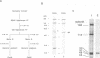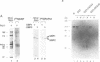Abstract
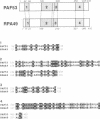
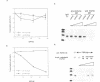
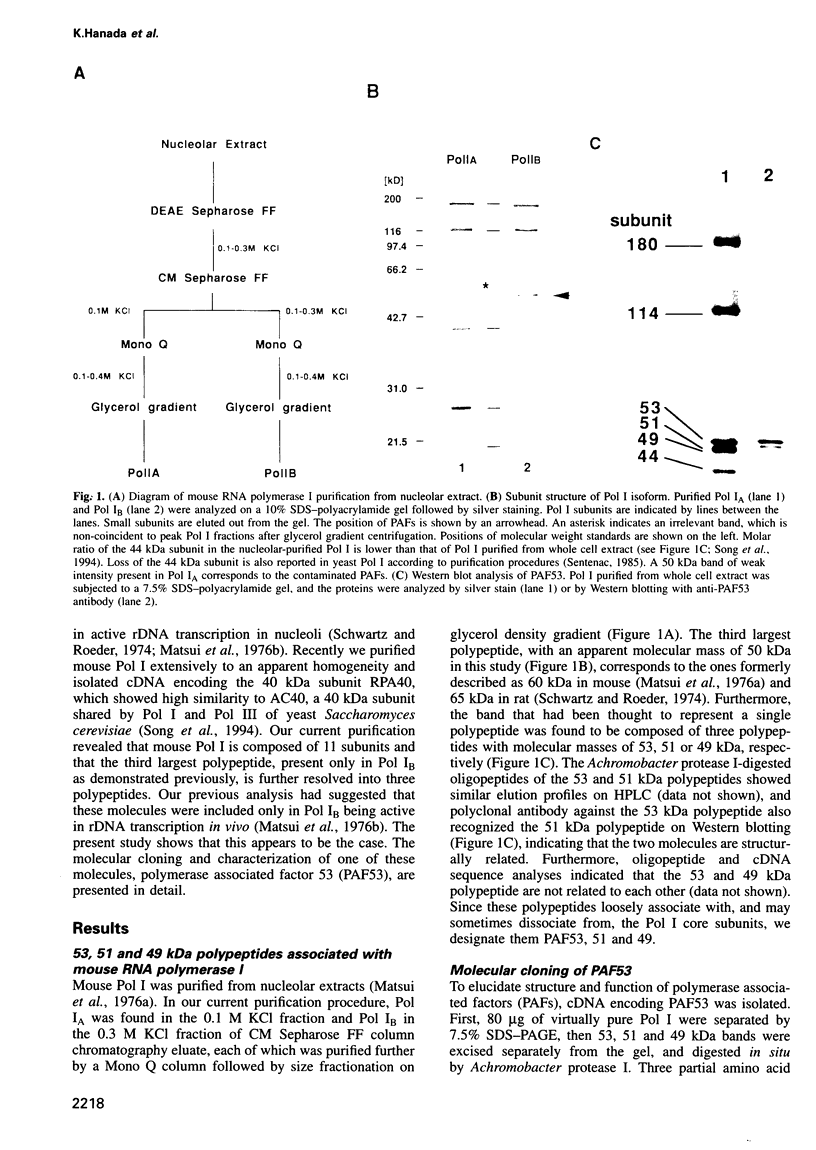
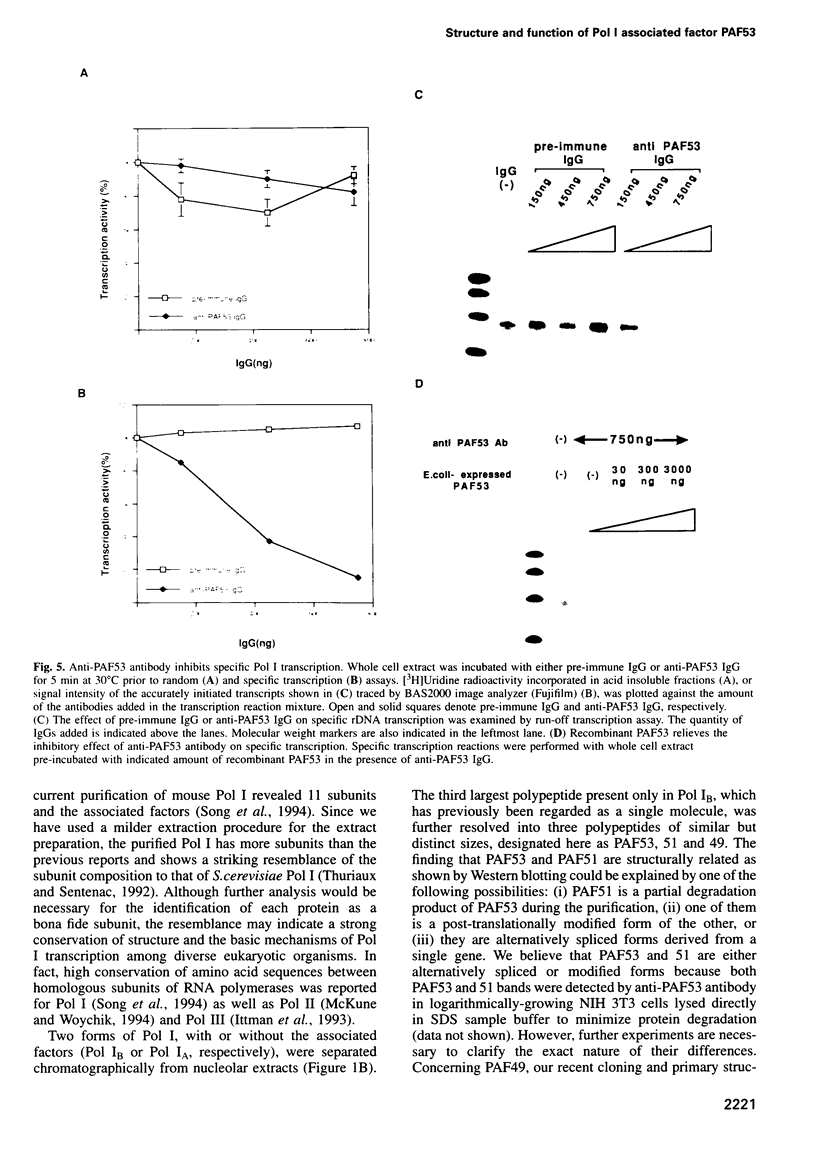
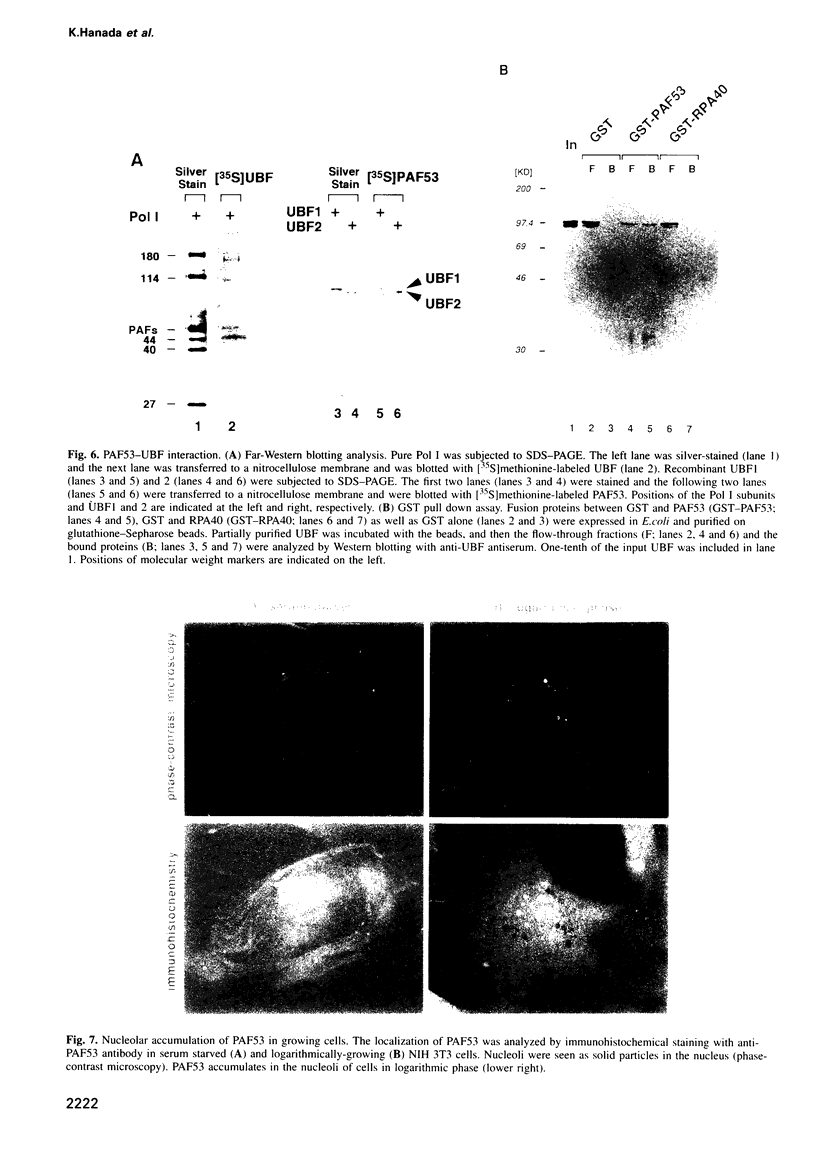
Mouse RNA polymerase I (Pol I) has, besides its 11 bona fide subunits, three polymerase associated factors, termed PAF53, 51 and 49 with respect to the size of each molecule. In order to analyze the function of PAFs, cDNA encoding PAF53 was isolated using an oligonucleotide probe derived from an oligopeptide sequence. The cDNA of PAF53 predicts a polypeptide of 434 amino acids with a sequence similarity to yeast Pol 1 49 kDa subunit. Anti-PAF53 antibody does not block the random transcription activity of Pol I, but blocks specific transcription from mouse ribosomal RNA promoter, demonstrating the requirement of PAF53 in the accurate initiation of Pol I transcription. Moreover, PAF53 interacted with mouse UBF in vitro, as revealed by Far-Western blotting and GST pull down assays. These results, together with the accumulation of PAF53 in the nucleolus of growing cells, suggest that PAF53 is involved in the formation of the initiation complex at the promoter by mediating the interaction between Pol I and UBF for the active rRNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brun R. P., Ryan K., Sollner-Webb B. Factor C*, the specific initiation component of the mouse RNA polymerase I holoenzyme, is inactivated early in the transcription process. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):5010–5021. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.5010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. L., Attardi L. D., Verrijzer C. P., Yokomori K., Tjian R. Assembly of recombinant TFIID reveals differential coactivator requirements for distinct transcriptional activators. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):93–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90403-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai L., Tanese N., Tjian R. The TATA-binding protein and associated factors are integral components of the RNA polymerase I transcription factor, SL1. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):965–976. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90039-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai L., Zomerdijk J. C., Beckmann H., Zhou S., Admon A., Tjian R. Reconstitution of transcription factor SL1: exclusive binding of TBP by SL1 or TFIID subunits. Science. 1994 Dec 23;266(5193):1966–1972. doi: 10.1126/science.7801123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Lu H., Killeen M., Greenblatt J., Burton Z. F., Reinberg D. The small subunit of transcription factor IIF recruits RNA polymerase II into the preinitiation complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9999–10003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gissinger F., Chambon P. Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. 2. Purification of calf-thymus AI enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 13;28(2):277–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gissinger F., Chambon P. Subunit SA3 is not mandatory for the activity of calf thymus DNA-dependent RNA polymerase AI. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):53–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80224-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha I., Roberts S., Maldonado E., Sun X., Kim L. U., Green M., Reinberg D. Multiple functional domains of human transcription factor IIB: distinct interactions with two general transcription factors and RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev. 1993 Jun;7(6):1021–1032. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.6.1021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. J., Darlison M. G. Random-primed cDNA synthesis facilitates the isolation of multiple 5'-cDNA ends by RACE. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):4002–4002. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.4002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashinakagawa T., Muramatsu M., Sugano H. Isolation of nucleoli from rat liver in the presence of magnesium ions. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Mar;71(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90264-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Dissociation of two polypeptide chains from yeast RNA polymerase A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3034–3038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihama A. Subunit of assembly of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Adv Biophys. 1981;14:1–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ittmann M., Ali J., Greco A., Basilico C. The gene complementing a temperature-sensitive cell cycle mutant of BHK cells is the human homologue of the yeast RPC53 gene, which encodes a subunit of RNA polymerase C (III). Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Jun;4(6):503–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Admon A., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):830–836. doi: 10.1038/344830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Chow A. M., King D. S., Tjian R. Multiple domains of the RNA polymerase I activator hUBF interact with the TATA-binding protein complex hSL1 to mediate transcription. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1950–1963. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr, Pallas D. C., DeCaprio J. A., Kaye F. J., Livingston D. M. Identification of cellular proteins that can interact specifically with the T/E1A-binding region of the retinoblastoma gene product. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):521–532. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90236-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Nagamine M., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Formation of the transcription initiation complex on mammalian rDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3418–3427. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen M. T., Greenblatt J. F. The general transcription factor RAP30 binds to RNA polymerase II and prevents it from binding nonspecifically to DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):30–37. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Cordes S., Tjian R. Purification and characterization of a transcription factor that confers promoter specificity to human RNA polymerase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1358–1369. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljelund P., Mariotte S., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A. Characterization and mutagenesis of the gene encoding the A49 subunit of RNA polymerase A in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9302–9305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan P. B., Thompson E. A. Hormonal regulation of transcription of rDNA. Purification and characterization of the hormone-regulated transcription factor IC. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16225–16233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Onishi T., Muramatsu M. Nucleolar DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from rat liver. 1. Purification and subunit structure. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Dec 11;71(2):351–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Onishi T., Muramatsu M. Nucleolar DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from rat liver. 2. Two forms and their physiological significance. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Dec 11;71(2):361–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKune K., Woychik N. A. Functional substitution of an essential yeast RNA polymerase subunit by a highly conserved mammalian counterpart. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):4155–4159. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.4155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Financsek I., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Fractionation and reconstitution of factors required for accurate transcription of mammalian ribosomal RNA genes: identification of a species-dependent initiation factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6659–6670. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Matsui T., Muramatsu M. The mechanism of decrease in nucleolar RNA synthesis by protein synthesis inhibition. J Biochem. 1979 Mar;85(3):807–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Stefanovsky V. Y. Promotion and regulation of ribosomal transcription in eukaryotes by RNA polymerase I. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1995;50:25–66. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60810-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paule M. R., Iida C. T., Perna P. J., Harris G. H., Knoll D. A., D'Alessio J. M. In vitro evidence that eukaryotic ribosomal RNA transcription is regulated by modification of RNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):8161–8180. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.8161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H. rRNA synthesis in the nucleolus. Trends Genet. 1990 Dec;6(12):390–395. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90298-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudloff U., Eberhard D., Tora L., Stunnenberg H., Grummt I. TBP-associated factors interact with DNA and govern species specificity of RNA polymerase I transcription. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 1;13(11):2611–2616. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp G., Santori F., Carles C., Riva M., Grummt I. The HMG box-containing nucleolar transcription factor UBF interacts with a specific subunit of RNA polymerase I. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):190–199. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Roeder R. G. Purification and subunit structure of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase I from the mouse myeloma, MOPC 315. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5898–5906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentenac A. Eukaryotic RNA polymerases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;18(1):31–90. doi: 10.3109/10409238509082539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Mougey E. B. News from the nucleolus: rRNA gene expression. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Feb;16(2):58–62. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90025-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song C. Z., Hanada K., Yano K., Maeda Y., Yamamoto K., Muramatsu M. High conservation of subunit composition of RNA polymerase I(A) between yeast and mouse and the molecular cloning of mouse RNA polymerase I 40-kDa subunit RPA40. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 28;269(43):26976–26981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Kato H., Ishikawa Y., Hisatake K., Tashiro K., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Sequence-specific binding of a transcription factor TFID to the promoter region of mouse ribosomal RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13836–13842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tower J., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rDNA is regulated by an activated subform of RNA polymerase I. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):873–883. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90514-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]