation efflux system from Alcaligenes eutrophus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7351–7355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Constitutive expression of metallothionein-III (MT-III), but not MT-I, inhibits growth when cells become zinc deficient. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1995 Nov;135(1):139–146. doi: 10.1006/taap.1995.1216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Findley S. D. Cloning and functional characterization of a mammalian zinc transporter that confers resistance to zinc. EMBO J. 1995 Feb 15;14(4):639–649. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07042.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Regulation of metallothionein genes by heavy metals appears to be mediated by a zinc-sensitive inhibitor that interacts with a constitutively active transcription factor, MTF-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1219–1223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe L. B., Nadeau J. H., Turner R., Frankel W. N., Letts V. A., Eppig J. T., Ko M. S., Thurston S. J., Birkenmeier E. H. Maps from two interspecific backcross DNA panels available as a community genetic mapping resource. Mamm Genome. 1994 May;5(5):253–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00389540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimori T., Yamamoto A., Moriyama Y., Futai M., Tashiro Y. Bafilomycin A1, a specific inhibitor of vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPase, inhibits acidification and protein degradation in lysosomes of cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17707–17712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalewski P. D., Forbes I. J., Betts W. H. Correlation of apoptosis with change in intracellular labile Zn(II) using zinquin [(2-methyl-8-p-toluenesulphonamido-6-quinolyloxy)acetic acid], a new specific fluorescent probe for Zn(II). Biochem J. 1993 Dec 1;296(Pt 2):403–408. doi: 10.1042/bj2960403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalewski P. D., Millard S. H., Forbes I. J., Kapaniris O., Slavotinek A., Betts W. H., Ward A. D., Lincoln S. F., Mahadevan I. Video image analysis of labile zinc in viable pancreatic islet cells using a specific fluorescent probe for zinc. J Histochem Cytochem. 1994 Jul;42(7):877–884. doi: 10.1177/42.7.8014471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Membrane proteins: from sequence to structure. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1994;23:167–192. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.23.060194.001123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]