Abstract
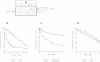
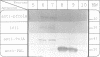
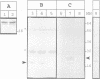
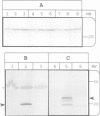
A bacterial signal sequence was fused to the colicin A pore-forming domain: the exported pore-forming domain was highly cytotoxic. We thus introduced a cysteine-residue pair in the fusion protein which has been shown to form a disulfide bond in the natural colicin A pore-forming domain between alpha-helices 5 and 6. Formation of the disulfide bond prevented the cytotoxic activity of the fusion protein, presumably by preventing the membrane insertion of helices 5 and 6. However, the cytotoxicity of the disulfide-linked pore-forming domain was reactivated by adding dithiothreitol into the culture medium. We were then able to co-produce the immunity protein with the disulfide linked pore-forming domain, by using a co-immunoprecipitation procedure, in order to show that they interact. We showed both proteins to be co-localized in the Escherichia coli inner membrane and subsequently co-immunoprecipitated them. The interaction required a functional immunity protein. The immunity protein also interacted with a mutant form of the pore-forming domain carrying a mutation located in the voltage-gated region: this mutant was devoid of pore-forming activity but still inserted into the membrane. Our results indicate that the immunity protein interacts with the membrane-anchored channel domain; the interaction requires a functional membrane-inserted immunity protein but does not require the channel to be in the open state.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baty D., Frenette M., Lloubès R., Geli V., Howard S. P., Pattus F., Lazdunski C. Functional domains of colicin A. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):807–811. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baty D., Knibiehler M., Verheij H., Pattus F., Shire D., Bernadac A., Lazdunski C. Site-directed mutagenesis of the COOH-terminal region of colicin A: effect on secretion and voltage-dependent channel activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1152–1156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavard D., Crozel V., Gorvel J. P., Pattus F., Baty D., Lazdunski C. A molecular, genetic and immunological approach to the functioning of colicin A, a pore-forming protein. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 5;187(3):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavard D., Lazdunski C. J. Purification and molecular properties of a new colicin. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun 1;96(3):519–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer W. A., Heymann J. B., Schendel S. L., Deriy B. N., Cohen F. S., Elkins P. A., Stauffacher C. V. Structure-function of the channel-forming colicins. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1995;24:611–641. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.24.060195.003143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Origins of DNA replication in metazoan chromosomes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duché D., Baty D., Chartier M., Letellier L. Unfolding of colicin A during its translocation through the Escherichia coli envelope as demonstrated by disulfide bond engineering. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 7;269(40):24820–24825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duché D., Letellier L., Géli V., Bénédetti H., Baty D. Quantification of group A colicin import sites. J Bacteriol. 1995 Sep;177(17):4935–4939. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.17.4935-4939.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duché D., Parker M. W., González-Mañas J. M., Pattus F., Baty D. Uncoupled steps of the colicin A pore formation demonstrated by disulfide bond engineering. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6332–6339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espesset D., Corda Y., Cunningham K., Bénedetti H., Lloubès R., Lazdunski C., Géli V. The colicin A pore-forming domain fused to mitochondrial intermembrane space sorting signals can be functionally inserted into the Escherichia coli plasma membrane by a mechanism that bypasses the Tol proteins. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Sep;13(6):1121–1131. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00503.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espesset D., Piet P., Lazdunski C., Géli V. Immunity proteins to pore-forming colicins: structure-function relationships. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Sep;13(6):1111–1120. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geli V., Baty D., Lazdunski C. Use of a foreign epitope as a "tag" for the localization of minor proteins within a cell: the case of the immunity protein to colicin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):689–693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geli V., Baty D., Pattus F., Lazdunski C. Topology and function of the integral membrane protein conferring immunity to colicin A. Mol Microbiol. 1989 May;3(5):679–687. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geli V., Knibiehler M., Bernadac A., Lazdunski C. Purification and reconstitution into liposomes of an integral membrane protein conferring immunity to colicin A. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jul 15;51(1):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90516-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geli V., Lazdunski C. An alpha-helical hydrophobic hairpin as a specific determinant in protein-protein interaction occurring in Escherichia coli colicin A and B immunity systems. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(20):6432–6437. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.20.6432-6437.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geli V., Lloubes R., Zaat S. A., van Spaendonk R. M., Rollin C., Benedetti H., Lazdunski C. Recognition of the colicin A N-terminal epitope 1C11 in vitro and in vivo in Escherichia coli by its cognate monoclonal antibody. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 May 15;109(2-3):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(93)90042-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Géli V., Koorengevel M. C., Demel R. A., Lazdunski C., Killian J. A. Acidic interaction of the colicin A pore-forming domain with model membranes of Escherichia coli lipids results in a large perturbation of acyl chain order and stabilization of the bilayer. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 17;31(45):11089–11094. doi: 10.1021/bi00160a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konisky J. Colicins and other bacteriocins with established modes of action. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:125–144. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakey J. H., van der Goot F. G., Pattus F. All in the family: the toxic activity of pore-forming colicins. Toxicology. 1994 Feb 28;87(1-3):85–108. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(94)90156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Calvez H., Fieschi J., Green J. M., Marchesi N., Chauveau J., Baty D. Paratope characterization by structural modelling of two anti-cortisol single-chain variable fragments produced in E. coli. Mol Immunol. 1995 Feb;32(3):185–198. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(94)00131-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloubes R., Baty D., Lazdunski C. The promoters of the genes for colicin production, release and immunity in the ColA plasmid: effects of convergent transcription and Lex A protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2621–2636. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez M. C., Lazdunski C., Pattus F. Isolation, molecular and functional properties of the C-terminal domain of colicin A. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1501–1507. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill A. R., Cramer W. A. Identification of a voltage-responsive segment of the potential-gated colicin E1 ion channel. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 18;29(37):8529–8534. doi: 10.1021/bi00489a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. W., Pattus F., Tucker A. D., Tsernoglou D. Structure of the membrane-pore-forming fragment of colicin A. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):93–96. doi: 10.1038/337093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom M. S. The fine art of pore formation. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Sep;1(9):563–567. doi: 10.1038/nsb0994-563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slatin S. L., Qiu X. Q., Jakes K. S., Finkelstein A. Identification of a translocated protein segment in a voltage-dependent channel. Nature. 1994 Sep 8;371(6493):158–161. doi: 10.1038/371158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]