Abstract
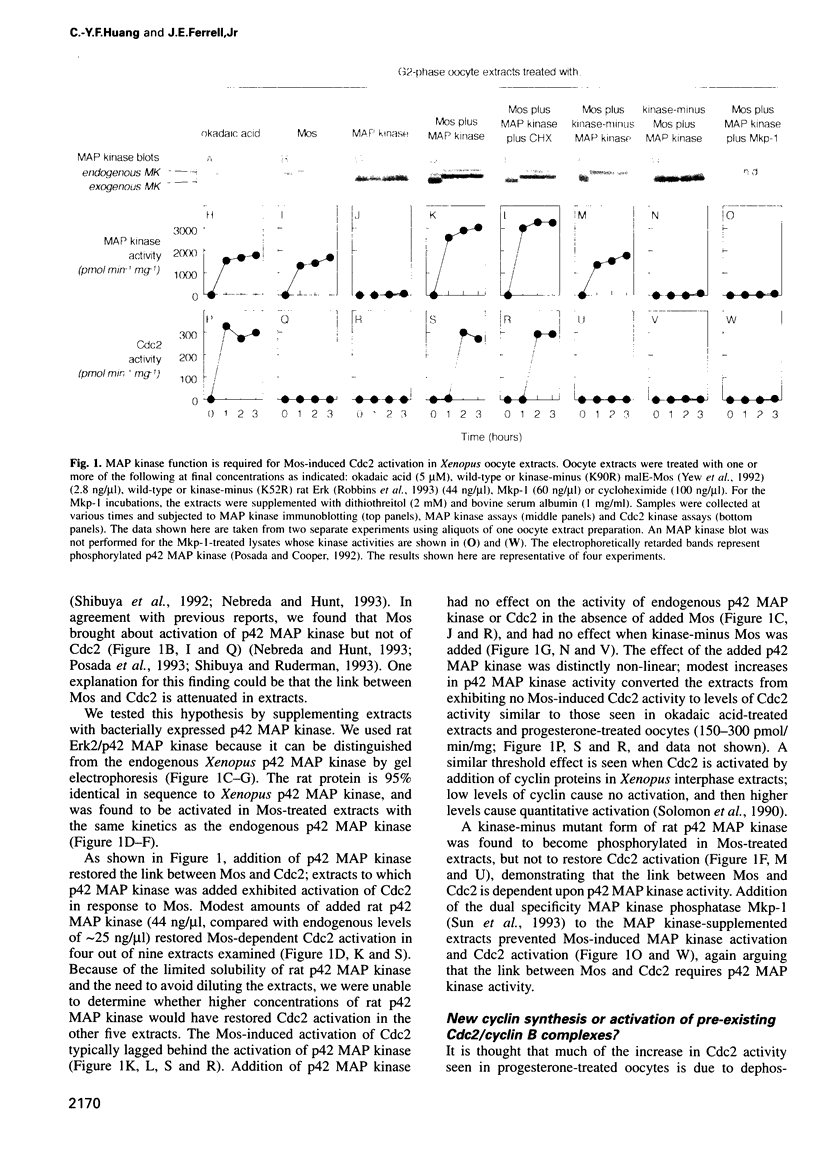
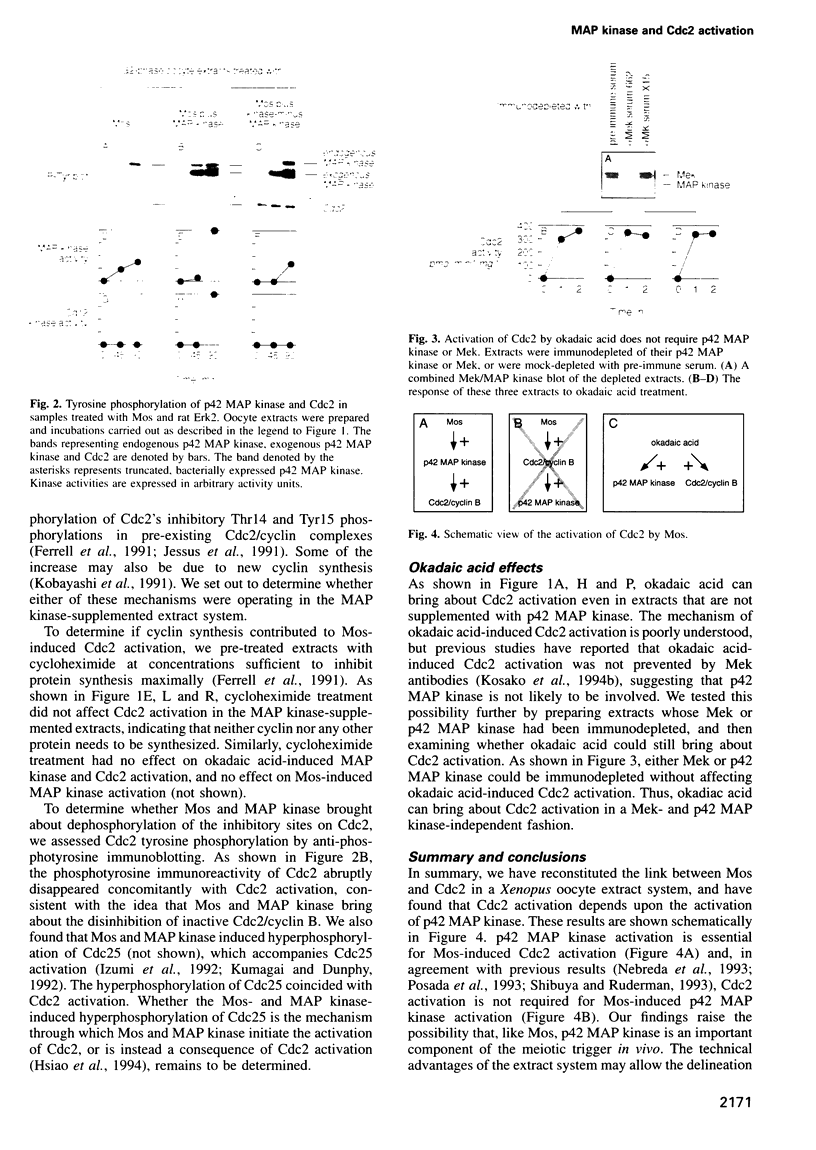
The progression of G2-arrested Xenopus laevis oocytes into meiotic M-phase is accompanied by the nearly simultaneous activation of p42 MAP kinase and Cdc2/cyclin B. This timing raises the possibility that the activation of one kinase might depend upon the other. Here we have examined whether Cdc2 activation requires p42 MAP kinase function. We have reconstituted Mos-induced Cdc2 activation in cell-free Xenopus oocyte extracts, and have found that Mos-induced Cdc2 activation requires active p42 MAP kinase, is inhibited by a MAP kinase phosphatase and is independent of protein synthesis. These findings indicate that p42 MAP kinase is an essential component of the M phase trigger in this system.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fabian J. R., Morrison D. K., Daar I. O. Requirement for Raf and MAP kinase function during the meiotic maturation of Xenopus oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(3):645–652. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.3.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Wu M., Gerhart J. C., Martin G. S. Cell cycle tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc2 and a microtubule-associated protein kinase homolog in Xenopus oocytes and eggs. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1965–1971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Moriyama K., Matsuda S., Okumura E., Kishimoto T., Kawasaki H., Suzuki K., Yahara I., Sakai H., Nishida E. Xenopus M phase MAP kinase: isolation of its cDNA and activation by MPF. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2661–2668. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haccard O., Lewellyn A., Hartley R. S., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Induction of Xenopus oocyte meiotic maturation by MAP kinase. Dev Biol. 1995 Apr;168(2):677–682. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.1112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao K. M., Chou S. Y., Shih S. J., Ferrell J. E., Jr Evidence that inactive p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase and inactive Rsk exist as a heterodimer in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5480–5484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumi T., Walker D. H., Maller J. L. Periodic changes in phosphorylation of the Xenopus cdc25 phosphatase regulate its activity. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Aug;3(8):927–939. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.8.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessus C., Rime H., Haccard O., Van Lint J., Goris J., Merlevede W., Ozon R. Tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc2 and p42 during meiotic maturation of Xenopus oocyte. Antagonistic action of okadaic acid and 6-DMAP. Development. 1991 Mar;111(3):813–820. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.3.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Minshull J., Ford C., Golsteyn R., Poon R., Hunt T. On the synthesis and destruction of A- and B-type cyclins during oogenesis and meiotic maturation in Xenopus laevis. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):755–765. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosako H., Gotoh Y., Nishida E. Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase is required for the mos-induced metaphase arrest. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 11;269(45):28354–28358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosako H., Gotoh Y., Nishida E. Requirement for the MAP kinase kinase/MAP kinase cascade in Xenopus oocyte maturation. EMBO J. 1994 May 1;13(9):2131–2138. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai A., Dunphy W. G. Regulation of the cdc25 protein during the cell cycle in Xenopus extracts. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):139–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90540-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muslin A. J., MacNicol A. M., Williams L. T. Raf-1 protein kinase is important for progesterone-induced Xenopus oocyte maturation and acts downstream of mos. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4197–4202. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebreda A. R., Hill C., Gomez N., Cohen P., Hunt T. The protein kinase mos activates MAP kinase kinase in vitro and stimulates the MAP kinase pathway in mammalian somatic cells in vivo. FEBS Lett. 1993 Oct 25;333(1-2):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80401-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebreda A. R., Hunt T. The c-mos proto-oncogene protein kinase turns on and maintains the activity of MAP kinase, but not MPF, in cell-free extracts of Xenopus oocytes and eggs. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1979–1986. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05847.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki K., Sagata N. MAP kinase activation is essential for oncogenic transformation of NIH3T3 cells by Mos. Oncogene. 1995 Mar 16;10(6):1149–1157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pham C. D., Arlinghaus R. B., Zheng C. F., Guan K. L., Singh B. Characterization of MEK1 phosphorylation by the v-Mos protein. Oncogene. 1995 Apr 20;10(8):1683–1688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posada J., Cooper J. A. Requirements for phosphorylation of MAP kinase during meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):212–215. doi: 10.1126/science.1313186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posada J., Yew N., Ahn N. G., Vande Woude G. F., Cooper J. A. Mos stimulates MAP kinase in Xenopus oocytes and activates a MAP kinase kinase in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2546–2553. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resing K. A., Mansour S. J., Hermann A. S., Johnson R. S., Candia J. M., Fukasawa K., Vande Woude G. F., Ahn N. G. Determination of v-Mos-catalyzed phosphorylation sites and autophosphorylation sites on MAP kinase kinase by ESI/MS. Biochemistry. 1995 Feb 28;34(8):2610–2620. doi: 10.1021/bi00008a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins D. J., Zhen E., Owaki H., Vanderbilt C. A., Ebert D., Geppert T. D., Cobb M. H. Regulation and properties of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1 and 2 in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):5097–5106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Daar I., Oskarsson M., Showalter S. D., Vande Woude G. F. The product of the mos proto-oncogene as a candidate "initiator" for oocyte maturation. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):643–646. doi: 10.1126/science.2474853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Oskarsson M., Copeland T., Brumbaugh J., Vande Woude G. F. Function of c-mos proto-oncogene product in meiotic maturation in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):519–525. doi: 10.1038/335519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets M. D., Fox C. A., Hunt T., Vande Woude G., Wickens M. The 3'-untranslated regions of c-mos and cyclin mRNAs stimulate translation by regulating cytoplasmic polyadenylation. Genes Dev. 1994 Apr 15;8(8):926–938. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.8.926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets M. D., Wu M., Wickens M. Polyadenylation of c-mos mRNA as a control point in Xenopus meiotic maturation. Nature. 1995 Apr 6;374(6522):511–516. doi: 10.1038/374511a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya E. K., Polverino A. J., Chang E., Wigler M., Ruderman J. V. Oncogenic ras triggers the activation of 42-kDa mitogen-activated protein kinase in extracts of quiescent Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9831–9835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya E. K., Ruderman J. V. Mos induces the in vitro activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in lysates of frog oocytes and mammalian somatic cells. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Aug;4(8):781–790. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.8.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Glotzer M., Lee T. H., Philippe M., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin activation of p34cdc2. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1013–1024. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun H., Charles C. H., Lau L. F., Tonks N. K. MKP-1 (3CH134), an immediate early gene product, is a dual specificity phosphatase that dephosphorylates MAP kinase in vivo. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):487–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe N., Vande Woude G. F., Ikawa Y., Sagata N. Specific proteolysis of the c-mos proto-oncogene product by calpain on fertilization of Xenopus eggs. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):505–511. doi: 10.1038/342505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yew N., Mellini M. L., Vande Woude G. F. Meiotic initiation by the mos protein in Xenopus. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):649–652. doi: 10.1038/355649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]