Abstract
The nearly invariant nature of the 'Universal Genetic Code' attests to its early establishment in evolution and to the difficulty of altering it now, since so many molecules are required for, and depend upon, faithful translation. Nevertheless, variations on the universal code are known in a handful of genomes. We have found one such variant in diplomonads, an early-diverging eukaryotic lineage. Genes for alpha-tubulin, beta-tubulin and elongation factor 1 alpha (EF-1alpha) from two unclassified strains of Hexamitidae were found to contain TAA and TAG (TAR) triplets at positions suggesting a variant code in which TAR codes for glutamine. We found confirmation of this hypothesis by identifying genes encoding glutamine-tRNAs with CUA and UUA anticodons. The alpha-tubulin and EF-1alpha genes from two other diplomonads, Spironucleus muris and Hexamita inflata, were also sequenced and shown to contain no such non-canonical codons. However, tRNA genes with the anticodons UUA and CUA were found in H.inflata, suggesting that this diplomonad also uses these codons, albeit infrequently. The high GC content of these genomes and the presence of two isoaccepting tRNAs compound the difficulty of understanding how this variant code arose by strictly neutral means.
Full text
PDF

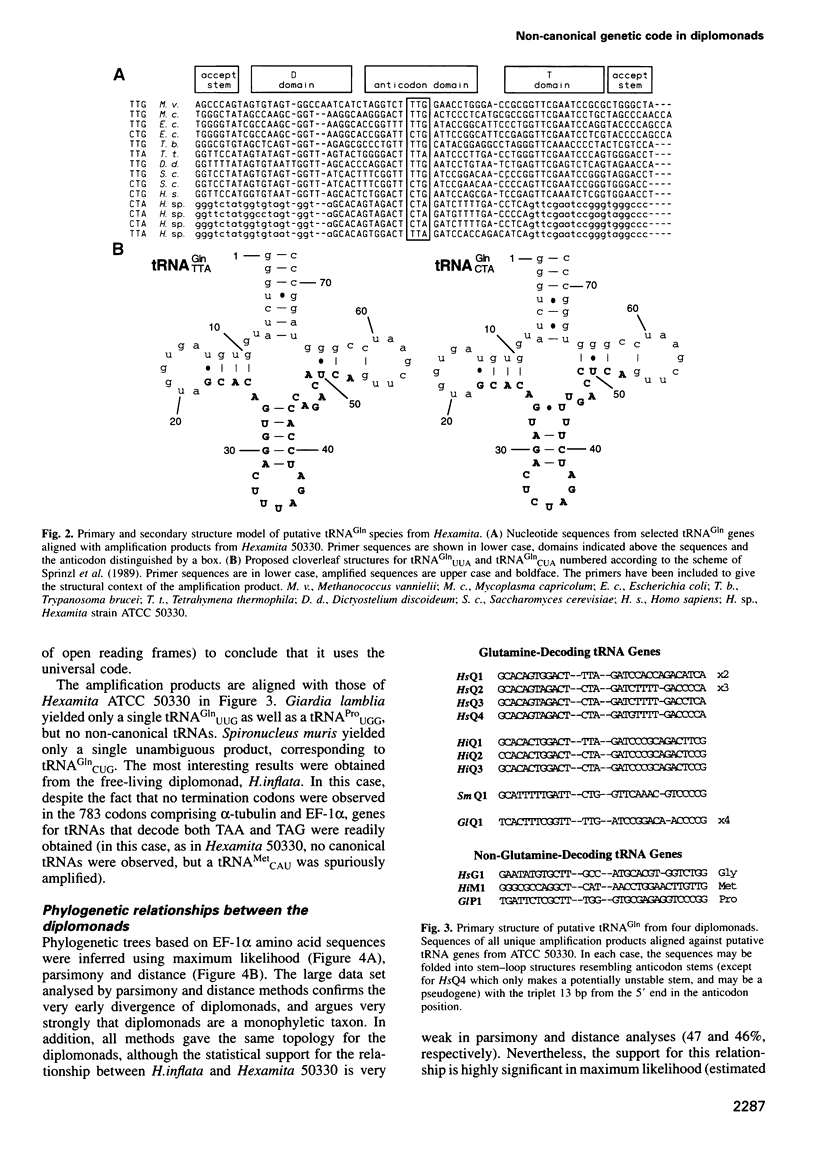
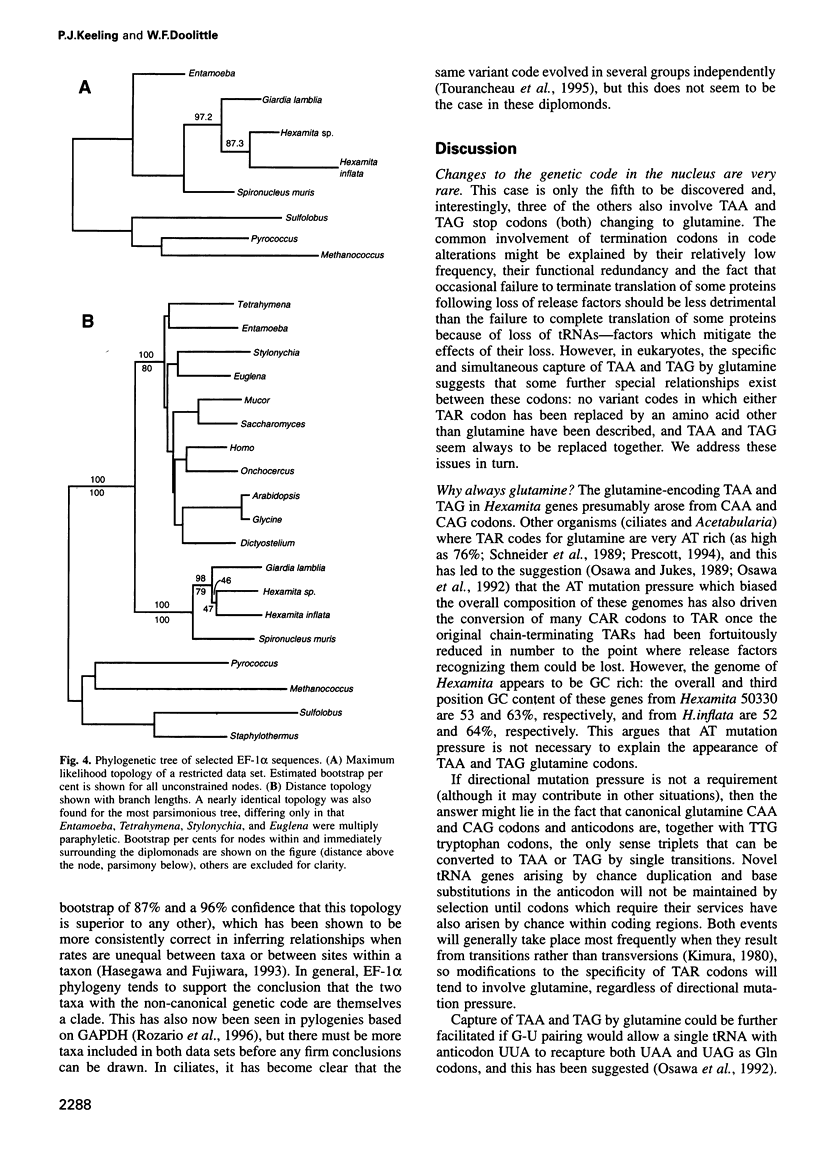


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caskey C. T., Tompkins R., Scolnick E., Caryk T., Nirenberg M. Sequential translation of trinucleotide codons for the initiation and termination of protein synthesis. Science. 1968 Oct 4;162(3849):135–138. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3849.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalier-Smith T. Kingdom protozoa and its 18 phyla. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Dec;57(4):953–994. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.4.953-994.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frolova L., Le Goff X., Rasmussen H. H., Cheperegin S., Drugeon G., Kress M., Arman I., Haenni A. L., Celis J. E., Philippe M. A highly conserved eukaryotic protein family possessing properties of polypeptide chain release factor. Nature. 1994 Dec 15;372(6507):701–703. doi: 10.1038/372701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanyu N., Kuchino Y., Nishimura S., Beier H. Dramatic events in ciliate evolution: alteration of UAA and UAG termination codons to glutamine codons due to anticodon mutations in two Tetrahymena tRNAs. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1307–1311. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04360.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa M., Fujiwara M. Relative efficiencies of the maximum likelihood, maximum parsimony, and neighbor-joining methods for estimating protein phylogeny. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 1993 Mar;2(1):1–5. doi: 10.1006/mpev.1993.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M. Was globin evolution very rapid in its early stages?: a dubious case against the rate-constancy hypothesis. J Mol Evol. 1981;17(2):110–113. doi: 10.1007/BF01732682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leipe D. D., Gunderson J. H., Nerad T. A., Sogin M. L. Small subunit ribosomal RNA+ of Hexamita inflata and the quest for the first branch in the eukaryotic tree. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 May;59(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90005-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa S., Jukes T. H. Codon reassignment (codon capture) in evolution. J Mol Evol. 1989 Apr;28(4):271–278. doi: 10.1007/BF02103422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa S., Jukes T. H., Watanabe K., Muto A. Recent evidence for evolution of the genetic code. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Mar;56(1):229–264. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.1.229-264.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott D. M. The DNA of ciliated protozoa. Microbiol Rev. 1994 Jun;58(2):233–267. doi: 10.1128/mr.58.2.233-267.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider S. U., Leible M. B., Yang X. P. Strong homology between the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase of two species of Acetabularia and the occurrence of unusual codon usage. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Sep;218(3):445–452. doi: 10.1007/BF00332408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E., Tompkins R., Caskey T., Nirenberg M. Release factors differing in specificity for terminator codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):768–774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tourancheau A. B., Tsao N., Klobutcher L. A., Pearlman R. E., Adoutte A. Genetic code deviations in the ciliates: evidence for multiple and independent events. EMBO J. 1995 Jul 3;14(13):3262–3267. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhouravleva G., Frolova L., Le Goff X., Le Guellec R., Inge-Vechtomov S., Kisselev L., Philippe M. Termination of translation in eukaryotes is governed by two interacting polypeptide chain release factors, eRF1 and eRF3. EMBO J. 1995 Aug 15;14(16):4065–4072. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00078.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Feltz M. J., Shivji M. K., Allen P. B., Heisterkamp N., Groffen J., Wiedemann L. M. Nucleotide sequence of both reciprocal translocation junction regions in a patient with Ph positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, with a breakpoint within the first intron of the BCR gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):1–10. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



