Abstract
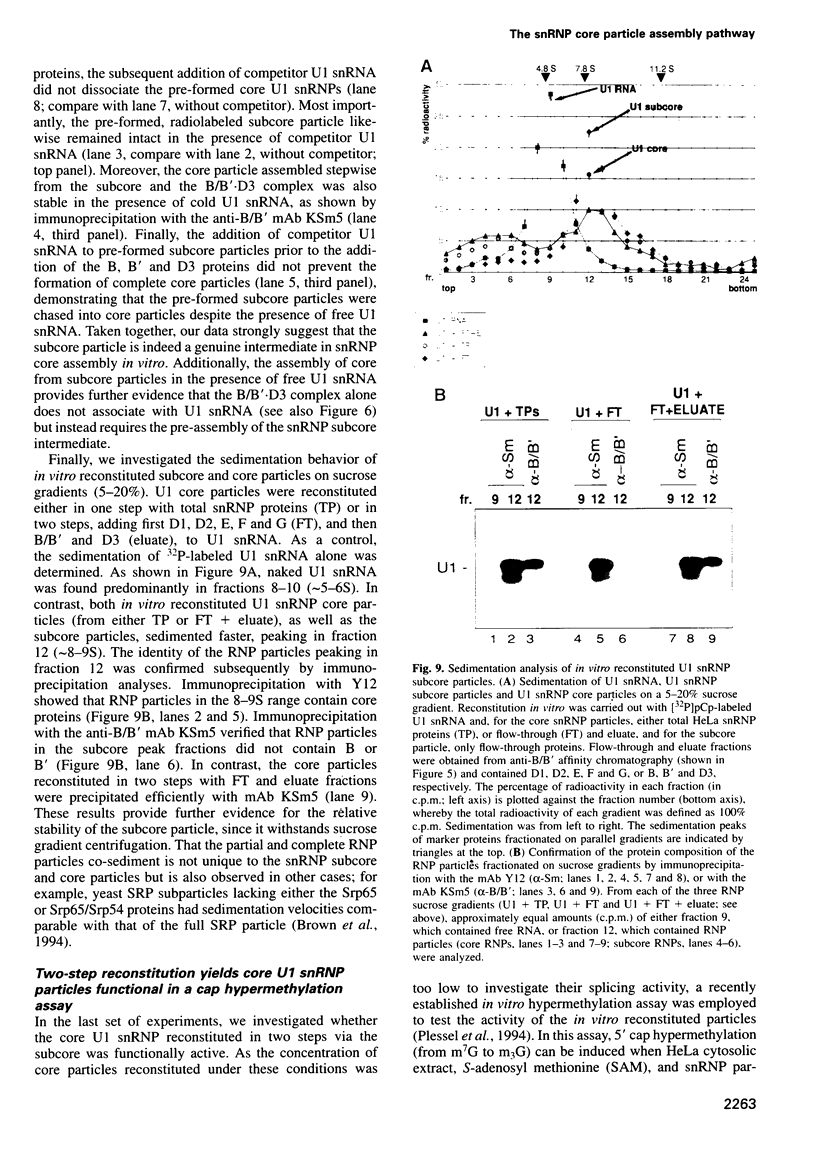
Stable association of the eight common Sm proteins with U1, U2, U4 or U5 snRNA to produce a spliceosomal snRNP core structure is required for snRNP biogenesis, including cap hypermethylation and nuclear transport. Here, the assembly of snRNP core particles was investigated in vitro using both native HeLa and in vitro generated Sm proteins. Several RNA-free, heteromeric protein complexes were identified, including E.F.G, B/B'.D3 and D1.D2.E.F.G. While the E.F.G complex alone did not stably bind to U1 snRNA, these proteins together with D1 and D2 were necessary and sufficient to form a stable U1 snRNP subcore particle. The subcore could be chased into a core particle by the subsequent addition of the B/B'.D3 protein complex even in the presence of free competitor U1 snRNA. Trimethylation of U1 snRNA's 5' cap, while not observed for the subcore, occurred in the stepwise-assembled U1 snRNP core particle, providing evidence for the involvement of the B/B' and D3 proteins in the hypermethylation reaction. Taken together, these results suggest that the various protein heterooligomers, as well as the snRNP subcore particle, are functional intermediates in the snRNP core assembly pathway.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Branlant C., Krol A., Ebel J. P., Lazar E., Haendler B., Jacob M. U2 RNA shares a structural domain with U1, U4, and U5 RNAs. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1259–1265. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00022.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. D., Hann B. C., Medzihradszky K. F., Niwa M., Burlingame A. L., Walter P. Subunits of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae signal recognition particle required for its functional expression. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 15;13(18):4390–4400. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06759.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu J. L., Elkon K. B. The small nuclear ribonucleoproteins, SmB and B', are products of a single gene. Gene. 1991 Jan 15;97(2):311–312. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90069-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M., Johnston L. H., Beggs J. D. Identification and characterization of Uss1p (Sdb23p): a novel U6 snRNA-associated protein with significant similarity to core proteins of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins. EMBO J. 1995 May 1;14(9):2066–2075. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07198.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijk J., Littlechild J. Purification of ribosomal proteins from Escherichia coli under nondenaturing conditions. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:481–502. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeney R. J., Sauterer R. A., Feeney J. L., Zieve G. W. Cytoplasmic assembly and nuclear accumulation of mature small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5776–5783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer U., Lührmann R. An essential signaling role for the m3G cap in the transport of U1 snRNP to the nucleus. Science. 1990 Aug 17;249(4970):786–790. doi: 10.1126/science.2143847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer U., Sumpter V., Sekine M., Satoh T., Lührmann R. Nucleo-cytoplasmic transport of U snRNPs: definition of a nuclear location signal in the Sm core domain that binds a transport receptor independently of the m3G cap. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):573–583. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05689.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. E., Conner G. E., Reeves W. H., Wisniewolski R., Blobel G. Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle assembly in vivo: demonstration of a 6S RNA-free core precursor and posttranslational modification. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):751–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90271-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habets W. J., Hoet M. H., De Jong B. A., Van der Kemp A., Van Venrooij W. J. Mapping of B cell epitopes on small nuclear ribonucleoproteins that react with human autoantibodies as well as with experimentally-induced mouse monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2560–2566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm J., Darzynkiewicz E., Tahara S. M., Mattaj I. W. The trimethylguanosine cap structure of U1 snRNA is a component of a bipartite nuclear targeting signal. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):569–577. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrichs V., Hackl W., Lührmann R. Direct binding of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein G to the Sm site of small nuclear RNA. Ultraviolet light cross-linking of protein G to the AAU stretch within the Sm site (AAUUUGUGG) of U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein reconstituted in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1992 Sep 5;227(1):15–28. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90678-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann H., Fabrizio P., Raker V. A., Foulaki K., Hornig H., Brahms H., Lührmann R. snRNP Sm proteins share two evolutionarily conserved sequence motifs which are involved in Sm protein-protein interactions. EMBO J. 1995 May 1;14(9):2076–2088. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07199.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastner B., Bach M., Lührmann R. Electron microscopy of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP) particles U2 and U5: evidence for a common structure-determining principle in the major U snRNP family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1710–1714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmeier T., Foulaki K., Lührmann R. Evidence for three distinct D proteins, which react differentially with anti-Sm autoantibodies, in the cores of the major snRNPs U1, U2, U4/U6 and U5. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6475–6484. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmeier T., Raker V., Hermann H., Lührmann R. cDNA cloning of the Sm proteins D2 and D3 from human small nuclear ribonucleoproteins: evidence for a direct D1-D2 interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):12317–12321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.12317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner E. A., Lerner M. R., Janeway C. A., Jr, Steitz J. A. Monoclonal antibodies to nucleic acid-containing cellular constituents: probes for molecular biology and autoimmune disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2737–2741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liautard J. P., Sri-Widada J., Brunel C., Jeanteur P. Structural organization of ribonucleoproteins containing small nuclear RNAs from HeLa cells. Proteins interact closely with a similar structural domain of U1, U2, U4 and U5 small nuclear RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 15;162(3):623–643. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90392-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luhrmann R., Appel B., Bringmann P., Rinke J., Reuter R., Rothe S., Bald R. Isolation and characterization of rabbit anti-m3 2,2,7G antibodies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7103–7113. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lührmann R., Kastner B., Bach M. Structure of spliceosomal snRNPs and their role in pre-mRNA splicing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Nov 30;1087(3):265–292. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90001-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütcke H., Prehn S., Ashford A. J., Remus M., Frank R., Dobberstein B. Assembly of the 68- and 72-kD proteins of signal recognition particle with 7S RNA. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;121(5):977–985. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.5.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W. Cap trimethylation of U snRNA is cytoplasmic and dependent on U snRNP protein binding. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):905–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., De Robertis E. M. Nuclear segregation of U2 snRNA requires binding of specific snRNP proteins. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90314-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Nagai K. Recruiting proteins to the RNA world. Nat Struct Biol. 1995 Jul;2(7):518–522. doi: 10.1038/nsb0795-518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plessel G., Fischer U., Lührmann R. m3G cap hypermethylation of U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP) in vitro: evidence that the U1 small nuclear RNA-(guanosine-N2)-methyltransferase is a non-snRNP cytoplasmic protein that requires a binding site on the Sm core domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):4160–4172. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.4160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römisch K., Webb J., Herz J., Prehn S., Frank R., Vingron M., Dobberstein B. Homology of 54K protein of signal-recognition particle, docking protein and two E. coli proteins with putative GTP-binding domains. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):478–482. doi: 10.1038/340478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauterer R. A., Goyal A., Zieve G. W. Cytoplasmic assembly of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles from 6 S and 20 S RNA-free intermediates in L929 mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):1048–1058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Boelens W., Dathan N. A., van Venrooij W. J., Mattaj I. W. Major determinants of the specificity of interaction between small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1A and U2B'' and their cognate RNAs. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):502–506. doi: 10.1038/345502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillekens P. T., Habets W. J., Beijer R. P., van Venrooij W. J. cDNA cloning of the human U1 snRNA-associated A protein: extensive homology between U1 and U2 snRNP-specific proteins. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3841–3848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02721.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R., Reddy R. Gamma-monomethyl phosphate: a cap structure in spliceosomal U6 small nuclear RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8280–8283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strub K., Walter P. Assembly of the Alu domain of the signal recognition particle (SRP): dimerization of the two protein components is required for efficient binding to SRP RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):777–784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumpter V., Kahrs A., Fischer U., Kornstädt U., Lührmann R. In vitro reconstitution of U1 and U2 snRNPs from isolated proteins and snRNA. Mol Biol Rep. 1992 Sep;16(4):229–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00419662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ségault V., Will C. L., Sproat B. S., Lührmann R. In vitro reconstitution of mammalian U2 and U5 snRNPs active in splicing: Sm proteins are functionally interchangeable and are essential for the formation of functional U2 and U5 snRNPs. EMBO J. 1995 Aug 15;14(16):4010–4021. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00072.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séraphin B. Sm and Sm-like proteins belong to a large family: identification of proteins of the U6 as well as the U1, U2, U4 and U5 snRNPs. EMBO J. 1995 May 1;14(9):2089–2098. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07200.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. G., Stocks M. R., Smith P. R., Maini R. N. Murine lupus monoclonal antibodies define five epitopes on two different Sm polypeptides. Immunology. 1986 Jul;58(3):495–500. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeller R., Nyffenegger T., De Robertis E. M. Nucleocytoplasmic distribution of snRNPs and stockpiled snRNA-binding proteins during oogenesis and early development in Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90462-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G. W., Sauterer R. A. Cell biology of the snRNP particles. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;25(1):1–46. doi: 10.3109/10409239009090604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dam A., Winkel I., Zijlstra-Baalbergen J., Smeenk R., Cuypers H. T. Cloned human snRNP proteins B and B' differ only in their carboxy-terminal part. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3853–3860. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]














