Abstract
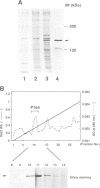
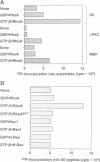
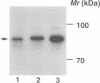
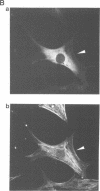
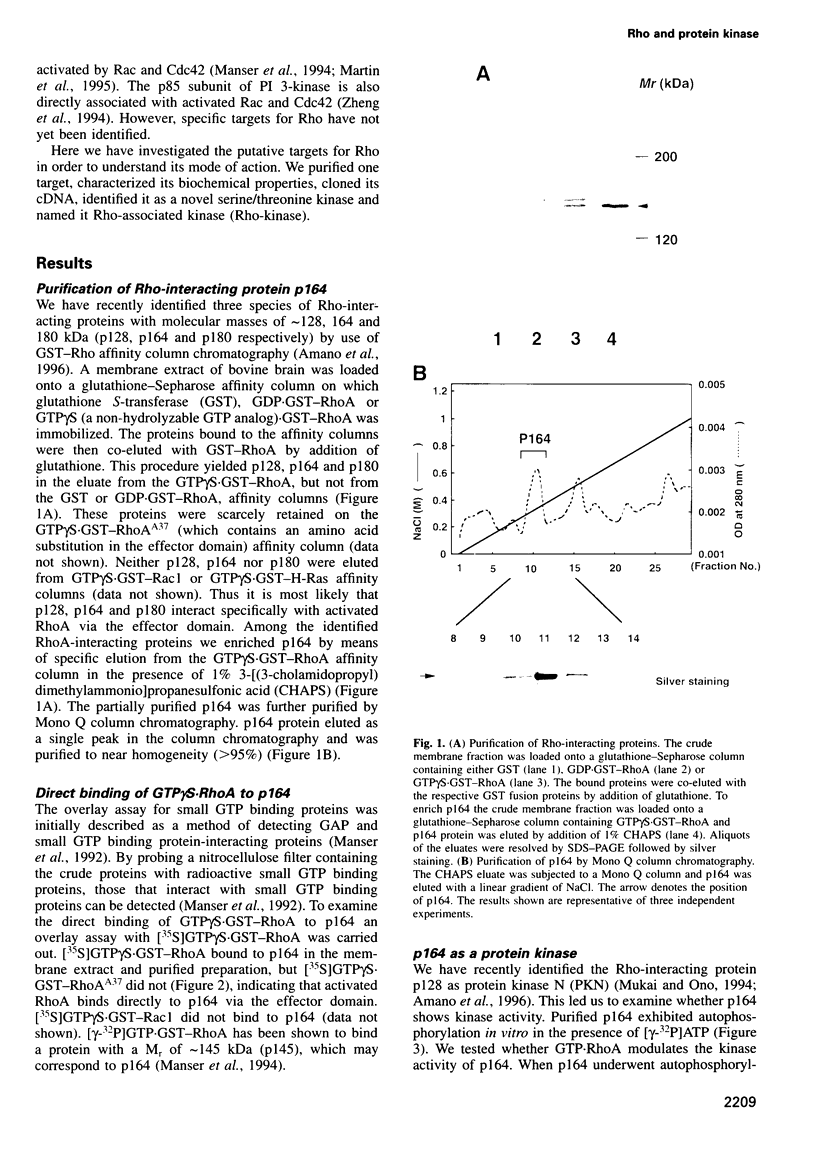
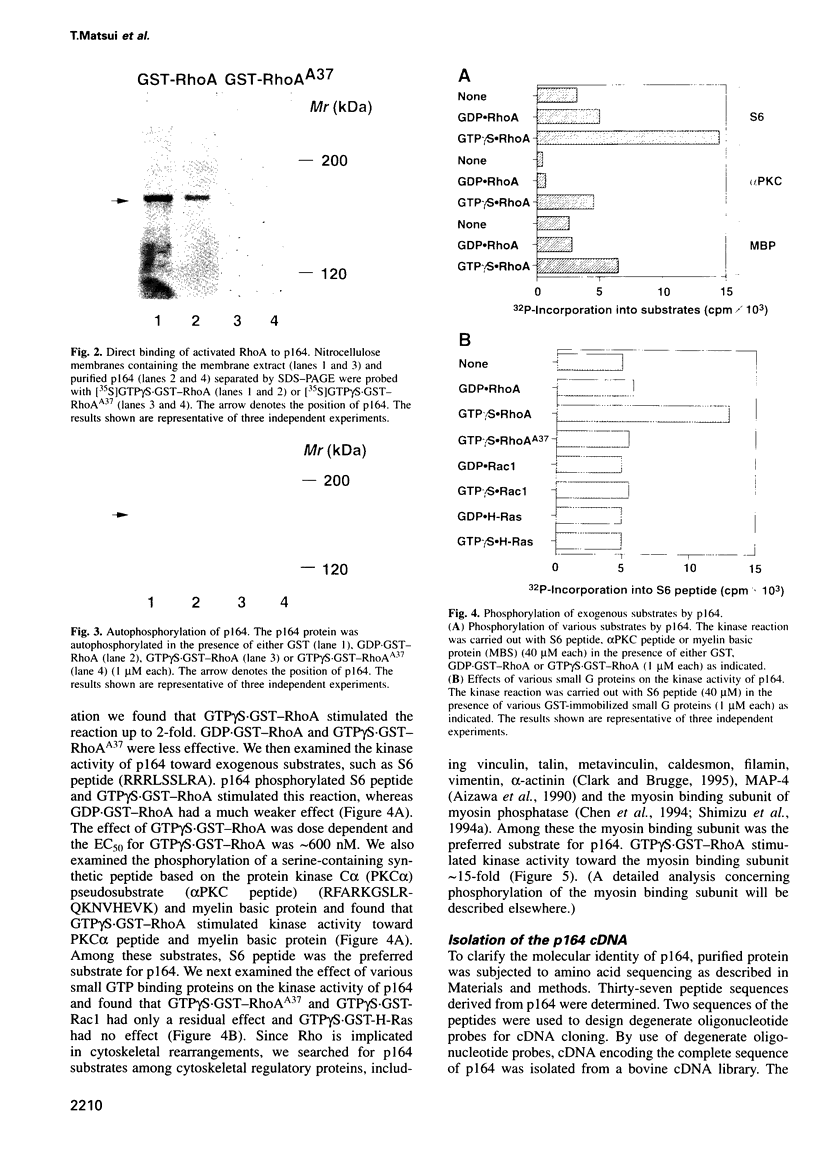
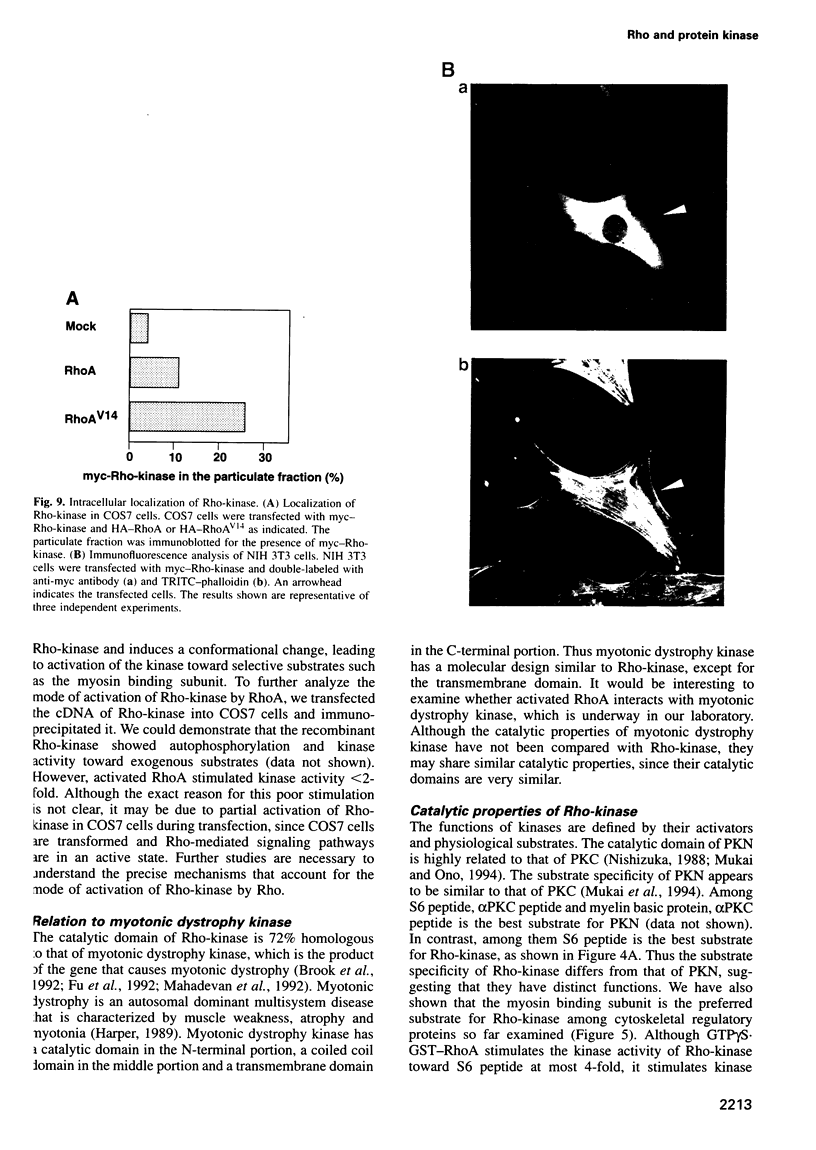
The small GTP binding protein Rho is implicated in cytoskeletal responses to extracellular signals such as lysophosphatidic acid to form stress fibers and focal contacts. Here we have purified a Rho-interacting protein with a molecular mass of approximately 164 kDa (p164) from bovine brain. This protein bound to GTPgammaS (a non-hydrolyzable GTP analog).RhoA but not to GDP.RhoA or GTPgammaS.RhoA with a mutation in the effector domain (RhoAA37).p164 had a kinase activity which was specifically stimulated by GTPgammaS.RhoA. We obtained the cDNA encoding p164 on the basis of its partial amino acid sequences and named it Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase). Rho-kinase has a catalytic domain in the N-terminal portion, a coiled coil domain in the middle portion and a zinc finger-like motif in the C-terminal portion. The catalytic domain shares 72% sequence homology with that of myotonic dystrophy kinase and the coiled coil domain contains a Rho-interacting interface. When COS7 cells were cotransfected with Rho-kinase and activated RhoA, some Rho-kinase was recruited to membranes. Thus it is likely that Rho-kinase is a putative target serine/threonine kinase for Rho and serves as a mediator of the Rho-dependent signaling pathway.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo A., Pick E., Hall A., Totty N., Teahan C. G., Segal A. W. Activation of the NADPH oxidase involves the small GTP-binding protein p21rac1. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):668–670. doi: 10.1038/353668a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aizawa H., Emori Y., Murofushi H., Kawasaki H., Sakai H., Suzuki K. Molecular cloning of a ubiquitously distributed microtubule-associated protein with Mr 190,000. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13849–13855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alting-Mees M. A., Short J. M. pBluescript II: gene mapping vectors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9494–9494. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amano M., Mukai H., Ono Y., Chihara K., Matsui T., Hamajima Y., Okawa K., Iwamatsu A., Kaibuchi K. Identification of a putative target for Rho as the serine-threonine kinase protein kinase N. Science. 1996 Feb 2;271(5249):648–650. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5249.648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook J. D., McCurrach M. E., Harley H. G., Buckler A. J., Church D., Aburatani H., Hunter K., Stanton V. P., Thirion J. P., Hudson T. Molecular basis of myotonic dystrophy: expansion of a trinucleotide (CTG) repeat at the 3' end of a transcript encoding a protein kinase family member. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):799–808. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90154-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Chen M. X., Alessi D. R., Campbell D. G., Shanahan C., Cohen P., Cohen P. T. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding the 110 kDa and 21 kDa regulatory subunits of smooth muscle protein phosphatase 1M. FEBS Lett. 1994 Dec 12;356(1):51–55. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01231-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong L. D., Traynor-Kaplan A., Bokoch G. M., Schwartz M. A. The small GTP-binding protein Rho regulates a phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase in mammalian cells. Cell. 1994 Nov 4;79(3):507–513. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90259-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark E. A., Brugge J. S. Integrins and signal transduction pathways: the road taken. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):233–239. doi: 10.1126/science.7716514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann D., Abo A., Johnston C., Segal A. W., Hall A. Interaction of Rac with p67phox and regulation of phagocytic NADPH oxidase activity. Science. 1994 Jul 22;265(5171):531–533. doi: 10.1126/science.8036496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Pizzuti A., Fenwick R. G., Jr, King J., Rajnarayan S., Dunne P. W., Dubel J., Nasser G. A., Ashizawa T., de Jong P. An unstable triplet repeat in a gene related to myotonic muscular dystrophy. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1256–1258. doi: 10.1126/science.1546326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto Y., Kaibuchi K., Hori Y., Fujioka H., Araki S., Ueda T., Kikuchi A., Takai Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel type of regulatory protein (GDI) for the rho proteins, ras p21-like small GTP-binding proteins. Oncogene. 1990 Sep;5(9):1321–1328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habets G. G., Scholtes E. H., Zuydgeest D., van der Kammen R. A., Stam J. C., Berns A., Collard J. G. Identification of an invasion-inducing gene, Tiam-1, that encodes a protein with homology to GDP-GTP exchangers for Rho-like proteins. Cell. 1994 May 20;77(4):537–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90216-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart M. J., Eva A., Evans T., Aaronson S. A., Cerione R. A. Catalysis of guanine nucleotide exchange on the CDC42Hs protein by the dbl oncogene product. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):311–314. doi: 10.1038/354311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. S., Wynne J., Treisman R. The Rho family GTPases RhoA, Rac1, and CDC42Hs regulate transcriptional activation by SRF. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1159–1170. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata K., Kikuchi A., Sasaki T., Kuroda S., Kaibuchi K., Matsuura Y., Seki H., Saida K., Takai Y. Involvement of rho p21 in the GTP-enhanced calcium ion sensitivity of smooth muscle contraction. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):8719–8722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma Y., Emori Y. A dual functional signal mediator showing RhoGAP and phospholipase C-delta stimulating activities. EMBO J. 1995 Jan 16;14(2):286–291. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07002.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horii Y., Beeler J. F., Sakaguchi K., Tachibana M., Miki T. A novel oncogene, ost, encodes a guanine nucleotide exchange factor that potentially links Rho and Rac signaling pathways. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 17;13(20):4776–4786. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06803.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamatsu A. S-carboxymethylation of proteins transferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes followed by in situ protease digestion and amino acid microsequencing. Electrophoresis. 1992 Mar;13(3):142–147. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150130129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. I., Pringle J. R. Molecular characterization of CDC42, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene involved in the development of cell polarity. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;111(1):143–152. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Mizuno T., Fujioka H., Yamamoto T., Kishi K., Fukumoto Y., Hori Y., Takai Y. Molecular cloning of the cDNA for stimulatory GDP/GTP exchange protein for smg p21s (ras p21-like small GTP-binding proteins) and characterization of stimulatory GDP/GTP exchange protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2873–2880. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishi K., Sasaki T., Kuroda S., Itoh T., Takai Y. Regulation of cytoplasmic division of Xenopus embryo by rho p21 and its inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange protein (rho GDI). J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1187–1195. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaus U. G., Heyworth P. G., Evans T., Curnutte J. T., Bokoch G. M. Regulation of phagocyte oxygen radical production by the GTP-binding protein Rac 2. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1512–1515. doi: 10.1126/science.1660188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozma R., Ahmed S., Best A., Lim L. The Ras-related protein Cdc42Hs and bradykinin promote formation of peripheral actin microspikes and filopodia in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;15(4):1942–1952. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.4.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai N., Morii N., Fujisawa K., Nemoto Y., Narumiya S. ADP-ribosylation of rho p21 inhibits lysophosphatidic acid-induced protein tyrosine phosphorylation and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation in cultured Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):24535–24538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster C. A., Taylor-Harris P. M., Self A. J., Brill S., van Erp H. E., Hall A. Characterization of rhoGAP. A GTPase-activating protein for rho-related small GTPases. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1137–1142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupas A., Van Dyke M., Stock J. Predicting coiled coils from protein sequences. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1162–1164. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabuchi I., Hamaguchi Y., Fujimoto H., Morii N., Mishima M., Narumiya S. A rho-like protein is involved in the organisation of the contractile ring in dividing sand dollar eggs. Zygote. 1993 Nov;1(4):325–331. doi: 10.1017/s0967199400001659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan M., Tsilfidis C., Sabourin L., Shutler G., Amemiya C., Jansen G., Neville C., Narang M., Barceló J., O'Hoy K. Myotonic dystrophy mutation: an unstable CTG repeat in the 3' untranslated region of the gene. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1253–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.1546325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manser E., Leung T., Monfries C., Teo M., Hall C., Lim L. Diversity and versatility of GTPase activating proteins for the p21rho subfamily of ras G proteins detected by a novel overlay assay. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16025–16028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manser E., Leung T., Salihuddin H., Zhao Z. S., Lim L. A brain serine/threonine protein kinase activated by Cdc42 and Rac1. Nature. 1994 Jan 6;367(6458):40–46. doi: 10.1038/367040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. A., Bollag G., McCormick F., Abo A. A novel serine kinase activated by rac1/CDC42Hs-dependent autophosphorylation is related to PAK65 and STE20. EMBO J. 1995 May 1;14(9):1970–1978. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07189.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Kaibuchi K., Ando S., Musha T., Hiraoka K., Takaishi K., Asada M., Nunoi H., Matsuda I., Takai Y. Regulation of the superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase by a small GTP-binding protein and its stimulatory and inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10215–10218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Kaibuchi K., Yamamoto T., Kawamura M., Sakoda T., Fujioka H., Matsuura Y., Takai Y. A stimulatory GDP/GTP exchange protein for smg p21 is active on the post-translationally processed form of c-Ki-ras p21 and rhoA p21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6442–6446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima S., Nagata S. pEF-BOS, a powerful mammalian expression vector. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5322–5322. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukai H., Kitagawa M., Shibata H., Takanaga H., Mori K., Shimakawa M., Miyahara M., Hirao K., Ono Y. Activation of PKN, a novel 120-kDa protein kinase with leucine zipper-like sequences, by unsaturated fatty acids and by limited proteolysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Oct 14;204(1):348–356. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukai H., Ono Y. A novel protein kinase with leucine zipper-like sequences: its catalytic domain is highly homologous to that of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Mar 15;199(2):897–904. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobes C. D., Hall A. Rho, rac, and cdc42 GTPases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia. Cell. 1995 Apr 7;81(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90370-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobes C., Hall A. Regulation and function of the Rho subfamily of small GTPases. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Feb;4(1):77–81. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90094-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson H. F., Self A. J., Garrett M. D., Just I., Aktories K., Hall A. Microinjection of recombinant p21rho induces rapid changes in cell morphology. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1001–1007. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. Signal transduction pathways regulating Rho-mediated stress fibre formation: requirement for a tyrosine kinase. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 1;13(11):2600–2610. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06550.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Paterson H. F., Johnston C. L., Diekmann D., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Settleman J., Albright C. F., Foster L. C., Weinberg R. A. Association between GTPase activators for Rho and Ras families. Nature. 1992 Sep 10;359(6391):153–154. doi: 10.1038/359153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaishi K., Sasaki T., Kato M., Yamochi W., Kuroda S., Nakamura T., Takeichi M., Takai Y. Involvement of Rho p21 small GTP-binding protein and its regulator in the HGF-induced cell motility. Oncogene. 1994 Jan;9(1):273–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga T., Sugie K., Hirata M., Morii N., Fukata J., Uchida A., Imura H., Narumiya S. Inhibition of PMA-induced, LFA-1-dependent lymphocyte aggregation by ADP ribosylation of the small molecular weight GTP binding protein, rho. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(6):1529–1537. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.6.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Matsui T., Nakafuku M., Iwamatsu A., Kaibuchi K. A novel GTPase-activating protein for R-Ras. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 22;270(51):30557–30561. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.51.30557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., King W. G., Dillon S., Hall A., Feig L., Rittenhouse S. E. Activation of platelet phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase requires the small GTP-binding protein Rho. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22251–22254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Y., Bagrodia S., Cerione R. A. Activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity by Cdc42Hs binding to p85. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 22;269(29):18727–18730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]