Abstract
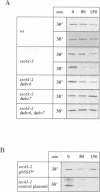
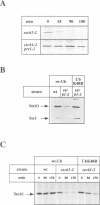
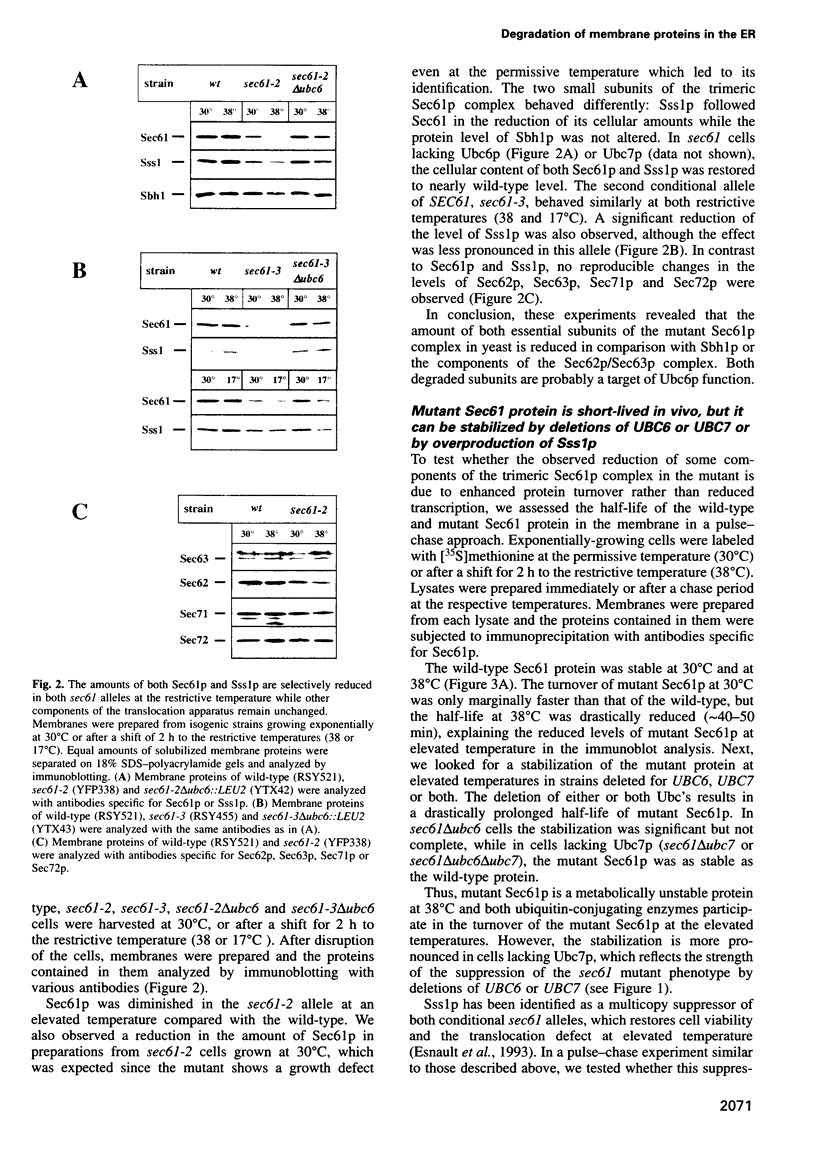
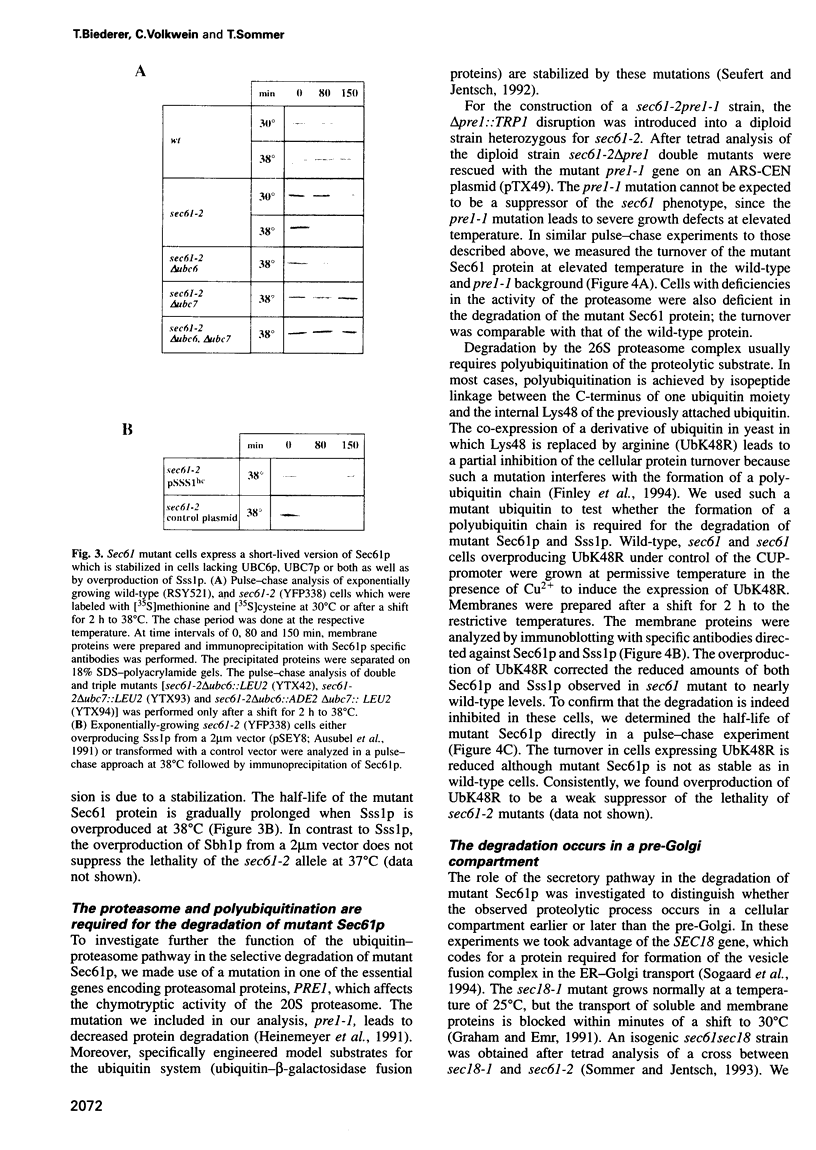
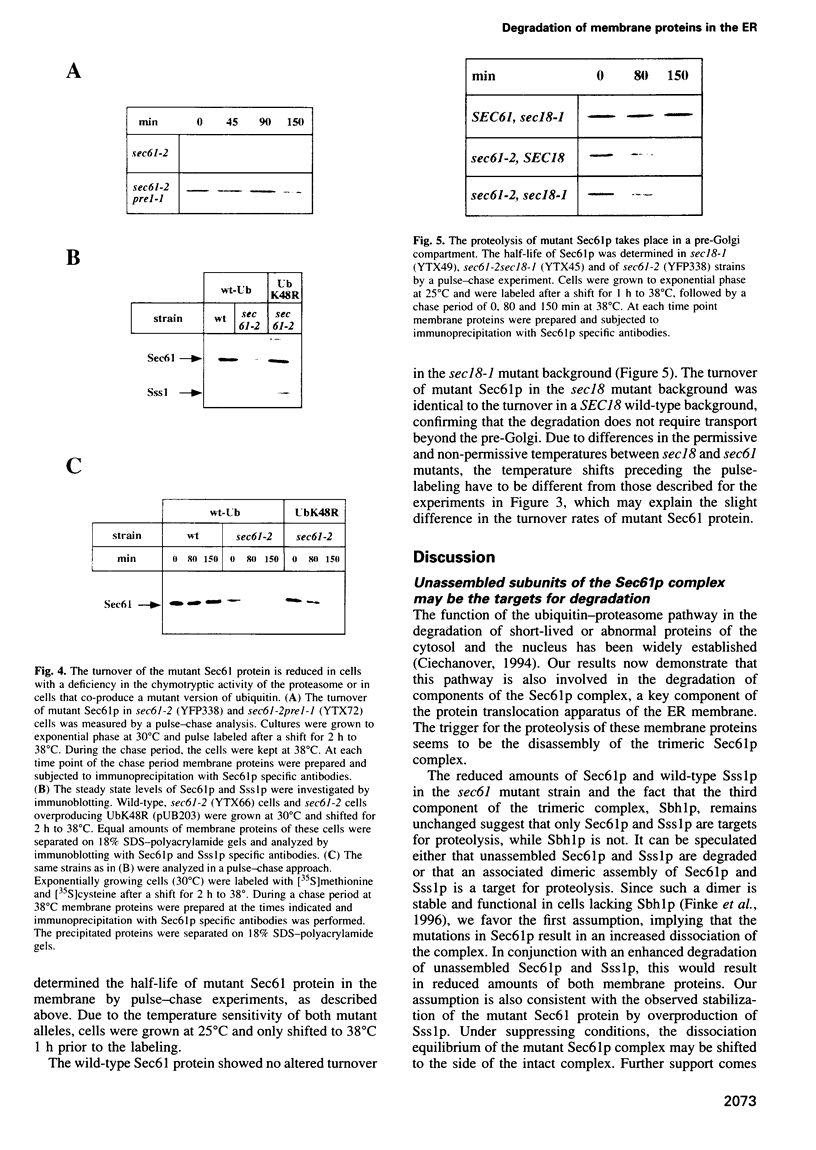
We have investigated the degradation of subunits of the trimeric Sec61p complex, a key component of the protein translocation apparatus of the ER membrane. A mutant form of Sec6lp and one of the two associated proteins (Sss1p) are selectively degraded, while the third constituent of the complex (Sbh1p) is stable. Our results demonstrate that the proteolysis of the multispanning membrane protein Sec61p is mediated by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, since it requires polyubiquitination, the presence of a membrane-bound (Ubc6) and a soluble (Ubc7) ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme and a functional proteasome. The process is proposed to be specific for unassembled Sec61p and Sss1p. Thus, our results suggest that one pathway of ER degradation of abnormal or unassembled membrane proteins is initiated at the cytoplasmic side of the ER.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonifacino J. S., Lippincott-Schwartz J. Degradation of proteins within the endoplasmic reticulum. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;3(4):592–600. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90028-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P., Johnson P., Sommer T., Jentsch S., Hochstrasser M. Multiple ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes participate in the in vivo degradation of the yeast MAT alpha 2 repressor. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90426-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90396-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Schekman R. A yeast mutant defective at an early stage in import of secretory protein precursors into the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):633–645. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deveraux Q., Ustrell V., Pickart C., Rechsteiner M. A 26 S protease subunit that binds ubiquitin conjugates. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7059–7061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esnault Y., Blondel M. O., Deshaies R. J., Scheckman R., Képès F. The yeast SSS1 gene is essential for secretory protein translocation and encodes a conserved protein of the endoplasmic reticulum. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4083–4093. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06092.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esnault Y., Feldheim D., Blondel M. O., Schekman R., Képès F. SSS1 encodes a stabilizing component of the Sec61 subcomplex of the yeast protein translocation apparatus. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 4;269(44):27478–27485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finke K., Plath K., Panzner S., Prehn S., Rapoport T. A., Hartmann E., Sommer T. A second trimeric complex containing homologs of the Sec61p complex functions in protein transport across the ER membrane of S. cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1996 Apr 1;15(7):1482–1494. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Sadis S., Monia B. P., Boucher P., Ecker D. J., Crooke S. T., Chau V. Inhibition of proteolysis and cell cycle progression in a multiubiquitination-deficient yeast mutant. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;14(8):5501–5509. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.8.5501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner A. M., Aviel S., Argon Y. Rapid degradation of an unassembled immunoglobulin light chain is mediated by a serine protease and occurs in a pre-Golgi compartment. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25940–25947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham T. R., Emr S. D. Compartmental organization of Golgi-specific protein modification and vacuolar protein sorting events defined in a yeast sec18 (NSF) mutant. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):207–218. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Prehn S., Hartmann E., Kalies K. U., Rapoport T. A. A mammalian homolog of SEC61p and SECYp is associated with ribosomes and nascent polypeptides during translocation. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):489–503. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90517-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Rapoport T. A. Protein translocation into proteoliposomes reconstituted from purified components of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):615–630. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann E., Sommer T., Prehn S., Görlich D., Jentsch S., Rapoport T. A. Evolutionary conservation of components of the protein translocation complex. Nature. 1994 Feb 17;367(6464):654–657. doi: 10.1038/367654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemeyer W., Kleinschmidt J. A., Saidowsky J., Escher C., Wolf D. H. Proteinase yscE, the yeast proteasome/multicatalytic-multifunctional proteinase: mutants unravel its function in stress induced proteolysis and uncover its necessity for cell survival. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):555–562. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen T. J., Loo M. A., Pind S., Williams D. B., Goldberg A. L., Riordan J. R. Multiple proteolytic systems, including the proteasome, contribute to CFTR processing. Cell. 1995 Oct 6;83(1):129–135. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90241-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungmann J., Reins H. A., Schobert C., Jentsch S. Resistance to cadmium mediated by ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):369–371. doi: 10.1038/361369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihara A., Akiyama Y., Ito K. FtsH is required for proteolytic elimination of uncomplexed forms of SecY, an essential protein translocase subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 9;92(10):4532–4536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.10.4532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Sitia R. Protein degradation in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):611–614. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90104-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp J., Dobberstein B. The membrane-spanning segment of invariant chain (I gamma) contains a potentially cleavable signal sequence. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1103–1112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90710-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löwe J., Stock D., Jap B., Zwickl P., Baumeister W., Huber R. Crystal structure of the 20S proteasome from the archaeon T. acidophilum at 3.4 A resolution. Science. 1995 Apr 28;268(5210):533–539. doi: 10.1126/science.7725097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins C., Lu Y., Campbell A., Fang H., Green N. A mutation affecting signal peptidase inhibits degradation of an abnormal membrane protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 21;270(29):17139–17147. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.29.17139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panzner S., Dreier L., Hartmann E., Kostka S., Rapoport T. A. Posttranslational protein transport in yeast reconstituted with a purified complex of Sec proteins and Kar2p. Cell. 1995 May 19;81(4):561–570. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90077-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. M. Proteasomes: protein degradation machines of the cell. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Sep;19(9):377–382. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Misra L. M., Vogel J. P. KAR2, a karyogamy gene, is the yeast homolog of the mammalian BiP/GRP78 gene. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1211–1221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid S. R., Spiess M. Deletion of the amino-terminal domain of asialoglycoprotein receptor H1 allows cleavage of the internal signal sequence. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16886–16891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seufert W., Jentsch S. In vivo function of the proteasome in the ubiquitin pathway. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3077–3080. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05379.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer T., Jentsch S. A protein translocation defect linked to ubiquitin conjugation at the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):176–179. doi: 10.1038/365176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirling C. J., Rothblatt J., Hosobuchi M., Deshaies R., Schekman R. Protein translocation mutants defective in the insertion of integral membrane proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Feb;3(2):129–142. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.2.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Søgaard M., Tani K., Ye R. R., Geromanos S., Tempst P., Kirchhausen T., Rothman J. E., Söllner T. A rab protein is required for the assembly of SNARE complexes in the docking of transport vesicles. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):937–948. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90270-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taura T., Baba T., Akiyama Y., Ito K. Determinants of the quantity of the stable SecY complex in the Escherichia coli cell. J Bacteriol. 1993 Dec;175(24):7771–7775. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.24.7771-7775.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward C. L., Omura S., Kopito R. R. Degradation of CFTR by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Cell. 1995 Oct 6;83(1):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuk M. H., Lodish H. F. Two pathways for the degradation of the H2 subunit of the asialoglycoprotein receptor in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(6 Pt 2):1735–1749. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.6.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]